Exercise Page: 181
In each of the questions 1 to 21, out of four options only one is correct. Write the correct answer.
Q.1. Which amongst the following is not a polyhedron?
(a)
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 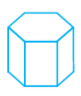
Ans: c
Solution: By the definition a polyhedron is regular if its faces are congruent regular polygons and the same number of faces meet at each vertex.
Q.2. Which of the following will not form a polyhedron?
(a) 3 triangles
(b) 2 triangles and 3 parallelogram
(c) 8 triangles
(d) 1 pentagon and 5 triangles
Ans: a
Solution: 3 triangles will not form a polyhedron because it must have more than four faces. So, it is not possible in 3 triangles which have 3 faces only.
Q.3. Which of the following is a regular polyhedron?
(a) Cuboid
(b) Triangular prism
(c) Cube
(d) Square prism
Ans: c
Solution: Because, a cube is a platonic solid because all six of its faces are congruent squares.
Q.4. Which of the following is a two Dimensional figure?
(a) Rectangle
(b) Rectangular Prism
(c) Square Pyramid
(d) Square Prism
Ans: a
Solution: Rectangle is a two dimensional figure. It has length and breadth.
Q.5. Which of the following can be the base of a pyramid?
(a) Line segment
(b) Circle
(c) Octagon
(d) Oval
Ans: c
Solution: A pyramid is a polyhedron whose base is a polygon and lateral faces are triangles.
Q.6. Which of the following 3D shapes does not have a vertex?
(a) Pyramid
(b) Prism
(c) Cone
(d) Sphere
Ans: d
Solution: The faces meet at edges which are line segments and the edges meet at a point called vertex. Since, a sphere has no vertex and no edges.
Q.7. Solid having only line segments as its edges is a
(a) Polyhedron
(b) Cone
(c) Cylinder
(d) Polygon
Ans: a
Solution: A polyhedron is formed by four or more polygons that intersect only at their edges. The faces of a regular polyhedron are all congruent regular polygons and the same number of faces intersect at each vertex.
Q.8. In a solid if F = V = 5, then the number of edges in this shape is
(a) 6
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 2
Ans: c
Solution: We have,
Euler’s formula for any polyhedron is, F + V – E = 2
Given, F = V = 5
Where, face (F) = 5, Vertex (V) = 5, Edge (E) =?
Then,
5 + 5 – E = 2
10 – E = 2
10 – 2 = E
Edges (E) = 8
Q.9. Which of the following is the top view of the given shape?
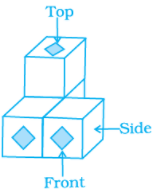
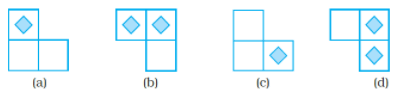
Ans: a
Q.10. The net shown below can be folded into the shape of a cube. The face marked with the letter L is opposite to the face marked with which letter?
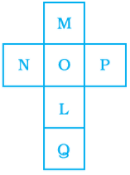
(a) M
(b) N
(c) Q
(d) O
Ans: a
Q.11. Which of the nets given below will generate a cone?
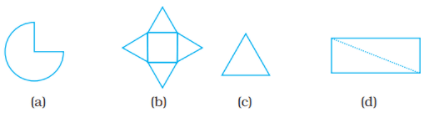
Ans: (a) Has circular base, which gives a cone.
Q.12. Which of the following is not a prism?
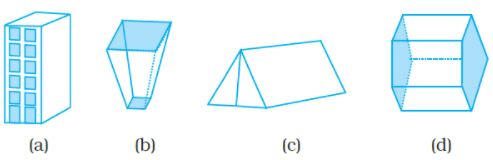
Ans: b
Solution: By observing option (b) figure, bottom and top faces are not congruent polygons.
Q.13. We have 4 congruent equilateral triangles. What do we need more to make a pyramid?
(a) An equilateral triangle.
(b) A square with same side length as of triangle.
(c) 2 equilateral triangles with side length same as triangle.
(d) 2 squares with side length same as triangle.
Ans: b
Solution: We have to add a square with same side length as of triangle to make a pyramid. As we know a pyramid is a polyhedron whose base is a polygon and lateral faces are triangles.
Q.14. Side of a square garden is 30 m. If the scale used to draw its picture is 1cm: 5m, the perimeter of the square in the picture is
(a) 20 cm
(b) 24 cm
(c) 28 cm
(d) 30 cm
Ans: b
Solution: Given, side of a square garden = 30m
Scale to draw garden picture is 1cm: 5m
So, perimeter of the square garden is = 4 × 30
= 120m
Then,
Perimeter to draw garden in picture = 120/5
= 24 cm
Q.15. Which of the following shapes has a vertex.
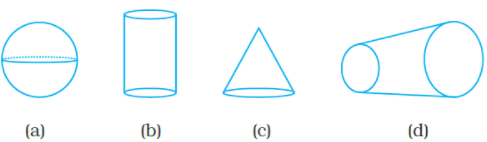
Ans: c
Solution: The edges meet at a point called vertex.
Q.16. In the given map, the distance between the places is shown using the scale 1 cm: 0.5 km. Then the actual distance (in km) between school and the book shop is
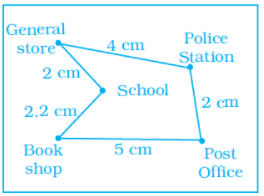
(a) 1.25
(b) 2.5
(c) 2
(d) 1.1
Ans: d
Solution: Given, Scale = 1 cm: 0.5km
Then the actual distance between school and the book shop is = 2.2 × 0.5
= 1.1 cm
Q.17. Which of the following cannot be true for a polyhedron?
