Family Description: Solanaceae, Fabaceae & Liliaceae | Science for ACT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Solanaceae Family |

|
| 2. Fabaceae Family |

|
| 3. Liliaceae Family |

|
| (FAQs) Frequently Asked Questions |

|
According to the plant taxonomists, it has been estimated that a total of 2 to 3 million plant species exists on our planet. Among them, around two lakh species are angiosperms (flowering plants), while others include gymnosperms, bryophytes, hydrophytes and other vascular and non-vascular plants. These plants are grouped into different families depending upon their characteristics.
Fabaceae, Solanaceae and Liliaceae are three families of the flowering plants. Let us know a little about these families:
1. Solanaceae Family
Solanaceae family is also known as the potato family. Around 2000 species of dicotyledonous plants belong to this family. They are present mostly in tropical, subtropical and temperate zones.
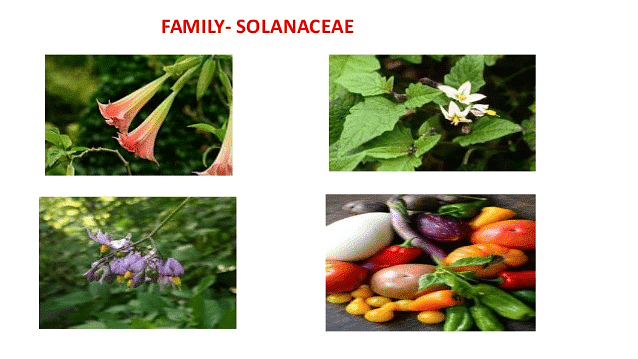
Its important characteristics are mentioned below.
Characteristics of Solanaceae Family
Following are the characteristic features of the Solanaceae family:
Vegetative Characters
- Plants are mostly herbs, shrubs, and occasionally small trees.
- Root System: Taproot system.
- Stem: Stem is usually herbaceous, but can be woody, aerial, erect, cylindrical, branched, solid, or hollow, and can be either hairy or glabrous. In potato (Solanum tuberosum), the stem is underground.
- Leaves: Leaves are alternate, simple, rarely pinnately compound, exstipulate, and have reticulate venation.
Floral characters
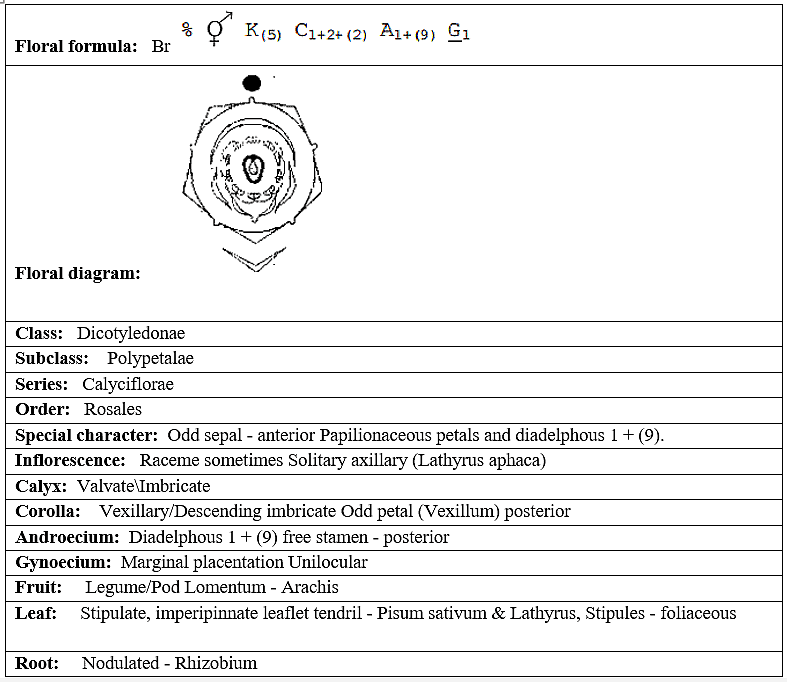
- Inflorescence: Racemose- terminal or axillary raceme; Cymose- solitary in Solanum.
- Flower: Complete, bisexual, actinomorphic, hypogynous.
- Calyx: Five sepals, gamosepalous (united); valvate aestivation.
- Corolla: Five petals, gamopetalous (united), valvate aestivation.
- Androecium: Five stamens, epipetalous; anthers basifixed.
- Gynoecium: Bicarpellary obligately placed, syncarpous ovary that is superior, bilocular, and has a swollen placenta with many ovules, axile.
- Fruit: Berry/ capsule.
- Seed: Numerous, endospermous
- Floral Formula:
Economic Importance
The economic importance of some plants belonging to the Solanaceae family are as follows:
- These are an important source of food. E.g. tomato, brinjal and potato
- These are important sources of spices. E.g. chilly
- The leaves of Nicotiana tabacum are a major source of tobacco which is used for fumigation.
- These are also used as ornamental plants. E.g. petunia
- Plants such as belladonna and ashwagandha are also used as medicinal plants.

