CBSE Sample Question paper - 09 Economics, Class 12 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce PDF Download
Class - XII
Economics
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 80
General Instructions :
1. This question paper contains two parts :
Part A : Macro Economics (40 marks)
Part B : Indian Economic Development (40 marks).
2. All questions in both sections are compulsory. Marks for questions are indicated against each question.
3. Question No. 1-10 and 18-27 (including two Case Based Questions) are very short answer questions carrying 1 mark each. They are required to be answered in one word or one sentence each.
4. Case Based Questions (CBQ’s) are Question No. 7-10 and Question No. 25-27.
5. Question No. 11-12 and 28-29 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to them should not normally exceed 60-80 words each.
6. Question No. 13-15 and 30-32 are also short answer questions carrying 4 marks each. Answers to them should not normally exceed 80-100 words each.
7. Question No. 16-17 and 33-34 are long answer questions carrying 6 marks each. Answers to them should not normally exceed 100-150 words each.
8. Answers should be brief and to the point and the above word limit be adhered to as far as possible.
9. There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions of one mark, 2 questions of three marks, 2 questions of four marks and 2 questions of six marks. Only one of the questions have to be attempted.
10. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary
PART — A
Q.1. Money supply includes __________
(i) All deposits in banks
(ii) Only demand deposits in banks
(iii) Only time deposits in banks
(iv) Currency with the banks.
Ans. (ii) only demand deposits in banks.
OR
Currency notes and coins are __________ tenders.
(i) Legal
(ii) Royal
(iii) Nominal
(iv) None of the above
Ans. (i) Legal
Q.2. Which of the following is not a revenue receipt?
(i) Recovery of Loans
(ii) Foreign Grants
(iii) Profits of Public Enterprises
(iv) Wealth Tax
Ans. (i) Recovery of Loan
Q.3. Supply of money refers to…
(i) currency held by the public
(ii) currency held by Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
(iii) currency held by the public and demand deposits with commercial banks
(iv) currency held in the government account
Ans. (iii) currency held by the public and demand deposits with commercial bank.
Q.4. _________________ which a commercial bank holds in other commercial banks, are not regarded as part of money supply.
(i) Interbank Deposits
(ii) Cash Reserve
(iii) Gold
(iv) Demand Deposit
Ans. (i) Interbank Deposits
Q.5. Accommodating items cause movements of goods and services across the borders.
(i) The statement is true
(ii) The statement is false
(iii) The statement is incomplete
(iv) Both (i) and (iii)
Q.6. Foreign Exchange Transactions dependent on other Foreign Exchange Transactions are called:
(i) Current account transactions
(ii) Capital account transactions
(iii) Autonomous transactions
(iv) Accommodating transactions.
Ans. (iv) Accommodating transactions.
Q.7. Cut in Repo rate by RBI is likely to ________ (increase/decrease) the demand for goods and services in the economy. (choose the correct alternative)
Ans. increase
Q.8. The fall in the savings is due to:
(i) Decrease in income
(ii) Increase in consumption
(iii) Increase in government expenditure
(iv) Using savings for consumption
Ans. (iv) Using savings for consumption
Q.9. The multiplier is affected by
(i) Income and consumption
(ii) Savings and consumption
(iii) Expenditure and Exports
(iv) Income and Expenditure
Ans. (i) Income and consumption
Q.10. Equilibrium position may be of full employment or may not be of full employment, and only determines the level of ________________.
(i) Income
(ii) Consumption
(iii) Saving
(iv) Investment
Ans. (i) Income
Q.11. State with valid reason, which of the following statement is true or false :
(i) Gross Value Added at market price and Gross Domestic Product at market price are one and the same thing.
(ii) Intermediate goods are always durable in nature.
Ans. (i) The given statement is false as Gross Domestic Product is the result of sum of Gross Value Added by all the producing units/firms in an economy, during an accounting year.
(ii) The given statement is false as intermediate goods are generally non-durable in nature. They are the goods used as raw material and they lose their identity in the production process for the creation of a new commodity, during an accounting year.
Q.12. Discuss briefly, the components of current account.
Ans. Components of Current Account:
(i) Visible : Refers to the merchandise/goods exported from or imported by a country. Exports which result inflows for the country are placed on the credit side whereas, imports are placed on the debit side as they result into outflow of foreign exchange from the country.
