Common Diseases in Humans - 1 | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
What are Diseases?
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting a healthy living organism. It is broadly divided into infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious diseases - These diseases are caused by the pathogens, such as bacteria, virus, fungi, parasites and can be easily transmitted from one person to another, hence it is also known as a contagious or communicable disease. Common Cold, Tuberculosis, flu, ringworm, malaria are some examples of infectious diseases.
Non-infectious diseases - Diseases which cannot be transmitted from one person to another are called non-infectious disease, it is also known as a noncommunicable disease. These diseases can be either caused by genetic disorders, unhealthy diets, lack of physical activity, excessive use of tobacco, drugs or alcohol and few environmental factors.
What are Pathogens?
 Pathogens
Pathogens
There is a wide range of organisms in existence, and some have the ability to flourish and reproduce within a host organism. When an organism is capable of causing infectious diseases, it is categorized as an infectious agent. Specifically, those infectious agents that can lead to illness and infection are known as pathogens.
Classification of Pathogens
Pathogens are microorganisms or agents that have the potential to cause disease in humans and other living organisms.
These disease-causing organisms can encompass a wide range of biological entities, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoans, and helminths (parasitic worms).
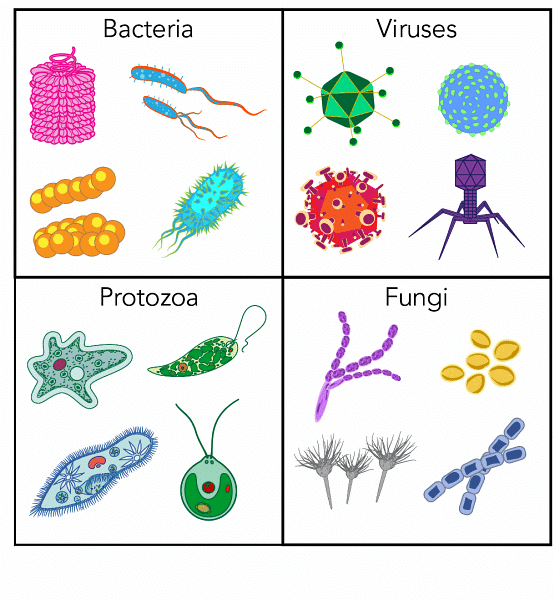 Types of Pathogens
Types of Pathogens
(a) Bacteria: Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that can be pathogenic (causing or capable of causing disease) .
- Many bacterial species are harmless or even beneficial, but certain strains can cause diseases when they enter the human body and multiply uncontrollably.
- Examples of pathogenic bacteria include Escherichia coli (E. coli), Streptococcus pyogenes (which causes strep throat), and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (which causes tuberculosis).
(b) Viruses: Viruses are even smaller than bacteria and are not considered living organisms because they cannot carry out metabolic processes on their own. Instead, they must infect host cells to replicate.
- Examples - influenza virus, HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), and the SARS-CoV-2 virus (responsible for COVID-19) are well-known examples of pathogens that cause diseases in humans.
(c) Fungi: Fungi are a group of eukaryotic microorganisms that can cause fungal infections in humans.
- These infections can range from superficial skin conditions like athlete's foot to more severe systemic infections.
- Common fungal pathogens include Candida species and Aspergillus species.
(d) Protozoans: Protozoans are single-celled eukaryotic organisms that can be parasitic and cause diseases in humans.
- Examples of protozoan pathogens include Plasmodium (causing malaria), Entamoeba histolytica (causing amoebic dysentery), and Trypanosoma (causing sleeping sickness).
(e) Helminths: Helminths are parasitic worms that can infect various parts of the human body. They are multicellular organisms and include nematodes (roundworms), cestodes (tapeworms), and trematodes (flukes).
- Helminth infections can lead to diseases such as intestinal worm infections, and filariasis.
Some Common Diseases In Humans
- A pathogenic bacterium known as Salmonella typhi is known to cause typhoid in humans. This fever can be confirmed by Widal test
- Pneumonia is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Hemophilus influenza
- Rhinovirus, a group of virus, is known to cause one of the most of infectious ailments in humans, cold.
- Plasmodium, a small protozoan causes malaria. Another protozoan, Entamoeba histolytica causing amoebiasis (amoebic dysentery)
- Ascaris(an intestinal parasite) causes ascariasis
- Wuchereria bancrofti, the filarial worm causes filariasis or elephantiasis
Some of the Diseases Caused by Protozoas
Protozoa are one-celled animals found worldwide in most habitats. Most species are free living, but all higher animals are infected with one or more species of protozoa.
