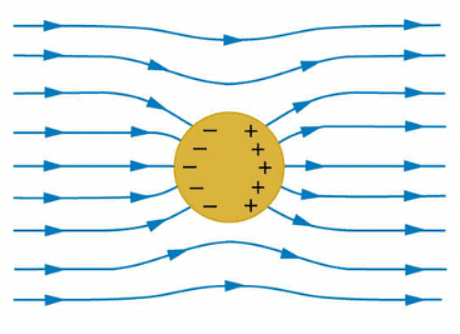
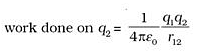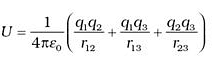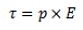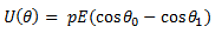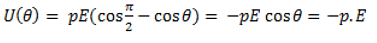Electric Potential Energy, Dielectrics & Potential | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
In general, potential energy can be defined as the capacity for doing work that arises from position or configuration. In the electrical case, a charge will exert a force on any other charge and potential energy arises from any collection of charges. In this document, we will study electrical potential energy and its calculation in detail.
What Is Electric Potential Energy?
- Imagine you have an electric charge, like a tiny particle with electricity. Now, electric potential energy is like a measure of the stored energy this charge has because of its position.
- The electric potential energy of a charge or a group of charges is determined by how much work an outside force does to bring that charge or group from very, very far away (like infinitely far) to where it is now, without making it speed up.
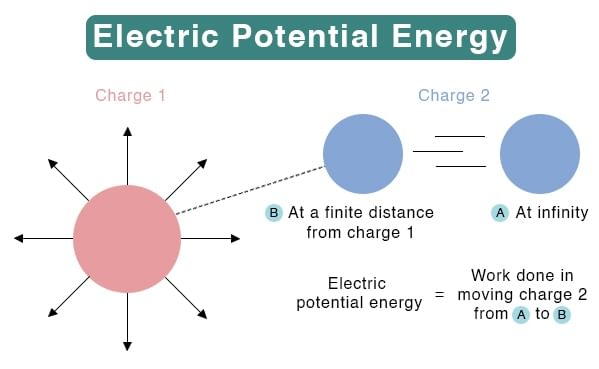
- Electric potential energy is a scalar quantity and possesses only magnitude and no direction. It is measured in terms of Joules and is denoted by V. It has the dimensional formula of ML2T-3A-1.
The electric potential energy of a system of point charges is defined as the work required to assemble this system of charges by bringing them close together, as in the system from an infinite distance.
There are two key elements on which the electric potential energy of an object depends:
- Its own electric charge.
- Its relative position with other electrically charged objects.
Potential Energy of A System of Charges
- Consider the charges q1 and q2 initially at infinity and determine the work done by an external agency to bring the charges to the given locations.
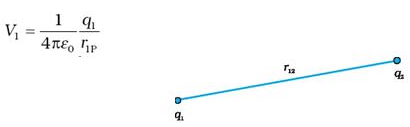
- Suppose, charge q1 is brought from infinity to the point r1. There is no external field against which work needs to be done, so work done in bringing q1 from infinity to r1 is zero. This charge produces a potential in space given by

where r1P is the distance of a point P in space from the location of q1. - From the definition of potential, work done in bringing charge q2 from infinity to the point r2 is q times the potential at r2 due to q1:

where r12 is the distance between points 1 and 2. - If q1q2 > 0, Potential energy is positive. For unlike charges (q1 q2 < 0), the electrostatic force is attractive.
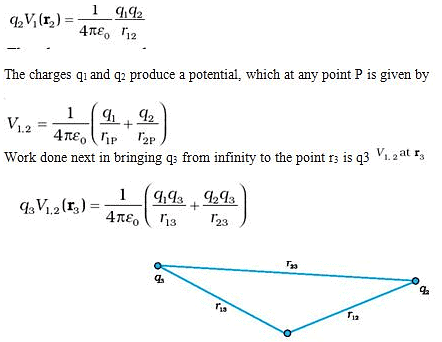
- Potential energy of a system of three charges q1, q2 and q3 located at r1, r2, r3, respectively. To bring q first from infinity to r1, no work is required.
