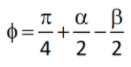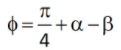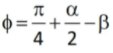Metal Cutting | Manufacturing Engineering - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Introduction
“A manufacturing process in which a sharp cutting tool is used to discard away material to leave the required part shape is known as machining”.
Shear deformation is the major cutting action involved in the machining of the work material to generate a chip; as the chip is removed, a new surface is exposed.

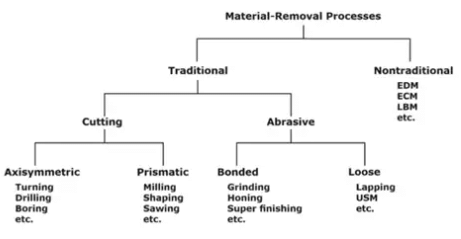
Classification of the Material removal process
One or more sharp cutting edges are present in a cutting tool and is made of a material that is harder than the work material.
Cutting tools are classified into two major groups:
- Single point cutting tools
- Multipoint cutting tools.
- Multipoint cutting tool: They have more than one cutting edge to remove excess material from the workpiece.
Example: Milling cutters, drills, reamers, broaches, and grinding wheels are multi-point cutting tools. - Single point cutting tool: In a single-point tool, there is one tool point from which the name of this cutting tool is derived. The point is rounded to a certain radius called the nose radius.
Geometry of Right Hand Single Point Cutting Tool
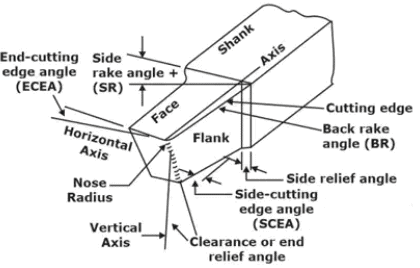 Right-hand single point cutting tool
Right-hand single point cutting tool
Tool Nomenclature/Angles
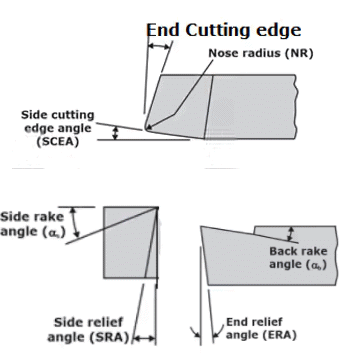 Single Point Cutting Tool
Single Point Cutting Tool
- ASA Tool Signature
Back rake angle - Side rake angle - End relief angle - Side relief angle - End cutting edge angle - Side cutting edge angle- Nose radius (ASA Tool signature)
In this system the geometry of the rake face is expressed in terms of back rake angle and side rake angle. - Normal Or Orthogonal Rake System(ORS)
A number of lines drawn perpendicular to the side cutting edge in the horizontal plane and the line which gives the maximum slope called Normal Rake Angle (αn).
If side cutting edge angle is zero, normal rake angle is equal to the side rake angle.
Tool signature in this system is given as:
I - αn - Side Relief angle - End Relief angle - End Cutting edge angle - Approach angle λ – Nose Radius R.
where, I-Angle of inclination
αn – normal rake angle
90o - side cutting edge angle = approach angle (λ)
Types of Metal Cutting Process
The metal cutting processes are of two types
- Orthogonal cutting process (Two-dimensional cutting)
Orthogonal cutting uses a wedge-shaped tool in which the cutting edge is perpendicular to the direction of cutting speed. The chip is produced by shear deformation along a plane known as the shear plane, as the tool is forced into the material, which is oriented at an angle ø with the surface of the work. - Oblique cutting (Three-dimensional cutting)
It is a form of cutting when the major cutting edge of the tool is presented to the work piece at an angle perpendicular to the direction of feed motion.
A general purpose metal cutting operation like turning or milling is three-dimensional and is commonly termed as oblique cutting.
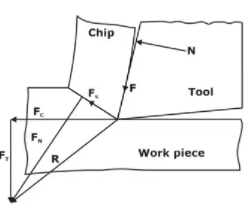 Various force acting in an orthogonal cutting
Various force acting in an orthogonal cutting
FC – Cutting Force
Ft -Force perpendicular to the primary tool motion (thrust force)
Fs -Force along the shear plane
FN - Force normal to the shear plane
F - Frictional force along the rake face
N - The Normal force perpendicular to the rake face
Merchant's Analysis for Chip Thickness Ratio
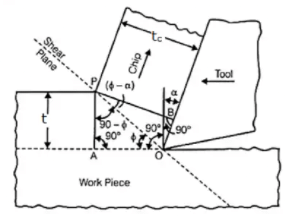 Orthogonal cutting analysis
Orthogonal cutting analysis
t = uncut chip thickness
tc = Chip thickness after cutting
ϕ = Shear plane angle
α = Back rake angle
The ratio of ‘t’ to ‘tc’ is called the chip thickness ratio (or simply the chip ratio) & it is designated by ‘r’.
t/tc = lc/l
where l = length of uncut chip
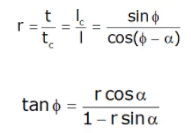
Where r is the chip thickness ratio α is rake angle
Velocity Triangle
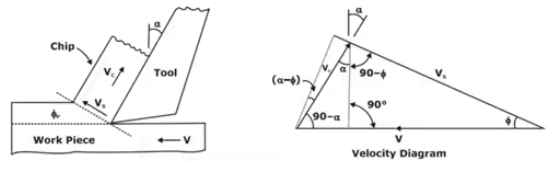 Velocity Triangle
Velocity Triangle
V = cutting speed = πDN/60
Vs = Shear velocity
Vc = Chip veloocity
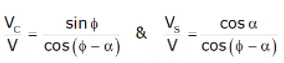
Shear Strain
shear strain is given as
γ = cotϕ + tan(ϕ - α)
Merchant’s Circle
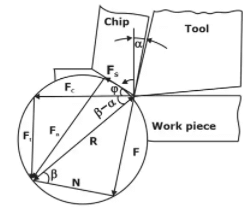 Merchant’s Cutting Force circle
Merchant’s Cutting Force circle
Fs - Fccos ϕ - FT Sin ϕ
FN= FTcos ϕ - Fc Sin ϕ
F = Fcsin α + FT COS α
N = Fccos α - FT Sin α
Material Removal Rate
MMR = fdv
where MMR material removal rate, mm3/s or (mm3/min)
v - cutting speed, m/s or (mm/s),
f - feed, mm (mm/revolution);
d - depth of cut, mm
Specific Cutting Energy
The specific cutting energy, is a parameter which can be obtained by dividing the total work done with the material removal rate.
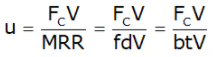
Different Shear Angle Relation
- Merchant’s shear angle relation

