Business Studies: CBSE Sample Question Papers (2020-21)- 1 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce PDF Download
Class - XII
Business Studies Theory
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 80
General Instructions :
1. This question paper contains 34 questions.
2. Marks are indicated against each question.
3. Answer should be brief and to the point.
4. Answers to the questions carrying 3 marks may be from 50 to 75 worlds.
5. Answers to the questions carrying 4 marks may be about 150 worlds.
6. Answers to the questions carrying 6 marks may be about 200 worlds.
7. Attempt all parts of the questions together.
Q.1. .......... step in the process of planning which is considered the “real point of decision-making”.
(a) Setting objectives
(b) Identifying alternatives
(c) Selecting the the best alternative
(d) Follow-up
Ans: c
Q.2. Delegation is to delegate the authority from superior to ........................... .
(a) Subordinate
(b) Superior
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Ans: Subordinate
Q.3. “Management also contains some fundamental principles which can be applied universally like the Principle of Unity of Command i.e. one man, one boss. This principle is applicable to all type of organization - business or non-business.”
In the above para, management is referred as:
(a) Science
(b) Art
(c) Profession
(d) Process
Ans: a
Q.4. Reema is one of the most successful managers of her company, Globe Ltd. She knows that the principles of management are intended to apply to all types of organisations, business as well as non-business, small as well as large, public sector as well as private sector.
Identify the point related to the nature of management principles being highlighted in the above description.
(a) Universally accepted
(b) General guidelines
(c) Flexible
(d) Contingent
Ans: a
Q.5. “During the lockdown, an estimated 14 crore (140 million) people lost employment while salaries were cut for many others. More than 45% of households across the nation have reported an income drop as compared to the previous year.”
Identify the dimension of the business environment stated above.
(a) Legal environment
(b) Economic environment
(c) Technological environment
(d) Political environment
Ans: b
Q.6. Devendra, the Plant Superintendent of Faulty Works Inc., is very energetic and he likes to deal with severe situations. He is a perfectionist who pursues quality management. He prepares a timetable every week to minimize departmental work and time waste. However, he was disturbed by the brutal competition among employees, which had a negative impact on overall production. Even if all these problems occur, he can handle the situation well. On February 26, he informed his boss that the goal he had been given had been achieved and the quality was the highest.
The best part is that there are two days left for the deadline, which is February 28. However, his boss was dissatisfied because the expenses incurred by his team to complete the project exceeded the allowable upper limit.
In the above case, find out the concepts of management followed
(a) Efficiency
(b) Controlling
(c) Planning
(d) Effectiveness
Ans: d
Q.7. .................... is concerned with doing the right task.
(a) Effectiveness
(b) Efficiency
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Ans: a
Q.8. “Some changes can be made in application of principles according to the requirement of the company. For example, the principle of centralisation insists on concentration of power and authority at top level, but the extent and degree of centralisation may vary according to nature of organisation and centralisation does not mean total centralisation; there can be use of decentralisation at lower level if organisation demands it.”
Identify the characteristic of principles of management discussed above.
(a) Flexibility
(b) Behavioural in nature
(c) General Guidelines
(d) Contingent
Ans: a
Q.9. ......................... is the act of increasing the knowledge and technical skills of an employee for doing a particular job efficiently.
(a) Training
(b) Controlling
(c) Organising
(d) None of the above
Ans: a
Q.10. When physiological needs are satisfied to a relative extent, one feels about another important need. Identify the ‘another’ need stated above:
(a) Social need
(b) Safety need
(c) Esteem need
(d) None of these
Ans: b
Q.11. ........................ gives shape to the organisation structure.
(a) Extent of delegation
(b) Span of Management
(c) No. of employees
(d) Planning
OR
.................... in management refers to the relationship between people, work and resources used to achieve the common objectives (goals).
(a) Organising
(b) Departmentalisation
(c) Delegation
(d) Decentralisation
Ans: b Or a
Q.12. Match the Levels of Packaging in Column I with their examples in Column II.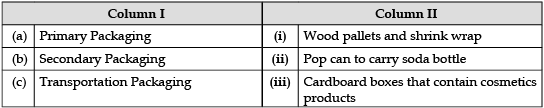
(a) (ii), (iii), (i)
(b) (i), (ii), (iii)
(c) (iii), (i), (ii)
(d) (ii), (i), (iii)
OR
Saumya decided to start a business of selling dress material from her house. She did various online surveys to find out about the preferences of prospective customers. Based on this, she prepared a detailed analysis of the business. She then made important decisions including deciding about the features, quality, packaging, labelling and branding of the dress material. Identify the element of Marketing Mix discussed above.
