Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Notes > Important Notes For NEET Biology - Biological Classification
Important Notes For NEET Biology - Biological Classification - Class 11 PDF Download
Biological Classification – Important Points, Summary, Revision, Highlights
Biological Classification
- The process of grouping together various organisms according to their similarities, dissimilarities and phylogenetic descent is known as biological classification. There have been various attempts to classify organisms. The earliest was by Aristotle, who classified plants into herbs shrubs and trees. He classified animals into two groups, based on the presence and absence of red blood. Linnaeus gave the Two Kingdom system of classification and divided living organisms into Plantae and Animalia.
 Biological Classification
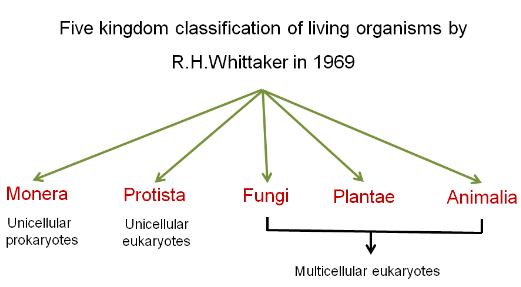
Biological Classification - R.H. Whittaker proposed the Five Kingdom system of classification and classified organisms, based on cellular structure, complexity, mode of nutrition, phylogenetic relationship and ecological role performed by them.


1. Monera
- This group includes all kinds of bacteria, having a prokaryotic cell.
- The cell does not contain a nucleus.
- There are different shapes of bacteria present; spherical- cocci, rod-shaped- bacillus, comma- vibrio and spiral- spirilla.
- They mainly reproduce by fission, spore formation under unfavourable conditions and also by DNA transfer from one bacterium cell to another.
- Mycoplasma lack the cell wall and are the smallest cell to survive without oxygen.
- Archaebacteria- These bacteria are present in the harshest environmental conditions such as salty, marshy and in hot springs. They are known as halophiles, methanogens, thermoacidophiles, respectively.
- Methanogens are present in the gut of ruminants and produce biogas.
- Eubacteria- These are true bacteria and have a rigid cell wall and motile organisms have flagella.
(a) Photosynthetic Autotrophs
- They include Cyanobacteria (Blue-green Algae).
- They have chlorophylls and carotenoids.
- They are unicellular, filamentous or colonial and body is covered by a mucilaginous sheath. Nostoc and Anabaena have heterocysts, where they can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
(b) Chemosynthetic Autotrophs
- They play an important role in recycling the nutrients.
- They get the required energy for ATP generation from the oxidation of various inorganic substances such as ammonia, nitrates and nitrites.
(c) Heterotrophic
- There is a wide variety of heterotrophic bacteria. They act as a decomposer. They are used for various purposes such as nitrogen-fixing, curd and antibiotics production. - Many bacteria are pathogen causing various diseases of plants and animals.
Example: citrus canker, tetanus, typhoid, cholera.
2. Protista
The group includes unicellular eukaryotes.
- A photosynthetic protist is a link between plants and animals.
- They contain a well-defined nucleus and other membrane-bound cell organelles.
- They include protozoan, slime moulds, chrysophytes, dinoflagellates and euglenoids.
➤ Chrysophytes
- Include diatoms and desmids (golden algae).
- They are mostly photosynthetic and have indestructible cell wall due to the presence of silica.
- The cell wall makes two thin overlapping shells, which fit like a soapbox on the outer surface.
- Diatomaceous earth is the deposit of the cell wall that gets accumulated. It is used for filtration and polishing.
➤ Dinoflagellates
- They are photosynthetic and marine
- They are found in many colours like yellow, green, red, blue, brown, according to the pigment present
- Stiff cellulose plates are present on the cell wall
- They multiply rapidly and cause red tide
- Many dinoflagellates emit blue-green light and are bioluminescent
➤ Euglenoids
- They are photosynthetic flagellated protist.
- They are a link between plants and animals. They perform photosynthesis but lack a cell wall.
- The characteristic feature is the presence of pellicle, a protein-rich layer, which makes their body flexible.
- In the absence of sunlight, they feed on small organisms and behave as a heterotroph.
➤ Slime moulds
- They are saprophytic protists feeding on organic materials from decaying twigs and leaves.
- Aggregation of slime moulds is called plasmodium, which they form under favourable conditions.
- Under unfavourable conditions, fruiting bodies containing spores develop at the tip of plasmodium.
- These spores can survive for very long under adverse conditions and have true walls.
➤ Protozoans
- The group contains all the unicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophs, which are parasites or predators
- These are divided into 4 major groups:
(a) Amoeboid- They are characterised by the presence of pseudopodia, which are used for movement and catching of prey, e.g. Amoeba. Marine amoeboids have silica shells. Some of the amoeboids are parasites, e.g. Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebic dysentery.
(b) Flagellated- They are characterised by the presence of flagella. Some of them are parasites causing various diseases, e.g Trypanosoma causes sleeping sicknes.
(c) Ciliated- They have thousands of cilia on their body surface. The coordinated movement of cilia helps in steering the water having food into the gullet (body cavity, which opens outside the body surface), e.g. Paramoecium.
(d) Sporozoans- They are characterised by the formation of spores, which is the infectious stage, e.g. Plasmodium
3. Fungi

