Geography: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 1 | CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Class - XII
Geography
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 70
General Instructions:
(i) Question paper is divided into 3 sections - A, B and C.
(ii) In Section A, question number 1 to 15 are Objective type Multiple choice questions carrying 1 mark each. Attempt any 14 questions. Write the correct answer only in your answer sheets.
(iii) In Section B, Question numbers 16 and 17 are Short Source Based and Graph Based questions respectively carrying 3 marks each. Answer any three questions out of 4. Each of these sub-questions carry 1 mark.
(iv) In Section C, Question numbers 18 to 22 are Short Answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 60-80 words.
(v) In Selection C, Question numbers 23 to 27 are Long Answer questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 120-150 words.
(vi) Question numbers 28 and 29 are related to location and labeling and Identification of geographical features on maps respectively, carrying 5 marks each.
(vii) Outline map of India and World provided to you must be attached within your answer book.
(viii) Use of template or stencils for drawing outline maps is allowed.
SECTION - A (OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS)
Q.1. Those factors which make the place of destination seem more attractive than the place of origin are known as ______.
Ans: Pull factors
Q.2. Arrange the following approaches of human development in a sequence order according to their introduction in the society.
1. Income approach
2. Welfare approach
3. Capability approach
4. Basic Needs approach
(a) 1 4 2 3
(b) 4 1 3 2
(c) 2 4 1 3
(d) 1 2 4 3
Ans. d
Q.3. Income approach is:
(a) One of the oldest approaches to human development.
(b) One of the recent approaches to human development.
(c) One of the latest approaches to human development.
(d) One of the widely rejected approaches to human development.
Ans. a
Q.4. The state with the highest population in India is:
(a) West Bengal
(b) Kerala
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Uttarakhand
Ans. c
Q.5. Which one of the following figures represents the working age group of the population
(a) 15 to 65 years
(b) 15 to 64 years
(c) 15 to 66 years
(d) 15 to 59 years
Ans: d
Q.6. _____________ are much larger than towns.
(a) Cities
(b) Villages
(c) Forests
(d) Sub-urbans
Ans. a
Q.7. The first urban settlement to reach a population of one million was __________.
Ans: London
Q.8. ____________ is referred to as the ‘super- metropolitan’ region extending as a union of conurbations.
(a) Town
(b) City
(c) Modern city
(d) Megalopolis
Ans. d
Q.9. What is the annual growth rate of world population?
(a) 0.10%
(b) 0.50%
(c) 1.10%
(d) 2.30%
Ans. c
Q.10. Arrange the correct sequence of column II against the column I 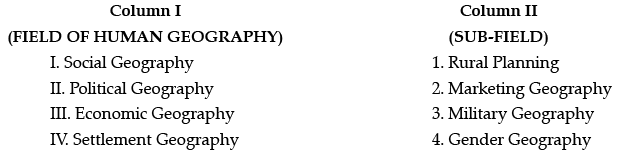
(a) III – 1, IV – 2, I – 3, II – 4
(b) I – 4, II – 3, III – 2, IV – 1
(c) IV – 3, I -4, II – 1, III – 2
(d) II -2, III – 1, IV – 4, I – 3
Ans. b
Q.11. The percentage of urban population in India is
(a) 71.16%
(b) 51.16%
(c) 31.16%
(d) 11.16%
Ans. c
Q.12. In which year was the actual migration recorded through census?
(a) 1857
(b) 1881
(c) 1947
(d) 1991
Ans. b
Q.13. About 97% of the coal reserve occurs in the valley of:
(a) Damodar
(b) Spiti
(c) Chhattisgarh
(d) Lahaul
Ans. a
Q.14. Palli and Nagla belong to one of the following rural settlements:
(a) Clustered
(b) Semi-clustered
(c) Hamleted
(d) Dispersed or isolated
Ans. c
Q.15. Which central authority supervises water quality of national aquatic resources?
(a) CPCB
(b) SPCB
(c) CCBB
(d) SCPB
Ans. a
SECTION - B (SOURCE BASED QUESTIONS)
Q.16. Read the note on Outsourcing given below and answer the questions that follow:
Outsourcing or contracting out is giving work to an outside agency to improve efficiency and reduce costs. When outsourcing involves transferring work to overseas locations, it is described by the term off - shoring, although both off - shoring and outsourcing are used together. Business activities that are outsourced include information technology (IT), human resources, customer support and call centre services and at times also manufacturing and engineering. Data processing is an IT related service easily carried out in Asian, East European and African countries. In these countries IT skilled staff with good English language skills are available at lower wages than those in the developed countries. Thus, a company in Hyderabad or Manila does work on a project based on GIS techniques for a country like the U.S.A or Japan. Overhead costs are also much lower making it profitable to get job-work carried out overseas, whether it is in India, China or even a less populous country like Botswana in Africa.
