Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Cyber Ethics: Revision Notes
Cyber Ethics: Revision Notes - Class 10 PDF Download
➢ Computer Ethics
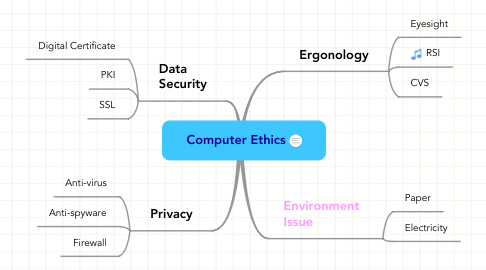
- Computer ethics are the set of moral standards that govern the use of computers. It is society ’s views about the use of computers, both hardware and software. Privacy concerns, intellectual property rights and effects on the society are some of the common issues of computer ethics.
➢ Netiquette
"Netiquette" refers to Internet etiquette. This simply means the use of good manners in online communication such as e-mail, forums, blogs, and social networking sites etc. It is important to use netiquette because online communication is non-verbal.
- Accuracy of information
- Use internet resources ethically
- Promote healthy discussions
- Ignore inflammatory comments by trolls

➢ Software License
- A software license agreement is a contract between the licensor or the author and the purchaser of a piece of software which establishes the purchaser's rights. It defines how that software can be used and what happens in the event of breach.

➢ Open Source Software Movement
- Open source software is free and openly available to everyone. People who create open source products publish the code and allow others to use and modify it. Communities of programmers often work together to develop the software and to support users. Open source products are usually tested in public by online contributors.
- Large companies such as Twitter, Facebook and the BBC make use of open source technology. For example, the BBC makes use of MySQL and it creates open source software, such as the program to improve the compatibility of iPlayer on smart TVs.

➢ Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
- Intellectual property rights are the legal rights that cover the privileges given to individuals who are the owners and inventors of a work, and have created something with their intellectual creativity. Individuals related to areas such as literature, music, invention, etc., can be granted such rights, which can be used in the business practices by them.
- The creator/inventor gets exclusive rights against any misuse or use of work without his/her prior information. However, the rights are granted for a limited period of time to maintain equilibrium. Intellectual Property Rights can be further classified into the following categories

➢ Plagiarism
- Plagiarism is the wrongful appropriation, stealing and publication of another author's language, thoughts, ideas as one's own original work.
Types of plagiarism are:
(i) Collusion
(ii) Complete plagiarism
(iii) Partial plagiarism
(iv) Self-plagiarism
(v) Copying and Pasting
(vi) Word Switch
(vii) Concealing sources
(viii) Inadvertently

➢ Digital Property Rights (DPR):
- DPR includes data, internet accounts and other rights in the digital world including contractual rights and intellectual property rights.
➢ Freedom of Information:
- In India, Freedom of Information Act was implemented in 2002. The main principle behind Freedom of Information legislation is that people have a right to know about the activities of public authorities held by government and government institutions. According to the Act, this information is in principle public and may only be withheld for legitimate reasons.
According to this Act,
(i) Everybody has a right to access official information. Non-disclosure of information should be the default.
(ii) An applicant does not need to give you a reason for wanting the information. On the contrary, the department must justify refusing them information.
(iii) All the requests have to be treated equally.

➢ Digital Divide
- The Digital Divide, or the digital split, is a social issue referring to the differing amount of information between those who have access to the Internet and those who do not have access. The term became popular among concerned parties, such as scholars, policy makers, and advocacy groups, in the late 1990s.

➢ E-commerce and Security
- In e-commerce, the transaction takes place over the network. e-commerce is the ability to do business online via the internet. The privacy in e-commerce means the protection of privacy of the parties involved in trading through e-commerce. Transaction security is vital in e-commerce.

➢ Fraud
- Fraud is an intentional false representation of a fact.
- Fraud comes in many forms like,
(i) Credit card fraud
(ii) Refund fraud
(iii) Card testing
(iv) Friendly fraud
(v) Identity theft
(vi) Phishing
(vii) Triangulation fraud
➢ Privacy Concerns
- Hacking: It is unlawful intrusion into a computer or a network. A hacker can intrude through the security levels of a computer system or network and can acquire unauthorised access to other computers.
- Malware: It means malicious software or virus which is created to mal-function computer system. Common malwares are viruses, spyware, worms and trojan horses. A virus can delete files from a hard drive, while a spyware can collect data from a computer.
- Data Protection: Also known as information privacy or data privacy, it is the process of safeguarding data which intends to influence a balance between individual privacy rights, while still authorising data to be used for business purposes.
- Anonymity: It is a way of keeping user's identity masked through various applications.
 ➢ Security
➢ Security
- Security is an essential part of any transaction that takes place over the internet. Customers will lose his / her faith in e-business if its security is compromised. Encryption is a technology which keeps the messages secret from unauthorized access. Digital signature is another security provision provided by the internet which ensures the authenticity of the information. A digital signature is a digital code that can be authenticated through encryption and password attached to an electronically transmitted message to uniquely identify the sender. Digital certificates are electronic files containing user name, user's public key, and name of certification authority such as Verisign, issuing the certificate. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is a security protocol developed by Netscape Communications to protect communication over the internet.
FAQs on Cyber Ethics: Revision Notes - Class 10
| 1. What is cyber ethics? |  |
Cyber ethics refers to the moral principles and guidelines that govern the appropriate use of technology, specifically in relation to the internet and computers. It involves understanding and practicing responsible behavior, respect for others' privacy, and the ethical implications of online actions.
| 2. Why is cyber ethics important? |  |
Cyber ethics is important because it helps individuals navigate the digital world in an ethical and responsible manner. It promotes honesty, respect, and accountability in online interactions, and helps prevent cyberbullying, harassment, identity theft, and other forms of cybercrime.
| 3. What are some common ethical issues in cyberspace? |  |
Some common ethical issues in cyberspace include online privacy concerns, intellectual property theft, cyberbullying, hacking, phishing, and spreading false information. These issues highlight the importance of cyber ethics in maintaining a safe and respectful online environment.
| 4. How can individuals practice cyber ethics? |  |
Individuals can practice cyber ethics by respecting others' privacy, being cautious with personal information online, using strong passwords and regularly updating them, avoiding cyberbullying and harassment, citing sources when using others' work, and being mindful of the impact of their online actions on others.
| 5. What are the consequences of unethical behavior in cyberspace? |  |
Unethical behavior in cyberspace can have serious consequences. It can result in legal and financial repercussions, damage to one's reputation, loss of trust from others, and even psychological harm to individuals who are targeted by cyberbullying or harassment. Additionally, unethical behavior can contribute to the erosion of online communities and the overall trust in the digital world.
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