(a) Promotion
(b) Market
(c) Product
(d) Place
Ans: a Or c
Q.13. Which method of floatation was used by Rajni Auto Manufacturers?
(a) Right issue
(b) Private placement
(c) Offer for sale
(d) E-IPOs
Ans: a
Q.14. Which type of account is being indicated here?
(a) Demat Account
(b) Saving Account
(c) Current Account
(d) Nominal Account
Ans: a
Q.15. Rajesh is the CEO of a leading petrochemical company. Recently, the company issued share capital to cover some expenses. However, in order to meet the floating cost of issuing shares, the company decided to conduct Bridge Financing. Therefore, it decided to issue a money market tool. The wise CEO’s wise decision wisely met the company’s requirements. Three months later, the company decided to issue new shares in the primary market again. According to the floating method it involves, it decided to adopt the method mainly adopted by listed companies and attract the masses by directly contacting the public. Again, success comes from the company’s approach and the realization of its goals. However, when the company tried the same type again three months later, the company had encountered many problems. The problem is to determine a key aspect related to the security of the new release. If the same process is carried out in the secondary market, the company will not care too much about this key aspect.
When the company repeated the same process again after three months, it faced problem in:
(a) Primary market
(b) Money market
(c) Commodity market
(d) None of the above
Ans: a
Q.16. Identify regulatory functions of this above mentioned organisation?
(a) Pricing of securities
(b) Spreading of equity cult
(c) Registration of brokers and sub-brokers
(d) Promotion of ethical and fair practices
Ans: c
Q.17. An FMCG company has recently launched a new type of biscuit in the market. The name of the biscuit is ‘Standard’. The company has made the biscuits of the highest quality possible. It wants to create an irreplaceable place for the new brand in the market. The price of the biscuit is also the highest in the market suggesting its quality. The CEO of the company in an interview said that the branding of the new biscuit will help the company to connect with the customers. A customer can ask for the promised quality in case the company deviates from it. As far as packaging of the biscuit is concerned it is different from others. The immediate outer covering is beautiful and an additional layer of cardboard box is provided to ensure protection to the shape of the biscuits.
Which characteristic of the good brand name can be seen in the brand name of the biscuit kept by the company?
(a) Suggesting benefits and qualities of the product
(b) Easily pronounceable
(c) Distinctive
(d) Stable
Ans: a
Q.18. That part of a brand which can be recognised but which is not utterable is called ................ .
(a) Brand Mark
(b) Trade Mark
(c) Brand Name
(d) None of these
Ans: a
Q.19. A tea manufacturing company has put labels on its packets stating the variety of tea it is selling. Currently it has three varieties—red, green and black. The tea of the company comes from a garden in Assam which is 100 years old. So the price of the tea is high but recently in order to stay in the market it has lowered down its prices by 20%. The company sells its tea in different markets of the world. Next year the company is thinking of selling its tea in the market of a nation having a very high population. The top management hasn’t yet decided the type of channel it should choose. Two years back the company started selling its tea online; the decision brought an indirect change in one of the elements of the marketing mix and, of course, one element saw change directly.
Which factor of price determination has affected the pricing of tea by the company?
(a) Extent of competition in the market
(b) Product cost
(c) Utility and demand
(d) Marketing methods used
Ans: a
Q.20. An FMCG company has recently launched a new type of biscuit in the market. The name of the biscuit is ‘Standard’. The company has made the biscuits of the highest quality possible. It wants to create an irreplaceable place for the new brand in the market. The price of the biscuit is also the highest in the market suggesting its quality. The CEO of the company in an interview said that the branding of the new biscuit will help the company to connect with the customers. A customer can ask for the promised quality in case the company deviates from it. As far as packaging of the biscuit is concerned it is different from others. The immediate outer covering is beautiful and an additional layer of cardboard box is provided to ensure protection to the shape of the biscuits.
Which level of packaging does ‘cardboard box’ come under?
(a) Primary packaging
(b) Secondary packaging
(c) Transportation
(d) None of these
Ans: b
Q.21. Explain how Principles of Management
(i) Provide useful insights into reality; and
(ii) Help in thoughtful decision-making.