- Next bring q2 from infinity to r2. As before, work done in this step is

- The total work done in assembling the charges at the given locations is obtained by adding the work done in different steps,

Potential Energy in an External Field
Potential Energy of a Single Charge
The potential energy of a charge q in an external electric field E is different from the potential energy due to its own field. Here, E is generated by external sources, not by q itself. The external sources may be known or unspecified, and we focus only on the external field's influence on q. The charge q is assumed to have a negligible effect on the external field.
If q is brought from infinity (where potential is zero) to a point P in the external field, the work done to move q equals the potential energy of q at that point. The potential energy U of q at a distance vector r is given by:
U = qV(r)
where V(r) is the external potential at r.
For an electron (charge e=1.6×10−19C) moved through a 1-volt potential difference, it gains energy e × ΔV=1.6×10−19 J, which is called 1 electron volt (eV). This unit (eV) is commonly used in atomic and nuclear physics.
Example 1: Suppose we have a point charge Q=+5μC located in space. Calculate the electrical potential energy of this single charged particle at a distance of r=2m from it.
Sol: 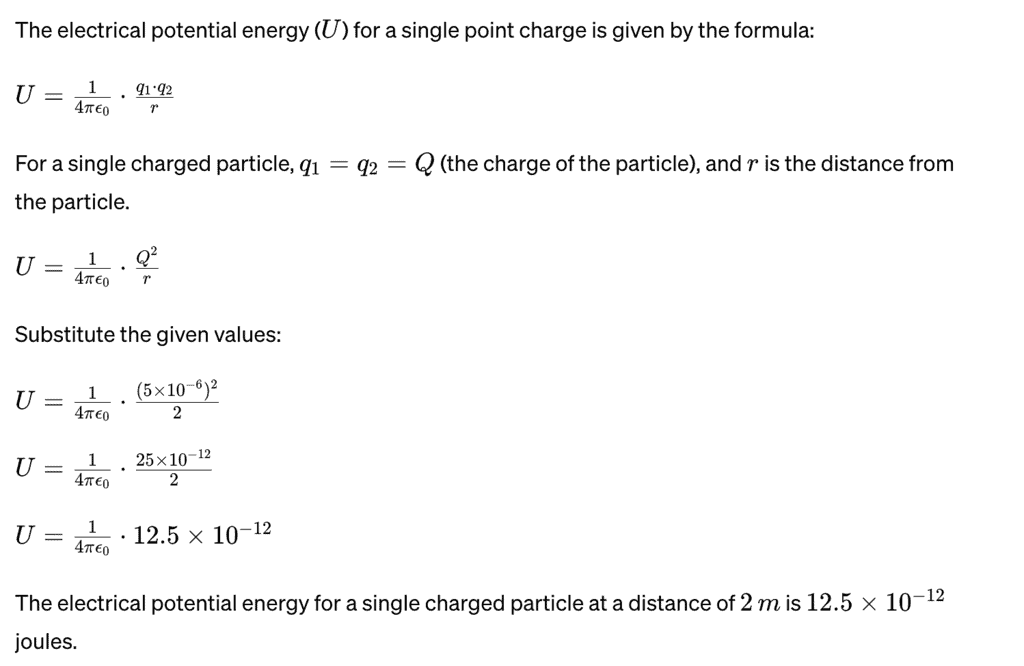
Potential Energy of a System of Two Charged Particles
The figure shows two + ve charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance r. The electrostatic interaction energy of this system can be expressed as work done in bringing charge q2 from infinity to the given separation from q1.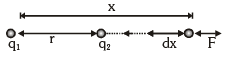 It can be calculated as
It can be calculated as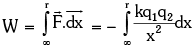
[ – ve sign shows that x is decreasing]

If the two charges are of opposite signs, then potential energy will be negative as:
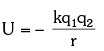
Example 2: Suppose we have two point charges Q1 = +3μC and Q2=−4μC separated by a distance of d=1m. Calculate the electrical potential energy of this system.
