File Organization | Database Management System (DBMS) - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
File Organization in DBMS
A database consist of a huge amount of data. The data is grouped within a table in RDBMS, and each table have related records. A user can see that the data is stored in form of tables, but in acutal this huge amount of data is stored in physical memory in form of files.
File: A file is named collection of related information that is recorded on secondary storage such as magnetic disks, magnetic tables and optical disks.
What is File Organization?
File Organization refers to the logical relationships among various records that constitute the file, particularly with respect to the means of identification and access to any specific record. In simple terms, Storing the files in certain order is called file Organization. File Structure refers to the format of the label and data blocks and of any logical control record.
Types of File Organizations
Various methods have been introduced to Organize files. These particular methods have advantages and disadvantages on the basis of access or selection . Thus it is all upon the programmer to decide the best suited file Organization method according to his requirements.
Some types of File Organizations are:
- Sequential File Organization
- Heap File Organization
- Hash File Organization
- B+ Tree File Organization
- Clustered File Organization
We will be discussing each of the file Organizations in further sets of this article along with differences and advantages/ disadvantages of each file Organization methods.
1. Sequential File Organization
The easiest method for file Organization is Sequential method. In this method the file are stored one after another in a sequential manner. There are two ways to implement this method:
- Pile File Method: This method is quite simple, in which we store the records in a sequence i.e one after other in the order in which they are inserted into the tables.
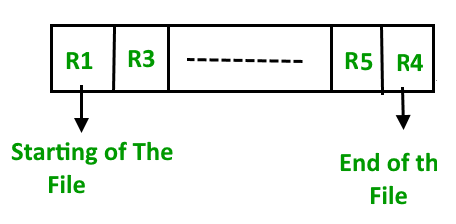 (i) Insertion of new record
(i) Insertion of new record
Let the R1, R3 and so on upto R5 and R4 be four records in the sequence. Here, records are nothing but a row in any table. Suppose a new record R2 has to be inserted in the sequence, then it is simply placed at the end of the file.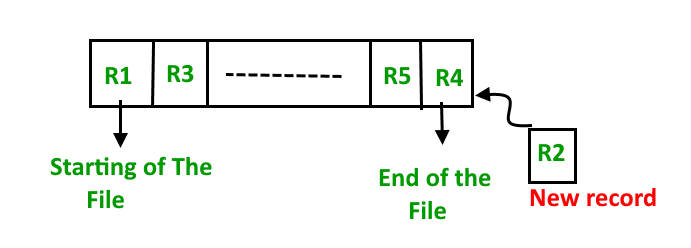
- Sorted File Method: In this method, As the name itself suggest whenever a new record has to be inserted, it is always inserted in a sorted (ascending or descending) manner. Sorting of records may be based on any primary key or any other key.
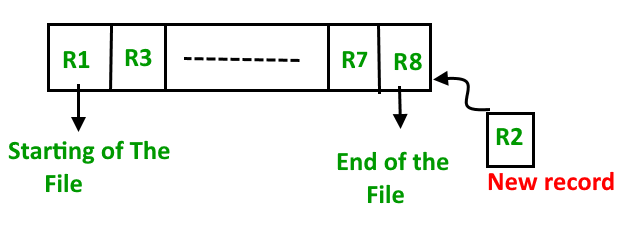 (i) Insertion of new record
(i) Insertion of new record
Let us assume that there is a preexisting sorted sequence of four records R1, R3, and so on upto R7 and R8. Suppose a new record R2 has to be inserted in the sequence, then it will be inserted at the end of the file and then it will sort the sequence .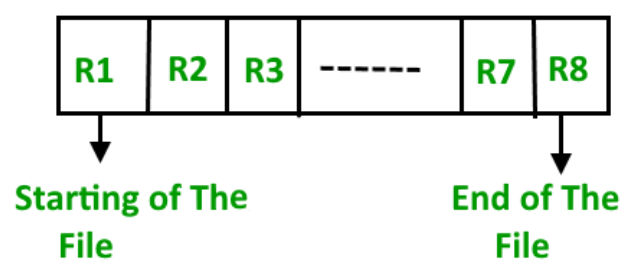 (ii) Pros and Cons of Sequential File Organization
(ii) Pros and Cons of Sequential File Organization
(a) Pros:
