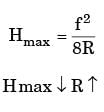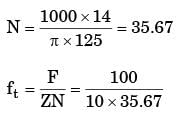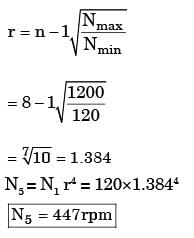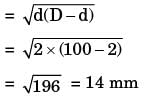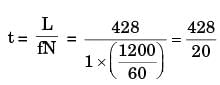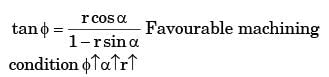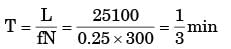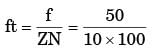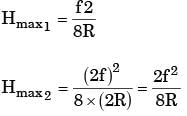Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Grinding ratio is defined as Volume of wheel wear
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:The binding material used in cemented carbide cutting tools is
[PI 2011]
Explanation
Cobalt used as a binding agent in cemented carbide tool. which increases the grain size transverse rapture strength increases & hot hardness decreases.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:During turning of a low carbon steel bar with TiN coated carbide insert, one needs to improve surface finish without sacrificing material removal rate. The achieve improved surface finish one should
[PI 2010]
Explanation
By increasing nose radius, surface finish increases.

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:A side and face cutter 125 mm diameter has 10 teeth. If operates at a cutting speed of 14 m/ min with a table traverse 100 mm/min the feed per tooth of the cutter is
[PI 2002]
Explanation
D = 125 mm Z = 10 teeth V = 14 m/min
F = 100 m/min

ft = 0.25 mm/tooth
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:A grinding wheel is said to be glazed if
[PI 1995]
Explanation
Glazing is when hard material is grounded by hard wheel.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:If the index crank of a dividing head is turned through one complete revolution and 10 holes in a 30 hole Circle plate, the workpiece turns through (in degrees)
[PI 1992]
Explanation
By one complete revolution of indexing crank the work piece turned through = 360/40 = 9
and by 1/3 Rotation 9/3 = 9
total rotation or turn of workpiece = 9 + 3 = 12°
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Find the speed range ratio for the drilling machine spindle if the minimum and maximum diameters of drills used are 5 mm and 25 mm respectively and if the machinability indices for the work materials are 120 (brass) and 40 (alloy steel)
[PI 1992]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
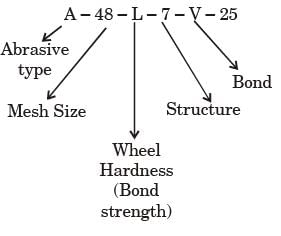
Try yourself:In a grinding wheel marked with AA-48-L-7-V25, L refers to
[PI 1992]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:A drilling machine has to be designed with 8 spindle speeds ranging approximately between 120 to 1200 rpm. The 5th spindle speed is
[PI 1991]
Explanation
Nmin = 120 Nmax = 1200
N = 8

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Assertion (A): Single start threads are used for fastening purposes.
Reason (R): Single start threads are easier to produce in a lathe.
[PI 1990]
Explanation
Single start thread on be made by single point cutting tool.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
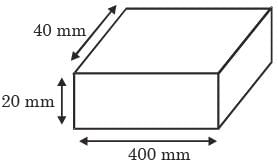
Try yourself:The length, width and thickness of a steel sample are 400 mm, 410 mm, 40 mm and 20 mm, respectively. Its thickness needs to be uniformly reduced by 2 mm in a single pass by using horizontal slab miling. The miling cutter (diameter : 100 mm, width ; 50 mm) has 20 teeth and rotates at 1200 rpm. The feed per tooth is 0.05 mm. The feed direction is along the length of the sample. If the over-travel distance is the same as the approach distance, the approach distance and time taken to complete the required machining task are :
[ME 2019,Set-1]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Better surface finish is obtained with a large rake angle because
[ME 2014,Set-4]
Explanation
As rake angle increase shear plane decreases so smaller force one required so smooth machining operation

