NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Crop Production & Management | Science Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Long Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Which one of the following conditions is not essential to grow maize?
(a) High temperature
(b) Humidity
(c) Low temperature
(d) Rainfall
Ans: c
Maize is grown in a warm and tropical climate. The optimum temperature for growing maize is between 18°c -27°c in day and 14°-15°c in the night. Hence a cold climate is not essential to grow maize.
Q.2. Propagation of ginger is generally done using
(a) Seed
(b) Stem (rhizome)
(c) Root
(d) Leaf
Ans: b
Ginger is a modified, underground stem that will propagate vegetatively by its stem. Ginger does not propagate by its root, stem or leaf.

Q.3. Which of the following statements is not true for organic manure?
(a) It enhances the water-holding capacity of the soil.
(b) It has a balance of all plant nutrients.
(c) It provides humus to the soil.
(d) It improves the texture of the soil.
Ans: b
Organic manure is obtained by the decomposition of plants and animal waste, which makes the soil nutrient-rich. However, it does not mean that organic manure provides all the nutrients in the required amount; hence, option b) is wrong.
Q.4. The term used for the process of separation of grains from the chaff is
(a) Sieving
(b) Threshing
(c) Winnowing
(d) handpicking
Ans: c
Winnowing is a process used to separate grains from the chaff by removing the scaly, inedible chaff surrounding the grain. A machine called Combine is used for this process. The combine is a mixture of harvester and thresher.
Q.5. Read the statements given below.
(i) Seeds require moisture for germination.
(ii) Plants can absorb nutrients mostly in dissolved form.
(iii) Irrigation protects crops from both frost and hot air currents.
(iv) Irrigation improves soil texture.
Choose the combination of statements that indicate the need to irrigate crops.
(a) i and ii
(b) i, ii, iii
(c) i, ii, iii, iv
(d) i and iii
Ans: a
Irrigation supplies water to the crops when required, and this will help the seed germinate by providing moisture to the seed. Plants readily absorb nutrients along with water in a dissolved form.
Q.6. Which of the following tools would a farmer use to remove weeds from the field?
(a) Hoe
(b) Plough
(c) Axe
(d) Cultivator
Ans: a
Hoe is used to remove weeds and to loosen the soil. Hoe works like a blade. An axe is used to cut the trees. Plough is used for tilling the soil. The cultivator is used for ploughing.
Q.7. Which of the following is not true for fertilizers?
(a) They increase the yield.
(b) Their excessive use disturbs the balance of nutrients in the soil.
(c) They are generally used in small quantities.
(d) They are environment-friendly.
Ans: d
Fertilizers are the chemical substance that is rich in particular nutrients. Fertilizers indeed help in yield increase. However, the long-term and excess usage of fertilizers will reduce soil fertility and pollute the water bodies. By seeing through the rain.
Q.8. Given below are statements about the harmful effects of weeds on crop plants.
(i) They interfere with harvesting.
(ii) They help crop plants to grow healthily.
(iii) They compete with crop plants for water, nutrients, space, and light.
(iv) They affect plant growth. Choose the correct combination of statements.
(a) i, iii, iv
(b) iii only
(c) iii, iv
(d) i, ii, iii, iv
Ans: a
Weeds are the unwanted plants that grow along with the grown crops. They compete for nutrients, water, and sunlight with crops, thereby affecting the health of crops and the yield.
Q.9. The process of loosening and turning of soil is called
(a) irrigation and manuring
(b) digging and winnowing
(c) tilling and ploughing
(d) harvesting and storage
Ans: c
Tilling and ploughing are the first steps in preparing the land for cultivation. Ploughing is done by using a plough, which is made of either wood or iron.
Q.10. The monsoon season in our country is during the months
(a) April to December
(b) June to September
(c) November to March
(d) January to May
Ans: b
The crops grown in this season are called kharif crops, e.g., paddy, maize, cotton, etc. The kharif crops sown in June are harvested towards the end of rainy season (October-November).
