Priority Queue | Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Priority Queue
A priority queue is a special type of queue in which each element is associated with a priority and is served according to its priority. If elements with the same priority occur, they are served according to their order in the queue.
Generally, the value of the element itself is considered for assigning the priority.
For example, The element with the highest value is considered as the highest priority element. However, in other cases, we can assume the element with the lowest value as the highest priority element. In other cases, we can set priorities according to our needs.Removing Highest Priority Element
Difference between Priority Queue and Normal Queue
In a queue, the first-in-first-out rule is implemented whereas, in a priority queue, the values are removed on the basis of priority. The element with the highest priority is removed first.
Implementation of Priority Queue
Priority queue can be implemented using an array, a linked list, a heap data structure, or a binary search tree. Among these data structures, heap data structure provides an efficient implementation of priority queues.
Hence, we will be using the heap data structure to implement the priority queue in this tutorial. A max-heap is implement is in the following operations. If you want to learn more about it, please visit max-heap and mean-heap.
A comparative analysis of different implementations of priority queue is given below.
Priority Queue Operations
Basic operations of a priority queue are inserting, removing, and peeking elements.
1. Inserting an Element into the Priority Queue
Inserting an element into a priority queue (max-heap) is done by the following steps.
- Insert the new element at the end of the tree.
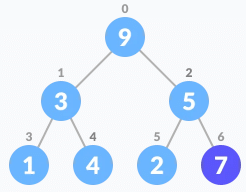 Insert an element at the end of the queue
Insert an element at the end of the queue
- Heapify the tree.
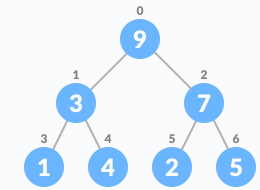
Algorithm for insertion of an element into priority queue (max-heap)
If there is no node,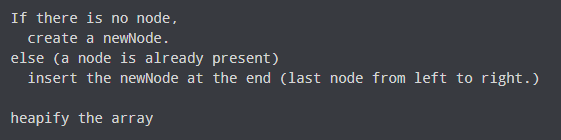
For Min Heap, the above algorithm is modified so that parent Node is always smaller than new Node.
2. Deleting an Element from the Priority Queue
Deleting an element from a priority queue (max-heap) is done as follows:
- Select the element to be deleted.
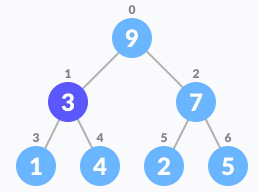 Select the element to be deleted
Select the element to be deleted
- Swap it with the last element
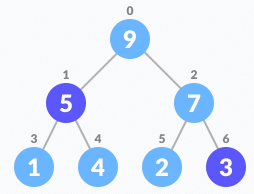 Swap with the last leaf node element
Swap with the last leaf node element
- Remove the last element.
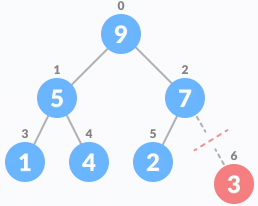 Remove the last element leaf
Remove the last element leaf
Heapify the tree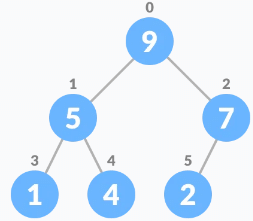
Algorithm for deletion of an element in the priority queue (max-heap)
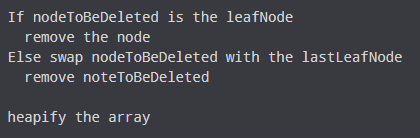
For Min Heap, the above algorithm is modified so that the both childNodes are smaller than currentNode.
3. Peeking from the Priority Queue (Find max/min)
Peek operation returns the maximum element from Max Heap or minimum element from Min Heap without deleting the node.
For both Max heap and Min Heap
4. Extract-Max/Min from the Priority Queue
Extract-Max returns the node with maximum value after removing it from a Max Heap whereas Extract-Min returns the node with minimum value after removing it from Min Heap.