A. Fast and efficient method for huge amount of data.
B. Simple design.
C. Files can be easily stored in magnetic tapes i.e cheaper storage mechanism.
(ii) Cons:
A. Time wastage as we cannot jump on a particular record that is required, but we have to move in a sequential manner which takes our time.
B. Sorted file method is inefficient as it takes time and space for sorting records.
2. Heap File Organization
Heap File Organization works with data blocks. In this method records are inserted at the end of the file, into the data blocks. No Sorting or Ordering is required in this method. If a data block is full, the new record is stored in some other block, Here the other data block need not be the very next data block, but it can be any block in the memory. It is the responsibility of DBMS to store and manage the new records.
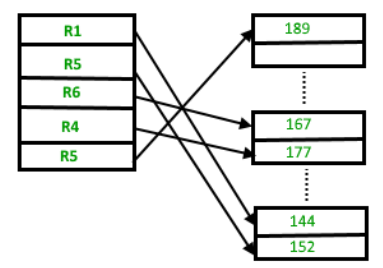
(i) Insertion of new record
Suppose we have four records in the heap R1, R5, R6, R4 and R3 and suppose a new record R2 has to be inserted in the heap then, since the last data block i.e data block 3 is full it will be inserted in any of the data blocks selected by the DBMS, lets say data block
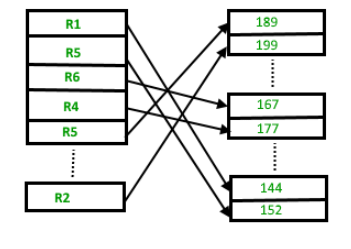
If we want to search, delete or update data in heap file Organization the we will traverse the data from the beginning of the file till we get the requested record. Thus if the database is very huge, searching, deleting or updating the record will take a lot of time.
(ii) Pros and Cons of Heap File Organization
- Pros
- Fetching and retrieving records is faster than sequential record but only in case of small databases.
- When there is a huge number of data needs to be loaded into the database at a time, then this method of file Organization is best suited.
- Cons
- Problem of unused memory blocks.
- Inefficient for larger databases.
In database management system, When we want to retrieve a particular data, It becomes very inefficient to search all the index values and reach the desired data. In this situation, Hashing technique comes into picture.
Hashing is an efficient technique to directly search the location of desired data on the disk without using index structure. Data is stored at the data blocks whose address is generated by using hash function. The memory location where these records are stored is called as data block or data bucket.
3. Hash File Organization
- Data bucket: Data buckets are the memory locations where the records are stored. These buckets are also considered as Unit Of Storage.
- Hash Function: Hash function is a mapping function that maps all the set of search keys to actual record address. Generally, hash function uses primary key to generate the hash index – address of the data block. Hash function can be simple mathematical function to any complex mathematical function.
- Hash Index: The prefix of an entire hash value is taken as a hash index. Every hash index has a depth value to signify how many bits are used for computing a hash function. These bits can address 2n buckets. When all these bits are consumed ? then the depth value is increased linearly and twice the buckets are allocated.