1. Malaria
Malaria is a potentially life-threatening infectious disease caused by parasitic protozoa of the genus Plasmodium. It is typically transmitted to humans through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
The parasites enter the bloodstream and travel to the liver, where they multiply and then infect red blood cells, leading to a variety of symptoms, including high fever, chills, sweats, fatigue, and, if not treated promptly, severe complications and even death.
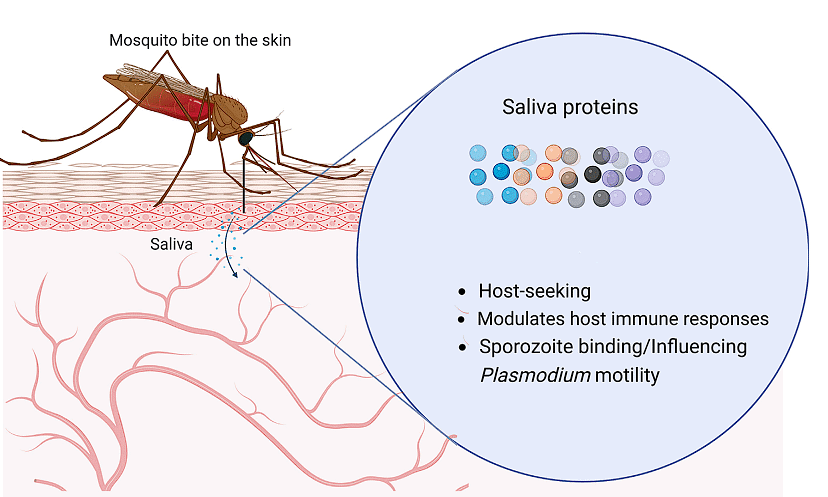 Transmission of Malaria
Transmission of Malaria
Types of Plasmodium
- Malaria is a disease that humans have been fighting for many years.
- It is caused by a tiny protozoan parasite called Plasmodium.
- Different species of Plasmodium, such as P. vivax, P. malariae, and P. falciparum, cause different types of malaria.
- The most serious and potentially fatal form of malaria is known as malignant malaria, and it is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
Symptoms of malaria
Symptoms of malaria are exhibited within 7 to 18 days of being infected. Common symptoms include:
- Fever, fatigue, chills, vomiting, and headaches
- Diarrhoea, anaemia and muscle pain
- Profuse sweating and convulsions
- Bloody stools.
- In severe cases, malaria can be devastating; it can lead to seizures, coma and eventually, death.
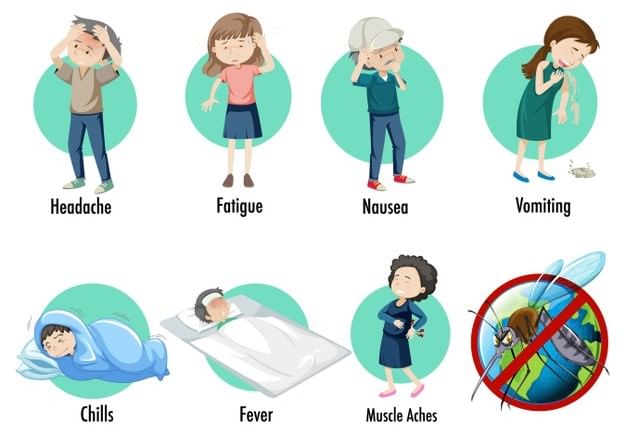 Symptoms of Malaria
Symptoms of Malaria
Sir Ronald Ross and his study on the transmission of the disease helped carve the way for future scientists to effectively combat the disease. His deep research showed that specifically, the female Anopheles mosquito is the vector ( disease carrier) of the disease, and addressing this problem will prevent malaria and in turn, save countless lives.