Priority Queue Implementations in Python, Java, C, and C++
- Python
# Priority Queue implementation in Python
# Function to heapify the tree
def heapify(arr, n, i):
# Find the largest among root, left child and right child
largest = i
l = 2 * i + 1
r = 2 * i + 2
if l < n and arr[i] < arr[l]:
largest = l
if r < n and arr[largest] < arr[r]:
largest = r
# Swap and continue heapifying if root is not largest
if largest != i:
arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i]
heapify(arr, n, largest)
# Function to insert an element into the tree
def insert(array, newNum):
size = len(array)
if size == 0:
array.append(newNum)
else:
array.append(newNum)
for i in range((size // 2) - 1, -1, -1):
heapify(array, size, i)
# Function to delete an element from the tree
def deleteNode(array, num):
size = len(array)
i = 0
for i in range(0, size):
if num == array[i]:
break
array[i], array[size - 1] = array[size - 1], array[i]
array.remove(size - 1)
for i in range((len(array) // 2) - 1, -1, -1):
heapify(array, len(array), i)
arr = []
insert(arr, 3)
insert(arr, 4)
insert(arr, 9)
insert(arr, 5)
insert(arr, 2)
print ("Max-Heap array: " + str(arr))
deleteNode(arr, 4)
print("After deleting an element: " + str(arr)) - Java
// Priority Queue implementation in Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Heap {
// Function to heapify the tree
void heapify(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int i) {
int size = hT.size();
// Find the largest among root, left child and right child
int largest = i;
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l < size && hT.get(l) > hT.get(largest))
largest = l;
if (r < size && hT.get(r) > hT.get(largest))
largest = r;
// Swap and continue heapifying if root is not largest
if (largest != i) {
int temp = hT.get(largest);
hT.set(largest, hT.get(i));
hT.set(i, temp);
heapify(hT, largest);
}
}
// Function to insert an element into the tree
void insert(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int newNum) {
int size = hT.size();
if (size == 0) {
hT.add(newNum);
} else {
hT.add(newNum);
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(hT, i);
}
}
}
// Function to delete an element from the tree
void deleteNode(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int num) {
int size = hT.size();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (num == hT.get(i))
break;
}
int temp = hT.get(i);
hT.set(i, hT.get(size - 1));
hT.set(size - 1, temp);
hT.remove(size - 1);
for (int j = size / 2 - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
heapify(hT, j);
}
}
// Print the tree
void printArray(ArrayList<Integer> array, int size) {
for (Integer i : array) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int size = array.size();
Heap h = new Heap();
h.insert(array, 3);
h.insert(array, 4);
h.insert(array, 9);
h.insert(array, 5);
h.insert(array, 2);
System.out.println("Max-Heap array: ");
h.printArray(array, size);
h.deleteNode(array, 4);
System.out.println("After deleting an element: ");
h.printArray(array, size);
}
} - C
// Priority Queue implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
int size = 0;
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *b;
*b = *a;
*a = temp;
}
// Function to heapify the tree
void heapify(int array[], int size, int i) {
if (size == 1) {
printf("Single element in the heap");
} else {
// Find the largest among root, left child and right child
int largest = i;
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l < size && array[l] > array[largest])
largest = l;
if (r < size && array[r] > array[largest])
largest = r;
// Swap and continue heapifying if root is not largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(&array[i], &array[largest]);
heapify(array, size, largest);
}
}
}
// Function to insert an element into the tree
void insert(int array[], int newNum) {
if (size == 0) {
array[0] = newNum;
size += 1;
} else {
array[size] = newNum;
size += 1;
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(array, size, i);
}
}
}
// Function to delete an element from the tree
void deleteRoot(int array[], int num) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (num == array[i])
break;
}
swap(&array[i], &array[size - 1]);
size -= 1;
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(array, size, i);
}
}
// Print the array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
printf("%d ", array[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int array[10];
insert(array, 3);
insert(array, 4);
insert(array, 9);
insert(array, 5);
insert(array, 2);
printf("Max-Heap array: ");
printArray(array, size);
deleteRoot(array, 4);
printf("After deleting an element: ");
printArray(array, size);
} - C++
// Priority Queue implementation in C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Function to swap position of two elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *b;
*b = *a;
*a = temp;
}
// Function to heapify the tree
void heapify(vector<int> &hT, int i) {
int size = hT.size();
// Find the largest among root, left child and right child
int largest = i;
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l < size && hT[l] > hT[largest])
largest = l;
if (r < size && hT[r] > hT[largest])
largest = r;
// Swap and continue heapifying if root is not largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(&hT[i], &hT[largest]);
heapify(hT, largest);
}
}
// Function to insert an element into the tree
void insert(vector<int> &hT, int newNum) {
int size = hT.size();
if (size == 0) {
hT.push_back(newNum);
} else {
hT.push_back(newNum);
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(hT, i);
}
}
}
// Function to delete an element from the tree
void deleteNode(vector<int> &hT, int num) {
int size = hT.size();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (num == hT[i])
break;
}
swap(&hT[i], &hT[size - 1]);
hT.pop_back();
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(hT, i);
}
}
// Print the tree
void printArray(vector<int> &hT) {
for (int i = 0; i < hT.size(); ++i)
cout << hT[i] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
// Driver code
int main() {
vector<int> heapTree;
insert(heapTree, 3);
insert(heapTree, 4);
insert(heapTree, 9);
insert(heapTree, 5);
insert(heapTree, 2);
cout << "Max-Heap array: ";
printArray(heapTree);
deleteNode(heapTree, 4);
cout << "After deleting an element: ";
printArray(heapTree);
}
Priority Queue Applications
Some of the applications of a priority queue are:
- Dijkstra's algorithm
- for implementing stack
- for load balancing and interrupt handling in an operating system
- for data compression in Huffman code
|
158 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Priority Queue - Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is a priority queue? |  |
| 2. How does a priority queue differ from a regular queue? |  |
| 3. What are the main operations supported by a priority queue? |  |
| 4. How is a priority queue implemented? |  |
| 5. What are some applications of priority queues? |  |
