Below given diagram clearly depicts how hash function work: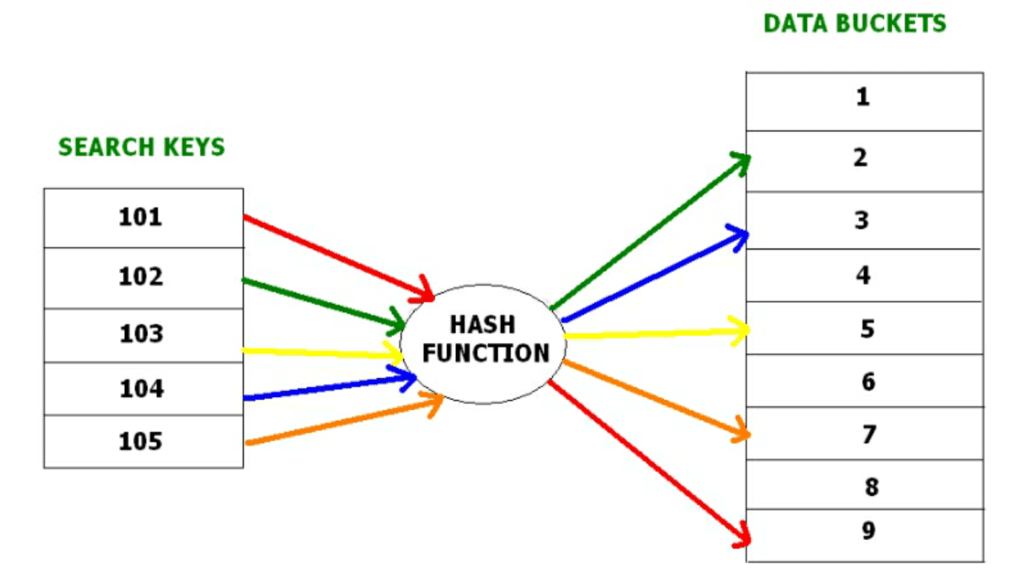
Hashing is further divided into two sub categories: 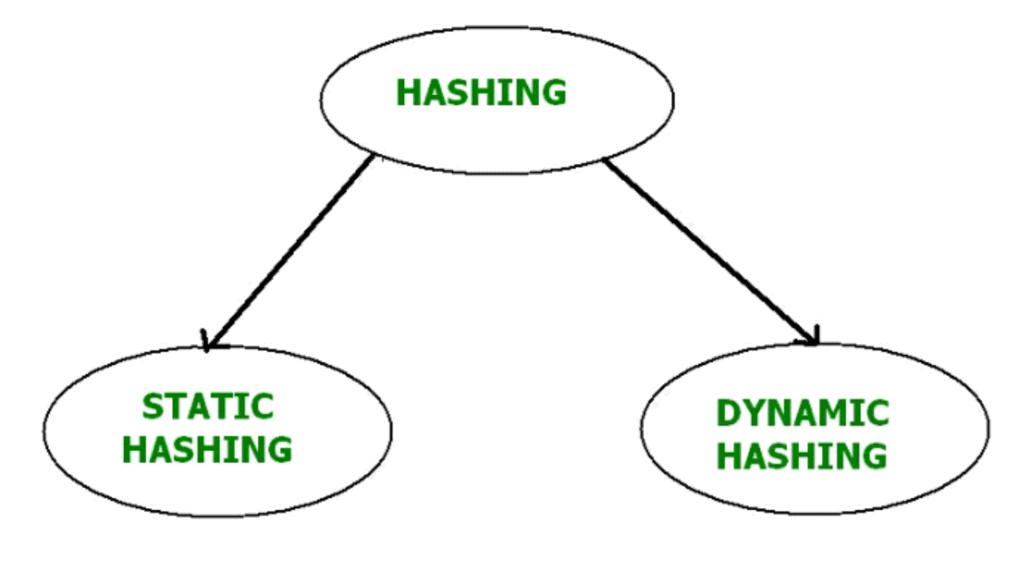
(i) Static Hashing
In static hashing, when a search-key value is provided, the hash function always computes the same address. For example, if we want to generate address for STUDENT_ID = 76 using mod (5) hash function, it always result in the same bucket address 4. There will not be any changes to the bucket address here. Hence number of data buckets in the memory for this static hashing remains constant throughout.
