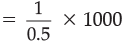Class - XII
Economics
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 80
General Instructions :
1. This question paper contains two parts :
Part A : Macro Economics (40 marks)
Part B : Indian Economic Development (40 marks).
2. All questions in both sections are compulsory. Marks for questions are indicated against each question.
3. Question No. 1-10 and 18-27 (including two Case Based Questions) are very short answer questions carrying 1 mark each. They are required to be answered in one word or one sentence each.
4. Case Based Questions (CBQ’s) are Question No. 7-10 and Question No. 25-27.
5. Question No. 11-12 and 28-29 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to them should not normally exceed 60-80 words each.
6. Question No. 13-15 and 30-32 are also short answer questions carrying 4 marks each. Answers to them should not normally exceed 80-100 words each.
7. Question No. 16-17 and 33-34 are long answer questions carrying 6 marks each. Answers to them should not normally exceed 100-150 words each.
8. Answers should be brief and to the point and the above word limit be adhered to as far as possible.
9. There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions of one mark, 2 questions of three marks, 2 questions of four marks and 2 questions of six marks. Only one of the questions have to be attempted.
10. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary
PART — A
Q.1. Inventory is a _________concept whereas the change in inventory is a _________concept. (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
(i) stock, flow
(ii) flow, stock
(iii) stock, stock
(iv) flow, flow
Ans. (i) stock, flow.
OR
If in an economy the value of Net Factor Income from Abroad is Rs. 200 crores and the value of Factor Income to Abroad is Rs. 40 crores. Identify the value of Factor Income from Abroad. (Choose the correct alternative)
(i) Rs. 200 crores
(ii) Rs. 160 crores
(iii) Rs. 240 crores
(iv) Rs. 180 crores
Ans. (iii) Rs. 240 crores.
Q.2. __________________ is a capital receipt of the government.
(i) Depreciation
(ii) Disinvestment
(iii) Tax
(iv) Fee
Ans. (ii) Disinvestment
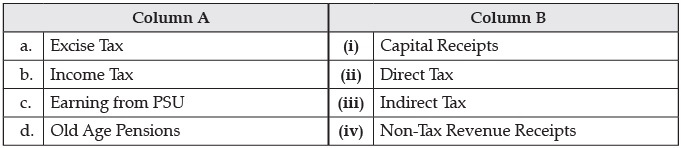
Q.3. Identify the correctly matched pair in Column A to that of Column B:
(i) a – (i)
(ii) b – (ii)
(iii) c – (iii)
(iv) d – (iv)
Ans. (ii) Income Tax – (b) Direct Tax
Q.4. Money supply constitutes money held by public (or outside the banks) and ___________________.
(i) Demand Deposits
(ii) Fixed deposit
(iii) Both (i) and (ii)
(iv) Neither (i) nor (ii)
Ans. (i) Demand Deposits
Q.5. Identify which of the following statements is true? (Choose the correct alternative)
(i) The flexible exchange rate system gives the government more flexibility to maintain large stocks of foreign exchange reserves.
(ii) In the Managed floating exchange rate system, the government intervenes to buy and sell foreign currencies.
(iii) In the Managed floating exchange rate system, the central bank intervenes to moderate exchange rate fluctuations.
(iv) In the Fixed exchange rate system, market forces fix the exchange rate.
Ans. (iii) In the Managed floating exchange rate system, the central bank intervenes to moderate exchange rate fluctuations.
Q.6. Other things remain unchanged, when in a country, the price of foreign currency rises, national income is:
(i) Likely to rise
(ii) Likely to fall
(iii) Likely to rise and fall both
(iv) Not affected
Ans. (ii) Likely to fall
Q.7. Read the Hypothetical case given below and answer the questions (7 to 10):
In an economy the Aggregate Demand is determined by consumption, government Expenditure and Net Exports in the Economy. This is affected by the Savings and Investment in the Economy. The Multipliers, that is investment multiplier, which is influenced by the ratio of total consumption and total income, regulates the flow of money in the economy influencing the Aggregate Demand and Supply. Any change in any of the factors leads to a big change in the economy’s equilibrium as a whole. It is to be kept in mind that the Economy needs to be in equilibrium condition mostly. When savings is less than the investments the aggregate demand is more than the aggregate supply, and vice versa.
