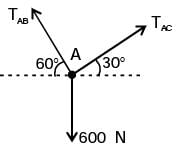
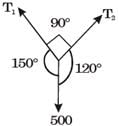
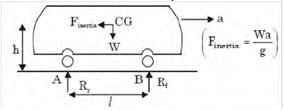
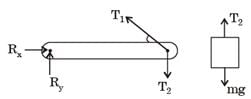
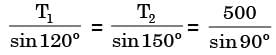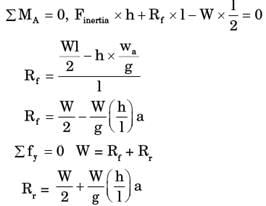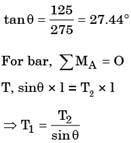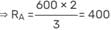GATE Past Year Questions: Equilibrium of a Particle | Engineering Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: Aluminium is casted in a cube-shaped mold having dimensions as 20 mm×20 mm×20 mm Another mold of the same mold material is used to cast a sphere of aluminium having a diameter of 20 mm. The pouring temperature for both cases is the same. The ratio of the solidification times of the cube-shaped mold to the spherical mold is ______ (answer in integer). (2024)
(a) 0.5
(b) 0.25
(c) 0
(d) 1
Ans: (d)
Sol: D=20 mm for sphere
Volume of cube =20×20×20 mm2
According chvorinov's rule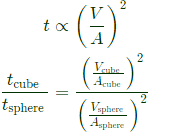
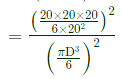
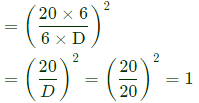
Q2: The allowance provided to a pattern for easy withdrawal from a sand mold is (2024)
(a) finishing allowance
(b) shrinkage allowance
(c) distortion allowance
(d) shake allowance
Ans;(d)
Sol:
Types of allowances:
Draft/taper allowances.
Machining allowance/finishing allowance.
Distortion allowances/camber allowance
Shrinkage allowance/contraction allowances.
Shake allowance/rapping allowance.
Shake allowance
Before withdrawal from the sand mould, the pattern is wrapped all around the vertical faces to enlarge the mould cavity slightly, which facilitates its removal. Since it enlarge the final casting made, it is desirable that the original pattern dimensions should be reduced to account for this increase. There is no sure way of quantifying this allowance, since it is highly dependent on the foundry personnel and practices involved. It is negative allowance and is to be applied only to those dimensions, which are parallel to the parting plane. One way of reducing this allowance is to increase the draft, which can be removed during the subsequent matching.
Draft/taper allowances
Once pattern is embedded in the moulding sand now it is required to withdrawing the pattern from moulding sand, for this propose a vertical force is required to lift the pattern. For easy removal of pattern from mould cavity there should be some degree or mm taper in the pattern.
If there is no taper in the pattern then more chance to break the mould cavity wall during withdrawing the pattern. Draft allowance varies with the complexity of job.
Machining or Finishing allowance
In sand casting operation machining/finishing allowances is given in the pattern as on solidification every metal get shrinked up to some extend and the outer surface of object (casting) is rough, therefore, to smoothing the outer surface of casting machining allowance is must.
Distortion allowance/Camber allowance
On just solidification of metal casting is weak, therefore, more chances to distorted casting. Chance of distortion are basically in U,V, then long section or complicated casting. Distortion can be minimized or eliminated by providing an allowance and constructed the pattern initially distorted, i.e. opposite in outer side direction. Among of distortion allowance varies from 1.5 20 mm. It is the tendency of all metals that they shrink after cooling except bismuth, Shrinkage is only due to inter atomic vibration which are implified by increasing in temperature. Metal shrink or contract in three ways :
Liquid Contraction
Solidification Contraction
Solid Contraction
Q3: In a metal casting process to manufacture parts, both patterns and moulds provide shape by dictating where the material should or should not go. Which of the option(s) given correctly describe(s) the mould and the pattern? (2023)
(a) Mould walls indicate boundaries within which the molten part material is allowed, while pattern walls indicate boundaries of regions where mould material is not allowed.
(b) Moulds can be used to make patterns.
(c) Pattern walls indicate boundaries within which the molten part material is allowed, while mould walls indicate boundaries of regions where mould material is not allowed.
(d) Patterns can be used to make moulds
Ans(a,b,d)
Sol: In some moulding processes like investment and full moulding, permanent moulds can be used for preparing the pattern.
Q4: Consider sand casting of a cube of edge length a. A cylindrical riser is placed at the top of the casting. Assume solidification time ts∝V/A where V is the volume and A is the total surface area dissipating heat. If the top of the riser is insulated, which of the following radius/radii of riser is/are acceptable? (2022Set2)
(a) 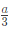
(b) 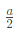
(c) 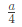
(d) 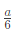
Ans:(a,b)
Sol: Riser should take more time for solidification than casting 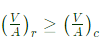
For top riser bottom area is not cooling surface and it is given that top cross section is also insulated. So only lateral area is cooling area.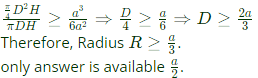
Q5: A cast product of a particular material has dimensions 75 mm x 125 mm x 20 mm. The total solidification time for the cast product is found to be 2.0 minutes as calculated using Chvorinov's rule having the index, n = 2. If under the identical casting conditions, the cast product shape is changed to a cylinder having diameter = 50 mm and height = 50 mm, the total solidification time will be __________ minutes (round off to two decimal places). (2021Set2)
(a) 1.25
(b) 2.83
(c) 2.48
(d) 3.12
Ans:(b)
Sol: Casting dimensions =75 mm×125 mm×20 mm
Total solidification time (ts)cu =2.0 min.
