NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Soil | Science Olympiad Class 7 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. The microorganisms present in the soil require moisture (water) and nutrients for growth and survival. Choose from the options below the habitat (place) where the soil has plenty of water and nutrients.
(a) Desert
(b) Forest
(c) Open field
(d) Cricket ground
Ans: b
Explanation:
In forests, there will be a lot of trees which hold the soil and prevents soil from erosion. Humus makes the soil fertile and provides nutrients to plants and microorganisms. Trees also absorb a lot of water from rainwater which keep the soil moist which provides moisture for the growth of microorganisms.
Q.2. Availability of water and minerals in the soil for maximum absorption by roots is in the –
(a) B-horizon
(b) C-horizon
(c) A-horizon
(d) surface of soil
Ans: c
Explanation:
A Horizon has the topsoil which is porous and soft which help in absorption and retaining water.
Q.3. Soil conservation measures are mainly aimed at protecting which of the following?
(a) Plants
(b) Topsoil
(c) Subsoil
(d) Soil organisms
Ans: b
Explanation:
Topsoil is rich in humus and consists of decaying remains of plants and animals. Humus improves the texture of the soil and provides nutrients for plant growth. So, it is the most fertile region and soil conservation measures are mainly aimed at protecting topsoil. If topsoil is protected or conserved then subsoil is also conserved as it lies below the topsoil.
Q.4. Read the following statements with reference to the soil.
- Weathering is a very fast process of soil formation.
- Percolation of water is faster in sandy soils.
- Loamy soil contains only sand and clay.
- Topsoil contains the maximum amount of humus.
Choose the correct statements from the above.
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Ans: a
Explanation:
Soil formation by the withering of rock is a slow process that takes years. Hence option a) is wrong. Loamy soil is a mixture of sand, silt and humus hence option c is wrong.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.5. The soil has particles of different sizes. Arrange the words given below in increasing order of their particle size.
Rock, Clay, Sand, Gravel, silt
Ans: Rock > Gravel > Sand > Silt > Clay
Q.6. The components of loamy soil are ______, ______ and ______.
Ans: Sand, Silt, Clay
Q.7. Read the following statements and give the appropriate terms for each of them.
(a) The process of breakdown of rocks by the action of wind, water, sunlight.
(b) Removal of topsoil during heavy rains or strong winds.
(c) Accumulation of wastes in the soil generated by human activity which alter the features of the soil.
(d) The process of movement of water into deeper layers of soil.
Ans:
(a) Weathering
(b) Erosion
(c) Soil pollution
(d) Percolation
Q.8. Unscramble the following jumbled words related to soil.

Ans:
(a) Humus
(b) Soil Profile
(c) Horizon
(d) Loam
(e) Weathering
(f) Percolation
Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Which of the following situations – ‘A’ or ‘B’ – is advantageous for the absorption of water and minerals? Why?
Situation ‘A’: Growth and branching of roots in the C-horizon.
Situation ‘B’: Growth and branching of roots in A and B horizons.
Ans:
Situation ‘B’ is advantageous to plants because horizon A- and B are rich in water, minerals and humus.
Q.2. How can a farmer convert acidic soil to neutral soil?
Ans: A farmer can convert acidic soil to neutral soil by adding a small quantity of quick lime or slaked lime solution to the soil.
Q.3. Is it a good practice to remove grass and small plants that are growing in an open, unused field? Give a reason to support your answer.
Ans: No, It is not a good practice because plants cover the soil surface and their roots bind the soil particles to hold them firmly. This prevents washout of the top layer of soil from strong winds and rains.
Q.4. A man digging a pit found that he could dig with ease initially but digging became difficult as he went deeper. He could not dig beyond a depth of 5 feet. Provide a suitable scientific explanation.
Ans: The top layer of soil is loose and easy to dig, as we down deep soil consists of weathered rocks or which makes digging difficult.
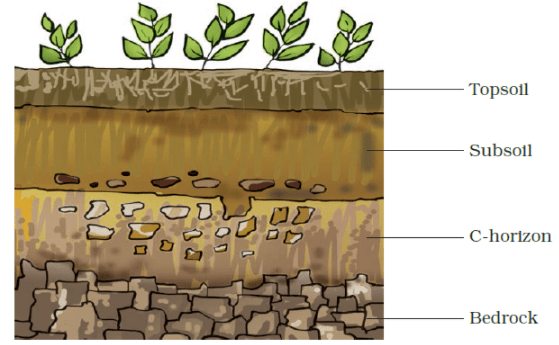
Q.4. Locate the following zones given as boxed items in Figure 9.1 which shows a diagram of the soil profile.
Top Soil, Subsoil, C-horizon, Bedrock

Ans:
Q.5. Rajasthan is a desert state in India. Once while travelling to Rajasthan by train, Boojho observed several streams and rivulets of rainwater during the journey but to his surprise, he did not see streams of water in the desert region even during rains. Help Boojho find a suitable explanation for this.
Ans: Deserts are filled with stretches of sand. When rain falls rainwater percolates immediately. Hence water streams are not found in deserts.