- Fungi are cosmopolitan and found everywhere
- They are heterotrophic and get the nutrients by absorption
- Their cell wall is made up of chitin or fungal cellulose
- Their mode of nutrition is saprophytic, parasitic or symbiotic and the main food reserve is glycogen
- Vegetative reproduction is by fragmentation, budding or fission
- Asexual reproduction is by spores formation such as conidia, zoospores, sporangiospores
- Sexual reproduction is by oospore, ascospore or basidiospore formation in distinct fruiting bodies
- In sexual reproduction, plasmogamy (fusion of protoplasm) is followed by karyogamy (fusion of nuclei)
- In basidiomycetes and ascomycetes, plasmogamy is not immediately followed by karyogamy, resulting in a distinct dikaryon (n+n) cell having 2 nuclei per cell
- Fungi are divided into four major classes on the basis of types and mode of spore formation and the structure of mycelium


Some Important Fungi
- Yeast- used in fermentation to make cheese, bread, beer
- Penicillium- antibiotics source
- Puccinia- causes wheat rust
- Ustilago- causes smut disease
- Symbionts- Lichens (symbiotic association of fungi with algae), Mycorrhiza (symbiotic association of fungi with roots of green plants)
- Rhizopus- the bread mould
- Albugo- the parasitic fungi on mustard
- Neurospora- extensively used in genetic and biochemical work
- Truffles and Morels- edible and are considered a delicacy
- Agaricus- edible as well as poisonous species
4. Plantae
- Mostly autotrophic, chlorophyll-containing, eukaryotic organisms
- Characterised by the presence of rigid cell wall made up of cellulose
- Some plants are partially heterotrophic such as Insectivorous (Venus flytrap, Bladderwort) and parasites (Cuscuta)
- Kingdom Plantae includes Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
5. Animalia
- All the heterotrophic, eukaryotic and multicellular organisms are included in the Kingdom Animalia
- They lack a cell wall.
- Members of this kingdom are also known as metazoa or multicellular animals. The kingdom has a maximum number and the most diverse types of organisms. It includes all the animals of the two kingdom classifications except Protozoa.
- Groups included are sponges, coelenterates, worms, molluscs, arthropods Starfishes and vertebrates like fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals. Insects, a group of arthropods, outnumber all other organisms in variety and number.
- The important characteristics of Animalia are:
(i) Organisms are multicellular eukaryotes.
(ii) Body form is regular.
(iii) Organs are internal.
(iv) Growth is definite, Well-defined growing points are absent.
(v) Cellular, tissue and organ system levels of organization occur in different groups. (vi) Response to stimuli is quick.
(vii) A cell does not possess a central vacuole. Instead, small vacuoles may occur. (viii) Centrioles occur in the cells.
(ix) A cell wall is absent.
(x) Plastids and photosynthetic pigments are absent.
Some of the acellular organism and lichens, which are not classified in the five-kingdom classification by Whittaker are the following:
1. Viruses
- Dmitri Ivanowsky gave the name “virus” to the causal organism of tobacco mosaic disease (TMV)
- Beijerinek called the fluid extracted from diseased plants of tobacco, “Contagium vivum fluidum” and observed it as being infectious to healthy plants
- Stanley crystallised TMV (tobacco mosaic virus) for the first time
- They are acellular containing nucleic acid core (either DNA or RNA), which is surrounded by a protein coat called the capsid
- Viruses use the host machinery to multiply inside the host cell, they exist in a crystalline form outside the host cell
- They are obligate parasite and cause various diseases in plants and animals, e.g. common cold, AIDS, polio, mumps, measles, chickenpox, etc. in animals and various mosaic diseases in plants such as tobacco, cucumber, tomato, etc. leaf curling, yellowing of vein, etc.
- Viruses that infect plants have single-stranded RNA
- Bacteriophages, viruses infecting bacteria have double-stranded DNA
2. Viroids
- They are the smallest infectious agents found. They consist of nucleic acid but lack a protein coat
- Diener discovered viroids as a causative agent of potato spindle tuber disease, that was a free RNA
3. Prions
- They contain abnormally folded proteins and have a size similar to viruses
- They can change the shape of normal proteins by transmitting their misfolded proteins
- They cause many neurodegenerative diseases, e.g. bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cattle and Cr-Jacob disease in humans.
4. Lichens
- They are a symbiotic, mutually beneficial association of algae (phycobiont) and fungi (mycobiont). The alga is autotrophic and provides food, whereas the fungus provides protection and shelter.
- Lichens do not grow in polluted areas so they are a good pollution indicator.
FAQs on Important Notes For NEET Biology - Biological Classification - Class 11
| 1. What is biological classification? |  |
Ans. Biological classification is the process of categorizing and organizing living organisms based on their shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. It involves placing organisms into various hierarchical taxonomic groups, such as kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
| 2. Why is biological classification important in the field of biology? |  |
Ans. Biological classification is important in biology because it helps in the systematic study of living organisms. It provides a framework for organizing and understanding the vast diversity of life on Earth. It allows scientists to identify and name new species, study their evolutionary relationships, and compare different species based on their shared characteristics.
| 3. What are the main criteria used for biological classification? |  |
Ans. The main criteria used for biological classification are morphology (physical characteristics), anatomy (internal structure), physiology (functioning of organs and systems), cytology (cellular structure), embryology (developmental stages), and molecular biology (genetic and molecular similarities).
| 4. How is biological classification helpful in the field of medicine? |  |
Ans. Biological classification is helpful in the field of medicine as it helps in identifying and classifying disease-causing organisms. It enables the development of effective treatments and vaccines by understanding the evolutionary relationships and shared characteristics of pathogens. It also aids in the study of genetic and molecular similarities between different species, which can provide insights into the development of new drugs and therapies.
| 5. What are the limitations of biological classification? |  |
Ans. Some limitations of biological classification include the difficulty in classifying organisms with complex evolutionary relationships or those that exhibit convergent evolution. It may also be challenging to classify organisms with poorly preserved or incomplete fossils. Additionally, the classification system may need to be revised as new scientific discoveries are made, leading to changes in the understanding of evolutionary relationships.
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches