Basic Reactions in Biological Systems & Role of Metal ions | Inorganic Chemistry PDF Download
Introduction
Metals such as iron, zinc, and copper all perform important roles in many of the enzymatic reactions that fuel the body’s metabolism. For instance, ions such as Fe2+ can bind to the hemoglobin and myoglobin protein to help transport oxygen to organs in the body. Other metals like magnesium and copper act to stabilize the shapes of enzymes. However, there are some metal ions that are highly toxic in excessive amounts. Thus, the body exerts strict control to assure that only one or two free metal atoms are present inside an individual cell.
In trigger and control mechanisms
- Na+, K+ play an important role in nerve cell membranes. They are electrical charge carries that conduct nerve cell impulses by moving back and forth across the membrane generating an voltage(difference in electrical charge), or potential across the membrane. These ions help communicate electrical signals in the nerves and heart.
- Ca2+ plays a critical role in muscle cell contraction and relaxation.
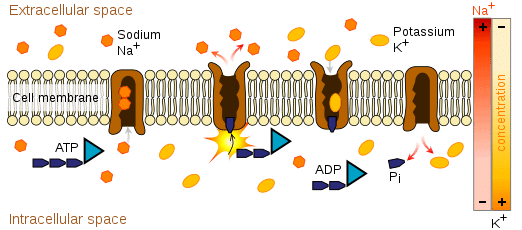 Sodium-Potassium pump generating a concentration gradient
Sodium-Potassium pump generating a concentration gradient
Structural influences
- Ca2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+ help stabilize a particular protein configuration.
- Mg2+ is used for cleavage and replication of DNA, RNA strands
- Bones and shells contain Ca2+ like the mineral hydroxyapatite Ca(OH)2.3Ca3(PO4)2
Lewis Acid Behavior
- Zn2+ and Co2+ catalyzes the hydrolysis of phospates by serving as Lewis acids.
- For example carboxypeptidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of C-terminal amino acid residues of proteins. It is released in pancreatic juice of animals for the digestion of proteins.
- Hemoglobin,myoglobin, hemocyanin, and hemerythrin provide O2 storage and transport.
Redox reactions and General Compounds
- Dehydrogenation; catalyzed by Cu, Mo and Fe by changing their oxidation states.
- Ribose turns into deoxyribose with a catalysis of Co.
Unhealthy Metals
Toxic metals can hinder important enzyme functions.
- Lead inhibits the body's ability to make hemoglobin by interfering with the synthesis of heme which disrupts the blood's oxygen transport system.
- Mercury binds to sulfur-containing molecules which can cause irreversible neurological damage.
- Arsenic can cause cancer in the skin and lungs.
 Mg2+ as a co-factor in an enzyme
Mg2+ as a co-factor in an enzyme
|
48 videos|92 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Reactions in Biological Systems & Role of Metal ions - Inorganic Chemistry
| 1. What are basic reactions in biological systems? |  |
| 2. What is the role of metal ions in biological systems? |  |
| 3. How do metal ions participate in enzymatic reactions? |  |
| 4. Which metal ions are commonly found in biological systems? |  |
| 5. How do metal ions contribute to the stability of biological molecules? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|