Answer any three questions:
(i) What is outsourcing called when it is transferred overseas?
(a) Contracting out
(b) Foreign sourcing
(c) Off-shoring
(d) Data processing
Ans. c
(ii) Data processing is related to which field?
(a) Production
(b) IT
(c) R&D
(d) HR
Ans. b
(iii) Why can outsourcing services be carried out easily in Asian countries?
(a) IT skilled staff
(b) Good English language skills
(c) Lower wages
(d) All of these
Ans. d
(iv) What is the nature of overhead costs in East European countries?
(a) Higher
(b) Lower
(c) Similar
(d) Unpredictable
Ans. b
Q.17. Study the given graph carefully and answer the following questions:
Answer any three questions
(i) Which class of towns constitutes the minimum share in distribution of urban population?
(a) II
(b) III
(c) IV
(d) VI
Ans. d
(ii) Which class of towns constitutes more than 50% share of the urban population?
(a) I
(b) III
(c) IV
(d) V
Ans. a
(iii) Which two classes of towns are likely to have similar distribution of urban population?
(a) I and III
(b) II and III
(c) I and IV
(d) III and V
Ans. b
(iv) If Class I towns have a population size of 1,00,000 and more and Class III towns have a population size of 20,000 to 49,999, which of these is most likely to be the population size of Class V towns?
(a) 2,00,000 and more
(b) 75,000 to 99,999
(c) 50,000 to 74,999
(d) 5,000 to 9,999
Ans. d
SECTION - C (SHORT ANSWER AND LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS)
Q.18. What led to the highest groundwater development in the state of Punjab?
OR
Why is irrigation important for Indian agriculture?
Ans. (i) The groundwater utilisation is very high in the state of Punjab because it is an advanced agricultural state.
(ii) Water is used mainly in irrigation. The share of the agriculture sector in total water utilization is much higher than other sectors. Irrigation is needed because of spatio-temporal variability in rainfall in the state.
(iii) This is the region where the green revolution was introduced. HYV crops, introduced during the Green Revolution, required regular supply of moisture.
OR
Importance of irrigation in Indian agriculture:
(i) Control of drought and famines: Insufficient, uncertain and irregular rain causes uncertainty in agriculture. Even during monsoon, the rainfall is scanty and undependable in many parts of the country. Sometimes, the monsoon gets delayed considerably while sometimes they cease prematurely. This pushes large areas of the country into drought conditions. With the help of irrigation, droughts and famines can be effectively controlled.
(ii) Higher productivity on irrigated land: Productivity on irrigated land is considerably more than the productivity on unirrigated land.
(iii) Multiple cropping possible: Provision of irrigation facilities can make the growing of two or three crops in a year in most areas of the country. This will considerably enhance agriculture production and productivity.
(iv) Role in new agricultural strategy: The successful implementation of the High Yielding Programme enhances agricultural production to a great intent. This has been made possible due to the expansion of irrigation facilities.
Q.19. Describe any three characteristics of the last stage of the “Demographic Transition Theory ”.
Ans. The three characteristics are:
(i) Birth and death rates are low, leading to total population being stable.
(ii) Death rates are low primarily due to lower rates of diseases and higher production of food.
(iii) The birth rate is low because people have more opportunities to choose if they want children; this is made possible by improvements in contraception or women gaining more independence and working opportunities.
Q.20. Describe quaternary services.
Ans. The quaternary services of the economy is a way to describe a knowledge based part of the economy, which typically includes services such as collection, production and dissemination of information or even the production of information.
Q.21. Describe the concept of Human Development as defined by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
OR
Explain the key areas of human development.
Ans. As per the World Human Development Report, human development is a process of improving the range of people’s choices, increasing their opportunities for education, healthcare, income and empowerment and covering the full range of human choices from a sound environment to economic, social and political freedom. Thus increasing the range of people’s choices is the most significant aspect of human development. It is just the opposite of the western or eurocentric view of development. People should be able to live a long and healthy life. They should be educated and have access to resources needed for a decent standard of living. These are necessary and nonnegotiable aspects of human development. (CBSE SQP Marking Scheme, 2020)
OR
The key areas a human development are:
(i) Access to resources
(ii) Health
(iii) Education (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2012)
Detailed Answer:
(i) Access to resources: Equal access to all available resources helps in human development. Individuals should be able to use them and benefit from all the specific available resources, be it material or financial.
(ii) Health: Individuals should have easy and timely access to health services at all times
(iii) Education: Free and fair education to all without any disparity. Education makes people aware of their rights and duties and plays an important role in human development.
Q.22. Describe any three major problems of slums in India.
Ans. The three problems faced by slum dwellers in India are:
(i) The areas in which they live (dilapidated houses) are overcrowded having narrow street patterns prone to serious hazards from fire.
(ii) Lack of basic amenities like drinking water, light and toilet facilities. They are also faced by poor ventilation and poor hygienic conditions.
(iii) These slums in the nearby areas cause a lot of pollution and thus result in health hazards. Since, they have no place to bathe, go to the toilet, wash their clothes, all this daily work is done in the open causing inconvenience to the residents of the areas.
Q.23. Classify and differentiate between two types of intensive subsistence agriculture.
Ans. Classification of intensive subsistence agriculture:
(i) Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation.
(ii) Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy.
Differentiation: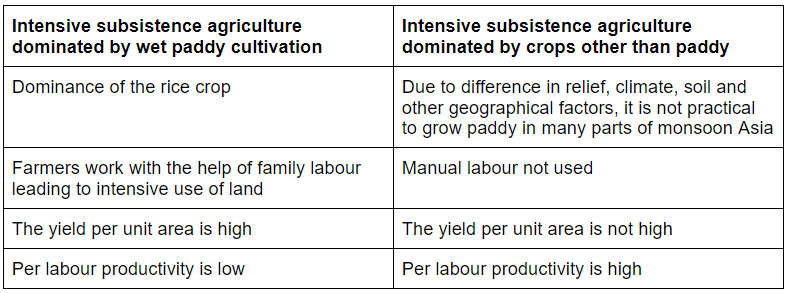
Q.24. Describe any five characteristics of ‘Pastoral Nomadism’ in the world.
OR
Describe any five characteristics of the economic activities of hunting and gathering practised in the world.
Ans. Characteristics of Pastoral Nomadism:
(i) It is a primitive subsistence activity.
(ii) The herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport.
(iii) They move from one place to another with their livestock, depending on the amount & quality of pasture and water.
(iv) Nomadic community occupies a well-identified territory.
(v) Wide variety of animals kept.
(vi) The number of pastoral nomads has been decreasing.
(vii) Any other relevant point.
Detailed Answer:
Characteristics of Pastoral Nomadism can be listed as under:
(i) Pastoral nomadism is a primitive subsistence activity, in which the herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. They move from one place to another along with their livestock, depending on the amount and quality of pastures and water.
(ii) Each nomadic community occupies a well-identified territory as a matter of tradition.
(iii) A wide variety of animals are kept in different regions. In tropical Africa, cattle are the most important livestock, while in Sahara and Asiatic deserts, sheep, goats and camel are reared. In the mountainous areas of Tibet and Andes, yak and llamas, and in the Arctic and sub-Arctic areas, reindeer are the most important animals.
(iv) Pastoral nomadism is associated with three important regions. The core region extends from the Atlantic shores of North Africa eastwards across the Arabian peninsula into Mongolia and Central China. The second region extends over the tundra region of Eurasia. In the southern hemisphere, there are small areas in Southwest Africa and on the island of Madagascar.
(v) Movement in search of pastures is undertaken either over vast horizontal distances or vertically from one elevation to another in the mountainous regions. In mountain regions, such as Himalayas, Gujjars, Bakarwals, Gaddis and Bhotiyas migrate from plains to the mountains in summers and to the plains from the high-altitude pastures in winters. Similarly, in the tundra regions, the nomadic herders move from south to north in summers and from north to south in winters.
OR
Characteristics of the economic activities of hunting and gathering:
(i) These are carried out at different levels with different orientations.
(ii) This is practised in regions with harsh climatic conditions.
(iii) It often involves primitive societies, who extract both plants and animals to satisfy their needs for food, shelter and clothing.
(iv) This type of activity requires a small amount of capital investment and operates at a very low level of technology.
(v) The yield per person is very low and little or no surplus is produced.