(ii) Invisible : Refers to the different types of services and transfers that take place between nations. They give rise to monetary receipts and payments for the nation.
Q.13. Why do we say that commercial banks create money while we also say that the Central Bank has the sole right to issue currency? Explain what is the likely impact of money creation by the commercial banks on the National Income?
Ans. Yes, it is true that Central Bank has the sole right to issue currency, but Currency is needed by the public and commercial banks directly deal with public. Thus, Commercial banks create money in the form of demand deposits related to the loans offered by them to public. Demand deposits of the commercial banks are many times more than their cash reserves. This is based on the historical experience of the banks that cash withdrawal of funds is only a small percentage of the total demand deposits.
The money created by the commercial banks in the form of demand deposits is mainly used for investment in production purposes. Any rise in investment leads to many times more increase in the National Income of an economy, via, the Multiplier effect.
Q.14. Define Credit Multiplier. What role does it play in determining the credit creation power of the banking system? Use a numerical illustration to explain.
Ans. Credit multiplier measures the amount of money that the banks are able to create in the form of deposits with every initial deposit.
The credit creation by commercial banks depends on credit multiplier as it is inversely related to LRR. Higher the credit multiplier, higher will be the total credit created and vice - versa.
For example, suppose the LRR is 0.2 and initial deposit is Rs. 1000
Credit multiplier = 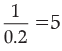
Total credit created = 5 × Rs. 1,000= Rs. 5,000
Whereas, suppose LRR is 0.5 and initial deposit is Rs. 1,000
Credit multiplier = 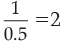
Total credit created = 2 × Rs. 1000 = Rs. 2,000
Thus, with the same initial deposit total credit creation decreases with an increase in the value of credit multiplier.
Q.15. ‘India’s GDP contracted 23.9% in the April-June quarter of 2020-21 as compared to same period of 2019-20, suggesting that the lockdown has hit the economy hard’. The Hindustan Times, 1st September 2020 State and discuss any two fiscal measures that may be taken by the Government of India to correct the situation indicated in the above news report.
Ans. The situation suggests that Aggregate Demand is less than Aggregate Supply. Following two fiscal measures may be taken to control it:
(a) Decrease in Taxes : To curb the situation, the government may decrease the taxes. This may increase the purchasing power in the hands of the general public. This may increase the Aggregate Demand in the economy to bring it equal to the Aggregate Supply.
(b) Increase in Government Expenditure : The government may also increase its expenditure. This may increase the purchasing power in the hands of the general public which in turn may increase the Aggregate Demand in the economy to bring it equal to the Aggregate Supply.
Q.16. What is government budget? Explain its major components.
Ans. Government Budget is defined as a statement of planned receipts and planned expenditure of the government during a fiscal year.
Its major components are :
(i) Revenue Receipts : The receipts which neither create a liability nor lead to reduction in assets.
(ii) Capital Receipts : he receipts which either create a liability or lead to reduction in assets.
(iii) Revenue Expenditures : The expenditure which does not lead to any creation of assets or reduction in liabilities.
(iv) Capital expenditures : The expenditure which leads to creation of assets or reduction in liabilities.
Q.17. (a) Calculate Net Value Added at Market Price.
(b) What is meant by Double Counting? Why should it be avoided?
OR
How should the following be treated while estimating national income? You must give reason in support of your answer:
(i) Bonus paid to employees.
(ii) Addition to stocks during a year.
(iii) Purchase of taxi car by a taxi driver.
Ans. (a) NVAMP = (iv) + (vii) − (i) − (ii)
= 2,000 + (−50) − 1,000−50
= Rs. 900 crore
(b) The problem of double counting arises when the value of certain goods and services are counted more than once while estimating National Income by Value Added Method. This happens when the value of intermediate goods is counted in the estimation of National Income along with the final value of goods and services.
Two methods to avoid the problem of double counting:
(i) To consider only the final value of output produced.
(ii) To consider only the value added of the output produced.
OR
(i) Bonus : It should be included because it is compensation paid to employees.
(ii) Addition to stock : It should also be included because it is investment, a final expenditure.
(iii) Purchase of a Taxi by Taxi Driver : It should be included because it is final expenditure on investment.
Q.18. Occupational structure refers to the distribution of ________________ (Working/Non-working) population into various sectors of economic activity.
OR
What is an Economic Plan ?