(ii) Operations
- Insertion: When a new record is inserted into the table, The hash function h generate a bucket address for the new record based on its hash key K.
Bucket address = h(K) - Searching: When a record needs to be searched, The same hash function is used to retrieve the bucket address for the record. For Example, if we want to retrieve whole record for ID 76, and if the hash function is mod (5) on that ID, the bucket address generated would be 4. Then we will directly got to address 4 and retrieve the whole record for ID 104. Here ID acts as a hash key.
- Deletion: If we want to delete a record, Using the hash function we will first fetch the record which is supposed to be deleted. Then we will remove the records for that address in memory.
- Updation: The data record that needs to be updated is first searched using hash function, and then the data record is updated.
Now, If we want to insert some new records into the file But the data bucket address generated by the hash function is not empty or the data already exists in that address. This becomes a critical situation to handle. This situation in the static hashing is called bucket overflow.
How will we insert data in this case?
There are several methods provided to overcome this situation. Some commonly used methods are discussed below:
(i) Open Hashing
In Open hashing method, next available data block is used to enter the new record, instead of overwriting older one. This method is also called linear probing.
For example, D3 is a new record which needs to be inserted , the hash function generates address as 105. But it is already full. So the system searches next available data bucket, 123 and assigns D3 to it.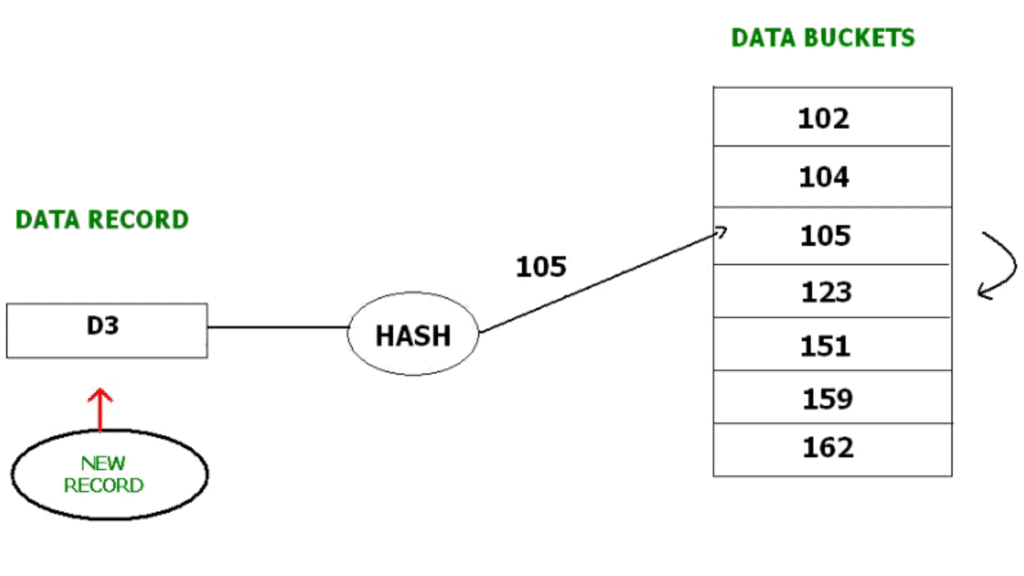
(ii) Closed hashing
In Closed hashing method, a new data bucket is allocated with same address and is linked it after the full data bucket. This method is also known as overflow chaining.