(vi) In some regions, gathering has become market oriented.
(vii) Gathering activity faces stiff competition from the synthetic products. (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2012)
Q.25. Define the term ‘nomadic herding’. Explain its four characteristics.
OR
Describe any five characteristics of ‘Subsistence agriculture’ practised in the world.
Ans: Nomadic herding can be defined as primitive subsistence activity in which the herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. They move from one place to another along with their livestock.
Characteristics: (i) Simple form of pastoralism in which herds and flocks graze on natural vegetation called pastures.
(ii) It is an ancient activity where each nomadic community occupies a well-defined territory as per their tradition and culture.
(iii) Animals of the nomads differ according to the cultural and physical characteristics. The camel is the most desired animal in North Africa and the Middle East followed by sheep and goats. Horses, yaks, reindeers and llamas are other important animals.
(iv) The nomadic herders are very much dependent on their animals as they provide them with food, clothing, transport and for materials from which their houses can be made.
(v) They move their herds from one place to another with change in seasons. This is known as transhumance. For example: Sheep or other animals may graze in Alpine meadows in the summers and be heralded back down into valleys for the winters.
(vi) Nomadic herding as a way of life is declining because of natural disasters such as droughts, loss of land area due to urban development and pressure from the government to lead a settled existence.
OR
Characteristics of subsistence agriculture:
(i) Farmers consume almost all their products, whatever they produce.
(ii) It is classified into two types: Primitive Subsistence Agriculture and Intensive Subsistence Agriculture.
(iii) Primitive subsistence agriculture or shifting cultivation is widely practised by many tribes in the tropics.
(iv) Intensive subsistence agriculture is practised in a densely populated region of monsoon Asia.
(v) Intensive subsistence agriculture is divided into intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation and intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy.
(vi) Any other relevant point. (Describe any five points) (CBSE Marking Scheme 2019) 5
Detailed Answer: Characteristics of Subsistence Agriculture:
(i) It is also called shifting agriculture/slash and burn/Jhuming/Milpa/Ladang: It is also called shifting agriculture as only a small plot of land is cleared and cultivated for a short period of time and then is abandoned and allowed to regain the lost fertility as the farmer moves to the next piece of land for cultivation.
(ii) It is widely practised by tribes in Tropics: Africa, South and Central America, South East Asia : The tribes living in Tropics practice such type of farming where it is based on maize cultivation and domestication of potatoes. Planting decisions are made principally with an eye towards what the family will need during the coming year.
(iii) Vegetation is cleared by fire and ashes add to soil fertility. This type of agriculture does not invest much in advanced technology but uses age old practice to add fertility to the soil as this type of agriculture caters only to the family requirements.
(iv) Farms are small: The farmers focus on growing enough food to feed themselves and their families, hence the size of the farms are small.
(v) They use primitive tools: The farmers use primitive tools as such farming is done only for their subsistence and not for market competition. The tools used are plough, harrow, hedges, etc.
(vi) The aim of such agriculture is not to compete in the market but to fend for the family members and store food for the next season as well.
(vii) Farmers work with family workers: The members of the same family work on the farm as the main aim is to fulfil the needs of its producers.
Q.26. Mention the measures proposed to promote sustainable development in the Command Area of Indira Gandhi Canal irrigation project which are meant to restore ecological balance.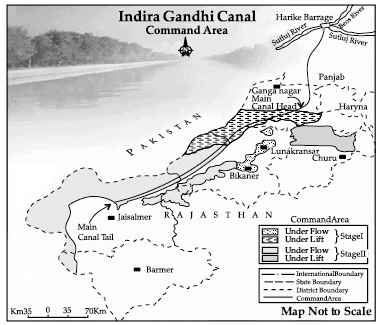
Ans. (i) The first requirement is strict implementation of water management policy. The canal project envisages protective irrigation in Stage-I and extensive irrigation of crops and pasture development in Stage -II.
(ii) In general, the cropping pattern shall not include water intensive crops. It shall be adhered to and people shall be encouraged to grow plantation crops such as citrus fruits.
(iii) The CAD programmes such as lining of water courses, land development levelling and Warabandi system (equal distribution of canal water in the command area of outlet) shall be effectively implemented to reduce the conveyance loss of water.
(iv) The areas affected by waterlogging and soil salinity shall be reclaimed.
(v) The eco-development through afforestation, shelter belt plantation and pasture development is necessary, particularly in the fragile environment of Stage-II.
