RS Aggarwal Sol:s: Real Numbers - 1 | Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF Download
Q1. What do you mean by Euclid's division lemma?
Sol: For any two given positive integers a and b there exist unique whole numbers q and r such that
a = bq + r, when 0 ≤ r < b.
Here, we call 'a' as a dividend, b as a divisor, q as the quotient and r as the remainder.
Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder
Q2. A number when divided by 61 gives 27 as quotient and 32 as remainder. Find the number.
Sol: Using Euclid’s division Lemma
Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder
= (61 × 27) + 32
= 1647 + 32
= 1679
Required number = 1679
Q3. By what number should 1365 be divided to get 31 as the quotient and 32 as the remainder?
Sol: By Euclid's Division Algorithm, we have:
Dividend = (Divisor X Quotient) + Remainder
⇒ 1365 = (Divisor × 31) + 32
⇒ (1365 - 32) / 31 = Divisor
⇒ 1333 / 31 = Divisor
Therefore, Divisor = 43
Q4. Using Euclid's algorithm, find the HCF of:
(i) 405 and 2520
(ii) 504 and 1188
(iii) 960 and 1575
Sol:
(i) On dividing 2520 by 405, we get
- Quotient = 6, remainder = 90
- Therefore, 2520 = (405 × 6) + 90
- Dividing 405 by 90, we get
- Quotient = 4, Remainder = 45
- Therefore, 405 = 90 × 4 + 45
- Dividing 90 by 45
- Quotient = 2, remainder = 0
- Therefore, 90 = 45 × 2
- H.C.F. of 405 and 2520 is 45
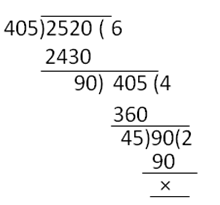
(ii) Dividing 1188 by 504, we get
- Quotient = 2, remainder = 180
- Therefore, 1188 = 504 × 2 + 180
- Dividing 504 by 180
- Quotient = 2, remainder = 144
- Therefore, 504 = 180 × 2 + 144
- Dividing 180 by 144, we get
- Quotient = 1, remainder = 36
- Dividing 144 by 36
- Quotient = 4, remainder = 0
- Therefore, H.C.F. of 1188 and 504 is 36
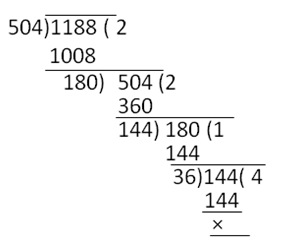
(iii) Dividing 1575 by 960, we get
- Quotient = 1, remainder = 615
- 1575 = 960 x 1 + 615
- Dividing 960 by 615, we get Quotient = 1, remainder = 345
- 960 = 615 x 1 + 345
- Dividing 615 by 345 Quotient = 1, remainder = 270
- 615 = 345 x 1 + 270
- Dividing 345 by 270, we get Quotient = 1, remainder = 75
- 345 = 270 x 1 + 75
- Dividing 270 by 75, we get Quotient = 3, remainder = 45
- 270 = 75 x 3 + 45
- Dividing 75 by 45, we get Quotient = 1, remainder = 30
- 75 = 45 x 1 + 30
- Dividing 45 by 30, we get Remainder = 15, quotient = 1
- 45 = 30 x 1 + 15
- Dividing 30 by 15, we get Quotient = 2, remainder = 0
- H.C.F. of 1575 and 960 is 15

Q5. Show that every positive integer is either even or odd.
Sol: Let a be a given positive integer.
On dividing a by 2, let q be the quotient and r be the remainder.
Then, by Eudid's algorithm, we have
a = 2q+ r, where 0 < r < 2
⇒ a = 2q + r, where r = 0,1
⇒ a = 2q or a = 2q + 1
When a = 2q for some integer q, then clearly a is even.
When a = 2q + 1 for some integer q, then dearly a is odd.
Thus, every positive integer is either even or odd.
Q6. Show that any positive odd integer is of the form (6m + 1), (6m + 3) or (6m + 5), where m is some integer.
Sol: Let a be a given positive integer.
On dividing a by 6, let q be the quotient and r be the remainder.
Then, by Eudid's algorithm, we have
a = 6q + r, where 0 < r < 6
⇒ a = 6q + r, where r = 0,1,2,3,4,5,6
⇒ a = 6q or a = 6q + 1 or a = 6q + 2 or a = 6q + 3 or a = 6q + 4 or a = 6q + 5
But, a = 6q, a = 6q + 2, a = 6q + 4 gives even values of a.
Thus, when a is odd, it is of the form
6q + 1, 6q + 3 or 6q + 5 for some integer q.
Q7. Show that any positive odd integer is of the form (4m + 1) or (4m + 3), wherein is some integer.
Sol:
Let a be a given positive odd integer.
On dividing by 4, let q be the quotient and r be the remainder.
Then, by Eudid's algorithm, we have
a = 4m + r, where 0 < r < 4
⇒ a = 4m + r, where r = 0,1,2,3
⇒ a = 4m or a = 4m + 1 or a = 4m + 2 or a = 4m + 3
But, a = 4m and a = 4m + 2 = 2(2m + 1) are clearly even.
Thus, when a is odd, it is of the form a = (4m + 1)or (4m + 3) for some integer m.
|
127 videos|584 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on RS Aggarwal Sol:s: Real Numbers - 1 - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10
| 1. What are real numbers, and how are they classified? |  |
| 2. How do you perform operations with real numbers? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the number line in understanding real numbers? |  |
| 4. What are some common properties of real numbers? |  |
| 5. How can I practice problems related to real numbers effectively? |  |






