(i) A plan is how the nation's resources can be used having some general goals and achieving specific objectives within a specified period.
(ii) A plan is a blueprint for infrastructure development.
(iii) A plan is the government budget.
(iv) A plan is the allocation of resources.
Ans. Working population
OR
(i) A plan is how the nation's resources can be used having some general goals and achieving specific objectives within a specified period.
Q.19. India entered the __________ stage of Demographic Transition after the year 1921. (Choose the correct alternative)
(i) forth
(ii) second
(iii) third
(iv) first
Ans. (ii) second
Q.20. Read the following statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A) : Green Revolution increased the production of food grains.
Reason (R) : The use of fertilizers and HYV seeds helped to increase the production.
Alternatives:
(i) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(iii) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(iv) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Ans. (i) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
Q.21. Relative Poverty is prevalent in :
(i) Capitalist Countries
(ii) Socialist Countries
(iii) Communist Countries
(iv) Developed Countries
Ans. (i) Capitalist Countries
Q.22. Read the following statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A) : India and Pakistan adopted the mixed economy model
Reason (R) : All the countries in the world were adopting mixed economy model Alternatives:
(i) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(iii) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(iv) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Ans. (iii) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Q.23. __________adopted ‘One Child Policy ’ as a measure to control population. (Choose the correct alternative)
(i) India
(ii) Pakistan
(iii) China
(iv) Russia
Ans. China
Q.24. Read, the following hypothetical Case Study, carefully and answer the question number 24 on the base of the same.
Since after Independence, the condition of the labour workforce has been improving in India, All the factors such as education policy and health care has led to the improvement of the work force. The growth of population has had posed some serious threats in the Economy with respect to the employment generation.
The prospects of the Rural development have been improving with the respect of the growth of many financial institutions in the rural areas. The NABARD oversees all the regional rural banks and regulates them for the proper functioning of the Rural Economy.
There have been many skill development initiatives taken by the government of India to improve the Human Capital as well.
Q. ____________ helps in formation of human capital.
(i) Health
(ii) Employment
(iii) Both (i) and (ii)
(iv) Neither (i) and (ii)
Ans. (iii) Both ( i) and (ii)
Q.25. The kind of unemployment in which workers seems to be working but its contribution to production is negligible is called:
(i) Seasonal Unemployment
(ii) Disguised Unemployment
(iii) Industrial Unemployment
(iv) Educated Unemployment
Ans. (ii) Disguised Unemployment
Q.26. Agriculture marketing does not comprise of _____________(Choose the correct alternative)
(i) Transportation of the produce to the market place for sale.
(ii) Grading of the produce according to the quality.
(iii) Storage of the produce for sale in future.
(iv) Credit taken to meet expenditure on agriculture.
Ans. (d) Credit taken to meet agriculture expenditure.
Q.27. __________ (Regional Rural Banks/ Land Development Banks) is the most prominent body responsible for providing loans for long term land development.
Ans. Land Development Banks
Q.28. What do you mean by agriculture and what are agricultural activities?
OR
Industrial development in India played a leading role. How?
Ans. Agriculture is the backbone of Indian economy. Agriculture is the practice and science of growing crops by cultivating the land.
Agricultural activities are as follows:
Primary activities: In primary activities, agricultural activities are included such as to grow food grains, pulses, vegetables, sugarcane, cotton, oil seeds, jute, etc.
Secondary activities: Allied activities are included in it such as animal husbandry, poultry farming, dairy farming, etc.
OR
An economy can progress only if they have a good industrial sector providing a sound capital base. Industrial development is important for an overall growth of a country due to the following reasons:
Industrialisation provides a strong basis for rapid and continuous increase in the income of the people.
Industrialisation leads to higher savings, investment and capital formation, thereby creating a solid foundation for self-sustaining development.
Industrialisation provides tremendous employment opportunities.
Q.29. Explain the term ‘affluence trap’.
Ans. Affluence means economic well-being. Trap is something in which we get caught and we cannot escape out of it.
Affluence trap means environmental degradation trap. With affluence or economic well-being more natural resources are used up causing environmental problems.
In the rich countries of the developed world, the high level of consumption associated with the high level of income is using up natural resources at a fast pace. As a consequence, these countries are getting trapped into a situation of severe environmental degradation.
Q.30. How is human development a broader term as compared to human capital?