Sol:

Potential Energy for a System of Charged Particles
When more than two charged particles are there in a system, the interaction energy can be given as the sum of interaction energies of all the different possible pairs of particles. For example, if a system of three particles having charges q1, q2, and q3 is given as shown in figure.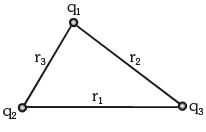 The total interaction energy of this system can be given as:
The total interaction energy of this system can be given as: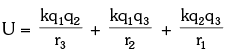
Example 3: Suppose we have three point charges Q1=+2μC, Q2=−3μC, and Q3=+4μC arranged at the vertices of an equilateral triangle with sides of length d =1m. Calculate the electrical potential energy of this system.
Sol:
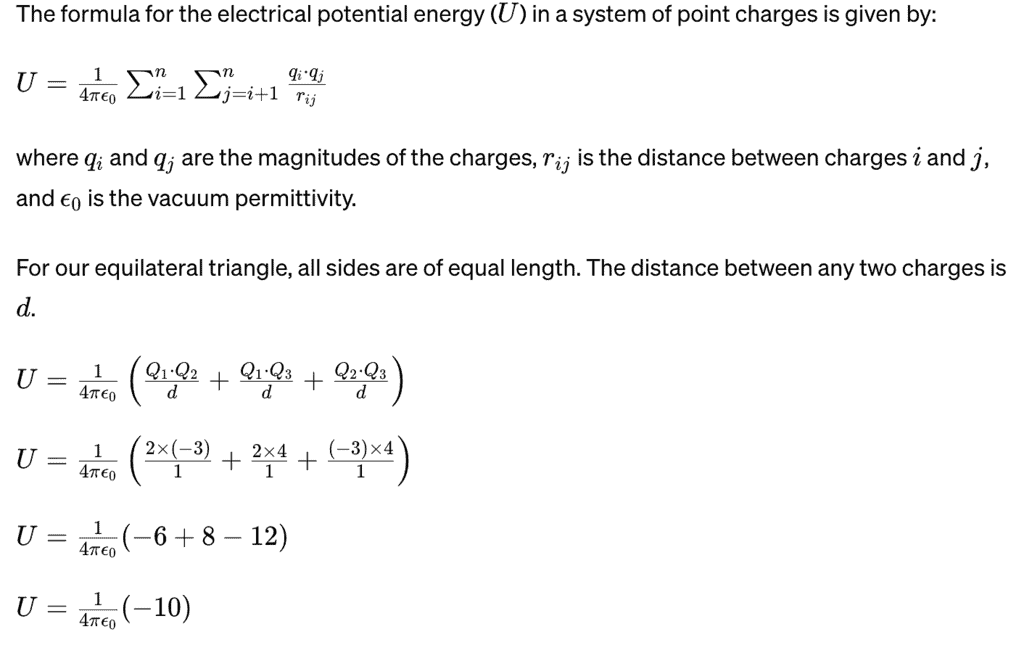
so, U = -10k
Potential energy of a dipole in an external field
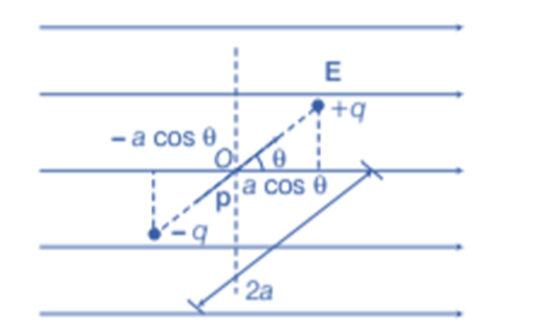
- Consider a dipole with charges q1 = +q and q2 = - q placed in a uniform electric field as shown in the figure. The charges are separated by a distance d and the magnitude of the electric field is E. The force experienced by the charges is given as –qE and +qE, as can be seen in the figure.