OR
Enumerate the three economic objectives of management.
Ans: (i) Principles of management provide useful insights into reality by enabling the managers to learn from the past mistakes and conserve time by solving recurring problems quickly.
(ii) Principles of management help in thoughtful decision-making because the decisions based on principles are not biased and based on the objective assessment of the situation.
OR
Following are the economic objectives of management
(1) Survival
(2) Profit
(3) Growth
Detailed Answer
Following are the economic objectives/ organisational objectives of Management:
(i) Survival : Management must strive to ensure the survival of the organisation by earning adequate revenues to cover its costs, produce or sell standardised goods or services, keeping the motivation level of the employees high.
(ii) Profit : Management should make every effort to minimise the cost and maximise profits and production. Profit provides a vital incentive for the continuous successful operations of the enterprise.
(iii) Growth : To grow in the industry, the management of an organisation must optimally utilise its all scarce resources.
Q.22. What is meant by Non-financial incentives? List any two Non-financial incentives.
OR
How does directing help in efficient and effective functioning of the organisation? Explain by giving any three points.
Ans: Non-financial Incentives are those incentives which cannot be measured in terms of money.
The two non-financial incentives are:
(i) Job Security;
(ii) Status;
(iii) Job enrichment; and
(iv) Career advancement opportunities.
OR
Importance or directing:
(i) Directing helps to initiate action in the organization towards attainment of desired objectives.
(ii) Directing integrates employees’ efforts in the organization in such a way that every individual effort contributes to the organisational performance.
(iii) Directing guides employees to fully realize their potential and capabilities by motivating and effective leadership.
(iv) Directing facilitates introduction of needed changes in the organisation,
(v) Effective directing helps to bring stability in the organization.
Q.23. “Similar to being a system of motivation, a good control mechanism also allows for the maintenance of discipline within a business.” In the light of this statement, explain how controlling helps in maintaining discipline.
Or
“Controlling, like most other processes, is composed of a number of steps followed in sequential order. The first step is establishment of standards.” Explain next to step of controlling process.
Ans: Similar to being a system of motivation, a good control mechanism also allows for the maintenance of discipline within a business. When there is a clear understanding of what is shunned and what is appreciated the employees will be disciplined in doing what is to be done and will not do those that are shunned, creating a stable and disciplined workforce.
Controlling is thus a very important and integral part of everyday management. It is a process that helps in ensuring business success and stability and cannot be separated from the other functions. This is because the effectiveness of planning and all other functions are gauged and understood through the process of controlling.
OR
(ii) Measurement of Actual Performance: The next step is measurement of actual performance. Performance should be measured in an objective and reliable manner. There are several techniques for measurement of performance. For example, personal observation, sample checking, performance reports, etc. As far as possible, performance should be measured in the same units in which standards are set as this would make their comparison easier.
(iii) Comparing Actual Performance with Standards: This step involves comparison of actual performance with the standard. Such comparison will reveal the deviation between actual and desired results. Comparison becomes easier when standards are set in quantitative terms. For instance, performance of a worker in terms of units produced in a week can be easily measured against the standard output for the week.
Q.24. Keeping in mind the emerging nature of the securities market in India, Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was entrusted with the twin task of regulation and development of securities market. Out of this, state the developmental functions of Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Ans: Developmental functions of SEBI are as follows:
(i) Training : Training of intermediaries of securities markets for their professional growth.
(ii) Developing Capital Markets : Undertaking measures to develop the capital markets by adopting a flexible approach.
(iii) Conducting Research : SEBI encourages research for improving the functioning of capital market, for streamlining the activities of stock exchange, for developing and strengthening the capital markets, etc.
.Q.25. Astra Builders has to deliver the flats to its buyers on time. Due to this there is a sudden rush of work.
Therefore, the company needs to arrange workers to work at the sites at a short notice. Suggest the source of recruitment which may be used by the company to tap the casual vacancy is. Also explain any three other sources which company might be used if there was no rush of work.
Ans: Direct Recruitment: Under the direct recruitment, a notice is placed on the notice board of the enterprise specifying the details of the jobs available.
Other Sources:
(i) Casual callers: It is an external source of recruitment in which a list of job seekers is prepared and screened to fill the vacancies as they arise, from the database of unsolicited applications kept in the office.
(ii) Labour Contractors: It is an external source of recruitment in which a Labour Contractor maintains close contacts with labourers and provides the required number of unskilled workers at short notice.
