Geography: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 2 | CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 1
Class - XII
Geography
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 70
General Instructions:
(i) Question paper is divided into 3 sections - A, B and C.
(ii) In Section A, question number 1 to 15 are Objective type Multiple choice questions carrying 1 mark each. Attempt any 14 questions. Write the correct answer only in your answer sheets.
(iii) In Section B, Question numbers 16 and 17 are Short Source Based and Graph Based questions respectively carrying 3 marks each. Answer any three questions out of 4. Each of these sub-questions carry 1 mark.
(iv) In Section C, Question numbers 18 to 22 are Short Answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 60-80 words.
(v) In Selection C, Question numbers 23 to 27 are Long Answer questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 120-150 words.
(vi) Question numbers 28 and 29 are related to location and labeling and Identification of geographical features on maps respectively, carrying 5 marks each.
(vii) Outline map of India and World provided to you must be attached within your answer book.
(viii) Use of template or stencils for drawing outline maps is allowed.
SECTION - A (OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS)
Q.1. Spacing or preventing the birth of children is known as __________.
Ans. family planning
Q.2. Arrange the following categories of towns in a sequence order according to their development in India.
1. Ancient towns
2. Ultra-modern towns
3. Metropolitans
4. Modern towns
(a) 1 4 3 2
(b) 4 1 3 2
(c) 2 4 1 3
(d) 3 2 4 1
Ans. a
Q.3. On an average, the world population reflects a sex ratio of:
(a) 102 males per 100 females
(b) 85 males per 100 females
(c) 90 males per 100 females
(d) 100 males per 100 females
Ans. a
Q. 4. The first complete population Census was conducted in India in:
(a) 1882
(b) 1881
(c) 1883
(d) 1880
Ans. b
Q.5. The open-cast mining is the easiest and the _________ way of mining minerals.
(a) useless
(b) expensive
(c) cheapest
(d) hardest
Ans: c
Q.6. ____________________ predominate the rural-to-urban stream of inter-state migration due to economic reasons.
(a) Children
(b) Women
(c) Men
(d) Old
Ans: c
Q.7. _________ is the other name of slash and burn agriculture.
Ans. Shifting agriculture
Q.8. What is the formula used to calculate sex ratio in India? 1
(a) 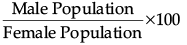
(b) 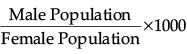
(c) 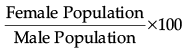
(d) 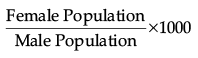
Ans. d
Q.9. Which of these is not a modern town?
(a) Surat
(b) Agra
(c) Daman
(d) Kochi
Ans: c
Q.10. Arrange the correct sequence of column II against the column I

(a) III – 1, IV – 2, I – 3, II – 4
(b) I – 4, II – 3, III – 2, IV – 1
(c) I – 3, III– 4, II – 1, IV – 2
(d) II – 2, III – 1, IV – 4, I – 3
Ans. c
Q.11. According to the 2011 census, which state of India has the lowest density of population?
(a) Assam
(b) Arunachal Pradesh
(c) Meghalaya
(d) Sikkim
Ans. b
Q.12. A city with at least a million inhabitants is known as:
(a) Million city
(b) Billion city
(c) Trillion city
(d) Overpopulated city
Ans. a
Q.13. ___________ is a state of deprivation.
(a) Illiteracy
(b) Overpopulation
(c) Unemployment
(d) Poverty
Ans. d
Q.14. Cities having more than 5 million population are known as
(a) Hyper city
(b) Metropolitan city
(c) Mega city
(d) Urban city
Ans. c
Q.15. Which one of the following does not follow monoculture?