 Dipole in a uniform external field
Dipole in a uniform external field
- As we know that, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field, both the charges as a whole do not experience any force, but it experiences a torque equal to τ which can be given as,

- This torque rotates the dipole unless it is placed parallel or anti-parallel to the field. If we apply an external and opposite torque, it neutralizes the effect of this torque given by τext and it rotates the dipole from the angle Ɵ0 to an angle Ɵ1 at an infinitesimal angular speed without any angular acceleration.
The amount of work done by the external torque can be given by:
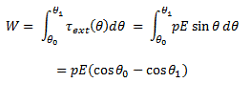
- As we know that the work done in bringing a system of charges from infinity to the given configuration is defined as the potential energy of the system, hence the potential energy U(Ɵ) can be associated to the inclination Ɵ of the dipole using the above relation:

- From the above equation, we can see that the potential energy of a dipole placed in an external field is zero when the angle Ɵ is equal to 90° or when the dipole makes an angle of 90°. Considering the initial angle to be the angle at which the potential energy is zero, the potential energy of the system can be given as:

Electrostatics of Conductors
- Conductors contain mobile charge carriers. In metallic conductors, these charge carriers are electrons.
- In a metal, the outer (valence) electrons part away from their atoms and are free to move.
- These electrons are free within the metal but not free to leave the metal.

- In an external electric field, they drift against the direction of the field. The positive ions made up of the nuclei and the bound electrons remain held in their fixed positions.
- In electrolytic conductors, the charge carriers are both positive and negative ions.
Some of the important points about the electrostatic properties of a conductor are as follows:
1. Inside a conductor, electrostatic field is zero
- In the static condition, whether a conductor is neutral or charged, the electric field inside the conductor is zero everywhere. This is one of the defining properties of a conductor.
- We know that a conductor contains free electrons which, in the presence of an electric field, experience a drift or a force. Inside the conductor, the electrons distribute themselves in such a way that the final electric field at all points inside the conductor is zero.
2. At the surface of a charged conductor, electrostatic field must be normal to the surface at every point
- We can say, if the electric field lines were not normal at the surface, a component of the electric field would have been present along the surface of a conductor in the static condition.
- Thus, free charges moving on the surface would also have experienced some force leading to their motion. But, this does not happen. Since there are no tangential components, the forces have to be normal to the surface.
3. The interior of a conductor can have no excess charge in the static situation
- We know that any neutral conductor contains an equal amount of positive and negative charges, at every point. This holds true even in an infinitesimally small element of volume or surface area.
- From the Gauss’s law, we can say that in the case of a charged conductor, the excess charges are present only on the surface.
- Let us consider an arbitrary volume element of the conductor, which we denote as ‘v’ and for the closed surface bounding the volume element, the electrostatic field is zero. Thus, the total electric flux through S is zero.
- So, from the Gauss law, it follows that the net charge enclosed by the surface element is zero.
- As we go on decreasing the size of the volume and the surface element, at a point we can say that when the element is vanishingly small, it denotes any point in the conductor. So the net charge at any point inside the conductor is always zero and the excess charges reside at the surface.
4. Electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume of the conductor and has the same value (as inside) on its surface
- The electrostatic potential at any point throughout the volume of the conductor is always constant and the value of the electrostatic potential at the surface is equal to that at any point inside the volume.
5. Electric field at the surface of a charged conductor 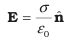
where is the surface charge density and 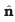 is a unit vector normal to the surface in the outward direction
is a unit vector normal to the surface in the outward direction
- To find the surface charge density σ at a conductor's surface, a Gaussian surface (a pill box) is used, as shown in the figure. The pill box is positioned partly inside and partly outside the conductor's surface with a small cross-sectional area δS and minimal height.