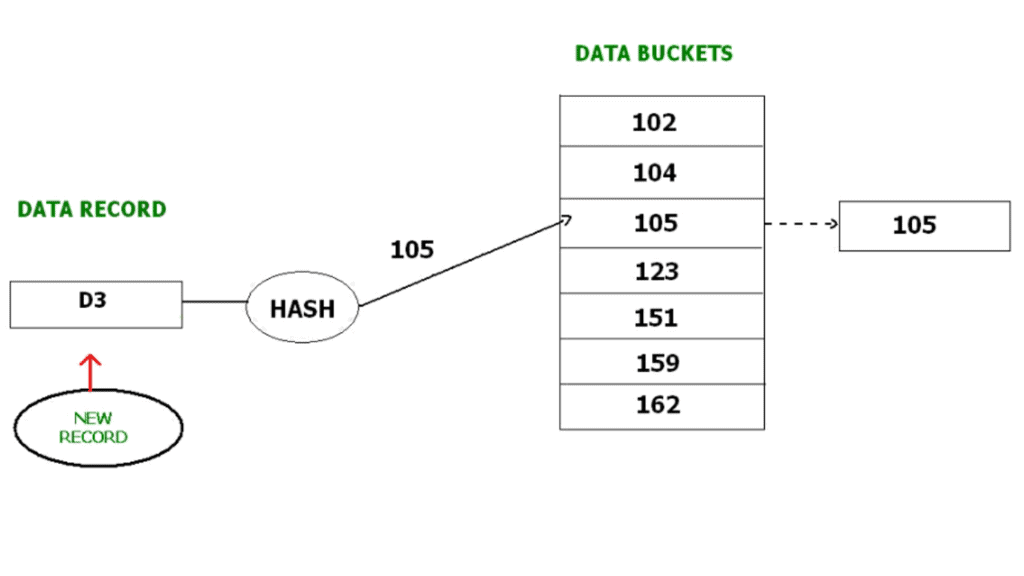
For example, we have to insert a new record D3 into the tables. The static hash function generates the data bucket address as 105. But this bucket is full to store the new data. In this case is a new data bucket is added at the end of 105 data bucket and is linked to it. Then new record D3 is inserted into the new bucket.
- Quadratic probing: Quadratic probing is very much similar to open hashing or linear probing. Here, The only difference between old and new bucket is linear. Quadratic function is used to determine the new bucket address.
- Double Hashing: Double Hashing is another method similar to linear probing. Here the difference is fixed as in linear probing, but this fixed difference is calculated by using another hash function. That’s why the name is double hashing.
(iii) Dynamic Hashing
The drawback of static hashing is that that it does not expand or shrink dynamically as the size of the database grows or shrinks. In Dynamic hashing, data buckets grows or shrinks (added or removed dynamically) as the records increases or decreases. Dynamic hashing is also known as extended hashing.
