Strings in C | Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
C Programming Strings
In this tutorial, you'll learn about strings in C programming. You'll learn to declare them, initialize them and use them for various I/O operations with the help of examples.
In C programming, a string is a sequence of characters terminated with a null character \0.
For example:
char c[] = "c string";
When the compiler encounters a sequence of characters enclosed in the double quotation marks, it appends a null character \0 at the end by default.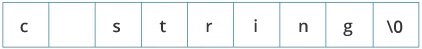 Memory Diagram
Memory Diagram
How to declare a string?
Here's how you can declare strings:
char s[5];
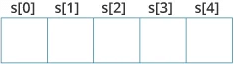 String Declaration in C
String Declaration in C
Here, we have declared a string of 5 characters.
How to initialize strings?
You can initialize strings in a number of ways.
char c[] = "abcd";
char c[50] = "abcd";
char c[] = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', '\0'};
char c[5] = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', '\0'};
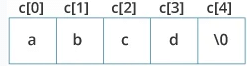 String Initialization in C
String Initialization in C
Let's take another example:
char c[5] = "abcde";
Here, we are trying to assign 6 characters (the last character is '\0') to a char array having 5 characters. This is bad and you should never do this.
Assigning Values to Strings
Arrays and strings are second-class citizens in C; they do not support the assignment operator once it is declared. For example,
char c[100];
c = "C programming"; // Error! array type is not assignable.
Note: Use the strcpy() function to copy the string instead.
Read String from the user
You can use the scanf() function to read a string.
The scanf() function reads the sequence of characters until it encounters whitespace (space, newline, tab, etc.).
Example 1: scanf() to read a string
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char name[20];
printf("Enter name: ");
scanf("%s", name);
printf("Your name is %s.", name);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter name: Dennis Ritchie
Your name is Dennis.
Even though Dennis Ritchie was entered in the above program, only "Dennis" was stored in the name string. It's because there was a space after Dennis.
How to read a line of text?
You can use the fgets() function to read a line of string. And, you can use puts() to display the string.
Example 2: fgets() and puts()
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char name[30];
printf("Enter name: ");
fgets(name, sizeof(name), stdin); // read string
printf("Name: ");
puts(name); // display string
return 0;
}
Output
Enter name: Tom Hanks
Name: Tom Hanks
Here, we have used fgets() function to read a string from the user.
fgets(name, sizeof(name), stdlin); // read string
The sizeof(name) results to 30. Hence, we can take a maximum of 30 characters as input which is the size of the name string.
To print the string, we have used puts(name);.
Note: The gets() function can also be to take input from the user. However, it is removed from the C standard.
It's because gets() allows you to input any length of characters. Hence, there might be a buffer overflow.
Passing Strings to Functions
Strings can be passed to a function in a similar way as arrays. Learn more about passing arrays to a function.
Example 3: Passing string to a Function
#include <stdio.h>
void displayString(char str[]);
int main()
{
char str[50];
printf("Enter string: ");
fgets(str, sizeof(str), stdin);
displayString(str); // Passing string to a function.
return 0;
}
void displayString(char str[])
{
printf("String Output: ");
puts(str);
}
Strings and Pointers
Similar like arrays, string names are "decayed" to pointers. Hence, you can use pointers to manipulate elements of the string. We recommended you to check C Arrays and Pointers before you check this example.
Example 4: Strings and Pointers
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
char name[] = "Harry Potter";
printf("%c", *name); // Output: H
printf("%c", *(name+1)); // Output: a
printf("%c", *(name+7)); // Output: o
char *namePtr;
namePtr = name;
printf("%c", *namePtr); // Output: H
printf("%c", *(namePtr+1)); // Output: a
printf("%c", *(namePtr+7)); // Output: o
}
Commonly Used String Functions
- strlen(): calculates the length of a string
- strcpy(): copies a string to another
- strcmp(): compares two strings
- strcat(): concatenates two strings
|
159 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Strings in C - Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What are strings in C programming? |  |
| 2. How do you declare and initialize a string in C? |  |
| 3. How do you read a string from the user in C programming? |  |
| 4. How do you find the length of a string in C? |  |
| 5. How do you concatenate two strings in C programming? |  |
















