NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Mensuration | Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 PDF Download
In questions 1 to 28, there are four options out of which one is correct. Write the correct answer.
Q.1. A cube of side 5 cm is painted on all its faces. If it is sliced into 1 cubic centimetre cubes, how many 1 cubic centimetre cubes will have exactly one of the
(a) 27
(b) 42
(c) 54
(d) 142
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
Given: The cube side = 5 cm
The side of cube 5cm is cut into 5 equal parts, in which each of 1 cm
Therefore, the total number of cubes of side 1 cm = 25 + 25 + 25 + 25 + 25 = 125
In one face of cube, there are total of 9 small cubes painted.
We know that, there are 6 faces in cube.
Thus, total of 9 x 6 faces will have one face painted.
(i.e.) 54
Q.2. A cube of side 4 cm is cut into 1 cm cubes. What is the ratio of the surface areas of the original cubes and cut-out cubes?
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 1 : 3
(c) 1 : 4
(d) 1 : 6
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
Given: The cube side is 4cm
The side of cube 4cm is cut into small cubes, in which each of 1 cm
Therefore, the total number of cubes = 4 x 16 = 64 cubes
Thus, the number of cut-out cubes = 64/1
Now, the surface area of the cut-out cubes = c x 1 cm2
The surface area of the original cube = 6 x 42
Hence, the required ratio obtained is:
= 6 x 42 / = 64 x 6
= 1: 4
Q.3. A circle of maximum possible size is cut from a square sheet of board. Subsequently, a square of maximum possible size is cut from the resultant circle. What will be the area of the final square?
(a) 3/4 of the original square.
(b) 1/2 of the original square.
(c) 1/4 of the original square.
(d) 2/3 of the original square.
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
Let “a” be the side of the square sheet
Thus, the area of the bigger square sheet = a2 …. (1)
Now, the circle of maximum possible size from it is given as:
The radius of the circle = a/2 … (2)
Then the diameter = a
We know that, any square in the circle of maximum size should have the length of the diagonal which is equal to the diameter of the circle.
It means that, the diagonal of a square formed inside a circle is “a”
Hence, the square side = a / √2
Thus, the area of square = a2 / 2
By equating the equations (1) and (2), we will get:
Area of the resultant square is ½ of the original square.
Q.4. What is the area of the largest triangle that can be fitted into a rectangle of length l units and width w units?
(a) lw /2
(b) lw /3
(c) lw/6
(d) lw/4
Ans: (a)
Explanation:
We know that, the area of a triangle is (1/2) x base x height
Let ABCD be a triangle with length “l” and width “w”.
Here, we have to construct a triangle of maximum area inside the rectangle in all possible ways.
Now, the maximum base length is “l”
Maximum height is “w”.
Therefore, the area of a largest triangle is (1/2) x l x w.
Q.5. If the height of a cylinder becomes 1/4 of the original height and the radius is doubled, then which of the following will be true?
(a) Volume of the cylinder will be doubled.
(b) Volume of the cylinder will remain unchanged.
(c) Volume of the cylinder will be halved.
(d) Volume of the cylinder will be1/4 of the original volume
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
We know that, the volume of a cylinder is π × r2 × h
We know that, base radius and height of the cylinder is “r” and “h” respectively.
Now, height “h” becomes (1/4)h and “r” becomes “2r”, then the volume of the cylinder is
(V) = π × 4r2 × (1/4) h = πr2h = v
Therefore, the volume of new cylinder = the volume of original cylinder.
Q.6. If the height of a cylinder becomes1/4 of the original height and the radius is doubled, then which of the following will be true?
(a) Curved surface area of the cylinder will be doubled.
(b) Curved surface area of the cylinder will remain unchanged.
(c) Curved surface area of the cylinder will be halved.
(d) Curved surface area will be 1/4 of the original curved surface.