OR
Suppose you are a resident of a village, suggest a few measures to tackle the problem of poverty of your village.
Ans. (i) Human development is a broader term as compared to human capital because human capital is a means to an end whereas human development is an end in itself. Human capital considers education and health as a means to make human being a good productive person. Human capital is a means to an end where means implies skills that are used in the process of production and end denotes the consequent increase in the productivity. The higher level of output can be achieved through extensive application of human capital.
(ii) On the other hand, human development is an end in itself which refers to the holistic development of the individuals. The development can be possible only by acquiring good education and attaining good health. Therefore, education and health are the two main features of human development. Human development occurs when majority of the people in the economy are educated and healthy. Thus, the end signifies the development of an individual via education and health. Therefore, we can conclude that human development is a broader term as compared to human capital.
OR
Suggestions to remove rural poverty :
(i) Gainful wages and self-employment opportunities for poor class.
(ii) Minimum indirect tax on wage goods consumed by workers and progressive taxation on income and wealth.
(iii) Ceiling on land holdings and surplus land for landless farmers with required amount of finance.
(iv) Minimum wages should be guaranteed by Government to every worker.
(v) Stringent measures against exploitation of child and women labour.
(vi) Adequate expansion of free social service; health and education for rural and urban poor.
(vii) Increased output of wage goods to be made available for the poor at reasonable prices.
(viii) A vailability of cheaper credit for poor so as to create self-employment opportunities for them.
Q.31. A‘tamnirbhar Bharat’ had been at the roots of the Indian planning process in the form of ‘self reliance’ as an objective of the planning process.
Do you agree with the given statement? Justify the rationale of the given statement.
Ans. The given statement is correct; in the early post-independence period the aim of the government’s policy was to reduce the dependence on the foreign countries for goods, services, technology and capital. It stressed on the use of domestic resources to avoid foreign interference, as it was feared that the dependence on the imported food supplies, foreign technology and foreign capital may increase foreign interference in the policies of our country.
Similarly, the main thrust of the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ is also to make India an economy that is selfreliant and self-sufficient.
Detailed Answer :
Yes, statement is correct as Atmanirbhar Bharat has been the part of the objective of Indian planning since the post-independence period. Self-reliance or atmanirbhar as an objective of economic planning is necessary for a developing country because a nation can promote economic growth and modernization by using its own resources or by using resources imported from other nations. The first Seven Five Year Plans gave importance to self-reliance which means avoiding imports of those goods which could be produced in India itself. This policy was considered a necessity in order to reduce our dependence on foreign countries especially for food. It is understandable that people who were recently freed from foreign domination should give importance to self-reliance. Similarly in Atmanirbhar bharat the focus is on making India self-reliant and self-sufficient in all the aspects of the economy.
OR
Discuss briefly any two major steps taken by the Government of India on ‘Financial Sector’ front under the Economic Reforms of 1991.
Ans.
Two steps taken by the government of India on financial sector under the Economic Reforms of 1991 were:
(i) Change in the role of Reserve Bank of India (RBI): The role of RBI was reduced from regulator to facilitator of financial sector. This means that financial sector was given greater autonomy (to take decisions) on many matters independent of RBI.
(ii) Origin of Private Banks: The reform process led to establishment of private sector banks of Indian as well as foreign origin.
Detailed Answer :
Financial Sector includes financial institutions such as commercial banks, investment consultants,stock exchange and foreign exchange market. RBI controls and regulates all the banks and other financial institutions in India. RBI decides the amount of money that the banks can lend and the amount they should keep as reserves, determines interest rates and prioritises lending to various sectors apart from regulating foreign exchange.
(a) Role of RBI: One of the major aims of financial sector reformsis to transform the role of RBI from regulator to facilitator of financial sector. This means that greater autonomy may be granted to the financial sector in taking decisions on various matters without consulting the RBI.
(b) Private Sector Banks: The reform policies led to establishment of private sector banks. Banks have been given freedom to setup new branches. Banks have also been given permission to generate resources from India and abroad through capital market.
Q.32. Comment on the growth rate trends witnessed in China and India in the last two decades.
Ans. India, with democratic institutions, performed moderately, but the majority of its people still depend up on agriculture. Infrastructure is lacking in many parts of the country. It is yet to raise the standard of living of more than one-fourth of its population that lives below the poverty line.