Life Cycle of Malaria
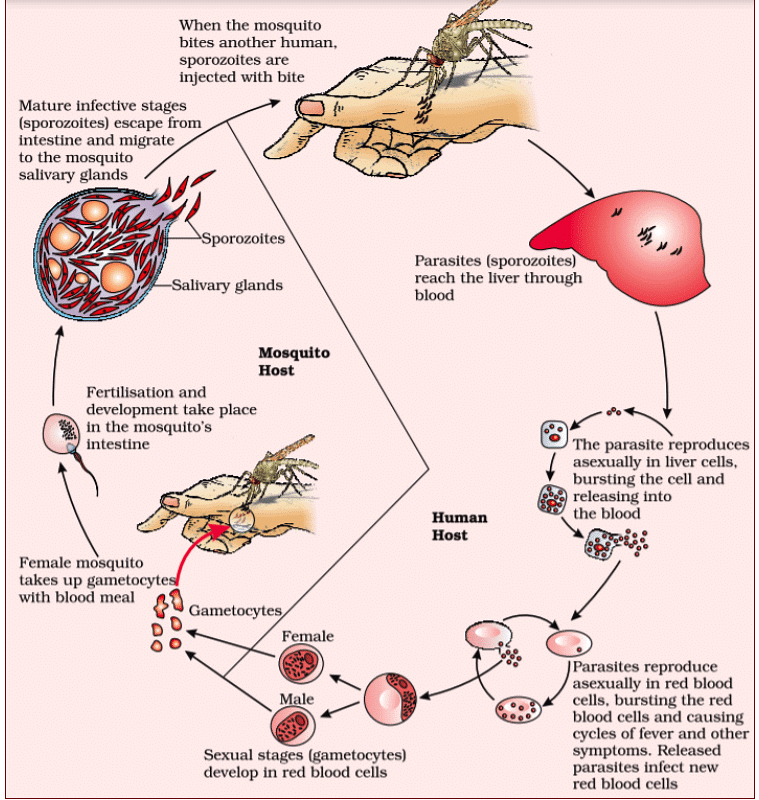 Stages of Life Cycle of Plasmodium
Stages of Life Cycle of Plasmodium
The life cycle of the malaria parasite Plasmodium involves several distinct stages mentioned below:
1. Sporozoites in Mosquito Salivary Glands
- The cycle begins when a female Anopheles mosquito infected with Plasmodium bites a human to obtain a blood meal.
- Plasmodium sporozoites, which are the infectious form of the parasite, are injected into the human host's bloodstream.
2. Liver Stage (Exoerythrocytic Stage)
- Sporozoites travel to the liver and invade liver cells (hepatocytes).
- Inside the liver cells, sporozoites multiply and develop into a different form known as merozoites.
3. Merozoite Release and Invasion of Red Blood Cells
- Merozoites are released from the liver cells and enter the bloodstream.
- They invade red blood cells (erythrocytes).
4. Blood Stage (Erythrocytic Stage)
- Inside the red blood cells, merozoites undergo further multiplication.
- As the parasites multiply, they cause the infected red blood cells to rupture, releasing more merozoites into the bloodstream.
- This cycle of invasion, multiplication, and bursting of red blood cells leads to the characteristic symptoms of malaria, such as fever and anemia.
5. Gametocyte Formation
- Some merozoites differentiate into male and female gametocytes within the red blood cells.
6. Mosquito Infection
- When a mosquito bites an infected human, it ingests the male and female gametocytes along with blood.
- Inside the mosquito's gut, gametocytes fuse to form zygotes.
7. Oocyst Formation
- The zygotes develop into oocysts on the mosquito's gut wall.
8. Sporozoite Formation
- Within the oocysts, sporozoites are produced through multiple divisions.
9. Migration to Mosquito Salivary Glands
- The sporozoites migrate to the mosquito's salivary glands, where they are ready to be transmitted to another human when the mosquito takes a blood meal.
10. Transmission to Human Host
- When the infected mosquito bites another human, sporozoites are injected into the human's bloodstream, restarting the cycle.
Prevention of malaria
Malaria is one of the major causes of preventable death in the world today. It affects more than 500 million people worldwide and causes 1 to 2 million deaths every year. It is a tropical infectious disease and almost 90 per cent of the cases are from Sub-Saharan Africa.
There are two ways to deal with malaria – prevent the mosquito bite from happening (i.e preventative steps) or attack the parasites once they have infected the body.
The first method advocates the use of mosquito nets and mosquito repellent such as permethrin to prevent mosquitoes from biting. The second form of treatment uses a chemical called Quinine present in the bark of a cinchona tree. A form of drug chloroquine has proven very effective against malaria even though it is not a vaccine.
2. Amoebiasis
Amoebiasis is also known as amoebic dysentery. It is caused by a protozoan parasite of the human large intestine, Entamoeba histolytica. They are cosmopolitan, they live in the large intestines and produce eggs or cysts, which are passed out of the body with the stool. It results in diarrhoea and colitis.
