Laws of Exponents for Real Numbers | Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 PDF Download
In Mathematics, there are different laws of exponents. All the rules of exponents are used to solve many mathematical problems which involve repeated multiplication processes. The laws of exponents simplify the multiplication and division operations and help to solve the problems easily. In this article, we are going to discuss the six important laws of exponents with many solved examples.
What are Exponents?
Exponents are used to show repeated multiplication of a number by itself. For example, 7 × 7 × 7 can be represented as 73. Here, the exponent is ‘3’ which stands for the number of times the number 7 is multiplied. 7 is the base here which is the actual number that is getting multiplied. So basically exponents or powers denotes the number of times a number can be multiplied. If the power is 2, that means the base number is multiplied two times with itself. Some of the examples are:
- 34 = 3×3×3×3
- 105 = 10×10×10×10×10
- 163 = 16 × 16 × 16
Suppose, a number ‘a’ is multiplied by itself n-times, then it is represented as an where a is the base and n is the exponent. 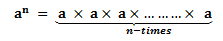
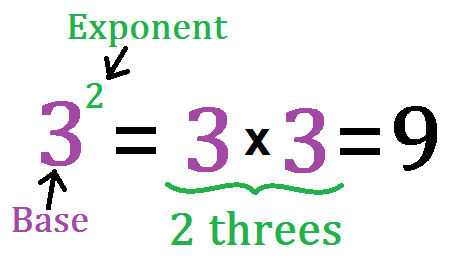 Example of Exponent
Example of Exponent
Exponents follow certain rules that help in simplifying expressions which are also called its laws. Let us discuss the laws of exponents in detail.
Rules of Exponents With Examples
As discussed earlier, there are different laws or rules defined for exponents. The important laws of exponents are given below: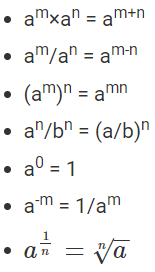
Product With the Same Bases
As per this law, for any non-zero term a,
- am×an = am+n
where m and n are real numbers.
Example 1: What is the simplification of 55 × 51 ?
Solution: 55 × 51 = 55+1 = 56
Example 2: What is the simplification of (−6)-4 × (−6)-7?
Solution: (−6)-4 × (−6)-7 = (-6)-4-7 = (-6)-11
Note: We can state that the law is applicable for negative terms also. Therefore the term m and n can be any integer.
Quotient with Same Bases
As per this rule,
- am/an = am-n
where a is a non-zero term and m and n are integers.
Example 3: Find the value when 10-5 is divided by 10-3.
Solution: As per the question;
10-5/10-3
= 10-5-(-)3
= 10-5+3
= 10-2
= 1/100
Power Raised to a Power
According to this law, if ‘a’ is the base, then the power raised to the power of base ‘a’ gives the product of the powers raised to the base ‘a’, such as;
- (am)n = amn
where a is a non-zero term and m and n are integers.
Example 4: Express 83 as a power with base 2.
Solution: We have, 2×2×2 = 8 = 23
Therefore, 83= (23)3 = 29
Product to a Power
As per this rule, for two or more different bases, if the power is same, then;
- an bn = (ab)n
where a is a non-zero term and n is the integer.
Example 5: Simplify and write the exponential form of: 1/8 x 5-3
Solution: We can write, 1/8 = 2-3
Therefore, 2-3 x 5-3 = (2 × 5)-3 = 10-3
Quotient to a Power
As per this law, the fraction of two different bases with the same power is represented as;
- an/bn = (a/b)n
where a and b are non-zero terms and n is an integer.
Example 6: Simplify the expression and find the value:153/53
Solution: We can write the given expression as;
(15/5)3= 33 = 27
Zero Power
According to this rule, when the power of any integer is zero, then its value is equal to 1, such as;
a0 = 1
where ‘a’ is any non-zero term.
Example 7: What is the value of 50 + 22 + 40 + 71 – 31 ?
Solution: 50 + 22 + 40 + 71 – 31 = 1+4+1+7-3= 10
Negative Exponent Rule
According to this rule, if the exponent is negative, we can change the exponent into positive by writing the same value in the denominator and the numerator holds the value 1.
The negative exponent rule is given as:
a-m = 1/am
Example 8: Find the value of 2-2
Solution:
Here, the exponent is a negative value (i.e., -2)
Thus, 2-2 can be written as 1/22
2-2 = 1/22
2-2 = 1/4
In other words, we can say that, if “a” is a non-zero number or non-zero rational number, we can say that a-m is the reciprocal of am.
Fractional Exponent Rule
The fractional exponent rule is used, if the exponent is in the fractional form. The fractional exponent rule is given by: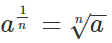
Here, a is called the base, and 1/n is the exponent, which is in the fractional form. Thus, a1/n is said to be the nth root of a.
Example 9: Simplify: 41/2
Solution:
Here, the exponent is in fractional form. (i.e., ½)
According to the fractional exponent rule, 41/2 can be written as √4
(i.e.,) 41/2 = √4
41/2 = 2 (As, the square root of 4 is 2)
Hence, the simplified form of 41/2 is 2.
|
44 videos|412 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on Laws of Exponents for Real Numbers - Mathematics (Maths) Class 9
| 1. What are the laws of exponents for real numbers? |  |
| 2. What is the product rule in the laws of exponents? |  |
| 3. How does the quotient rule work in the laws of exponents? |  |
| 4. What is the power rule in the laws of exponents? |  |
| 5. How does the zero exponent rule work in the laws of exponents? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|

