2. Fabaceae Family
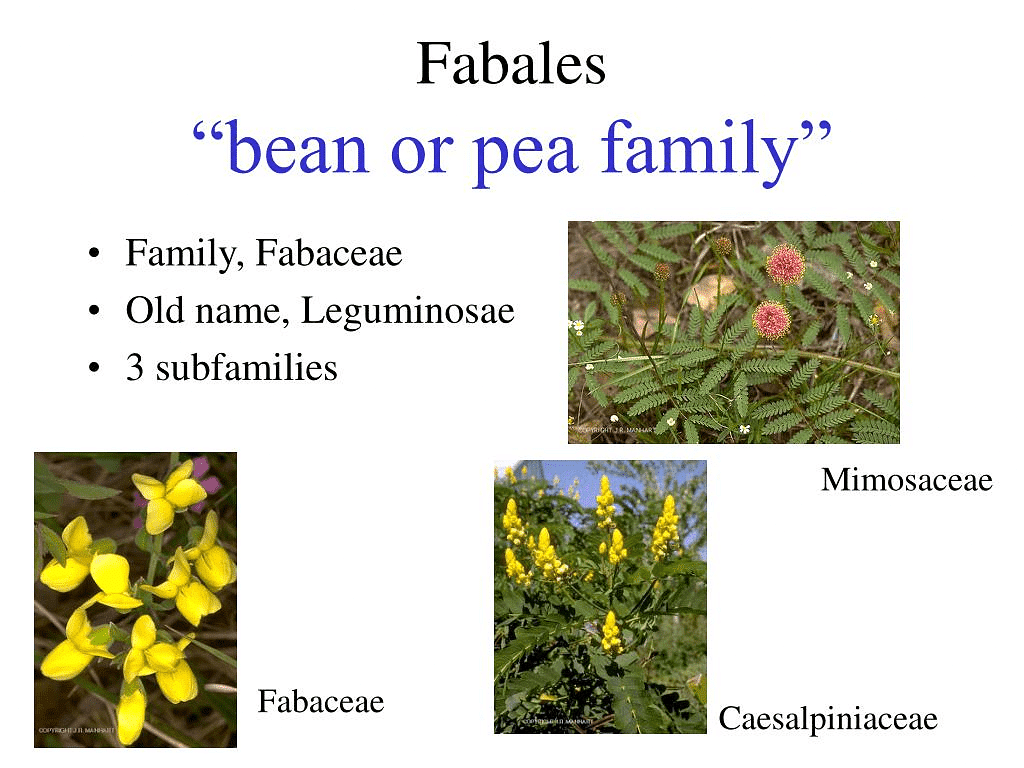
The Fabaceae family is a large family of the plant kingdom, including several economically important plants. The family Fabaceae is also known as Leguminosae or Papilionaceae since it belongs to the pea or legume family. There are around 20,000 species of dicotyledonous Fabaceae plants widely distributed all over the world.
Characteristics of Fabaceae Family
Listed below are the morphological and floral characteristics of the Fabaceae family.
Vegetative Characters
- Root: Dicotyledons, taproot with root nodules.
- Stem: Erect or climber; Fabaceae includes shrubs, herbs, trees and majorly climbers.
- Leaves: Petiolate, pinnately compound or simple; pulvinus leaf base, stipulate; reticulate venation.
- Floral Characters
- Inflorescence: Racemose.
- Flower: Complete, bisexual, zygomorphic, hypogynous, bracteate/ ebracteate.
- Calyx: Five sepals, gamosepalous; valvate or imbricate aestivation.
- Corolla: Five petals, polypetalous, papilionaceous, vexillary aestivation.
- Androecium: Ten stamens (9+1), diadelphous, anther dithecous.
- Gynoecium: Superior ovary, monocarpellary, unilocular, single, short -style and flat, hairy-stigma.
- Fruit: Legume.
- Seed: One or more, non-endospermic.
Economic Importance
Many plants belonging to this family are economically useful. Few of them are listed below:
- The plants of this family are unique and have root nodules which contain nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacteria, capable of transforming atmospheric nitrogen into fixed nitrogen or ammonia.
- Pulses like gram, moong, soya bean are the main source of food.
- Mulethi plant is known for its medicinal value.
- Soya bean and groundnuts are used to extract oil that is used for cooking.
- Sunn hemp is the source of timber and fibre.
- Indigofera is used to make dye.
- Sesbania and Trifolium are the sources of fodder or livestock feed.
- Lupin and sweet pea are known as ornamental plants.
3. Liliaceae Family
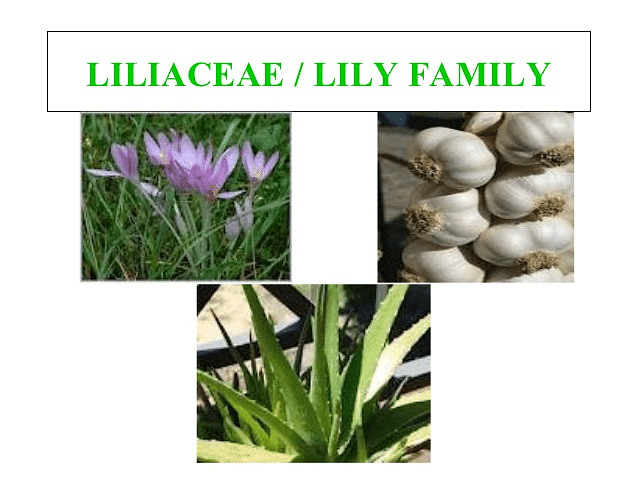