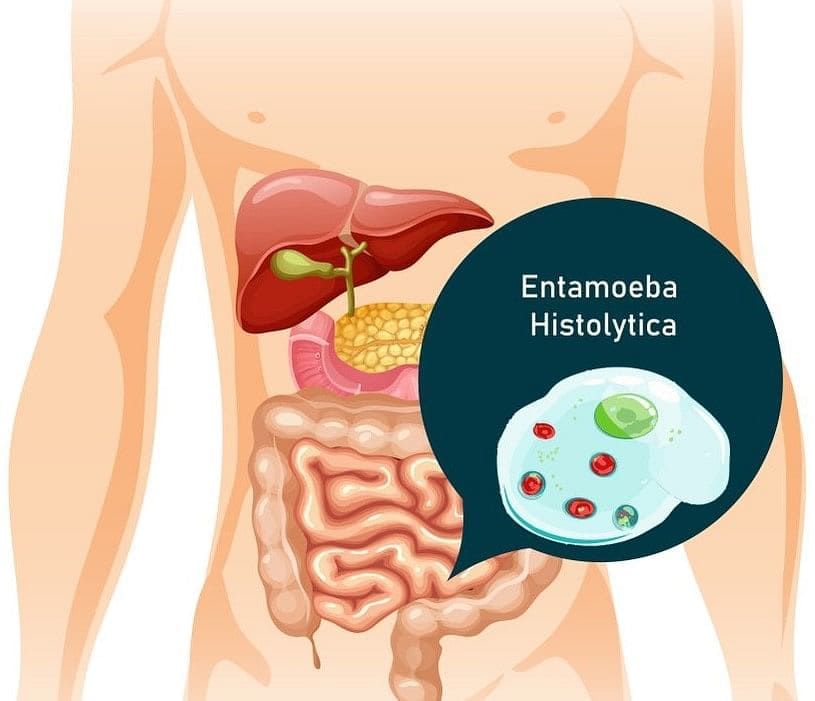 Entamoeba Histolyica in Human Gut
Entamoeba Histolyica in Human Gut
Let us have a detailed look at the symptoms and causes of amoebiasis.
Causes of Amoebiasis
Amebiasis is caused by the following ways:
- Living in areas with poor sanitary conditions.
- Ingesting water or food, contaminated by faeces of infected people.
- By swallowing cysts of the parasite. It can also occur by oral-anal sexual contact with an infected person.
Symptoms of Amoebiasis
An individual infected with E. histolytica may have mild to severe symptoms. Sometimes a person may show no symptoms of the disease.
- Fever
- Chills
- Nausea
- Weight loss
- Abdominal discomfort
- Diarrhoea that may include blood or mucus with periods of constipation
Treatment of Amoebiasis
Symptomatic amoebiasis can be treated with administration of metronidazole, followed by eliminating any organisms present in the colon by a luminal amoebicide. Asymptomatic carriers are treated by giving a luminal amebicide. This reduces the risk of transmission.
Some diseases caused by Helminths
Helminths are parasitic worms that can infect various parts of the human body. These infections are often referred to as helminthiases. Helminth infections can vary in severity, and the symptoms they cause depend on the type of worm, the location of the infection.
1. Filariasis
 Lymphatic Filariasis is also known as Elephantiasis
Lymphatic Filariasis is also known as Elephantiasis
What is Filariasis?
Filariasis a parasitic disease transmitted by black flies and mosquitoes. These parasites are thin, round, worm-like organisms. They appear white or translucent when observed under a microscope. The life span of filariae would be around 5 to 7 years. During their lifespan, they produce millions of larvae. The size of the female is between 250 and 300 μm long and the size of the males is roughly half as long as the females.
How is Filariasis Transmitted?
The causative organisms for Filariasis is a roundworm of the Filarioidea type. However, this is a vector-borne disease, with the primary vectors being mosquitoes and black flies. The infection spreads when a mosquito bites an already infected individual and then, goes on to bite a healthy person. This causes the larva of this parasite to enter the bloodstream of a healthy host and multiply. The complete stage of the larva to adult filarial worms is carried out within the lymphatic system. Once matured, the adult filarial worm starts to release larval forms called microfilariae. The newly generated microfilariae again enter into the mosquito along with the host’s blood and the cycle repeats itself. This parasitic disease is categorized on the basis of which body part is infected:
- Lymphatic filariasis: As the name suggests, this type affects the lymphatic system.
- Subcutaneous filariasis: In this case, the bottom layer of the skin and white part of the eyes are infected by the worms.
- Serous cavity filariasis: In the case of this disorder, the serous cavity of the abdomen is infected.