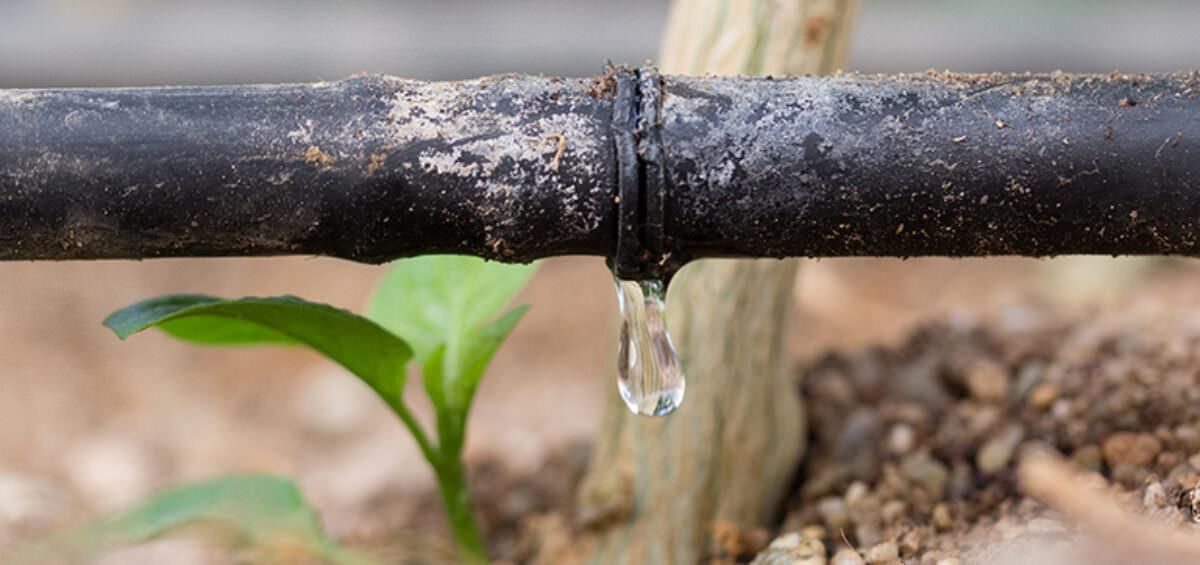
Q.11. The system of irrigation wherein water is supplied drop by drop near the roots of plants, is called
(a) pulley system
(b) drip system
(c) sprinkler system
(d) lever system
Ans: b
A drip system is a method of irrigation that conserves water and avoids wastage as water is made to fall drop by drop at the position of the roots. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, trees, and gardens.
A sprinkler system is also a modern method of irrigation that efficiently uses water in the form of sprinklers. It is useful for uneven lands, while pulley and lever systems are traditional methods of irrigation where a lot of water is wasted.

Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Pick out the odd one from the following words given in the box and give the reason for it.
Plough, Seed Drill, Hoe, Chain Pump, Sickle
Ans: The seed drill is the odd one in the above-given set of tools as it is a modern agricultural tool used to sow seeds at uniform distances and to properly cover them with soil.
The rest of the tools, i.e. plough (used for tilling), hoe (for removal of weeds and loosening of soil), chain pump (irrigation method) and sickle (tool for removing weeds) are all traditional implements used in agriculture.
Q.2. If you are given a dry piece of land for cultivation what will you do before sowing the seeds?
Ans: If the field is dry for the cultivation of crops, soil preparation is done accordingly before sowing the crops. Preparation of dry soil includes adequate watering to restore the moisture content and then tilling and ploughed to allow growth of microbes and aeration, Finally, the soil is turned and its crumbs are leveled and manures are mixed. The soil is ready for the sowing of crops in the field.
Q.3.State whether the following statements are True or False. Correct the false statements.
(i) Using good quality seed is the only criterion to get a high yield.
(ii) Growing different crops in different seasons in the same field will deplete the soil of nutrients.
(iii) All crop plants are sown as seeds in the field.
(iv) Cells of root nodules of leguminous plants fix nitrogen.
(v) Freshly harvested grains must be dried before storing.
Ans:
(i) False
To get good yield appropriate agricultural practice, nutrients water is very essential along with good quality seeds.
(ii) False
It enriches the soil. Different crops utilize different nutrients, which permits the replenishment of used nutrients. This method is also called crop rotation.
(iii) False
Some crops need transplantation. Ex: Ginger
(iv) False
Bacteria called Rhizobium present in the root nodules of leguminous plants fix nitrogen.