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Cutting tool is much harder than the workpiece.Yet the tool wears out during the tool-work interaction, because
[ME 2014,Set-3]
Explanation
Metal cutting takes place in plastic deformation zone where work hardening takes place as chip get strained.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:The time taken to drill a hole through a 25 mm thick plate with the drill rotating at 300 rpm and moving at a feed rate of 0.25 mm/rev is
[ME 2002]
Explanation

T = 20 sec
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:The hardness of a grinding wheel is determined by the
[ME 2002]
Explanation
Bond strength gives the hardness of wheel for soft material strong bond material is used for hard material soft bond material is used.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
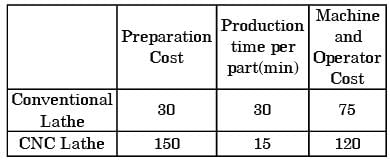
Try yourself:A conventional lathe and a CNC lathe are under consideration for machining a given part. The relevant data are shown below:

The machine preferred for producing 100 pieces is
[ME 2000]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Abrasive material used in grinding wheel selected for grinding ferrous alloys is
[ME 2000]
Explanation
Less chance of wheel wear. Other wise all other to ferrous material.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Plain milling of mild steel plates produces
[ME 1995]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Among the conventional machining processes, maximum specific energy is consumed in
[ME 1995]
Explanation
Grinding because of smaller chips, large cutting area.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Cutting power consumption in turning can be significantly reduced by
[ME 1995]
Explanation
By increasing the back rake angle the drag between chip & tool decreased hence cutting power consumption decreased.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:A grinding wheel A 27 K 7 V is specified for finish grinding of a HSS cutting tool. What do you understand about the wheel from the above code.
Is this an appropriate choice?
[ME 1994]
Explanation
Grain size is given for rough cut.
27 → rough cut
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:A milling cutter having 8 teeth is rotating at 150 rpm. If the feed per tooth is 0.1 mm, the speed in mm per minute is
[ME 1993]
Explanation
F = ft ZN
= 0.1 × 8 × 150
F = 120mm/min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:A milling cutter having 10 teeth is rotating at 100 rpm. The table feed is set at 50-mm per minute. The feed per tooth in mm is
[ME 1991]
Explanation

ft = 0.05 mm
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:For cutting double start screw threads of pitch 1.0 mm on a lathe, the thread cutting tool should have a feed rate of
[ME 1991]
Explanation
Pitch = 1mm
Start = Double Start
Feed rate = 2 × 1 = 2 mm/res.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
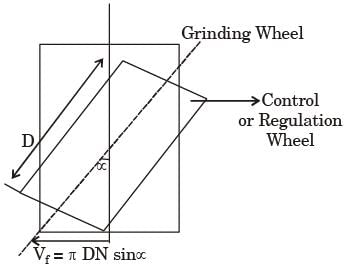
Try yourself:If the longitudinal feed in centreless grinding is expressed by Vf = πDN sinα, D stands for
[ME 1990]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Pure metal pose machinability problem in turning operations. The reason is the
[ME 1988]
Explanation
Pure metals are ductile, produces long & continuous chip
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:Cutting speed in grinding is set to a high value to
[ME 1988]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:The ideal cutting fluid for low speed machining of metals should be one which
[ME 1988]
Explanation
Function of cutting fluid
(1) Cooling
(2) Lubrication
(3) Cleaning
(4) Save from external contamination.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
Try yourself:If in a turning operation both the feed rate and the nose radius are doubled the surface finish value will be
[ME 1987]
Explanation

High of surface roughness be doubled means surface finished hill be decreased by 50%
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Machining Processes
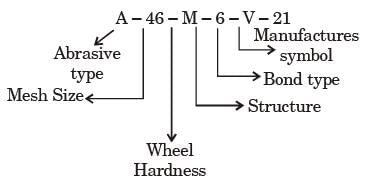
Try yourself:The standard specification of a grinding wheel is A-46-M-6-V-21. It means a wheel of
[ME 1987]
Explanation
Report a problem