Q. The ratio of total consumption expenditure to total income is called___________________.
(i) MPS
(ii) MPC
(iii) APC
(iv) APS
Ans. (ii) MPC
Q.8. AD increases, __________ increases.
(i) Employment
(ii) Unemployment
(iii) AS
(iv) Multiplier
Ans. (i) Employment.
Q.9. The difference by which actual Aggregate Demand exceeds the Aggregate Demand, required to establish full employment equilibrium is known as___________(inflationary gap/deflationary gap). (choose the correct alternative)
Ans. inflationary gap
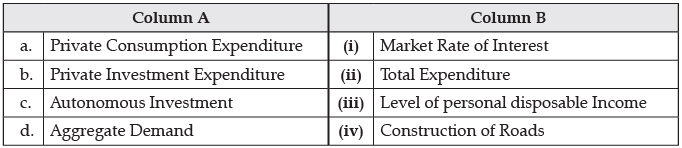
Q.10. Match the following by choosing the correct set from Column A and Column B:
Choose the correct alternatives :
(i) a-(iii), b-(i), c-(iv), d-(ii)
(ii) a-(ii), b-(i), c-(iv), d-(iii)
(iii) a-(iv), b- (iii), c-(ii), d-(i)
(iv) a-(ii), b-(iv), c-(iii), d-(i)
Ans. (i) a-(iii), b-(i), c-(iv), d-(ii)
Q.11. Giving reason explain how the following will be entered in
(a) current account or capital account
(b) on credit side or debit side of balance of payments:
(i) Imports of Machinery
(ii) Investments from abroad
OR
Explain the distinction between the flexible exchange rate and the managed floating exchange rate.
Ans. (i) Imports of Machinery :
(a) Recorded as visible items in the current account, because it does not change any liability or an asset.
(b) Recorded on debit side because it leads to outflow of foreign exchange.
(ii) Investments from aboard :
(a) Recorded in capital account because it creates a liability to pay foreign exchange.
(b) Recorded on credit side because it leads to inflow of foreign exchange.
OR
Flexible exchange rate is the rate which is determined by the supply and demand forces in foreign exchange market. It is free from intervention other than market forces.
Whereas,managed floating exchange rate is the market rate which can be influenced by the intervention of the central bank in the foreign exchange market. It is a tool to control unfavourable impacts of flexible exchange rate.
Q.12. State the effect of the following on the balance of payment situation.
(i) Increase in import duty of gold
(ii) Rise in the price of foreign currency
Ans. (i) This will reduce import of gold and thus will have a favourable effect on BOP situation, as demand for foreign exchange will fall.
(ii) Rise in price of foreign currency will make imports costlier, so import will fall, and it will be favourable for BOP, as demand for foreign exchange will fall.
Q.13. (i) Define money multiplier.
(ii) ‘Credit creation is inversely related to the reserve deposit ratio’. Justify the given statement, using a hypothetical example.
Ans. (i) Money multiplier is the process by which the commercial banks create credit, based upon the reserve ratio and initial deposits.
(ii) Reserve deposit ratio is the minimum reserves which a commercial bank must maintain as per the instructions of the Central Bank.
Credit Creation = 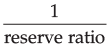
Thus, credit creation is inversely related to the reserve deposit ratio.
For Example: Suppose the Reserve Ratio is 0.2 and initial deposit is Rs. 1000 crores.
Total Credit Created = 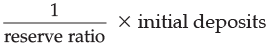
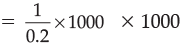
= Rs. 5,000 crores.
Now, suppose reserve ratio is increased to 0.5
Total Credit Created = 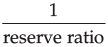 × initial deposits
× initial deposits
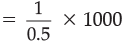
= Rs. 2,000 crores.
Thus, on the basis of the above illustration we can say that there exists an inverse relation between reserve and credit creation.
Q.14. Explain how the economy achieves equilibrium level of income using Consumption + Investment (C + I) approach.