In dynamic hashing, the hash function is made to produce a large number of values. For Example, there are three data records D1, D2 and D3 . The hash function generates three addresses 1001, 0101 and 1010 respectively. This method of storing considers only part of this address – especially only first one bit to store the data. So it tries to load three of them at address 0 and 1.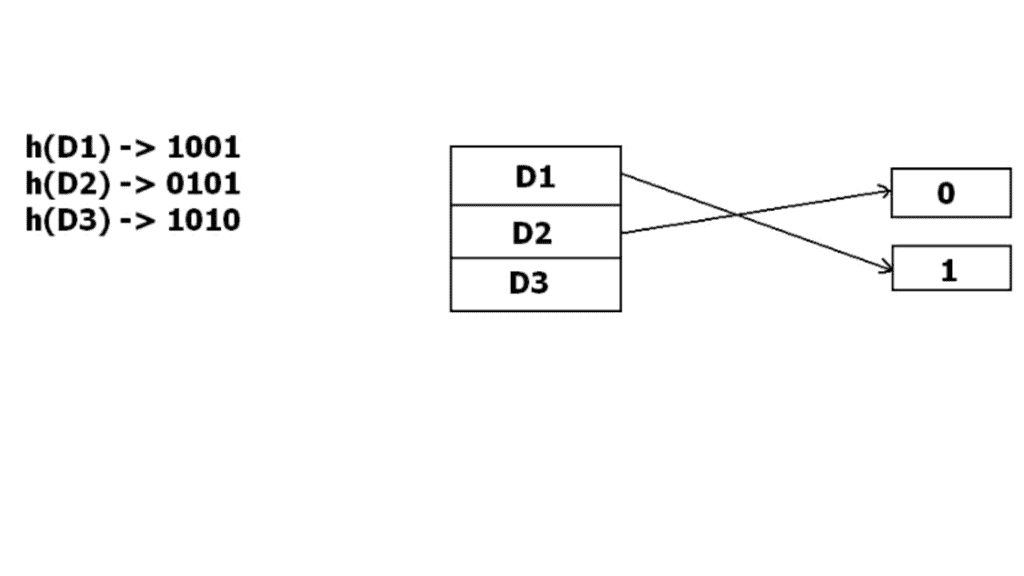
But the problem is that No bucket address is remaining for D3. The bucket has to grow dynamically to accommodate D3. So it changes the address have 2 bits rather than 1 bit, and then it updates the existing data to have 2 bit address. Then it tries to accommodate D3.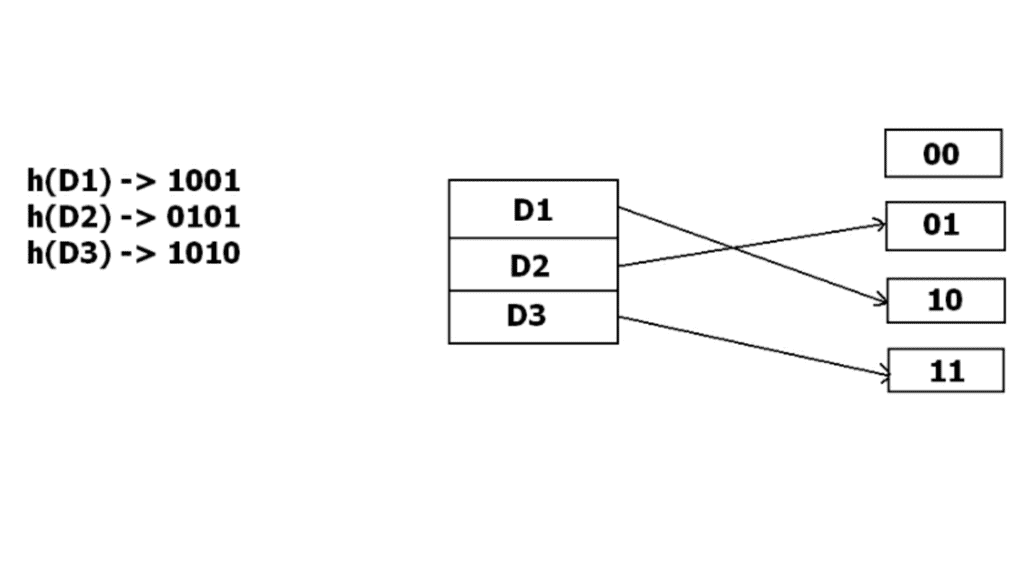
4. B+ Tree File Organization
B+ Tree, as the name suggests, It uses a tree like structure to store records in File. It uses the concept of Key indexing where the primary key is used to sort the records. For each primary key, an index value is generated and mapped with the record. An index of a record is the address of record in the file.