(iii) Advertisement: Advertisement in media is generally used when a wider choice is required. Example – Newspapers, Internet, Radio, Television, etc.
Q.26. Huma is working in a company on a permanent basis. As per the job agreement, she had to work for 8 hours a day and was free to work overtime. Huma worked overtime, due to which she fell ill and had to take leave from her work. No one showed concern and enquired about her health. She realised that she was fulfilling only some of her needs while some other needs still remained to be fulfilled.
(i) By quoting the lines from the above para, identify the needs of Huma which she is able to fulfil.
(ii) Also explain two other needs of Huma followed by the above needs.
Ans: (i) (a) “Huma is working in a company on a permanent basis” - Safety/security needs.
(b) “As per the job agreement she had to work 8 hours a day and was free to work overtime”- Basic physiological needs.
(ii) Explanation of two other needs of Huma which still remained to be satisfied are:
(a) Affiliation/Belongingness Needs: These needs refer to affection, sense of belongingness; acceptance and friendship, cordial relations with the colleagues.
(b) Esteem Needs: These include factors such as self-respect, autonomy status, job title, recognition and attention.
Q.27. What is the meaning of motivation? State the features of motivation as an element of Directing.
OR
Explain the concept of leadership and its various styles.
Ans: Motivation: Motivation means incitement or inducement to act or move. It means the process of making subordinates to act in a desired manner to achieve certain organisational goals.
Features of motivation :
(i) It is an internal feeling.
(ii) It produces goal-directed behaviour.
(iii) It can be either positive or negative.
(iv) It is a complex process.
Detailed Answer
Features of Motivation are:
(i) Motivation is an Internal Feeling : The urges, drives, desires, aspirations, strivings or needs of human beings which are internal, influence human behaviour. For example, people may have different urges like possessing a car, flat, AC, etc. It may be noted that urges are internal to an individual.
(ii) Motivation produces Goal-directed Behaviour : Motivation induces people to behave in such a manner that they can achieve their goals. For example, if a person has strong desire to get a promotion, he will work efficiently to achieve his goal.
(iii) Motivation is a Complex Process : Individuals are heterogeneous in their expectations, perceptions and reactions. A technique of motivation may not have a uniform effect on all the people. Some are motivated by financial incentives while others prefer non-financial incentives like recognition, well-furnished office, etc.
(iv) Motivation is a Continuous Process : Human beings are wanting animals. Their needs are unlimited and keep on changing continuously. Satisfaction of one need gives rise to another. So, the managers have to continuously perform the function of motivation.
OR
Leadership is the process of influencing behaviour of the people so that they strive willingly and enthusiastically towards the achievement of group goals.
The various Leadership styles are :
(i) Autocratic or Authoritarian Leadership
(ii) Democratic or Participative Leadership
(iii) Laissez Faire or Free – Rein Leadership
Detailed Answer :
(i) Autocratic Leadership or Authoritarian Leadership : The autocratic leadership style allows managers to make decisions alone without the input of others. Managers possess total authority and impose their will on the employees. No one challenges the decisions of autocratic leaders. An autocratic leader centralizes power and decision-making in himself. He gives orders, assigns tasks and duties without consulting the employees. In this style of leadership, a leader has complete command and hold over their employees/team. The team cannot put forward their views even if they are best for the teams or organisational interests.
(ii) Democratic Leadership or Participative Leadership : Participative or Democratic Leaders decentralise authority. It is characterised by consultation with the subordinates and their participation in the formulation of plans and policies. He encourages people participation in decision-making process.
(iii) Laissez Faire or free-rein leadership : The Laissez Faire or non-interfering type of leader passes on the responsibility for decision-making to his subordinates and takes a minimum of initiative in the administration. He gives no direction and allows the group to establish its own goals and work out its own problems. The leader plays only a minor role. His idea is that each member of the group, when left to himself, will put forth his best effort and the maximum results can be achieved in this way.
Q.28. Zintax Ltd. is engaged in the business of export of leather shoes. In the past, the performance of the company had been upto the expectations. In line with the latest demand in the market, the company decided to venture into sports goods and snickers for which it required specialised machinery. For this, the Finance Manager Ritesh prepared a financial blueprint of the organisation’s future operations to estimate the amount of funds required and the timings with the objective to ensure that enough funds are available at right time. he also collected the relevant data about the profit estimates in the coming years. By doing this, he wanted to be sure about the availability of funds from the internal sources of the business, For the remaining funds, he is trying to find out alternative sources from outside.