On the other hand, the lack of political freedom and its implication in China are the major concern in the last two decades. The country used the market system without losing political commitment and succeeded in raising the level of growth along with poverty alleviation.
China used the market mechanism to create additional social and economic opportunities. The country has also ensured social security in the rural areas by retaining collective farming known as Commune System.
Public intervention in social infrastructure prior to the introduction of the economic reforms has brought positive results in the human development indicators of China.
Q.33.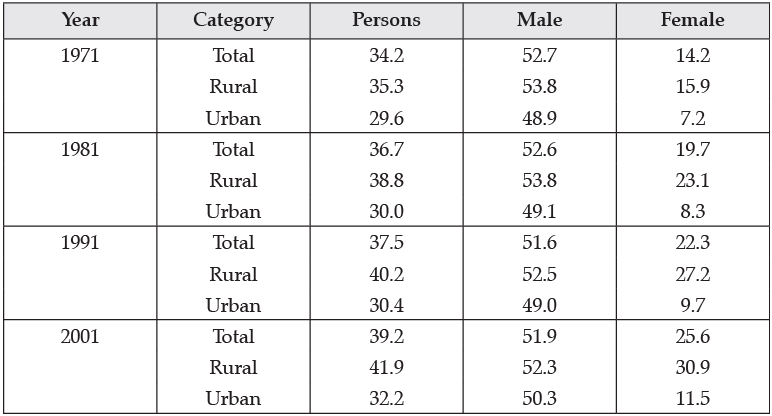
Workforce Participation in India
Looking at the trend given in the table what can we say about the women workforce participation in rural and urban areas? Comment on why such a trend is there prevalent in the country.
Or
‘Discuss the main limitations of health care system in India.
Ans. The percentage of female workforce in the rural areas is nearly 30.9% while it is only 11.5% in the urban areas in the 2001 census. This depicts that as compared to the urban women, more rural women accounts for higher share in the female workforce. While on the one hand, the rural women are less educated, unskilled and low productive, on the other hand, urban women being more skilled and productive have higher probability to get employment. Ironically, the urban female accounts for lesser share in the female workforce as compared to their rural counterparts.
The following are the reasons for low share of urban females in the total female workforce :
(i) As in the agricultural and allied activities, high degree of skills and specialisations are not required. So, rural women engage themselves to support their family on farms.
(ii) As poverty in the rural areas is more widespread than in the urban areas, so, the rural women engage themselves in low productive jobs just to support the livelihood of their families.
(iii) As the urban families usually earn comparatively higher income than the rural families and further poverty in the urban areas is not as widespread as that of in the rural areas So, there is lesser need for female members to get themselves employed.
(iv) The decision to take up jobs by the female members depends on the family rather than herself.
(v) Although female literacy in India is improving, yet it has to get much better before urban female accounts for higher share in the total female workforce.
OR
The health system in India has undoubtedly improved over the years but the paceof improvement has been unreasonably slow and truly we carry an unhealthy health system.
Following may be the most important concerns ailing Indian health system :
(a) Low Public Expenditure : In India the health expenditure as a percentage of GDP is absolutely low as compared to some of the major developing countries. It stood at around 4.7% of the total GDP in the year 2014-15.
(b) Urban Rural Divide : People living in rural India do not have sufficient medical infrastructure. Nearly 70% of the population lives in rural are as which have only 20% of the total hospitals of the country.
(c) Women and child health issues : More than 50 per cent of married women in the age group of 15–49 years have iron deficiency, which has contributed to maternal deaths. Infant Mortality Rate per 1,000 live births in India is 34. Malnutrition and inadequate supply of vaccines lead to the death of millions of children every year.
Q.34. ‘Features of Indian agriculture itself explain the story of its backwardness’. Put out your views in the reference to this statement.
Ans. Indian agriculture is backward, despite the fact that it is of significant importance in the Indian economy.
The main features of Indian agriculture are :
(i) Agricultural output depends largely on rainfall and other natural factors like floods, droughts, storms, etc.
(ii) The historical, social and cultural background of state affects agricultural output.
(iii) Over three-fourth of land holdings are of small size. Thus, agriculture is the source of livelihood for poor farmers.
(iv) Farming is a way of life rather than a commercial activity. Thus, production is mainly for selfconsumption.
(v) There is little use of modern machinery and fertilisers and pesticides.
|
130 docs|5 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|

