B+ Tree is very much similar to binary search tree, with the only difference that instead of just two children, it can have more than two. All the information is stored in leaf node and the intermediate nodes acts as pointer to the leaf nodes. The information in leaf nodes always remain a sorted sequential linked list.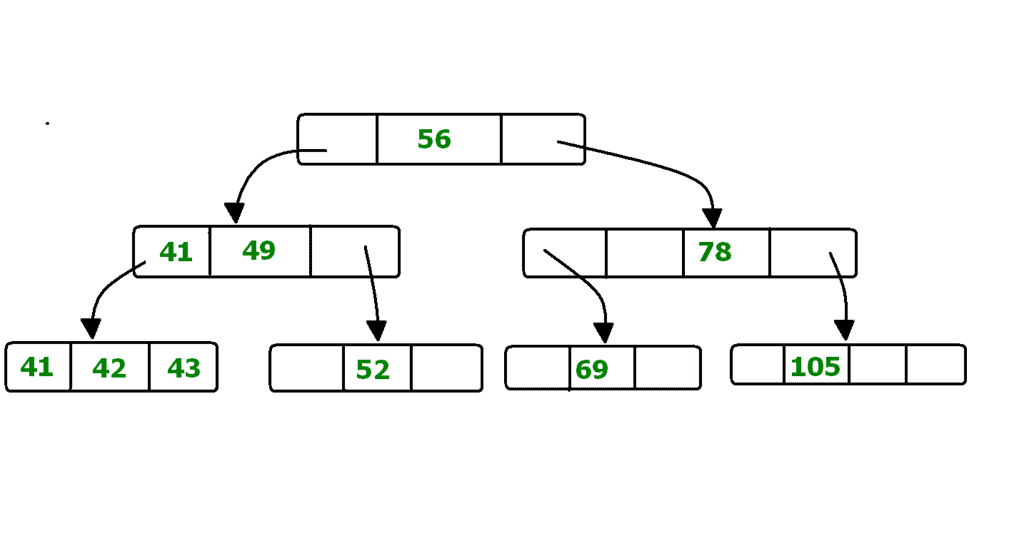
In the above diagram 56 is the root node which is also called the main node of the tree.
The intermediate nodes here, just consist the address of leaf nodes. They do not contain any actual record. Leaf nodes consist of the actual record. All leaf nodes are balanced.
Pros and Cons of B+ Tree File Organization
- Pros
- Tree traversal is easier and faster.
- Searching becomes easy as all records are stored only in leaf nodes and are sorted sequential linked list.
- There is no restriction on B+ tree size. It may grows/shrink as the size of data increases/decreases.
- Cons
- Inefficient for static tables.
5. Cluster File Organization
In cluster file organization, two or more related tables/records are stored withing same file known as clusters. These files will have two or more tables in the same data block and the key attributes which are used to map these table together are stored only once.
Thus it lowers the cost of searching and retrieving various records in different files as they are now combined and kept in a single cluster.