Identify the financial concept discussed in the above paragraph. Also, state the objectives to be achieved by the use of financial concept so identified.
Ans: Financial Planning : Objectives of Financial Planning :
(i) Ensures availability of adequate funds at the right time : This includes a proper estimation of funds required for different purposes such as for the purchase of long-term assets or to meet dayto-day expenses of business. It estimates the time at which the funds are to be made available. Based on these facts, funds could be raised from short-term and long-term sources.
(ii) Sees that the firm does not raise resources unnecessarily : Excess funding is almost as bad as inadequate funding. So, the financial manager must see to it that the company does not raise more capital that the requirement of the business. In case, there is surplus cash or liquidity, the excess funds should be utilised judiciously.
Q.29. Somnath Ltd. is engaged in the business of export of garments. In the past, the performance of the company had been up to the expectations. In line with the latest technology, the company decided to upgrade its machinery. For this the Finance Manager, Dalmia estimated the amount of funds required and the timings. This will help the company in linking the investment and the financial decisions on a continuous basis. Dalmia therefore, began with the preparation of a sales forecast for the next four years. He also collected the relevant data about the profit estimates in the coming years.
By doing this he wanted to be sure about the availability of funds from the internal sources of the business. For the remaining funds, he is trying to find out alternative sources from outside.
Identify the financial concept discussed in the above para. Also state the objectives to be achieved by the use of financial concept, so identified.
Ans: Financial Planning: Financial planning refers to the planning regarding financial needs of the enterprise, various sources of raising funds and their optimum utilisation.
Objectives of financial planning:
(i) To ensure availability of adequate funds at the right time: This includes a proper estimation of fund required for different purposes such as for the purchase of long-term assets or to meet day-to-day expense of business. Apart from this, it is essential to estimate the time at which the funds are to be made available. Based on these facts, funds could be raised from short-term and long-term sources.
(ii) To see that the firm does not raise resources unnecessarily: Excess funding is almost as bad as inadequate funding. So, the financial manager must see to it that the company does not raise more capital than the requirement of the business. In case there is surplus cash or liquidity, the excess funds should be utilized judiciously.
Q.30. State any four directions which can be issued by the consumer court to the opposite party if it is satisfied about the genuineness of the complaint.
Ans: If the Consumer Court is satisfied with the genuineness of the complaint, it can issue one or more of the following directions to the aggrieved party as reliefs :
(i) To remove the defect in goods or the deficiency in services.
(ii) To replace the defective product with a new one, free from any defect.
(iii) To refund the price paid for the product.
(iv) To pay a reasonable amount of compensation for any loss or injury suffered by the consumer due to negligence of the opposite party.
(v) To pay punitive damages in appropriate circumstances.
(vi) To discontinue the unfair/restrictive trade practice and not to repeat the same in future.
(vii) Not to offer hazardous goods for sale.
(viii) To withdraw hazardous goods from sale.
(ix) To cease manufacture of hazardous goods.
(x) To pay any amount not less than 5% of the value of the defective goods to be credited to the Consumer Welfare Fund or any other organisation/person, to be utilised in the prescribed manner.
(xi) To issue corrective advertisement to neutralise the effect of misleading advertisement.
(xii) To pay adequate costs to the appropriate party.
Q.31. ‘Scientific Management means knowing exactly what you want your men to do and seeing that they do it in the best and the cheapest way’. Taylor developed various techniques for application of Scientific Management principles and was able to achieve a three-fold increase in productivity in Bethlehem Steel Company, where he worked. One of the techniques helps to determine the number of workers to be employed; frame suitable incentive schemes and determine labour costs.
Another technique recognises those workers who are able to accomplish/exceed the fair day’s work and is based on the premise that efficiency is the result of the joint efforts of the managers and the workers.
Quoting the lines from the above paragraph, identify and explain the two techniques of Scientific Management.
Ans: The two techniques of scientific management are :
(i) Time study
Line – one of the techniques helps to determine the no. of ................ labour costs
(ii) Differential piece wage rate system
Line – Another technique recognise ................... the workers
(i) Time Study : It is a technique which is used to determine the standard time taken by a worker to perform a well-defined job. It determines how much work an employee should be able to do in a given period of time.