(a) Commercial grain farming
(b) Plantation agriculture
(c) Mixed farming
(d) Dairy farming
Ans. c
SECTION - B (SOURCE BASED QUESTIONS)
Q.16. Read the note on outsourcing given below and answer the questions that follow:
The Naturalisation of Humans
Benda lives in the wilds of the Abujhmad area of central India. His village consists of three huts deep in the wilds. Not even birds or stray dogs that usually crowd villages can be seen in these areas. Wearing a small loin cloth and armed with his axe, he slowly surveys the penda (forest) where his tribe practices a primitive form of agriculture called shifting cultivation. Benda and his friends burn small patches of forest to clear them for cultivation. The ash is used for making the soil fertile. Benda is happy that the Mahua trees around him are in bloom. How lucky I am to be a part of this beautiful universe, he thinks as he looks up to see the Mahua, Palash and Sal trees that have sheltered him since childhood. Crossing the penda in a gliding motion, Benda makes his way to a stream. As he bends down to scoop up a palmful of water, he remembers to thank Loi-Luigi, the spirit of the forest for allowing him to quench his thirst. Moving on with his friends, Benda chews on succulent leaves and roots. The boys have been trying to collect Gajjhara and Kuchla, from the forest. These are special plants that Benda and his people use. He hopes the spirits of the forest will be kind and lead him to these herbs. These are needed to barter in the madhai or tribal fair coming up the next full moon. He closes his eyes and tries hard to recall what the elders had taught him about these herbs and the places they are found in. He wishes he had listened more carefully. Suddenly there is a rustling of leaves. Benda and his friends know it is the outsiders who have come searching for them in the wilds. In a single fluid motion Benda and his friends disappear behind the thick canopy of trees and become one with the spirit of the forest.
Answer any three questions:
(i) Which of these types of agriculture is practiced in the village of Benda?
(a) Traditional Cultivation
(b) Intensive Cultivation
(c) Shifting Cultivation
(d) Large Scale Cultivation
Ans. c
(ii) What is used to make the soil fertile?
(a) Fertilizers
(b) Manure
(c) Insecticides
(d) Ash
Ans. d
(iii) What is the name of the spirit of the forest?
(a) Loi-Luigi
(b) Chi-Mini
(c) Gajhara-Kuchla
(d) Benda-Benda
Ans. a
(iv) Who had come to search Benda and his friends in the wilds?
(a) Wild animals
(b) Outsiders
(c) Tribals
(d) None of these
Ans. b
Q.17. Study the given graph carefully and answer the following questions:
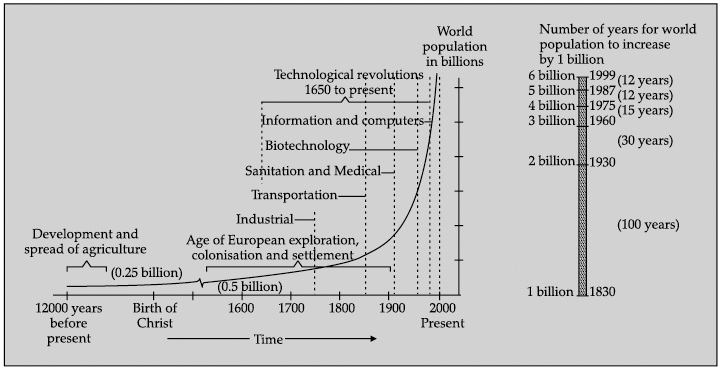
Answer any three questions:
(i) Which of these periods closely represents the European explorations?
(a) 1 CE to 1600 CE
(b) 1500 CE to 1700 CE
(c) 1520 CE to 1900 CE
(d) 1650 CE to 1950 CE
Ans. c
(ii) In how many years did world population increase from 4 billion to 5 billion?
(a) 12 years
(b) 15 years
(c) 30 years
(d) 100 years
Ans. a
(iii) What is the speciality of the period 1650 CE to present?
(a) Development and spread of agriculture
(b) Colonisation
(c) Technological revolutions
(d) Transportation
Ans. c
(iv) What was the approximate population of the world in the 1600s?
(a) 0.25 billion
(b) 0.5 billion
(c) 0.75 billion
(d) 1 billion
Ans. b
SECTION - C (SHORT ANSWER AND LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS)
Q.18. State any three characteristics of quaternary activities.