Ans. C + I approach
Aggregate demand, given by C + I, is the planned demand by the various sectors of the economy.
Whether this planned demand is realized or not, depends on amount of goods and services (aggregate output or Y) produced in the economy. Thus, it is only when planned expenditure is equal to the aggregate output does the economy achieving equilibrium. i.e., AD = Y
If AD > Y, inventory level with producers falls and they increase output. This happens till AD = Y Opposite happens if AD < Y.
Q.15. Explain how government budget can be used to influence distribution of income?
Ans. Government can impose higher rate of tax on income of the rich and on the goods consumed by the rich. This will bring down disposable income of the rich. The amount so collected can be spent on providing free services, like education subsidized food to the poor people, e.g., this will raise disposable income of the poor reducing the gap between rich and poor.
Q.16. (a) State three objectives of a government budget.
(b) Is the following, a revenue receipt or a capital receipt in the context of government budget and why?
(i) Tax receipts,
(ii) Disinvestment.
Ans. (a) Objectives of a government budget are as follows :
(i) Re-distribution of income and wealth, with a view to increase equality.
(ii) Re-distribution of resources with a view to maintain balance between the goods of profit maximization and social welfare.
(iii) Achieving economic stability.
(b) (i) Tax Receipts : These are revenue receipts because these neither create any liability nor reduce asset.
(ii) Disinvestment : These are capital receipts because it reduces assets.
Q.17. (i) Elaborate the objective of allocation of resources in the Government budget.
(ii) Discuss briefly how the Government budget can be used as an effective tool in the process of employment generation.
Ans. (i) Allocation of resources: Government seeks to allocate resources with a view to balance the goals of all sections of the society. Production of goods and services which are injurious to health may be discouraged through taxation policy. Similarly, production of goods of socially beneficial nature may be encouraged through subsidies. If the private sector does not take initiative in certain activities (Public Goods), the government may directly control them like water supply and sanitation etc.
Detailed Answer :
Reallocation of Resources:
(i) The government aims to reallocate resources according to economic and social priorities through its budgetary policy.
(ii) Government encourages the production of certain commodities by giving subsidies or tax reliefs. For e.g. government encourages the use of ‘khadi products’ by providing subsidies.
(iii) Government can discourage the production of harmful goods like liquor or cigarettes, by imposing heavy excise duties or taxes. In India, we use progressive taxation, i.e., higher taxes from rich people and distribute these receipts through various welfare activities.
(iv) Government budget can be used as an effective tool in the process of employment generation in various ways. Investment in infrastructural projects like construction of flyovers, bridges, expansion of roads etc. creates jobs for different sections of the workforce. In rural/urban areas government can provide jobs through various employment generation schemes like MGNREGA, SJSRY, PMRY etc.
Detailed Answer :
The Government budget can help in generating employment. When the government increases its expenditure in developmental projects, it not only helps in economic growth but also increases Employment opportunities. The investment in infrastructural projects such as building roads, railways, bridges, hospitals, etc., leads the government to generate employment for the workers as they will need employees to work on these infrastructure projects. The employment generated through this process enables different sections of the society to be in the workforce. Thus it also leads to social welfare and distribution of wealth. The government budget allocation in various employment generation schemes like MGNREGA, SJSRY, PMRY etc, enables the government to freely use the funds on the employment generation and infrastructural projects to generate employment.