Cylindrical casting =H=D=50 min
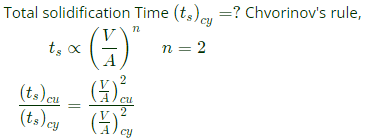
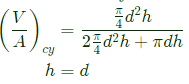
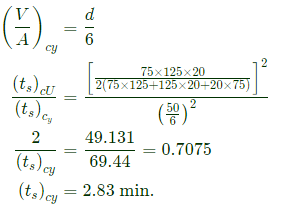
Q6: A true centrifugal casting operation needs to be performed horizontally to make copper tube sections with outer diameter of 250 mm and inner diameter of 230 mm. The value of acceleration due to gravity ,g=10m/s2 If a G-factor (ratio of centrifugal force to weight) of 60 is used for casting the tube, the rotational speed required is _____rpm (round off to the nearest integer). (2021Set1)
(a) 124
(b) 284
(c) 662
(d) 847
Ans: (c)
Sol:
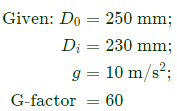
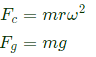
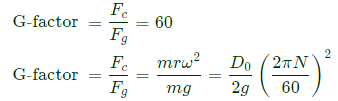
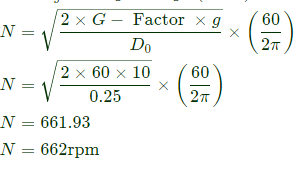
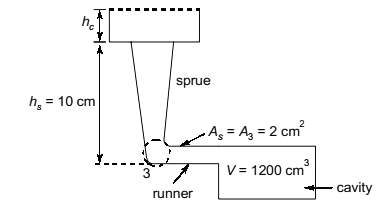
Q7: A mould cavity of 1200cm3volume has to be filled through a sprue of 10 cm length feeding a horizontal runner. Cross-sectional area at the base of the sprue is 2cm 2.Consider acceleration due to gravity as 9.81m/s2. Neglecting frictional losses due to molten metal flow, the time taken to fill the mould cavity is _______ seconds (round off to 2 decimal places). (2020Set2)
(a) 10.6
(b) 2.24
(c) 4.28
(d) 15.3
Ans:(c)
Sol:
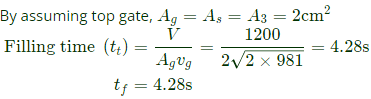
Q8: The figure shows a pouring arrangement for casting of a metal block. Frictional losses are negligible. The acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s2. The time (in s, round off to two decimal places) to fill up the mold cavity (of size 40 cm x 30 cm x 15 cm) is ___
(2019Set 2) (a) 12.55
(a) 12.55
(b) 45.28
(c) 28.92
(d) 36.28
Ans: (c)
Sol:
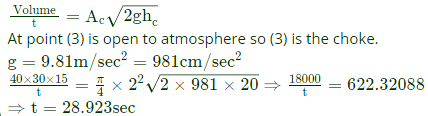
Q9: The fluidity of molten metal of cast alloys (without any addition of fluxes) increases with increase in
(a) viscosity (2019 Set2)
(b) surface tension
(c) freezing range
(d)degree of superheat
Ans:(d)
Sol: Fluidity increases with increase of degree of super heat.
Q10: Match the following sand mold casting defects with their respective causes. (2019Set1)
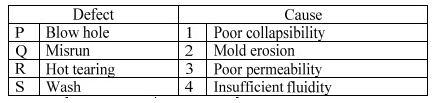
(a) P-4, Q-3, R-1, S-2
(b)P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-1
(c) P-2, Q-4, R-1, S-3
(d) P-3, Q-4, R-1, S-2
Ans: (d)
Sol:
Blow hole ⇒ Poor Permeability
Misrun ⇒ Insufficient Fluidity
Hot tearing ⇒ Poor Collapsibility
Wash ⇒ Mold erosion
[2006]
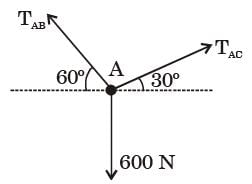
[2015]
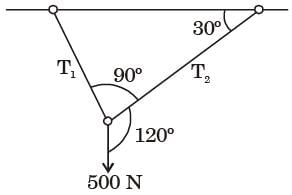
[2019]
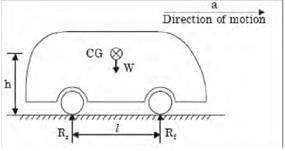
[1997]
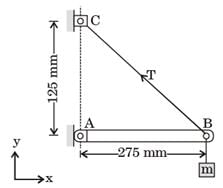
[2014]
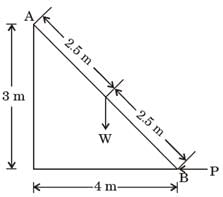
[1995]
|
24 videos|69 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Equilibrium of a Particle - Engineering Mechanics - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is meant by equilibrium of a particle? |  |
| 2. How do you determine if a particle is in equilibrium? |  |
| 3. What are the conditions for a particle to be in static equilibrium? |  |
| 4. Can a particle be in equilibrium if it is moving? |  |
| 5. How can the equilibrium of a particle be disturbed? |  |