OR
What is the effect of technology on the environment of human beings?
Ans. Three characteristics of quaternary activities are:
(i) Quaternary activities centre around research, development and may be seen as an advanced form of services involving specialised knowledge, technical skills and administrative competence.
(ii) It is information driven knowledge outsourcing.
(iii) KPO enables companies to create additional business opportunities. Examples of research and development, e-learning, business research, intellectual property (IP) research, legal profession and banking sector.
OR
With the passage of time, people began to understand their environment and the forces of nature. With social and cultural development, humans developed better and more efficient technology. They moved from a state of necessity to a state of freedom. They created possibilities with the resources they obtained from nature. The earlier scholars termed it as ‘possibilism’ wherein humans harnessed the opportunities provided by nature and developed technology that helped them utilize the resources and loosen the shackles of nature on humans.
Q.19. Explain the basic needs approach and capability approach to human development.
Ans. Basic Needs Approach: This approach was initially proposed by the International Labour Organisation (ILO). Six basic needs, i.e., health, education, food, water supply, sanitation, and housing were identified. The question of human choices is ignored and the emphasis is on the provision of basic needs of defined sections.
Capability Approach: This approach is associated with Prof. Amartya Sen. Building human capabilities in the areas of health, education and access to resources is the key to increasing human development.
Q.20. Explain any three characteristics each of hamleted and dispersed rural settlement in India.
Ans. Hamleted Rural Settlements:
(i) They are fragmented into many units.
(ii) This segmentation is motivated by social and ethnic factors.
(iii) Such settlements are found in the Northern Plains, etc.
(iv) These units are locally called Panna, Para, Nagla, Dhani, etc., in various parts of the country.
Dispersed Rural Settlements: (i) It appears in India in the form of isolated huts or hamlets. They are isolated settlements.
(ii) Safety of these households is threatened because of isolation.
(iii) Households have to travel a long distance for basic commodities.
(iv) Many areas in Meghalaya, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Kerala have this type of settlement.
Q.21. Explain the causes and consequences of rural-urban migration in India with suitable examples.
OR
How does intermixing of people from diverse cultures due to migration have positive values? Explain.
Ans. Migration is a response to the uneven distribution of opportunities over space. There are two main types of factors which cause people to migrate.
(a) Push factors which cause people to leave their place of residence.
(b) Pull factors which attract people from different places.
(i) In India, people migrate from rural to urban areas due to push factors like poverty, high population, pressure on the land, lack of basic infra-structural facilities like healthcare, education, and natural disasters such as floods, droughts, cyclonic storms, earthquakes, tsunami, wars and local conflicts.
(ii) The factors that attract people to urban areas are better opportunities, availability of regular work, relatively higher wages, better education, better health care and sources of entertainment. Migration also has certain consequences like economic, social, demographic and environmental consequences.
(i) Economic Consequences:
(a) A major benefit of migration is the remittance sent by the migrants.
(b) Remittances from international migrants are a great source of foreign exchange.
(c) Punjab, Kerala, Tamil Nadu receive the highest remittances from international migrants
(d) Remittances are mainly used for food, repayments of debts, treatment, marriages, children’s education, etc.
(e) Migration from rural areas of Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Odisha are due to the success of the green revolution.
(f) Unregulated migration to metro cities causes overcrowding. This is a negative consequence of migration as it causes the formation of slums.
(ii) Demographic Consequences:
(a) Migration leads to redistribution of population.
(b) Rural-urban migration contributes to the population growth of cities.
(c) Age and skill selective out-migration from rural areas have adverse effects on the rural demographic structure.
(d) High male-dominated out-migration from rural areas of MP, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand, Maharashtra etc., has led to serious imbalances in the age and sex composition.
(iii) Social Consequences:
(a) Migrants act as agents of social change.
(b) New ideas related to new technology, family planning, girls’ education, etc., get diffused to rural areas through people.