(iv) True
The freshly harvested grains must be dried. The moisture content in them can spoil the grains or microbial infection may occur. Drying reduces’ the moisture content in grains, thus preventing the attack of different organisms.
Q.4. During which months do farmers grow mustard in India?
Ans: During the months of October and March, the farmers grow mustard in India. Mustard is a Rabi crop that farmers start sowing at the beginning of the winter season, that is, October and November, as they need low temperatures. The mustard is harvested in the months of April and May.
Q.5. Which activity of the farmer can promote the growth of earthworms and microbes in the field?
Ans: Ploughing the soil could aid a farmer in increasing the quantity of earthworms and bacteria in his or her field. The ploughing creates space in the soil, which leads to aeration, and the loose soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes.

Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Beera wants to practice crop rotation in his field. Suggest a Rabi crop and a Kharif crop which will replenish his field with nitrogen. Which crop replenishes nitrogen and why?
Ans: The examples of Rabi crops are pea, wheat, and mustard, whereas Kharif crops are paddy, maize, and soybean. These crops are grown in different temperatures in different seasons, so the rotation of the crops is really very easy.
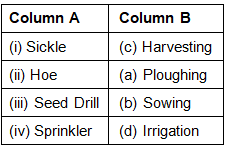
Q.2. Match the agricultural implements given in Column A with their use given in Column B.
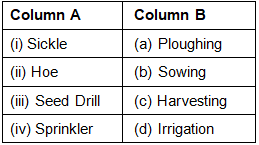
Ans:
Q.3. What are organic foods?
Ans: The crops that are cultivated without using any of the harmful chemicals, fertilizers, and pesticides and which don’t affect humans or any animals are known as organic foods. These crops can be cultivated by using traditional fertilizers.
Q.4. From the word puzzle given as Figure find at least eight words that are ‘farmer’s friends.’ Classify them into living and non-living.
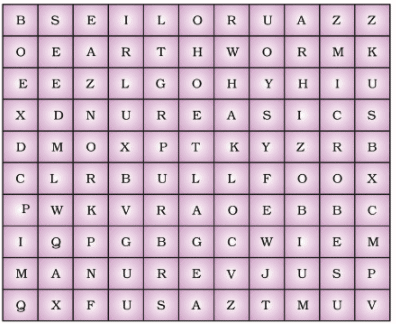
Ans:
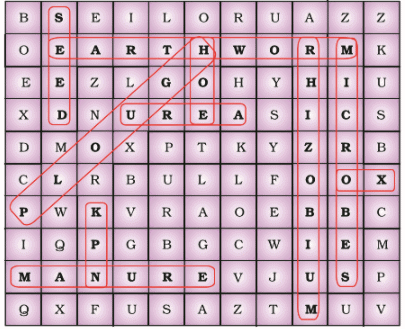
Living: Seed, Earthworm, Rhizobium, Microbes, Ox
Non-living: Plough, Urea, NPK, Manure, Hoe
Q.5. (a) Name the tool used with a tractor for sowing seeds in a field.
Ans: The Seed Drill is a tool that is used with a tractor. It's used to spread seeds at a uniform spacing. It plants the seeds in the ground and then covers them with dirt. This process is a manual process.
(b) What are the advantages of using this tool?
Ans: The advantages of seed drill are as follows
- It saves time and labor.
- After sowing, seeds are covered by soil, which will protect seeds from.
- Seeds are sown at uniform distances and depths. This avoids overcrowding of the seeds in one location.
Q.6. (a) Name the practice followed for large-scale rearing of farm animals.
(b) What facilities are provided to farm animals?
Ans: The domestication process of animals and their rearing is called animal husbandry. This process is used to increase the livestock of pigs, buffalos, horses, etc. This practice needs good care and very fine livestock management.
(b) What facilities are provided to farm animals?
Ans: The following are the facilities that are being provided to the animals-
(i) The water and food.
(ii) The appropriate shelter facilities for them.
(iii) The medical facilities for them.
(iv) The good hygienic practices.
Q.7. Classify the following crops into Kharif and Rabi crops and write in the tabular column given below: Maize, paddy, mustard, pea, gram, wheat, groundnut, and cotton.