PART — B
18. During British period, Indian Economy was:
(i) Semi-feudal Economy
(ii) Disintegrated Economy
(iii) Colonial economy
(iv) All of the above
Ans. (iv) All of the above
OR
First attempt to estimate the National Income in India during British period was made by:
(i) Findley Shirras
(ii) William Digby
(iii) Dada Bhai Naoroji
(iv) V.K.R.V. Rao
Ans. (iv) V.K.R.V. Rao
Q.19. Match the items in Column A to that of Column B and choose the correct option:
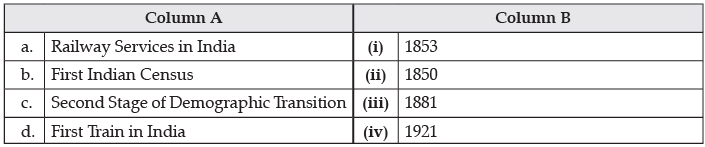
(i) a -(iii), b-(ii), c-(iv), d-(i)
(ii) a-(ii), b-(iii), c-(iv), d-(i)
(iii) a-(iii), b-(i), c-(iv), d-(ii)
(iv) a-(ii), b-(iv), c-(iii), d-(i)
Ans. (ii) a – (ii), b – (iii), c – (iv), d – (i)
Q.20. Out of the following, which industry is reserved for public sector:
(i) Atomic energy
(ii) Industrial explosive
(iii) Medicines
(iv) Defence equipment
Ans. (i) Atomic energy
Q.21. Read the following statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below :
Assertion (A) : Every year government fixes a target for disinvestment of Public Sector Enterprises (PSEs).
Reason (R) : Disinvestment is an excellent tool for discarding the loss incurring Public Sector Enterprises (PSEs).
Alternatives :
(i) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(iii) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(iv) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Ans. (ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
Q.22. The nature of Pakistan’s economy is:
(i) Capitalist
(ii) Socialist
(iii) Mixed
(iv) Communist
Ans. (iii) Mixed
Q.23. First Five-Year Plan of _______________ (China/Pakistan) commenced in the year 1956.
Read, the following hypothetical Case Study, carefully and answer the question numbers 24 - 27 on the base of the same.:
In order to produce in an Economy, there are the four factors, i.e., land, labour, capital and entrepreneur are required. It is the duty of the government to help and nurture all the factors. Moreover the major investment needs to be done on Capital. There are two types of Capital, namely Physical and Human Capital. In order to increase the physical capital the government needs to invest in infrastructure and acquisition of new technologies. These leads to generation of employment, leading to the reduction in the problem of unemployment, that the country like India is suffering with.
There are different types of unemployment present in India, namely seasonal, disguised, industrial, fictional and many other. Most of the employment problems can be solved if the government focuses on investment in education to improve the quality of Human Capital, and for skill development, increase in efficiency and productivity and overall growth of the economy, for all the three sectors in the economy.
Ans. Pakistan
Q.24. Read, the following hypothetical Case Study, carefully and answer the question number 24 on the base of the same:
In July 2017, the Government of India introduced the new indirect Tax regime called the Goods and Service Tax, that subsumed all the other types of taxes, so that India could have the single tax system all over the country for better transparent tax collection.
Other than that, GST has enabled the increase in the efficiency of the agricultural marketing as well. The simplified tax regime has confined and made it easier to transact in the economy.
Not only GST, but the government has done a lot of other initiatives to boost the agricultural sector of India. The emphasis on diversification of Agriculture and schemes like National Rural Health Mission, National Health Insurance Scheme, MGNREGA and others have helped in improving the rural livelihood and the condition of the rural households. The states like Punjab, Haryana and Himachal Pradesh has prospered a lot from agricultural diversification, but GST had no role to play in it, neither did it actually help these states. Even though GST was introduced to subsume all the indirect taxes, but still the centre still levies custom duty, excise duty etc and petroleum product still has VAT charged. Though the government has its own reasons for doing so, but it hinders the actual base of GST itself.
Q. GST abolished all the direct tax levied in India. (True / False)
Ans. False
Q.25. Some economists argue that debt waiver schemes are extremely beneficial to the poor and marginalised farmers, as these schemes reduce the burden of _________(indebtedness/personal expenditures)
Ans. indebtedness
Q.26. Human Capital includes:
(i) Health
(ii) Education
(iii) Professional Skill
(iv) All of the above
Ans. (iv) All of the above
Q.27. Name the active factor in production.
(i) Land
(ii) Physical Capital
(iii) Human Capital
(iv) None of the above
Ans. (iii) Human Capital
Q.28. “Foreign exchange crisis was the basis of economic policies of liberalisation, privatisation and globalisation.” Justify.
Or
Why should plans have goals?