(c) It has positive contributions such as the evolution of composite culture, widening of the mental horizon of people etc.
(d) It also has negative consequences such as anonymity, and a feeling of dejection which creates a social vacuum leading to criminal activities and drug abuse.
(iv) Environmental Consequences:
(a) Overcrowding has put pressure on existing social and physical infrastructure in urban areas.
(b) Unplanned growth of urban settlement leads to formation of slums and shanty colonies.
(c) Over exploitation of resources, cities are facing acute problems of depletion of groundwater, air pollution, disposal of sewage and management of groundwater.
(CBSE Marking Scheme, 2018)
OR
Intermixing of people from diverse cultures due to migration has positive values in following ways:
- Evolution of composite culture.
- Breaking through the narrow considerations.
- Widens up the mental horizon of the people at large.
- Any other relevant point.
Detailed Answer: The intermixing of people from diverse culture due to migration have positive values in the following ways:
(i) Spread of ideas from urban to rural areas: Due to migration from rural to urban areas, the ideas of poverty planning, girl education, health awareness, etc. spread from urban to rural areas.
(ii) Broadens mental horizons: Intermixing of people from different cultures broadens the mental horizons. People develop cultural and religious tolerance and accept new ideas from different cultures.
(iii) Creation of complex culture: Intermixing of people from different cultures leads to the creation of a complex culture. Different ideas and practices from different cultures are adopted by the people. This makes the culture more complex and broader.
Thus, all these positive values are developed by intermixing people from different cultures.
Q.22. Future of shifting cultivation is bleak. Discuss.
OR
Why Mediterranean agriculture is considered as one of the best and profitable types of agriculture?
Ans. The future of shifting cultivation is bleak because:
(i) Shifting cultivation is basically a primitive form of agriculture which is mostly popular only among the tribes who show acceptance towards the advancement of technology.
(ii) One of the major problems due to which the future of shifting cultivation is bleak is the fact that the cycle of jhum becomes less and less due to loss of fertility in different parcels.
OR
Mediterranean agriculture is considered as one of the best and profitable type of agriculture because:
(i) It is highly specialised commercial agriculture.
(ii) Viticulture is highly specialised commercial agriculture.
(iii) Best quality wines in the world with distinctive flavours are produced from high quality grapes. Inferior grapes are dried into raisins and currents.
(iv) Olives and figs are produced in this region.
(v) More valuable crops such as fruits and vegetables are grown in winters when there is great demand in European and North American markets.
Q.23. Define the term “Demographic Cycle”. Explain the three-staged model of Demographic Transition Theory.
Ans. Demographic Cycle: The population of any region changes from high birth rates and high death rates to low birth rates and low death rates as the society progresses from rural agrarian and illiterate to urban, industrial and literate society. These changes are termed as demographic cycles.
Transition theory is a three-staged model:
(i) First stage: High fertility and high mortality
(ii) Second stage: High fertility and mortality declines
(iii) Third stage: Both fertility and mortality declines (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2016)
Detailed Answer:
Demographic Cycle: The population of any region changes from high birth rates and high death rates to low birth rates and low death rates as the society progresses from rural agrarian and illiterate to urban, industrial and literate society. These changes are termed as demographic cycles.
Transition theory is a three-staged model:
The characteristics of the first stage of the ‘Demographic Transition Theory’ are:
(i) High fertility and high mortality rate
(ii) Slow rate of population growth
(iii) High rate of illiteracy
The characteristics of the second stage of ‘Demographic Transition Theory’ are:
(i) In the beginning of the second stage, the fertility rate remains high but gradually declines with time.
(ii) Mortality rate is reduced due to the improved sanitation.
(iii) Mortality rate is reduced due to better health conditions due to which the net addition to population is high.
Q.24. “Development is a mixed bag of opportunities as well as deprivation for India.”Support the statement with suitable examples.
OR
“A meaningful life is just not a long one, it must be purposeful.” Support the statement with any three suitable arguments.