There are more than a hundred species of filarial worms currently discovered. Among them, only 8 to 9 are categorized as filarial parasites, which causes infections in human beings.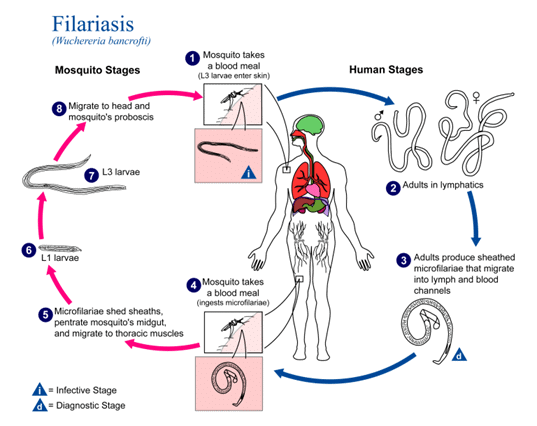 Filariasis Life Cycle: From larvae to adult
Filariasis Life Cycle: From larvae to adult
Filariasis Symptoms
The general filariasis symptoms during its early stages include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Skin lesions are observed in the beginning stage i.e., between three months to nine months after the insect bite
The filariasis symptoms seen in the later stage include:
- Blockage in the lymphatic system which leads to oedema.
- Swelling, redness, and pain in the arms and legs.
- Accumulation of pus in cells.
Treatment for Filariasis
Currently, there is no vaccine available for filariasis. Scientists are still working on developing a cure for filariasis. Prevention is better than cure. As we all know, this disease is caused by the bite of mosquitoes, it is better to prevent the cause of this disease by:
- Wearing long sleeves and pants to prevent the bite of mosquitoes
- Preventing the build-up of stagnant water
- Using mosquito mats, coils and nets if possible
- Though scientifically unproven, dark-coloured clothing attracts mosquitoes, so it might be beneficial to avoid them.
In spite of all these measures, if filariasis is contracted, the best treatment would be a course of anthelmintic drugs or antibiotics. Anthelmintic would be the best option as it directly kills the worms. But if this isn’t feasible, antibiotics are a great alternative because they target the symbiotic bacteria that are present inside the worms. When the antibiotics kill these bacteria, the worms cannot survive and thrive inside their hosts, eventually hampering reproduction.
2. Ascariasis
Helminths are parasitic worms that can infect various parts of the human body. These infections are often referred to as helminthiases. Helminth infections can vary in severity, and the symptoms they cause depend on the type of worm, the location of the infection.
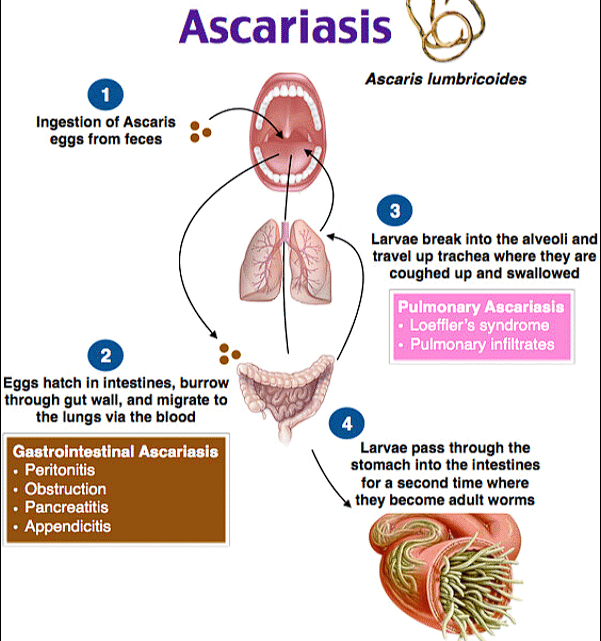 Mode of Transmission Ascariasis
Mode of Transmission Ascariasis
Causes of Ascariasis
(a) Transmission: The infection is typically transmitted when a person ingests Ascaris eggs. These eggs are passed in the feces of infected individuals and can contaminate soil, water, or food sources.
(b) Ingestion of Contaminated Substances: Ascariasis occurs when a person unknowingly ingests Ascaris eggs, often through contaminated hands, food, or water. This commonly happens in areas with poor sanitation practices.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Common Diseases in Humans - 1 - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are diseases? |  |
| 2. What are pathogens? |  |
| 3. How are pathogens classified? |  |
| 4. What are some diseases caused by protozoa? |  |
| 5. Which diseases are caused by helminths? |  |

