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
We know that the curved surface area of a cylinder with radius “r” and height “h” is given as
The curved surface area of a cylinder = 2πrh … (1)
Now, the new curved surface area of cylinder with radius 2r and height (1/4)h, then the new curved surface area is
= 2π(2r)(1/4)h
= πrh
Now, multiply an divide the new curved surface area by 2, we will get
= (1/2) (2) πrh …. (2)
Now, by comparing (1) and (2), we get:
The new curved surface area of a cylinder is (1/2) times of the original curved surface area of a cylinder.
Q.7. If the height of a cylinder becomes 1/4 of the original height and the radius is doubled, then which of the following will be true?
(a) Total surface area of the cylinder will be doubled.
(b) Total surface area of the cylinder will remain unchanged.
(c) Total surface of the cylinder will be halved.
(d) None of the above.
Ans: (d)
Explanation:
We know that, the total surface area of a cylinder is 2π r(h + r), when the radius is “r” and height is “h”.
If the radius is 2r and the height is (1/4)h, then the total surface area becomes,
= 2π (2r) ((1/4)h + 2r)
= 4 πr [(h+8r)/4]
= πr (h+8r)
Q.8. The surface area of the three coterminous faces of a cuboid are 6, 15 and 10 cm2 respectively. The volume of the cuboid is
(a) 30 cm3 (b) 40 cm3 (c) 20 cm3 (d) 35 cm3
Ans: (a)
Explanation:
It is given that, the coterminous faces of a cuboid is given as:
l × b = 6
l × h = 15
b × h = 10
The formula for volume of a cuboid is l × b × h
l2 × b2 × h2 = 6 × 15 × 10
√ (lbh) = √ (900) = 30
Q.9. A regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle of radius r. The perimeter of the regular hexagon is
(a) 3r
(b) 6r
(c) 9r
(d) 12r
Ans: (b)
Explanation: We know that a hexagon contains six equilateral triangles, where one of the vertices of each equilateral triangles meet at the centre of the hexagon.
The radius of the smallest which is inscribing the hexagon is equal to the sides of the equilateral triangle.
Therefore, the perimeter of a regular hexagon is 6r, as each side of the hexagon is equal to the radius of the hexagon.
Q.10. The dimensions of a godown are 40 m, 25 m and 10 m. If it is filled with cuboidal boxes each of dimensions 2 m × 1.25 m × 1 m, then the number of boxes will be
(a) 1800
(b) 2000
(c) 4000
(d) 8000
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Given that, the dimensions of the godown are 40 m, 25 m and 10 m
Volume = 40 m × 25 m × 10 m = 10000 m3
Given that, volume of each cuboidal box is 2 m × 1.25 m × 1 m = 2.5 m3
Hence, the total number of boxes to be filled in the godown is
= 10000/2.5 = 4000
Q.11. The volume of a cube is 64 cm3. Its surface area is
(a) 16 cm2
(b) 64 cm2
(c) 96 cm2
(d) 128 cm2
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
Let “a” be the side of the cube
Given that, the volume of cube is 64 cm3
It means that a3 = 64 cm3
Hence, a = 4 cm
Therefore, the surface area of a cube = 6 x 42 = 6 x 16 = 96
Q.12. If the radius of a cylinder is tripled but its curved surface area is unchanged, then its height will be
(a) tripled
(b) constant
(c) one sixth
(d) one third
Ans: (d)
Explanation:
We know that the curved surface area of a cylinder is 2πrh, when the radius is “r” and height is “h”.
Let “H” be the new height.
When the radius of a cylinder is tripled, then the CSA of a cylinder becomes,
CSA = 2π (3r) H
CSA = 6πr. H
Now, compare the CSA of the cylinder to find the height
6πrH = 2πrh
H = 2πrh / 6πr
H = (1/3)h
Hence, the new height of the cylinder is one-third of the original height.
Q.13. How many small cubes with edge of 20 cm each can be just accommodated in a cubical box of 2 m edge?