(a) V = 4, F = 4, E = 6
(b) V = 6, F = 8, E = 12
(c) V = 20, F = 12, E = 30
(d) V = 4, F = 6, E = 6
Ans: d
Solution: We have,
Euler’s formula for any polyhedron is, F + V – E = 2
Where, face (F) = 6, Vertex (V) = 4, Edge (E) =6
Then,
6 + 4 – 6 = 2
LHS 6 + 4 -6
10 – 6
4
RHS= 2
By comparing LHS and RHS
LHS ≠ RHS
Q.18. In a blueprint of a room, an architect has shown the height of the room as 33 cm. If the actual height of the room is 330 cm, then the scale used by her is
(a) 1:11
(b) 1:10
(c) 1:100
(d) 1:3
Ans: b
Solution: From the question it is given that,
An architect has shown the height of the room as 33 cm
The actual height of the room is 330 cm
Then, the scale used by an architect is = Drawn size/actual size
= 33/330 … [divide both by 33]
= 1/10
= 1: 10
Q.19. The following is the map of a town. Based on it answer question 19-21.
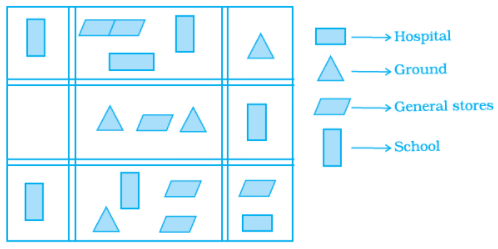
The number of hospitals in the town is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans: b
Q.20. The ratio of the number of general stores and that of the ground is
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 1
(c) 2 : 3
(d) 3 : 2
Ans: d
Solution: By observing the given map,
The number of general stores = 6
The number of ground = 4
Then,
The ratio of the number of general stores and that of the ground is = 6/4
= 3/2
= 3: 2
Q.21. According to the map, the number of schools in the town is
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 2
Ans: c
Solution: In questions 22 to 41, fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
Q.22. Square prism is also called a _______.
Ans: Square prism is also called a cube.
A cube is a platonic solid because all six of its faces are congruent squares.
Q.23. Rectangular prism is also called a ________.
Ans: Rectangular prism is also called a Cuboid.
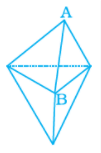
Q.24. In the figure, the number of faces meeting at B is ________.
Ans: The number of faces meeting at B is 4.
Q.25. A pyramid on an n sided polygon has ______ faces.
Ans: A pyramid on an n sided polygon has n+1 faces.
Q.26. If a solid shape has 12 faces and 20 vertices, then the number of edges in this solid is ______.
Ans: If a solid shape has 12 faces and 20 vertices, then the number of edges in this solid is 30.
We have,
Euler’s formula for any polyhedron is, F + V – E = 2
Given, F = 12, V = 20
Where, face (F) = 12, Vertex (V) = 20, Edge (E) =?
Then,
12 + 20 – E = 2
32 – E = 2
32 – 2 = E
Edges (E) = 30
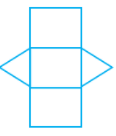
Q.27. The given net can be folded to make a ______.
Ans: The given net can be folded to make a prism.
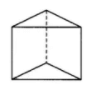
Q.28. A solid figure with only 1 vertex is a ______.
Ans: A solid figure with only 1 vertex is a cone.
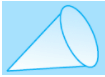
Q.29. Total number of faces in a pyramid which has eight edges is______.
Ans: Total number of faces in a pyramid which has eight edges is 5.
Q.30. The net of a rectangular prism has ______ rectangles.
(Hint: Every square is a rectangle but every rectangle is not a square.)
Ans: The net of a rectangular prism has six rectangles.
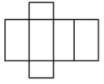
Q.31. In a three-dimensional shape, diagonal is a line segment that joins two vertices that do not lie on the ______ face.
Ans: In a three-dimensional shape, diagonal is a line segment that joins two vertices that do not lie on the same face.
Q.32. If 4 km on a map is represented by 1 cm, then 16 km is represented by ______ cm.
Ans: If 4 km on a map is represented by 1 cm, then 16 km is represented by 4 cm.
= 16/4
= 4 cm
Q.33. If actual distance between two places A and B is 110 km and it is represented on a map by 25 mm. Then the scale used is ______.
Ans: If actual distance between two places A and B is 110 km and it is represented on a map by 25 mm. Then the scale used is 1: 4400000
From the question it is given that,
Actual distance between two places A and B is = 110km
Distance is represented on a map by = 25 mm
So, the scale used is = Size drawn on map/ actual distance
= 25 mm/110 km
We know that, 1km = 1000m
1m = 100cm
1cm = 10mm
1 km = 10,00,000
So, 110km = 11,00,00,000 mm
Therefore = 25/11,00,00,000
= 1/4400000
= 1: 4400000
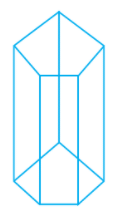
Q.34. A pentagonal prism has ______ faces.
Ans: A pentagonal prism has 7 faces.
Q.35. If a pyramid has a hexagonal base, then the number of vertices is ______.
Ans: If a pyramid has a hexagonal base, then the number of vertices is 7.