Just beneath the surface of the conductor, the electric field is zero, while just outside, it has a magnitude E perpendicular to the surface. The total electric flux through the pill box only comes from the external side, which equals EδS (positive if σ>0, negative if σ<0). Over the small area δS, E and δS are nearly parallel, so the charge enclosed by the pill box is σδS.
Applying Gauss's law: 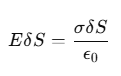
Simplifying, we get:
E=σ/ϵ0
This equation indicates that the electric field is perpendicular to the surface, pointing outward if σ>0 and inward if σ<0.
6. Electrostatic Shielding
- The third kind of shielding is a protection against electric induction, commonly called electrostatic induction. (Electrostatic induction is really a misnomer; this induction is better called electric induction, because it depends upon the continuous fluctuation of the charges induced.)
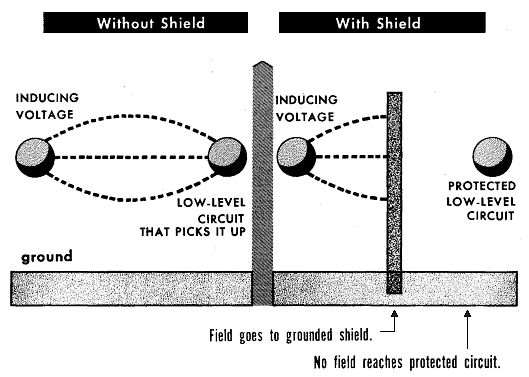 Electrostatic Shielding
Electrostatic Shielding
- Electric shielding consists of interposing a grounded shield between the interfering voltage and the low-level circuit that might pick up the electric field. The voltage induced is immediately carried off to ground, and the electric field is prevented from reaching the circuit that is shielded.
- Unlike either form of protection against magnetic fields, shielding against electric fields can be almost 100% effective. All that is necessary is to insure that no path is left through which the electric field can pass. For this reason, much more attention is given to the prevention of induction by magnetic fields.
Example 4: Assertion: A point charge is placed inside a cavity of the conductor as shown. Another point charge Q is placed outside the conductor as shown. Now as the point charge Q is pushed away from the conductor, the potential difference (VA – VB) between two points A and B within the cavity of sphere remains constant.
Reason: The electric field due to charge on the outer surface of the conductor and outside the conductor is zero at all points inside the conductor
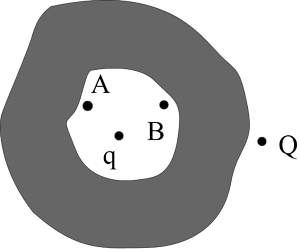
A. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion
B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
C. Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
D. Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct
Sol: Option A. As we know that that the electric field inside the conductor is zero, so the field inside the conductor is constant. Therefore the potential between point A and B will remain constant.
Dielectrics
Dielectrics are non-conducting substances. They are the insulating materials and are bad conductors of electric current. Dielectric materials can hold an electrostatic charge while dissipating minimal energy in the form of heat. Examples of dielectric are Mica, Plastics, Glass, Porcelain and Various Metal Oxides.
You must also remember that even dry air is also an example of a dielectric.
Classification of Dielectrics
Dielectrics are of two types:
- Polar Molecules: Polar Molecules are those type of dielectric where the possibilities of the positive and negative molecules coinciding with each other are null or zero. This is because they all are asymmetric in shape.
Examples: H2O, CO2, NO2 etc.
When the electric field is not present, it causes the electric dipole moment of these molecules in a random direction. This is why the average dipole moment is zero. If the external electric field is present, the molecules assemble in the same direction as the electric field. - Non-Polar Molecule: Unlike polar molecules, in non-polar molecules, the centre of positive charge and negative coincide, that is it is not zero. The molecule then has no permanent (or intrinsic) dipole moment. Examples: O2, N2, H2 etc.