(a) 10
(b) 100
(c) 1000
(d) 10000
Ans: (c)
Explanation: We know that, the volume of cube is (side)3
Therefore, the volume of each small cube is (20)3
= 8000 cm3
When it is converted into m3, we get
V = 0.008 m3
It is given that, the volume of the cuboidal box is 23 = 8 m3
Now, the number of small cubes that can be accommodated in the cuboidal box is
= 8/ 0.008 = 1000
Q.14. The volume of a cylinder whose radius r is equal to its height is
(a) 1/4 πr3
(b) πr3/32
(c) πr3
(d) πr3/8
Solution: (c)
Explanation:
The volume of cylinder = πr2 h
Given that r = h
Then, the volume of cylinder = πr2 (r)
V = πr3
Q.15. The volume of a cube whose edge is 3x is
(a) 27x3
(b) 9x3
(c) 6x3
(d) 3x3
Ans: (a)
Explanation:
The volume of a cube is (side)3
V = (3x)3
V = 27x3
Q.16. The figure ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB = CD and BC = AD. Its area is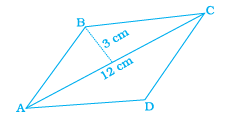
(a) 72 cm2
(b) 36 cm2
(c) 24 cm2
(d) 18 cm2
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
From the given figure, it is clear that, a quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram. Here, the diagonal AC divides the parallelogram into two equal triangles.
Hence, the area of a triangle ABC = (1/2) bh
Here, b = 12 and h = 3
= (1/2) (12)(3)
= 18
Therefore, the area of a parallelogram ABCD = 2 (18) = 36 cm2
Q.17. What is the area of the rhombus ABCD below if AC = 6 cm, and BE = 4cm?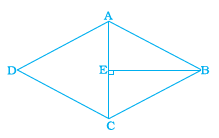
(a) 36 cm2
(b) 16 cm2
(c) 24 cm2
(d) 13 cm2
Ans: (c)
Explanation: From the given figure, the diagonal AC divides the rhombus into two triangles of equal area.
Therefore, the area of a triangle ABC = (1/2) bh
= (1/2) (4) (6)
=12 cm2
Therefore, the area of a rhombus ABCD = 2(12) = 24
Q.18. The area of a parallelogram is 60 cm2 and one of its altitude is 5 cm. The length of its corresponding side is
(a) 12 cm (b) 6 cm (c) 4 cm (d) 2 cm
Ans: (a)
Explanation:
The area of a parallelogram = base x altitude
b. h = A
b (5) = 60
b = 60/5
b = 12cm
Q.19. The perimeter of a trapezium is 52 cm and its each non-parallel side is equal to 10 cm with its height 8 cm. Its area is
(a) 124 cm2
(b) 118 cm2
(c) 128 cm2
(d) 112 cm2
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
Given:
The perimeter of a trapezium = 52 cm
The sum of its parallel sides = 52 – (10+10) = 32 cm
We know that, the area of a trapezium = (1/2) (a+b) h
A = (1/2) (32) (8)
A = 128 cm2
Q.20. Area of a quadrilateral ABCD is 20 cm2 and perpendiculars on BD from opposite vertices are 1 cm and 1.5 cm. The length of BD is
(a) 4 cm
(b) 15 cm
(c) 16 cm
(d) 18 cm
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
Given that, the area of a quadrilateral = 20 cm2
We know that, the area of a quadrilateral = (1/2) (diagonal) (sum of the altitudes)
20 = (1/2) (1+1.5) BD
20 = (1/2) (2.5) BD
20×2 = 2.5 BD
40 = 2.5 BD
BD = 16 cm
Q.21. A metal sheet 27 cm long, 8 cm broad and 1 cm thick is melted into a cube. The side of the cube is
(a) 6 cm
(b) 8 cm
(c) 12 cm
(d) 24 cm
Ans: (a)
Explanation:
Given that, the metal sheet dimension is 27 cm long, 8 cm broad and 1 cm thick.