Ans. During the fiscal year 1990-91, foreign exchange reserves fell to a lower level of Rs. 2,400 crores. Which was just enough for the payments of three weeks imports.
The crisis was so serious that Chandra Shekhar government had to mortgage gold reserves with other countries to pay off interest and foreign debts.
Therefore, it forced India to adopt a new set of measures to accumulate foreign exchanges reserve by way of liberalization, privatization and globalization.
OR
Every plan should have specified goals which it seeks to pursue. Goals are the ultimate targets the achievement of which ensures the success of plans. A plan specifies the means and ways to allocate scarce resources in an optimum manner so as to achieve these desired goals. Without specific goals, a plan would be directionless, and resources would not be utilised in a proper manner without wastage.
Following goals are focused in every plan:
(i) Growth
(ii) Modernisation
(iii) Self-reliance
(iv) Equity
Q.29. Discuss briefly the concept of 'informalisation of workforce', in the context of Indian economy.
Ans. In the recent years, India has witnessed an unprecedented shift of the workforce from the formal sector to informal sector. This process whereby, the proportion of informal worker in the total workforce increases is known as informalisation of workforce.
Detailed Answer :
Informalisation of workforce means a situation in which the percentage of casual workers in total workforce has a tendency to increase over a period of time. Recently in India there has been a shift in the working population from formal sector to the informal sector due to the competition or strict labour laws. This is because of the following reasons:
(a) Illiteracy of the rural population.
(b) Many industries employ the workers on contractual basis.
(c) The need for the regular workers has decreased in the economy, as companies outsource their jobs to third parties.
Q.30. Infrastructure contributes to the economic development of a country. Do you agree? Explain.
OR
What are the needs of sustainable development?
Ans. Yes, Infrastructure acts as a support system for production activity in the economy and thereby contributes to economic development. The following point explain the role of infrastructure :
(i) Infrastructure increases productivity : Infrastructure facilitates production. The availability of quality infrastructure guarantees increases in production and productivity. Infrastructure ensures easy movement of goods and raw materials there by reducing inefficiencies and lead to efficient utilisation of scarce resources and eliminate wastages.
(ii) Infrastructure encourages investment : Infrastructure provides an environment that is conducive to investment, lack of facilities discourage investment. For example, an investor will not invest in absence of basic infrastructure such as transport and communication.
(iii) Infrastructure generates linkages in production : Infrastructure promotes economic development by way of various linkages : forward and backward linkages. In other words,infrastructure provides scope for expansion of one industry due to the expansion of the other by way of forward and backward linkages. The process of economic growth becomes a dynamic process in the presence of sufficient infrastructure facilities.
(iv) Infrastructure enhances size of the market : Infrastructure widens the size of the market. The fast and cost-effective movement of raw materials and finished goods in bulk enables a producer to offer his products across the country and even across the international boundaries.
OR
The needs of sustainable development are as follows:
(i) Limiting the human population to a level within the carrying capacity of the environment.
(ii) Technological progress should be input efficient and not input consuming.
(iii) Renewable resources should be extracted on a sustainable basis, i.e., the rate of extraction should not exceed the rate of regeneration.
(iv) For non-renewable resources, rate of depletion should not exceed the rate of creation of renewable substitutes.
(v) Inefficiencies arising from pollution should be corrected. (Any four)
Q.31. Write about the causes of poverty in India?
Ans. The main causes of poverty in India are as follows :
(i) Slow economic growth rate: Economic growth rate during plan period was only 4.1 % whereas, population growth rate was around 1.9 % per annum. So, real per capita income increased by 1.7% per annum. As a result, purchasing power of the people declined.
(ii) Increase in population: In India, population is increasing continuously. As a result, despite higher rate of increase in national income, per capita income is not increasing to a desired level.
(iii) Increase in unemployment: Poverty increases with the increase in unemployment. Despite best efforts made by government of India during the five year plans, unemployment increased continuously.
(iv) Backwardness of Indian agriculture: Indian agriculture is backward. So, agriculture productivity in India is lower in comparison to developed countries. As a result, most of the Indian people are living below poverty line.
Q.32. Why are regional and economic groupings formed?