- Lee and Shaffer relation

- Stabler relation

Types of Chips
The chip formation in metal cutting could be broadly categorized into three types:
- Discontinuous chip
- Continuous chip
- Continuous chip with Built up Edge(BUE)
- Continuous Chips
Few conditions that promote continuous chips in metal cutting are listed below:
(i) sharp cutting edge,
(ii) Low feed and depth of cut
(iii) Large rake angle
(iv) High cutting speed
(v) Ductile work materials
(vi) Lower amount of friction between chip tool interfaces through efficient lubrication - Discontinuous Chips
Some ideal conditions that promote discontinuous chips in metal cutting are:
(i) Brittle materials (e.g., cast irons)
(ii) Low cutting speeds
(iii) High tool–chip friction
(iv) Large feed and depth of cut
(v) Small rake angles - Chips Formation with Built up Edge
Some ideal conditions that promote discontinuous chips in metal cutting are:
(i) Low cutting speed
(ii) Ductile material
(iii) High feed and depth of cut
(iv) Low rake angle
Taylor’s Tool Life Equation
“Tool life is defined as the duration of cutting time that the tool can be used until failure takes place”.
VTn = C
V = cutting speed
T = tool life.
C = machining constant.
n = Tool life exponent (depends only on tool material)
Economics of Machining
“The use of optimum process parameters to obtain the required economic conditions during machining is called economics of machining.”
The various costs associated with machining process are:
- The manpower cost, C1 which is measured in Rs. Per unit time, generally hours that operator is employed.
- The machine tool operating (overhead) cost, Cm under which we include machine depreciation, and other costs associated with the running of the machine tool such as power consumed, maintenance overheads, consumables such as oils, etc.
- The job handling cost, which comes because of the time spent in loading and unloading of the job, during which the machine tool is kept idle, and the operator needs to attend to the job.
(a) Minimum Cost Criteria
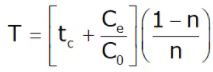
(b) Maximum production rate
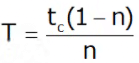
Tool Wear
- Crater wear: The crater is present on the rake face and is almost like a circle. The crater not necessarily extends to the tooltip, but may end at a distance little away from the tooltip.
Diffusion plays an important role in the development of a crater - Flank wear: Wear land or Flank wear is present on the clearance surface of the tool. Length of wear land is used for the characterization of the wear land.
Machinability
The ease with which a given material may be worked with a cutting tool is Machinability. Factors that affect Machinability are:
- Tool life: The longer the tool life it enables at a given cutting speed better is the Machinability
- Surface finish: Two materials are machined under identical cutting conditions and material which produces a good finish is considered to be more machinable material. This criterion is used in finished cuts.
- Cutting Forces: Two materials are machined under identical cutting conditions and the material which requires smaller cutting forces is considered to be more machinable, This criterion is used in smaller and old machines.
|
53 videos|53 docs|29 tests
|
FAQs on Metal Cutting - Manufacturing Engineering - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is metal cutting in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. What are the different methods of metal cutting? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the cutting performance in metal cutting? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of metal cutting in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 5. What safety precautions should be taken during metal cutting? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|