Thus, the volume of the sheet = (27)(8)(1) = 216 cm3
It is given that, the metal sheet is melted to make a cube
Let the edge be “a”
Hence, a3 = 216 cm3
a = 6 cm
Q.22. Three cubes of metal whose edges are 6 cm, 8 cm and 10 cm respectively are melted to form a single cube. The edge of the new cube is
(a) 12 cm
(b) 24 cm
(c) 18 cm
(d) 20 cm
Ans: (a)
Explanation:
Given that, the sum of the volume of the three metal cubes = 63 + 83 +103
V = 216+ 512+ 1000
V = 1728 cm3
Let the side of the new cube be “a”
Therefore, the volume of the new cube = sum of the volume of the three cubes
a3 = 1728
Hence, a = 12 cm
Q.23. A covered wooden box has the inner measures as 115 cm, 75 cm and 35 cm and thickness of wood as 2.5 cm. The volume of the wood is
(a) 85,000 cm3
(b) 80,000 cm3
(c) 82,125 cm3
(d) 84,000 cm3
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
The thickness of the wooden box is 2.5 cm
Then the outer measure of the wooden box be 115+5, 75+5, 35+5
Thus, the outer volume be = (120)(80)(40)
Outer volume = 384000 cm3
Given that, the inner volume = (115)(80)(40)
Inner volume = 301875 cm3
Hence, the volume of a wood = Outer volume – Inner volume
V = 384000 – 301875 cm3
V= 82125 cm3
Q.24. The ratio of radii of two cylinders is 1: 2 and heights are in the ratio 2:3. The ratio of their volumes is
(a) 1:6 (b) 1:9 (c) 1:3 (d) 2:9
Solution: The correct answer is option (a) 1:6
Explanation:
Assume that r and R be the radii of the two cylinders and h and H be the height of the two cylinders
It is given that r/R = ½ and h/H = 2/3
We know that the volume of a cylinder = πr2 h
Now, v/V = πr2 h / πR2 H
v/ V = (r/R)2 (h/H)
v/V = (1/2)2 (2/3)
v/V = (1/4) (2/3) = 1/6
Therefore, the ratio of their volume is 1/6
Q.25. Two cubes have volumes in the ratio 1:64. The ratio of the area of a face of first cube to that of the other is
(a) 1:4
(b) 1:8
(c) 1:16
(d) 1:32
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
Let a and b be two cubes
It is given that, a3/b3 = 1/64
Then a/b = 1/4
Thus, the ratio of the areas are:
(a/b)2 = (1/4)2 = 1/16
Q.26. The surface areas of the six faces of a rectangular solid are 16, 16, 32, 32, 72 and 72 square centimetres. The volume of the solid, in cubic centimetres, is
(a) 192
(b) 384
(c) 480
(d) 2592
Ans: (a)
Explanation:
It is given that, the solid has a rectangular faces, hence,
lb=16 …(1)
bh = 32 ….(2)
lh = 72 …(3)
Multiply the equations (1), (2), (3), we will get
(l)2(b) 2 (h) 2 = (16)(32)(72) = 36864
lbh = 192
Therefore, the volume of a solid is 192 cubic centimetre.
Q.27. Ramesh has three containers.
(a) Cylindrical container A having radius r and height h,
(b) Cylindrical container B having radius 2r and height 1/2 h, and
(c) Cuboidal container C having dimensions r × r × h
The arrangement of the containers in the increasing order of their volumes is
(a) A, B, C
(b) B, C, A
(c) C, A, B
(d) cannot be arranged
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
(i) If the cylinder have radius r and height h, then the volume will be πr2h
(ii) If the cylinder have radius 2r and height (1/2)h, then the volume will be 2πr2h
(ii) The volume of the cuboidal container with dimensions is r2 h
Then, the arrangement of the containers in the increasing order of their volumes is C, A, B
Q.28. If R is the radius of the base of the hat, then the total outer surface area of the hat is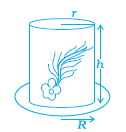 (a) πr (2h + R)
(a) πr (2h + R)
(b) 2πr (h + R)
(c) 2 πrh + πR2 (d) None of these
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
The total surface area of a hat = CSA + TSA + Base Surface Area
= 2πrh + πr2 + π (R2-r2)
= 2πrh + πR2
In questions 29 to 52, fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
Q.29. A cube of side 4 cm is painted on all its sides. If it is sliced in 1 cubic cm cubes, then number of such cubes that will have exactly two of their faces painted is __________.
