Internet Protocol: Revision Notes - Class 10 PDF Download
➢ Internet Protocol: Internet Protocol (IP) is the principal set of rules data transfer (or communications protocol) of digital message formats and rules for exchanging messages between computers across a single network or a series of interconnected networks, using the Internet Protocol Suite (often referred to as TCP/IP).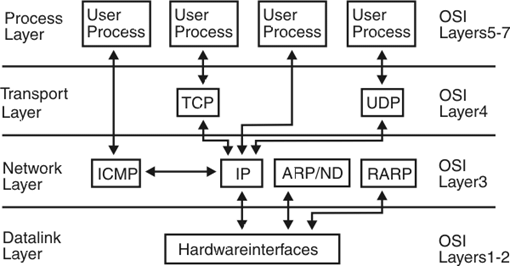 ➢ TCP/IP: TCP/IP or Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, is a suite or packages of communica- tion protocols used to interconnect network devices on the internet. TCP/IP can also be used as a communications protocol in a private network.
➢ TCP/IP: TCP/IP or Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, is a suite or packages of communica- tion protocols used to interconnect network devices on the internet. TCP/IP can also be used as a communications protocol in a private network. ➢ SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is the standard protocol for e-mail services on a TCP/IP network. SMTP provides the ability to send and receive e-mail messages. SMTP is an application-layer protocol that enables the transmission and delivery of e-mail over the Internet. SMTP is created and maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
➢ SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is the standard protocol for e-mail services on a TCP/IP network. SMTP provides the ability to send and receive e-mail messages. SMTP is an application-layer protocol that enables the transmission and delivery of e-mail over the Internet. SMTP is created and maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).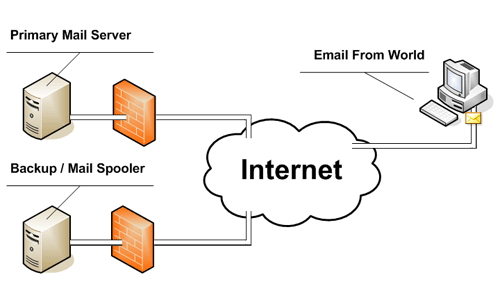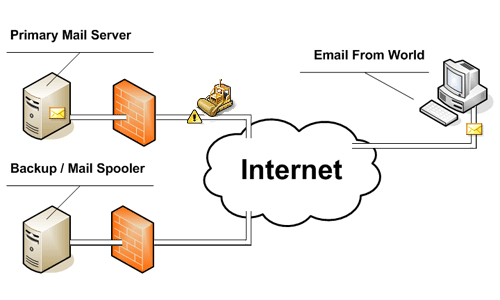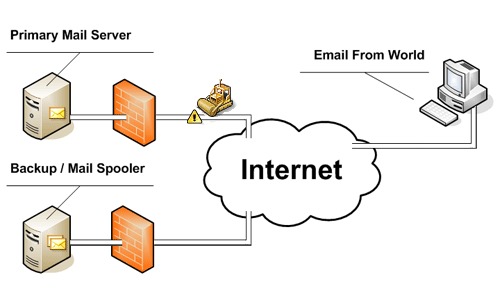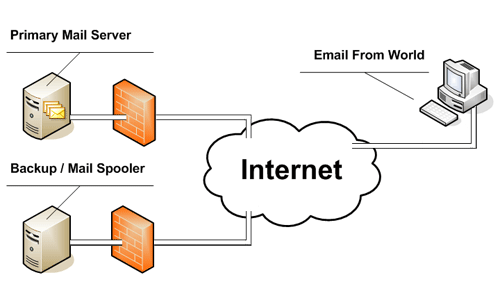 ➢ POP3: Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) is the most recent version of a standard protocol for receiving e-mail. POP3 is a client/server protocol in which e-mail is received and held for you by your Internet server. Periodically, you (or your client e-mail receiver) check your mail-box on the server and download any mail, probably using POP3. This standard protocol is built into most popular e-mail products, such as Eudora and Outlook Express. It is also built into the Netscape and Microsoft Internet Explorer browsers.
➢ POP3: Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) is the most recent version of a standard protocol for receiving e-mail. POP3 is a client/server protocol in which e-mail is received and held for you by your Internet server. Periodically, you (or your client e-mail receiver) check your mail-box on the server and download any mail, probably using POP3. This standard protocol is built into most popular e-mail products, such as Eudora and Outlook Express. It is also built into the Netscape and Microsoft Internet Explorer browsers.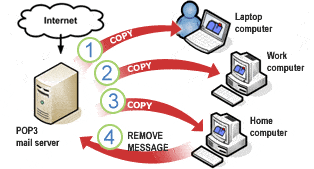 ➢ HTTP: HTTP means HyperText Transfer Protocol. HTTP is the underlying protocol used by the World Wide Web and this protocol defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and what actions Web servers and browsers should take in response to various commands.
➢ HTTP: HTTP means HyperText Transfer Protocol. HTTP is the underlying protocol used by the World Wide Web and this protocol defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and what actions Web servers and browsers should take in response to various commands. ➢ HTTPS: HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is a variant of the standard web transfer protocol that adds a layer of security on the data in transit through a Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol connection. HTTPS enables encrypted communication and secure connection between a remote user and the primary web server.