Liliaceae is the family of around 2500 species of perennial, herbaceous monocots. It is also known as the ‘lily family’. Its characteristics are discussed below.
Characteristics of Liliaceae Family
Following are the important characteristics of the Liliaceae family.
Vegetative Characters
- Root: Fibrous root system.
- Stem: Erect; Liliaceae includes perennial herbs which propagate through bulbs or rhizomes.
- Leaves: Alternate, simple; exstipulate; parallel venation.
- Floral characters
- Inflorescence: Cymose- solitary; umbellate clusters.
- Flower: Complete, bisexual, actinomorphic; hypogynous, perianth present.
- Perianth: Indistinctive sepal and petal; six tepals (3+3), often united tepals; valvate aestivation.
- Androecium: Six stamens in two whorls (3+3).
- Gynoecium: Syncarpous, tricarpellary, trilocular, superior ovary with axile placentation.
- Fruit: Mostly Capsule and sometimes berry.
- Seed: Endospermic seeds.
Economic Importance
The economic importance of the plants belonging to the Liliaceae family are:
- Source of Medicine -Aloe vera, Smilax and Colchicine.
- Ornamental Plants -Lilium, tulips, Gloriosa and Ruscus.
- Source of food (or) Vegetables-Asparagus.
- Bulbs of Allium cepa and the roots of various species of Smilax are used as flavouring agents.

(FAQs) Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Which plant belongs to the Solanaceae family?
The Solanaceae family includes a variety of ornamental plants like Petunia, Lycianthes, Browallia, as well as other plants such as Atropa belladonna, Mandragora, and Datura.
Q. Which vegetables are part of the Solanaceae family?
The Solanaceae family encompasses popular vegetables like potatoes, eggplant, tomato, capsicum, and chilly.
Q. What is the significance of the Fabaceae family?
The Fabaceae family, also known as leguminous plants, holds both ecological and economic importance. These plants enrich the soil with nitrogen and serve as a valuable source of protein for humans and livestock.
Q. What types of plants are classified under the Fabaceae family?
The Fabaceae family, commonly referred to as legumes, are pollinated by insects and are known for their entomophilous nature.
|
486 videos|517 docs|337 tests
|
FAQs on Family Description: Solanaceae, Fabaceae & Liliaceae - Science for ACT
| 1. What are the common characteristics of plants in the Solanaceae family? |  |
| 2. Which plants belong to the Fabaceae family and what is their significance? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of plants in the Liliaceae family? |  |
| 4. Are there any poisonous plants in the Solanaceae family? |  |
| 5. How do plants in the Fabaceae family contribute to sustainable agriculture? |  |

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|


