Ans. The regional and economic grouping are formed due to :
(i) With the objective of understanding various means and strategies to strengthen the economies, different nations of the world are motivated to form regional and global economic groups like SAARC, European Union, ASEAN, etc.
(ii) The formation of such regional and economic groups helps the member countries to know the development strategies and measures adopted by other member countries.
(iii) This enables them to analyse their strength and weakness and thereby, formulate policies to accelerate social progress and cultural development among its member countries. Secondly, another important purpose behind setting up of these groups is maintenance of peace and stability among member countries.
(iv) These groups provide a common platform to raise their voice in a unified manner on common issues to safeguard their common interest.
Q.33. (i) ‘If the rate of resource extraction exceeds the rate of regeneration, it leads to reduction in carrying capacity of the environment.”
Discuss the rationale of the given statement with valid reasons.
(ii) ‘Calorie-based norm is not an adequate measure to identify the poor. Establish the rationale of the given statement with valid reasons.
OR
(i) Why are less women found in regular salaried employment?
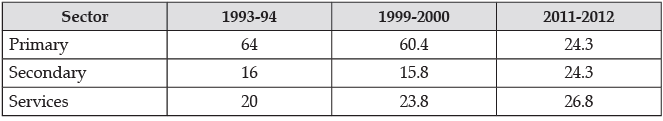
(ii) Analyse the recent trends in sectoral distribution of workforce in India :
Trends in Employment Pattern (Sector wise), 1993-2012 (in %)
Ans. (i) The environment is able to perform its functions uninterruptedly so long as the demand for these functions is within the carrying capacity of the environment. This means that the resources are not extracted beyond the rate of their regeneration.
If there is a disequilibrium (demand being more than supply), the environment fails to replenish itself and it will lead to environmental crisis. Thus, to maintain a healthy environment, the carrying capacity of the environment must be valued and respected.
(ii) The calorie based norms is not an adequate measure to identify the poor as this method does not differentiate between the very poor and the other poor. This mechanism takes into account expenditure on food and a few other items as proxy for income. It ignores many other vital factors associated with poverty; for instance, the accessibility to basic education, health care, drinking water and sanitation.
OR
Lesser women are found in regular salaried employment in India, because:
(i) jobs generally require skills and high level of literacy.
(ii) lack of mobility among women in India due to social constraints.
The given data indicates that over the given period, the proportion of workforce in primary sector has gone down from 64% in 1993-94 to 24.3% in 2011-12, this account to nearly a fall of 20% over the years. Whereas, the employment share of both secondary and the services sector has increased in India.
The share of secondary sector has gone up by approximately 9% (from 16% in 1993-94 to 24% approximately in 2011-12), the corresponding figure for services sector has gone up by 7% (from 20% in 1993-94 to 27% approximately in 2011-12).
These sectoral changes have been very significant in the growth journey of India, showing the gradual shift of the workforce from primary sector to the secondary and tertiary sector.
Q.34. ‘In spite of the increase in public health expenditure Indian Health System is an ailing system in itself ’. Defend the statement citing any three major problems of Health sector in India.
Ans. The health system in India has undoubtedly improved over the years but the pace of improvement has been unreasonably slow and truly we carry an unhealthy health system.
Following may be the most important concerns ailing Indian health system:
(i) Low Public Expenditure : In India the health expenditure as a percentage of GDP is abysmally low as compared to some of the major developing countries. It stood at around 4.7% of the total GDP in the year 2014-15.
(ii) Urban Rural Divide : People living in rural India do not have sufficient medical infrastructure. Nearly 70% of the population lives in rural areas which have only 20% of the total hospitals of the country.
(iii) Women and child health issues : More than 50 per cent of married women in the age group of 15–49 years have iron deficiency, which has contributed to maternal deaths. Infant Mortality Rate per 1,000 live births in India is 34. Malnutrition and inadequate supply of vaccines lead to the death of millions of children every year.


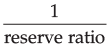
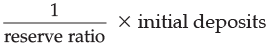
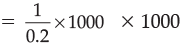
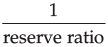 × initial deposits
× initial deposits