Ans. For India, development is a mixed bag of opportunities as well as neglect and deprivations. There are a few areas like the metropolitan centres and other developed enclaves that have all the modern facilities available to a small section of its population. At the other extreme of it, there are large rural areas and the slums in the urban areas that do not have basic amenities like potable water, education and health infrastructure available to the majority of this population. It is a well-established fact that the majority of the scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, landless agricultural labourers, poor farmers and slums dwellers, etc., are the most marginalized group. A large segment of the female population is the worst sufferer among all. The sex ratio is 943 of females to that of 1000 of males. The state of Haryana has the lowest rate of sex ratio in India and the figure shows a number of 877 females to that of 1000 males. There is a wide gender disparity in the literary rate of India: effective literacy rates (age 7 and above) in 2011 were 82.14% for men and 65.46% for women.
OR
“A meaningful life is not just a long one; it must be purposeful”. This refers to the fact that people should be happy, healthy, able to develop some talent, productive towards the society and free to achieve their goals. The concept of human development was introduced by Dr. Mahbub -ul- Haq. Dr. Haq has described human development as development that increases people’s choices, improves their lives and widens their level of well -being. For example, an uneducated child cannot make the choice to be a doctor because the choice has got limited by lack of education. Similarly, very often poor people cannot choose to take medical treatment for disease because their choice is very limited by their lack of resources. In India, a large number of women and people belonging to socially and economically backward groups dropout of school. This shows how the choices of these groups get limited by not having access to knowledge. Therefore, access to resources, health and education are the key areas in human development.
Q.25. ‘Services are a very important aspect for economic development of the country ’. Analyse the statement by explaining five components of a service sector.
OR
Define the term ‘medical tourism’. Explain the four tourist attractions with examples.
Ans. The major components of a service sector are:
(i) Business sector
(ii) Finance
(iii) Wholesale and retail trading
(iv) Transportation and communication
(v) Entertainment
(vi) Government of different levels
(vii) Non-Government Agencies (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2011)
Detailed Answer: The service sector produces intangible goods, more precisely services instead of goods.
(i) Business Sector: Business sector or corporate sector is a part of the economy made up of companies. It is a subset of the domestic economy, excluding the economic activities of general government, of private households and non-profit organisations serving individuals.
(ii) Finance: Finance is a field that deals with the study of investment.
(iii) Wholesale and Retail Trading: Wholesale trade means trading in large quantities and retail trade means selling in small quantities. In wholesale trade, the goods are mainly sold to the retailer who sells it to the customers.
(iv) Transportation and Communication: Modern transportation and communication plays an important role in integrated economic development.
(v) Entertainment: Entertainment sector consists of many different segments under its fold such as television, print, radio, internet and films.
OR
Medical tourism can be defined as the process of travelling outside the country of residence for the purpose of receiving medical care. Originally, the term refers to the travel of patients from less-developed countries to developed nations in pursuit of the treatments not available in their homeland. The four tourist attractions with examples are:
(i) China: China is fast emerging as a desirable destination for individuals seeking medical care in a wide range of medical specialities.
(ii) India: India's medical tourism is growing at a rapid speed. People from all over the globe are looking to visit India for their medical needs.
(iii) Israel: Israel’s high ratio of doctors and specialists to patients make it highly attractive to health travellers.
(iv) Thailand: Visitors who come to Thailand and other countries for various medical procedures and tests combine it with some rest and relaxation.
Q.26. Explain the five push factors that cause‘ migration of population’ in India.
Ans. (i) Large numbers of young people are migrating because rural India is saturated and cannot provide employment opportunities for a growing population.
(ii) Most women migrants have migrated after marriage. In North India, women are not supposed to marry a man from the same village. So, invariably marriage means migration.
(iii) Many end up as ragpickers or casual construction workers. Many don’t get employment throughout the year and commute between urban and rural areas. After the harvest, they migrate to urban areas for a few months before the rainy season.
(iv) Joining family members is the reason for urban migration. First, the husband gets employment and settles. Then, if he gets a decent house he brings his family. Finally, migration for education also takes place.