The objectives of time study are:
(a) To determine the number of workers required to do a job
(b) To determine standard time required to perform a job
(c) To categorise the workers in efficient and inefficient categories
(d) To determine the cost of labour
(ii) Differential Piece Wage System : According to this, there are different rate of wage payment, higher rate for the efficient members who performed above standard and lower rate for those who perform below standards.
(a) This technique is the strongest motivator for a worker to reach standard performances.
(b) This system emphasizes on paying different rate of wage for efficient and inefficient employees.
(c) In this two different wage rates are used : one is the higher wage rate and the other is the lower wage rate and the basic aim of fixing two different rates is to differentiate between efficient and inefficient workers and to suitably reward the efficient workers.
(d) Higher wage rates are fixed for those workers who produce equal to or more than the standard output and lower wage rates are fixed for those workers who do not reach the standard output.
Q.32. Ajanta Garments Limited manufactures ready-made garments. The manager wants to increase profit by :
(i) Purchasing new high speed machines; or
(ii) Increasing the sales price; or
(iii) Using the waste materials in manufacturing stuffed toys.
The manager decided that using the waste materials in manufacturing stuffed toys is the best option for him.
(i) Identify the management function involved.
(ii) Mention the steps involved in the above function by quoting the lines from the above.
(iii) To complete the function identified in (i) what further steps the manager should take?
Or
Suhasini, a home science graduate from a reputed college, has recently completed a cookery course. She wished to start her own venture with a goal to provide ‘health food’ at reasonable price. She discussed her idea with her teacher (mentor) who encouraged her. After analysing various options for starting her business venture, they shortlisted the option to sell ready-made and ‘ready to make’ vegetable shakes and sattu milk shakes. Then, they weighed the pros and cons of both the shortlisted options.
(i) Name the function of management being discussed above.
(ii) Also discuss briefly any four limitations of the function discussed above.
Ans: (i) The function of management involved is planning.
(ii) Steps involved in the function are:
(a) Setting objectives: Wants to increase profit.
(b) Identifying alternatives: Purchasing new high speed machines, increasing sales price or using the waste materials in manufacturing stuffed toys.
(c) Selecting the best alternative: Using waste materials in manufacturing stuffed toys.
(iii) To complete the function identified in (i), the manager should take the following steps:
(a) Implement the plan of manufacturing stuffed toys using waste materials.
(b) Follow-up action to ensure that the plan is implemented effectively.
OR
The function of management discussed above is Planning.
Limitations of Planning:
(i) Planning leads to rigidity: In an organisation, a well-defined plan is drawn up with specific goals to be achieved within a specific time frame. These plans then decide the future course of action and managers may not be in a position to change it. This kind of rigidity in plans may create difficulty. Managers need to be given some flexibility to be able to cope with the changed circumstances. Following a predecided plan, when circumstances have changed, may not turn out to be in the organisations interest.
(ii) Planning may not work in a dynamic environment: The business environment is dynamic, nothing is constant. The environment consists of a number of dimensions, economic, political, physical, legal and social dimensions. The organisation has to constantly adapt itself to changes. It becomes difficult to accurately assess future trends in the environment, if economic policies are modified or political conditions in the country are not stable or there is a natural calamity.
(iii) Planning reduces creativity: Planning is an activity which is done by the top management. Usually, the rest of the members just implement these plans. As a consequence, middle management and other decision-makers are neither allowed to deviate from plans nor they are permitted to act on their own. Thus, much of the initiative or creativity inherent in them also gets lost or reduced. Thus, planning in a way reduces creativity since people tend to think along the same lines as others. There is nothing new or innovative.
(iv) Planning involves huge costs: When plans are drawn up huge costs are involved in their formulation. These may be in terms of time and money. For example, checking the accuracy of facts may involve a lot of time. Detailed plans require scientific calculations to ascertain facts and figures. The costs incurred sometimes may not justify the benefits derived from the plans. There are a number of incidental costs as well, like expenses on board meetings, discussions with professional experts and preliminary investigations to find out the viability of plans.
(v) Planning is a time-consuming process: Sometimes, plans to be drawn up take so much of time that there is not much time left for their implementation.
(vi) Planning does not guarantee success: The success of an enterprise is possible only when plans are properly drawn up and implemented. Any plan needs to be translated into action or it becomes meaningless. Managers have a tendency to rely on previously tried and tested successful plans. It is not always true that just because a plan had worked before, it will work again.