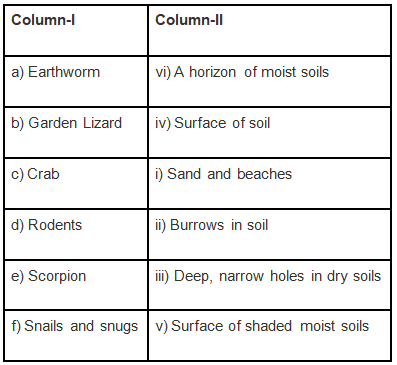
Q.6. Match the animals in Column I with their natural place of dwelling (habitat) in Column II.
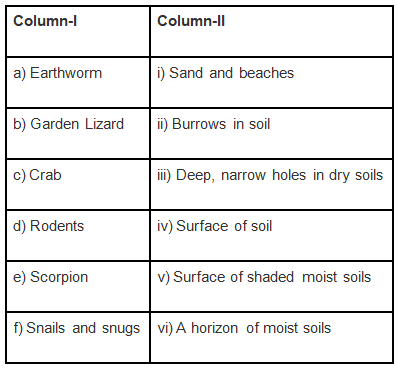
Ans:
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. Continuously water-logged soils are disadvantageous for plant growth. Why
Ans: Roots possess living cells that require oxygen for respiration and production of energy. These living cells absorb oxygen that is present in the spaces between soil particles. But in waterlogged soils, water occupies the spaces between soil particles and pushes the oxygen out into the atmosphere. Thus, roots are deprived of oxygen and this affects root and plant growth.
Q.2. Why is soil erosion relatively less in dense forests as compared to barren, open fields?
Ans: In dense forests, the tree cover (canopy) prevents rainwater from directly falling on the ground/soil. Also, roots of the vegetation bind the soil particles and hold them together. As a result soil erosion is minimised.
But in barren, open fields the soil is exposed to the falling rain. The soil particles become loose due to the impact of raindrops and the flow of water carries them away. The flowing water further erodes the soil surface aggravating erosion.
Q.3. Gardeners gently dig up the soil around the roots of garden herbs (plants) frequently. Give reasons.
Ans: Gardeners gently dig up the soil around the roots of garden herbs for the following reasons
- For enabling easy root growth;
- For easier percolation of water;
- (c) For aerating the soil/enabling air to get into deeper layers of soil;
- (d) For removing the weeds.
Q.4. In towns and cities, generally, the bore wells have to be dug very deep to get water as compared to bore wells dug in villages. Give suitable reasons.
Ans: In towns and cities, generally, the bore wells have to be dug very deep to get water as compared to bore wells dug in villages. It is so because of the following reasons :
- Excessive use of water in towns and cities depletes the groundwater.
- Towns and cities have asphalted roads and vast areas of soil are concreted. As a result, rainwater cannot percolate to recharge groundwater and the groundwater level further decreases. Villages have larger areas of the open soil surface and fewer asphalted roads and concrete surfaces. Thus, larger soil surface area is available for rainwater to percolate into the soil easily and recharge the groundwater. As a result, even shallow bore wells yield water in the village.
Q.5. Several terms related to soil are hidden in the squares given as Figure Spot them and make a list. Two examples are given to you.
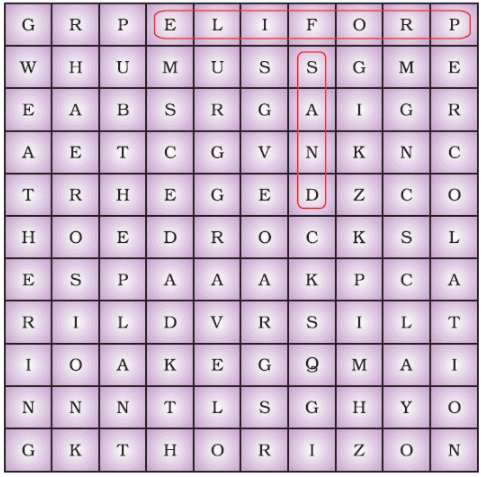
Ans:
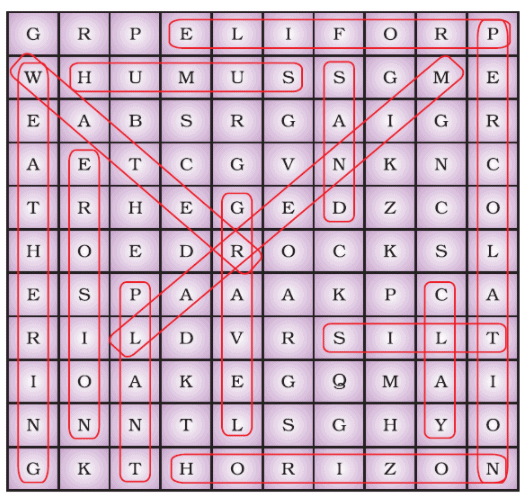
|
34 videos|88 docs|54 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Soil - Science Olympiad Class 7
| 1. What is the importance of soil in agriculture? |  |
| 2. How is soil formed? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of soil? |  |
| 4. How can soil erosion be prevented? |  |
| 5. How does soil pH affect plant growth? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|

