Induced Electric Dipole Moment
When we apply an external electric field in a non-polar molecule, all the protons travel towards the direction of the electric field and electrons in opposite direction. Due to the presence of an electric field, this process continues unless the internal forces balance them.
Due to this, there is a creation of two centres of charge. They are Polarised and we call them as the Induced Electric Dipole. The dipole moment is the Induced Electric Dipole Moment.
Polarisability
Applied field is directly proportional to induced dipole moment and is independent of the temperature. The direction of induced dipole moment (x) is parallel to the direction of electric field Ê and for a single polar atom. The Polarisability determines the dynamical response of a bound system to external fields.
It also provides an insight into a molecule‘s internal structure. In a solid, polarisability is the dipole moment per unit volume of the crystal cell: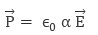
where ‘a’ is the Atomic Polarisability. The S.I. unit of polarisability is m3 and its dimensions are the same as it’s volume.
Electric Polarisation
When we place a dielectric slab is in an electric field, then the molecule gains the dipole moment. In such cases, we say that the dielectric is polarized. The Electric Polarisation is dipole moment per unit volume of a dielectric material. The polarisation is denoted by P.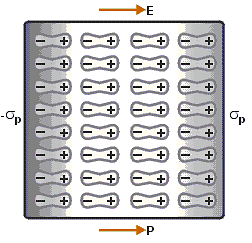 Polarization
Polarization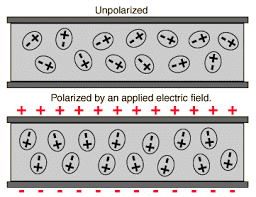 Polarization Process
Polarization Process
Dielectric Constant
When we place a dielectric slab between the parallel plates, the ratio of the applied electric field strength to the strength of the reduced value of electric field capacitor is the Dielectric Constant.
The formula is: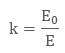
- E is always less than or equal to E where Eo is dielectric and E is the net field.
- The larger the dielectric constant, the more charge can be stored. Completely filling the space between capacitor plates with a dielectric increase the capacitance by a factor of the dielectric constant.
- C = κCo, where Co is the capacitance with no dielectric between the plates.
Dielectric Strength
For an insulating material, the dielectric strength is the maximum electric field strength that it can withstand intrinsically without experiencing failure of its insulating properties.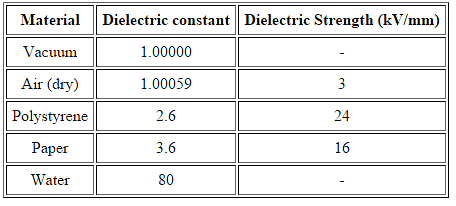
Dielectric Polarisation
When we apply an external electric field to a dielectric material, we get the Dielectric Polarisation. It is the displacement of charges (positive and negative) upon applying an electric field. The main task of the dielectric polarisation is to relate macroscopic properties to microscopic properties.
Polarisation occurs through the action of an electric field or other external factors, such as mechanical stress, as in the case of piezoelectric crystals. Piezoelectric crystals are those solid materials which accumulate electric charge within them.
Dielectric Polarisation can also arise spontaneously in pyroelectric crystals, particularly in ferroelectrics. Ferroelectricity is a property of certain materials that have a spontaneous electric polarisation that can be reversed by the application of an external electric field.
Example 5. Which of the following is/are non-polar dielectrics?
(a) HCl
(b) Water
(c) Benzene
(d) NH3
Sol: Option C – Benzene. Ammonia and HCl are polar molecules since they have a net dipole moment towards a particular direction. Both water and benzene are non-polar molecules. But water is a conductor of electricity, whereas benzene is a dielectric (insulator).
|
97 videos|336 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Electric Potential Energy, Dielectrics & Potential - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is electric potential energy and how is it defined in electrostatics? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the potential energy of a system of two charged particles? |  |
| 3. What is the role of dielectrics in electric potential energy? |  |
| 4. How does the presence of an external electric field affect the potential energy of a charged particle? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of electrostatics in conductors and how does it relate to potential energy? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|