Ans:
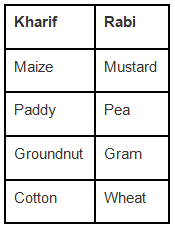
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. Despite favorable climatic conditions, a farmer’s crop failed to give a good yield. Give the possible reasons for this.
Ans: Possible reasons for failed crops despite favorable climatic conditions are
- Weeds are not removed.
- His land was not irrigated.
- A farmer might not have used quality seeds.
- The soil was not ploughed and tilled properly.
- The farmer did not use appropriate fertilizer and manure.
Q.2. Paddy is a major cereal crop in our country.
(a) In which season is paddy cultivated?
Ans: The paddy is a kharif crop and it is cultivated during the rainy season.
(b) Discuss the method of sowing.
Ans: First, the seeds of the paddy are grown in a nursery, and when they are grown up for sowing, these are taken to the field and planted. Only the healthy seed plants are planted in the field. The damaged and weak plants are useless for the sowing.
(c) What measures must be taken to prevent spoilage and insect attack of harvested grains?
Ans: The measures which are to be taken to prevent spoilage and insect attack of the harvested grains are as follows-
- Expose them to sunlight by which the moisture is removed from the freshly harvested crops.
- The dried neem leaves are applied to the crops to protect them from insects.
- Chemicals and insecticides are also applied.
- The fumigation process is applied to clear the insects.
Q.3. Unscramble the words related to crop production and its management and write in the boxes given beneath them.
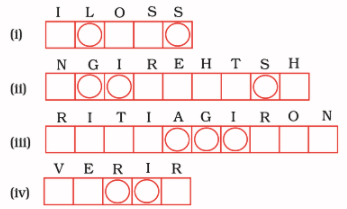
Now, using the circled letters, form one word which is an activity carried out in fields, after maturation of crops.
Ans:
i) SILOS
ii) THRESHING
iii) IRRIGATION
iv) RIVER
Q.4. Given below is a conversation between two farmers Heera and Beera.
Heera: Brother Beera, your maize crops look beautiful! They have grown pretty fast.
Beera: Yes, I have sprayed urea this time. What about you?
Heera: Well, I am still relying on good old cow dung. I am saving money on buying a tractor.
Beera: That’s good. Tractor saves a lot of time and labor.
Heera: Yes, it’s been very labor intensive for me and now these weeds have come up.
Beera: Try weedicides, they are very effective.
Now answer the following questions.
- List the practices that are not environment-friendly and why.
- What is the advantage of modern agriculture implements over traditional ones?
- Name one weedicide and the precautions farmers must take during its application.
Ans:
- The use of fertilizers, pesticides, weedicides, and other chemicals is not an eco-friendly way of cultivation as their usage will reduce the fertility of the soil and also pose a threat to human health.
- Modern agricultural practices lot of time and labor for the farmers. Modern agricultural practices impose the accuracy and efficiency of farming procedures.
- 2,4-D is a weedicide.
Farmers should take the following precautions before applying weedicide
- Cover Nose and Mouth
- Avoid excess usage of weedicide
Q.5. Terms related to the agricultural practice are given below. Rearrange them in the correct sequence.
harvesting, sowing, manuring, tilling and ploughing, irrigation, de-weeding.
Ans:
The correct sequence of agricultural practices is
i) Tilling and Ploughing
ii) Sowing
iii) Manuring
iv) Irrigation
v) Weeding
vi) Harvesting
i) Tilling and ploughing: One of the most important tasks in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen it. This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil. The process of loosening and turning the soil is called tilling or plowing.
ii) Sowing: After tilling and ploughing, healthy seeds are collected, and they are sown into considerable depth.
iii) Manuring: Plants are manured with humus, which improves the texture of the soil and replenishes nutrients in the soil
iv) Irrigation: Irrigation helps water the plants regularly, which helps keep the plants moist.
v) Weeding: Weeds are removed before they mature as they compete with crops for water, nutrients, and sunlight.
vi) Harvesting: Cutting and gathering matured crops is known as harvesting. Harvesting can be done manually or by using harvesters.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Crop Production & Management - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the main methods of crop production? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of crop rotation? |  |
| 3. How do irrigation methods affect crop production? |  |
| 4. What are the common pests and diseases affecting crops? |  |
| 5. What role does soil play in crop production? |  |





