(vi) The social sustainability in the region can be achieved only if the land allottees having poor economic background are provided adequate financial and institutional support for cultivation of land.
(vii) The economic sustainability in the region cannot be attained only through development of agriculture and animal husbandry. The agricultural and allied activities have to develop along with other sectors of economy. This shall lead to diversification of economic base and establishment of functional linkages between basic villages, agro-service centres and market centres.
Q.27. Explain any five major problems of the rural settlements faced in India.
Ans: Problems of rural settlements faced in India are:
(i) Rural settlements in India have poor infrastructure facilities.
(ii) Supply of water to rural settlements is not adequate. People in villages, particularly in mountainous and arid areas have to walk long distances to fetch drinking water.
(iii) Water borne diseases such as cholera and jaundice are common problems because of lack of safe drinking water and unhygienic conditions.
(iv) Villages are adversely affected by the conditions of drought and flood. This in turn affects the crop cultivation.
(v) The absence of toilet and garbage disposal facilities cause health-related problems.
(vi) The houses made up of mud, wood and thatch get damaged during heavy rains and floods.
(vii) Most of the houses do not have proper ventilation.
(viii) Unmetalled roads and lack of modern communication network cause difficulties in providing emergency services during floods.
(ix) It is also difficult to provide adequate health and educational infrastructure for a large population. The problem is particularly serious where houses are scattered over a large area.
Q.28. On the outline map of India mark and indicate the following features (any five):
(a) State having the highest urban population
(b) Software technology park of Telangana
(c) International airport located in Assam
(d) Eastern terminal point of Golden Quadrilateral
(e) Copper mine located in Rajasthan
(f) Bauxite mines in Odisha
(g) Southern terminal station of North-South corridor
Ans.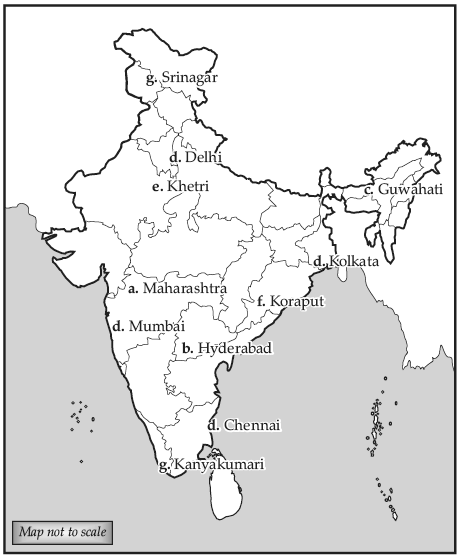
Q.29. In the outline map of the world, five features are shown. Identify them with the help of the information given below and write the correct names.
(a) Grasslands of Australia associated with commercial grain farming.
(b) Grasslands of South Africa associated with commercial grain farming.
(c) Grasslands of North America associated with commercial grain farming.
(d) One area of subsistence gathering in North America.
(e) One area of nomadic herding in Asia.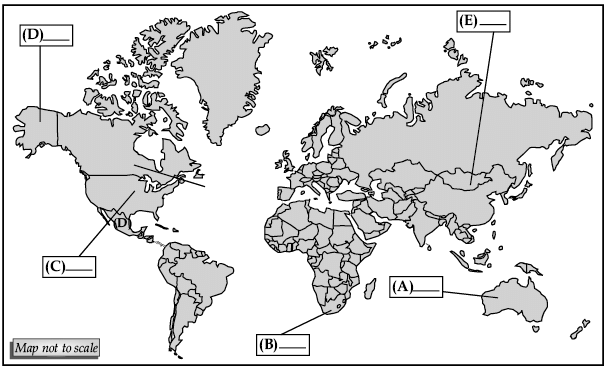
Ans.
(a) Downs of Australia
(b) Velds of South Africa
(c) Prairies of North America
(d) Alaska
(e) Mongolia
|
145 docs|4 tests
|
FAQs on Geography: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 1 - CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the format of the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Geography (2020-21)? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for the CBSE Geography exam using the Sample Question Paper? |  |
| 3. Are the questions in the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Geography (2020-21) similar to the actual exam questions? |  |
| 4. Can I use the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Geography (2020-21) as the sole study material for the exam? |  |
| 5. How can I effectively utilize the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Geography (2020-21) to improve my performance in the exam? |  |





