(v) Lack of basic facilities in the rural areas also works as a push factor for migration.
(CBSE Marking Scheme, 2013)
Q.27. How has Noise pollution become hazardous in many big cities of India? Explain by giving suitable examples.
Ans: Noise pollution has become hazardous in many big cities of India like Delhi, Mumbai, etc. due to following factors:
(i) With the increase in population, the volume of traffic and passengers has increased. This has led to more noise pollution.
(ii) More people have become prosperous in the cities. As a result of this, the number of private vehicles such as cars have increased significantly. This has led to traffic jams during peak hours, i.e. in the morning and in the evening when people go and come from office. This has increased noise pollution on the roads.
(iii) Rapid industrialisation in and around the residential colony has also increased noise pollution. Small and cottage industries are set up in the areas near the market.
(iv) The construction activities have increased to accommodate the ever-increasing population in the big cities. These activities become hazardous as too much noise is created by them.
(v) Religious activities, social functions, rallies, etc. create noise pollution particularly in the late hours of the day.
Q.28. On the outline map of India mark and indicate the following features (any five):
(a) The state with the highest level of urbanization.
(b) The leading state in the production of coffee.
(c) The steel plant setup in collaboration with the U.K.
(d) An international airport in Assam.
(e) The major seaport in Odisha.
(f) The Headquarters of North-Eastern Railway.
(g) Singareni coal mines.
Ans. 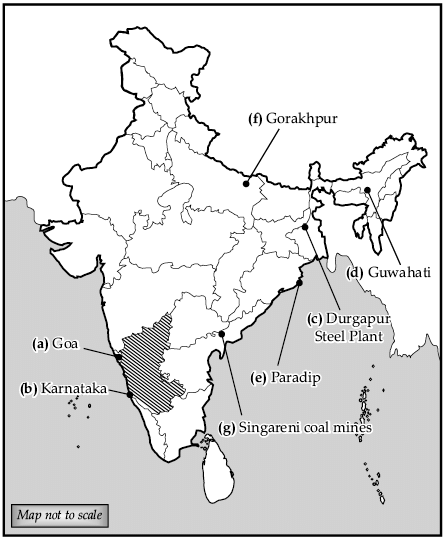
Q.29. In the outline map of the world, five features are shown. Identify them with the help of the information given below and write the correct names.
(a) A mega city
(b) A major sea-port
(c) Grasslands of Africa with extensive commercial grain farming
(d) An important shipping canal
(e) Industrial region of the US.
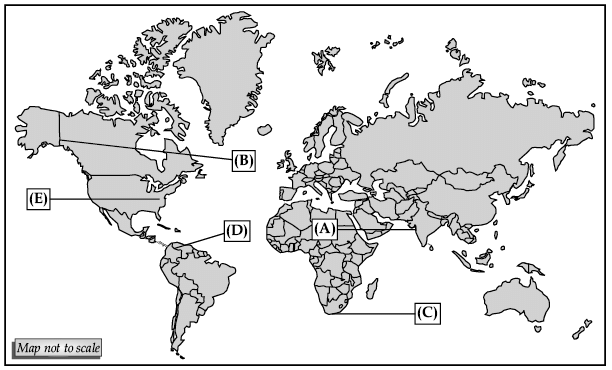
Ans.
(a) Mumbai
(b) Vancouver
(c) Velds
(d) Panama
(e) Appalachians
|
145 docs|4 tests
|
FAQs on Geography: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 2 - CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the CBSE sample question paper for Geography? |  |
| 2. How can the CBSE sample question paper for Geography be beneficial for students? |  |
| 3. How can students access the CBSE sample question paper for Geography (2020-21)? |  |
| 4. Are the questions in the CBSE sample question paper for Geography similar to the actual exam questions? |  |
| 5. How can students make the most out of the CBSE sample question paper for Geography? |  |





















