Physical Properties & Methods of Preparation: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Physical Properties of Haloalkanes
Haloalkanes are hydrocarbons in which hydrogen in a normal alkane is replaced by a halogen (group 17 elements). The physical properties of haloalkanes are mostly like a normal covalent compound. Halogens not being much reactive functional group as a carboxyl group or aldehyde doesn’t affect the overall physical properties by much. Still, few differences can be seen as we move down in the homologous series of the haloalkanes group due to the difference in atomic masses of the compound.
1. Colour
Alkyl halides are colourless when pure but bromides and iodides develop colour when exposed to light because they decompose into halogens.

2. Melting and Boiling Points
- The melting points and boiling points of haloalkanes are higher than those of corresponding hydrocarbons due to the higher molecular mass of haloalkanes.
- The melting and boiling points increase with the increase in size due to higher van der Waal's forces. Hence the order is : R−I > R−Br > R−Cl > R−F
- The boiling points of isomeric haloalkanes decrease with an increase in branching as the surface area decreases on branching and Vander Waal's forces decrease.

- The boiling points of isomeric dihalobenzene are nearly the same.
- The melting point of p-dihalobenzene is always higher than those of the o- and p- isomers. Because p-isomers are more symmetrical and hence their molecules pack closely in the crystal lattice. This leads to stronger molecular forces of attraction.

3. Solubility
- Haloalkanes and haloarenes, though polar, are immiscible with water because they neither form H-bond nor break the already existing H-bonds (because the new attraction of water and haloalkanes is weaker).
- Haloalkanes are soluble in organic solvents of low polarity like ether, benzene etc. because new intermolecular forces are similar to those in the low polarity solvents.
4. Density
- Alkyl fluorides and alkyl chlorides are generally lighter than water whereas alkyl bromides and alkyl iodides are heavier. The relative densities follow the order: RI > RBr > RCl.
- The densities of the alkyl halides decrease as the size of the alkyl group increases.
5. Stability
The stability of the haloalkanes having the same alkyl group decreases in the order: R−F > R−Cl > R−Br > R−I since the strength of the C−X bond decreases in the order: C−F > C−Cl > C−Br > C−I
6. Dipole Moment
The dipole moment of methyl halides follows the order: CH3Cl > CH3F > CH3Br > CH3I. Due to the very small size of F, fluorides have lower dipole moments than chlorides.
Methods of Preparation of Haloalkane & Haloarenes
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes can be prepared from other organic compounds by numerous methods. Different methods of preparation include conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides, the addition of halogens to alkenes, and hydrohalogenation of alkenes. The preparation techniques were so reliable and efficient that they became an inevitable part of industrial chemistry.
There are primarily 4 different types of preparation techniques of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes.
- Alcohols
- Hydrocarbons
- Alkenes by addition of hydrogen halides and halogens
- Halogen exchange reaction.
So let’s learn about the methods of preparation of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes.
Preparation of Haloalkanes
1. From Alcohols:
Alkyl halides can easily be prepared from alcohols upon the addition of halides. In this reaction, the hydroxyl group of alcohol is replaced with the halogen atom attached to the other compound involved. This reaction requires a catalyst for primary and secondary alcohols whereas it doesn’t require any catalyst for tertiary alcohols.
The general reaction looks like this: ROH + HX → RX + H2O
a. Reaction with HCl:

b. Reaction with Bromine: CH3CH2OH + HBr → CH3CH2Br + H2O
c. Reaction with Phosphorous Halide:

d. Reaction with Thionyl Chloride:

2. From Alkenes:
The addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes follows either Markovnikov’s rule or exhibit the Kharash effect. All the electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes following the Markovnikov rule are known as Markovnikov addition reactions. A general example of such reaction is given below:


3. From Free Radical Halogenation:
In free radical halogenation, we get a mixture of mono-substituted, di-substituted, tri-substituted, and even tetra-substituted halo-alkanes (alkyl halides). Since we require only one type of alkyl halide and not all in the form of a mixture, So this method is not used.

4. From Halogen Exchange:
a. Finkelstein Reaction:
In this reaction, an alkyl chloride or alkyl bromide reacts with sodium iodide in acetone to form alkyl iodides.

The solubility difference of alkyl halides in acetone is used for driving the reaction in the forward direction. We know that sodium iodide is soluble in acetone but NaCl or NaBr are insoluble. Therefore, they precipitate out in the reaction which is easy to remove from the reaction mixture.
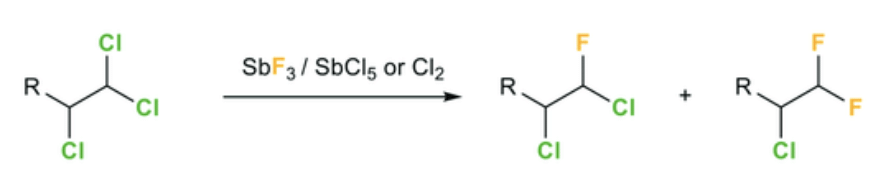
b. Swartz Reaction:
In this reaction, alkyl fluorides formation is possible by heating of Alkyl fluorides RBr/RCl. The reaction is carried out in the presence of metallic fluoride such as SbF3, Hg2F2, AgF, CoF2.
Preparation of Haloarenes
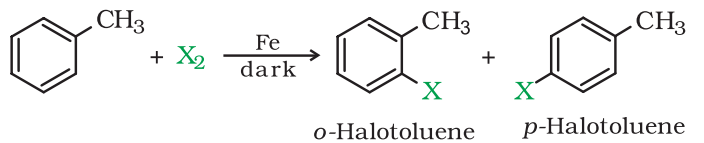
1. From hydrocarbons by Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
Aryl halides can be prepared by electrophilic aromatic substitution of arenes with halogens in the presence of a Lewis acid.
Mechanism of Electrophilic Substitution Reaction:
- In the above reaction, two different isomers of the aryl chlorides are formed. They are Ortho and para isomer.
- The π-electron in the benzene ring attacks the Cl+ electrophile to produce an intermediate complex. However, the H+ bond from the intermediate complex moves in order to compensate for the positive charge of the carbon atom.
- Thus the reaction forms two different isomers of the product-ortho and para. The melting points of both the isomer differ significantly. And para-isomer has a higher boiling point than ortho-isomer. Therefore, they can be easily separated from each other.

2. From amines by Sandmeyer’s reaction:
Sandmeyer’s Reaction is a two-step method that includes:
- Diazonium salt formation
- Diazonium salt reaction with a cuprous halide (Cu2X2)
Primary aromatic amine reacts with sodium nitrite in the presence of cold mineral acid to form the diazonium salt. In this case, HNO2 is prepared within the reaction by reacting sodium nitrite and HX at a temperature of 273-278K.

Mechanism of the Sandmeyer’s Reaction:
- In the first step: NaNO2 + HCl → HNO2 + NaCl
- The HNO2 formed in the presence of H+ undergo protonation to form NO+ as the electrophile.
- The lone pair of the atom from the primary amine will react with the electrophile to form an intermediate compound which further gives diazonium salt after elimination of H2O.
- In the second step, the diazonium salt reacts with cuprous halide to form the respective aryl halide.

|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on Physical Properties & Methods of Preparation: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are some physical properties of haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 2. How are haloalkanes and haloarenes prepared? |  |
| 3. What is a common method of preparation for haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 4. What are some key differences between haloalkanes and haloarenes in terms of physical properties? |  |
| 5. Can haloalkanes and haloarenes form hydrogen bonds with other molecules? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