Q.33. In 2015, Naveen left his luxurious life in Mumbai, where he worked as a manager for Blue Birds Ltd. He shifted to Begampur, Chhattisgarh to fulfil his grandmother’s dream of converting their 25-acre ancestral land into a fertile farm. For this, he set out specific goals along with the activities to be performed to achieve the goals.
Every activity was a challenge since he was clueless about farming. He learnt every activity from tilling the land to sowing the seeds. To aid farmers, he launched his own company ‘Innovative Agriculture Solutions Pvt. Ltd’.
It was difficult initially as no one trusted an urban youth telling farmers about farming. But when everything was discussed in detail, the farmers started taking interest. He wanted to ensure that the future events meet effectively the best interests of the company. Through sales forecasting, he prepared an annual plan for production and sales.
He also found that the farmers grew only paddy, which was an activity of 3-4 months and the land remained idle for the rest 8-9 months of the year. He not only identified but evaluated various alternatives through which the farms could be utilised for the remaining months of the year. Through correct foresight and logical and systematic thinking based on analysis of all facts, all alternatives were examined and evaluated. He presented a plan to the farmers, where after harvesting paddy, vegetables could be grown.
The above case highlights the features of one of the functions of management. By quoting lines from the above identify the function stated and explain its features.
Ans: Features of planning are :
(i) Planning focuses on achieving objectives
‘He set out specific goals along with the activities to be performed to achieve the goals’. Planning focuses on achieving objectives as specific goals set out in the plans along with activities to be undertaken to achieve the goals.
(ii) Planning is futuristic :
‘He wanted to ensure that the future events meet effectively the best interests of the company’.
OR
‘Through sales forecasting, he prepared an annual plan for production and sales’
Planning is futuristic as it involves looking ahead and preparing for the future.
(iii) Planning involves decision making
‘He not only identified but evaluated various alternatives through which the farms could be utilised for the remaining months of the year’.
OR
‘…. all alternatives were examined and evaluated’
Planning involves decision making as it involves a choice from among the various alternative courses of action.
(iv) Planning is a mental exercise
‘Through correct foresight and logical and systematic thinking based on analysis of all facts…’.
Planning is a mental exercise as it is intellectual activity of thinking rather than doing.
Q.34. Explain any six characteristics that you will keep in mind while choosing a brand name.
OR
Explain the four important elements of marketing mix.
Ans: A good brand name should contain the following characteristics :
(i) Simple and Short : A brand name should be simple and short so that there is no complication related to its name.
(ii) Easily Pronounceable : A brand name should be easily pronounceable e.g., TATA, GLUCOSE, etc.
(iii) Suggestive : Brand name should be self-explanatory thereby, suggesting the inherent quality of the product. For example, HAJMOLA indicates the curing of indigestion.
(iv) Distinctive : Brand name should be so distinctive that it highlights itself in the group of other brand names, such as Tide, Rin, Surf Excel, etc.
(v) Stability : The brand name should have a stable life, its life should not be affected by the changes in fashion or style. Phillips, Bournvita, Saridon, Surf, and HMT are some of the examples in this regard.
(vi) Registration : The brand name should be capable of being registered. This will protect the brand holder from imitation by the rivals.
OR
The important elements of Marketing Mix are :
(i) Product Mix : Product mix is related to the decisions regarding planning, developing and producing the right type of products and services for the consumers. It includes branding, labelling, trademark and packaging.
(ii) Price Mix : Price mix involves different pricing methods, pricing strategies, pricing policies and price changes.
(iii) Place Mix : Place or Physical Distribution mix includes activities that make firm’s products available to the targeted customers. It consists of all the activities involved in transferring ownership and physical possession of the product to the consumers.
(iv) Promotion Mix : Promotion mix consists of all the activities aimed at persuading customers to buy the product through advertising, personal selling, sales promotion and publicity.
|
130 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Business Studies: CBSE Sample Question Papers (2020-21)- 1 - Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce
| 1. What is the CBSE sample question paper for Business Studies Class 12? |  |
| 2. How can I access CBSE sample question papers for Business Studies Class 12? |  |
| 3. Why are CBSE sample question papers important for Class 12 Business Studies exam preparation? |  |
| 4. Are the CBSE sample question papers for Business Studies Class 12 similar to the actual exam paper? |  |
| 5. Can I rely solely on CBSE sample question papers for my Class 12 Business Studies exam preparation? |  |
