Ans: 24
Explanation: Given that, the cube side is 4 cm, then the volume of cube is 43 = 64 cm3
When it is sliced into 1 cubic cm, we will get 64 small cubes
In each side of the larger cube, the smaller cubes in the edges should have more than one face painted. Therefore, the cube which are located at the corner of the larger cube, have three faces painted.
Hence, in each edge two small cubes are left, in which two faces painted.
It is known that the total numbers of edges in a cubes = 12.
Thus, the number of small cubes with two faces painted = 12 × 2 = 24 small cubes.
Q.30. A cube of side 5 cm is cut into 1 cm cubes. The percentage increase in volume after such cutting is __________.
Ans: No change
Explanation:
Volume of cube = 53 = 125
Now, when the cube is cut into 1 cubic cm, we will get 125 small cubes
Therefore, the volume of the big cube = volume of 125 cm with 1 cubic cm.
It means that, there is no change in the volume.
Q.31. The surface area of a cuboid formed by joining two cubes of side a face to face is __________.
Ans: 10a2
Explanation:
Let “a” be the side of two cubes.
When the two cubes are joined face to face, the figure obtained should be a cuboid having the same breadth and height. As the combined cube has a length twice of the length of a cube.
It means that l = 2a, b = a and h = a
Hence, the total surface area of cuboid = 2(lb + bh + hl)
= 2(2a × a + a × a + a × 2a)
Simplify the above expression, we get
= 2[2a2 + a2 + 2a2]
= 10a2
Q.32. If the diagonals of a rhombus get doubled, then the area of the rhombus becomes __________ its original area.
Ans: 4 times
Explanation:
Let p and q be the two diagonals of the rhombus
We know that area of a rhombus = pq/2
If the diagonals are doubled, we will get
A= (4p)(4q)/2
Take 4 outside, we will get
A = 4(pq/2)
Q.33. If a cube fits exactly in a cylinder with height h, then the volume of the cube is __________ and surface area of the cube is __________.
Ans: volume is h3 and surface area is 6h2
Explanation:
Each side of a cube = h
Thus, volume of cube = h3
Surface area of a cube = 6 (h2)
Q.34. The volume of a cylinder becomes __________ the original volume if its radius becomes half of the original radius.
Solution: ¼ times
Explanation:
Volume of cylinder = πr2h (when radius is r and height is “h”)
When the radius is halved, then it becomes
V = π (r/2)2h
V = ¼ (πr2h)
Q.35. The curved surface area of a cylinder is reduced by ____________ per cent if the height is half of the original height.
Ans: 50%
Explanation:
The CSA of cylinder with radius “r” and height “h” is 2πrh
When the height is halved, then new CSA is 2πr (h/2) = πrh
Hence, the percentage reduction in CSA = [(2πrh – πrh) (100)]/ 2πrh = 50%
Q.36. The volume of a cylinder which exactly fits in a cube of side a is
__________.
Ans: πa3 /4
Explanation:
When the cylinder exactly fits in the cube of side “a”, the height equals to the edges of the cube and the radius equal to half the edges of a cube.
It means that,
h = a, and r = a/2
Then the volume of a cylinder be = πr2h
= π(a/2)2(a)
= πa3/4
Q.37. The surface area of a cylinder which exactly fits in a cube of side b is
__________.
Ans: πb2
Explanation: When the cylinder exactly fits in the cube of side “b”, the height equals to the edges of the cube and the radius equal to half the edges of a cube.
It means that,
h = b, and r = b/2
Then the CSA of a cylinder be = 2πrh
= 2π (b/2)(b)
= πb2
38. If the diagonal d of a quadrilateral is doubled and the heights h1 and h2 falling on d are halved, then the area of quadrilateral is __________.