For example we have two tables or relation Employee and Department. These table are related to each other.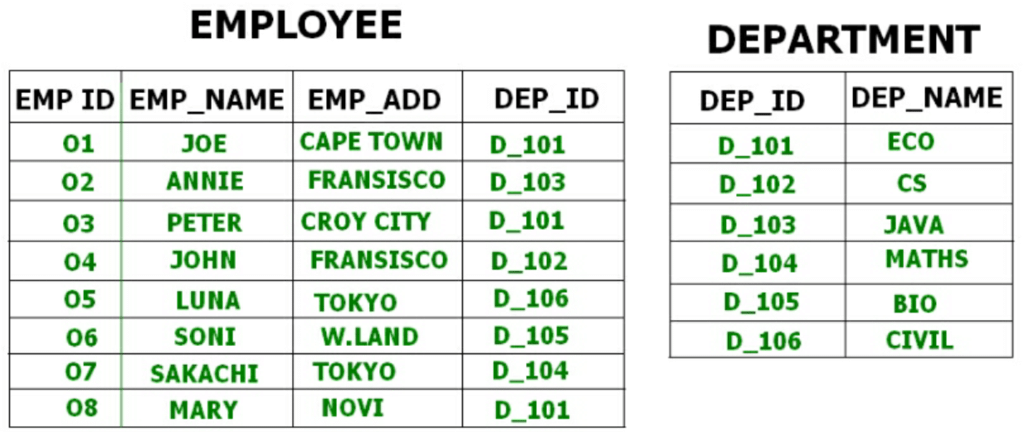
Therefore these table are allowed to combine using a join operation and can be seen in a cluster file.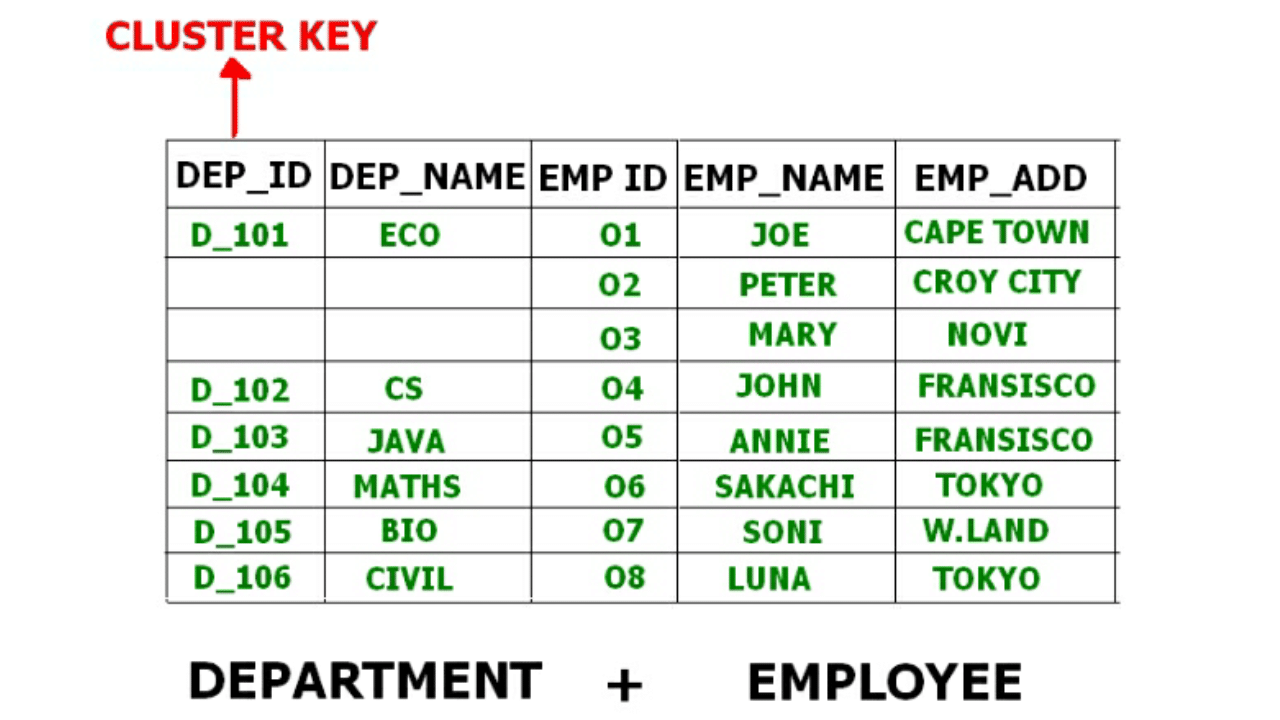
If we have to insert, update or delete any record we can directly do so. Data is sorted based on the primary key or the key with which searching is done. Cluster key is the key with which joining of the table is performed.
Types of Cluster File Organization: There are two ways to implement this method:
- Indexed Clusters: In Indexed clustering the records are group based on the cluster key and stored together. The above mentioned example of Emplotee and Department relationship is an example of Indexed Cluster where the records are based on the Department ID.
- Hash Clusters: This is very much similar to indexed cluster with only difference that instead of storing the records based on cluster key, we generate hash key value and store the records with same hash key value.
|
62 videos|99 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on File Organization - Database Management System (DBMS) - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is file organization in DBMS? |  |
| 2. What is sequential file organization? |  |
| 3. What is indexed sequential file organization? |  |
| 4. What is direct file organization? |  |
| 5. What is hashed file organization? |  |
