➢ HTTPS: HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is a variant of the standard web transfer protocol that adds a layer of security on the data in transit through a Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol connection. HTTPS enables encrypted communication and secure connection between a remote user and the primary web server.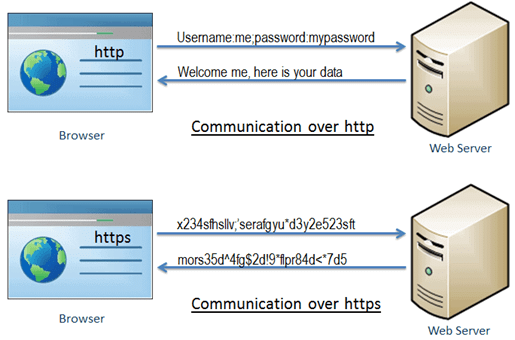 ➢ SSH: SSH, also known as Secure Shell or Secure Socket Shell, is a network protocol that gives users, particularly system administrators, a secure way to access a computer over an unsecured network. SSH also refers to the suite of utilities that implement the SSH protocol. Secure Shell provides strong authentication and encrypted data communications between two computers connecting over an open network such as the internet. SSH is widely used by network administrators for managing systems and applications remotely, allowing them to log into another computer over a network, execute commands and move files from one computer to another.
➢ SSH: SSH, also known as Secure Shell or Secure Socket Shell, is a network protocol that gives users, particularly system administrators, a secure way to access a computer over an unsecured network. SSH also refers to the suite of utilities that implement the SSH protocol. Secure Shell provides strong authentication and encrypted data communications between two computers connecting over an open network such as the internet. SSH is widely used by network administrators for managing systems and applications remotely, allowing them to log into another computer over a network, execute commands and move files from one computer to another.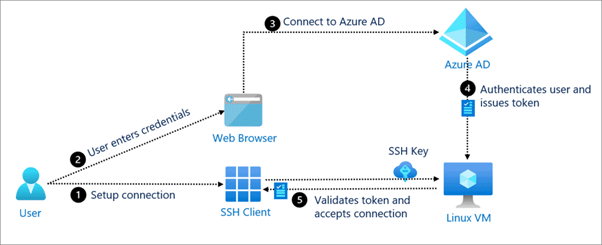 ➢ FTP: File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard internet protocol for transmitting files between computers on the Internet over TCP/IP connections. FTP is a client-server protocol where a client will ask for a file, and a local or remote server will provide it. The end-users machine is typically called the local host machine, which is connected via the internet to the remote host—which is the second machine running the FTP software.
➢ FTP: File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard internet protocol for transmitting files between computers on the Internet over TCP/IP connections. FTP is a client-server protocol where a client will ask for a file, and a local or remote server will provide it. The end-users machine is typically called the local host machine, which is connected via the internet to the remote host—which is the second machine running the FTP software.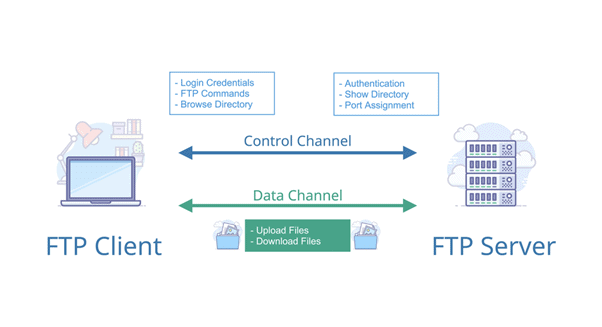 ➢ SCP: Secure Copy Protocol (SCP) is a file transfer protocol, which helps in transferring computer files securely from a local host to a remote host. It works on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol technique. The SCP protocol is a file transfer network protocol, which supports encryption and authentication features.
➢ SCP: Secure Copy Protocol (SCP) is a file transfer protocol, which helps in transferring computer files securely from a local host to a remote host. It works on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol technique. The SCP protocol is a file transfer network protocol, which supports encryption and authentication features.
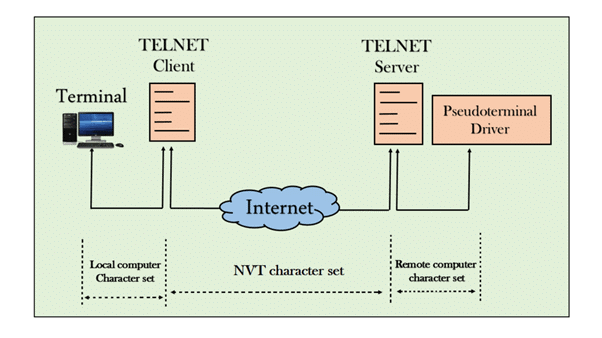
➢ TELNET: Telnet stands for Terminals Network. It is a networking protocol and software program used to access remote computers and terminals over the Internet or a TCP/IP computer network. Telnet was developed in 1969 and standardized as one of the first Internet standards by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).