Ans: ½ (h1 +h2) d
Explanation:
Assume that ABCD be a quadrilateral, h1 and h2 are the heights on the diagonal BD = d, then, the area of a quadrilateral be
= (1/2)(h1 +h2) BD
Since the diagonal is doubled and the heights are halved, we will get
= (1/2) [ (h1/2) +(h2/2) ] 2d
= ½ (h1 +h2) d
Q.39. The perimeter of a rectangle becomes __________ times its original perimeter, if its length and breadth are doubled.
Ans: Two times
Explanation:
We know that the perimeter of a rectangle is 2(l + b)
When the length and breadth of the perimeter are doubled, we will get
P = 2(2l +2b)
Now take 2 outside,
P = 2 [2(l+b)]
Q.40. A trapezium with 3 equal sides and one side double the equal side can be divided into __________ equilateral triangles of _______ area.
Ans: 3, equal areas
Explanation: By using SSS congruency rule of triangle, we can show that a trapezium can be divided into three equilateral triangle with equal areas.
Q.41. All six faces of a cuboid are __________ in shape and of ______ area.
Ans: Rectangular shape, different
Explanation: It is known that, a cuboid is made up of 6 rectangular face which different lengths and breadths. Hence, it has different area.
Q.42. Opposite faces of a cuboid are _________ in area.
Ans: Equal
Explanation: A cuboid is made up of 6 rectangular faces, but the opposite sides have equal length and breadth. Hence, the opposite areas are equal.
Q.43. Curved surface area of a cylinder of radius h and height r is _______.
Ans: 2πrh
Explanation:
The CSA of a cylinder with radius “r” and height “h” is
CSA = 2π(r)(h)
Q.44. Total surface area of a cylinder of radius h and height r is _________
Ans: 2πh(r + h)
Explanation:
Given radius = h and height = r
TSA of cylinder = CSA of cylinder + Area of top surface + Base area
TSA = 2πrh + πh2 + πh2 = 2πh(r + h)
Q.45. Volume of a cylinder with radius h and height r is __________.
Solution: πh2r cubic units
Q.46. Area of a rhombus =1/2 product of _________.
Ans: Diagonals
Explanation:
We know that the area of a rhombus = pq/2
Where p and q are diagonals.
Q.47. Two cylinders A and B are formed by folding a rectangular sheet of dimensions 20 cm × 10 cm along its length and also along its breadth respectively. Then volume of A is ________ of volume of B.
Ans: Twice
Explanation:
Rectangular sheet dimension is 20 cm × 10 cm
When a cylinder is folded along its length, which is 20 cm, then the resultant cylinder is with height 10 cm.
Again, if a cylinder is folded along its breadth, which is 10 cm, then the resultant cylinder is with height 20 cm
When the above conditions are applied in the volume of cylinder formula,
Then we get v = 2V
Q.48. In the above question, curved surface area of A is ________ curved surface area of B.
Ans: Same
Explanation:
For cylinder A, h= 10 cm and r = 10/π
Thus, CSA of cylinder A = 2πrh = 200
For cylinder B, h= 12 cm and r = 5/π
Thus, CSA of cylinder B = 2πrh = 200
Q.49. __________ of a solid is the measurement of the space occupied by it.
Ans: Volume
Explanation: The space occupied by any solids or three dimensional shaped are always measured in terms of volume.
Q.50. __________ surface area of room = area of 4 walls.
Ans: Lateral
Explanation: We know that, the rooms are in the cuboid shape. The walls are considered as the lateral faces of the cuboid shaped room.
- Perimeter-Length of the boundary of a simple closed figure
- Area-Lateral Surface area and Total surface area
- Volumes-Amount of space occupied by a solid
- Different types of shapes and solids such as rectangle, square, triangle, parallelogram, circle, trapezium, rhombus, cube, cuboid, cylinder.
|
81 videos|423 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Mensuration - Mathematics (Maths) Class 8
| 1. What are the different formulas used in mensuration? |  |
| 2. How do I calculate the volume of a cone? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between surface area and volume? |  |
| 4. How can I find the area of a trapezium? |  |
| 5. How do I calculate the diagonal of a rectangular solid? |  |

















