Thermal Properties of Matter | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Heat
The energy that is being transferred between two bodies or between adjacent parts of a body as a result of temperature difference is called heat.
- Thus, heat is a form of energy. It is energy in transit whenever temperature differences exist. Once it is transferred, it becomes the internal energy of receiving body.
- It should be clearly understood that the word "heat" is meaningful only as long as the energy is being transferred. Thus, expressions like "heat in a body" or "heat of body" are meaningless.
- When we say that a body is heated it means that its molecules begin to move with greater kinetic energy.
- S.I. unit of heat energy is joule (J).
- Another common unit of heat energy is calorie (cal).
Temperature
- We have already understood that heat is the form of energy that leads to an increase or decrease in the internal energy of the body. This internal energy is also known as temperature. In other words, the temperature is a measurement by which we may measure the degree of hotness or coolness present in a body.
- Temperature is measured in degrees. The measuring unit for temperature in Celsius and Fahrenheit. However, these measures are used in your daily life. For scientific measurement, we use the Kelvin scale.

Let us now find out the equation for the three measurements.
- °F = (9/5 × °C) +32
- °C = (9/5)(°F- 32)
- K = C + 273°
What is a Clinical Thermometer? How is it Different from a Laboratory Thermometer?
- A clinical thermometer is the one which we use to measure our body temperature. The thermometer which you normally find at your home or at a doctor’s clinic is a clinical thermometer. The clinical thermometer is a long narrow tube made of glass. There is a silver looking bulb attached at the end of it. This bulb contains mercury, thereby making it look silver.
 Clinical Thermometer
Clinical Thermometer
- When this temperature is exposed to heat, the mercury in the bulb rises and depending upon the heat of the object points to the small numbers etched on the glass tube, indicating the temperature.
- One can also use the clinical thermometer to measure hot water.
- A laboratory thermometer looks pretty much like the clinical thermometer, which has a long narrow uniform glass tube with mercury in it; however, the temperature range of a clinical thermometer ranges from 35 degrees to 42 degrees Celsius.
- On the other hand, the temperature range of a laboratory thermometer ranges from -10 degrees to 110 degrees Celsius.
- We use a clinical thermometer to measure the temperature of a human body; however, we cannot use a laboratory thermometer to measure human body temperature.
- While using a clinical thermometer, we have the liberty to tilt it as per our convenience.
- But a laboratory thermometer has to be kept upright if we need to get a proper reading.
- The range of a laboratory thermometer is far wider than the clinical one and therefore it has to be used with precision.
Q1: The quantity of heat energy required to change the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius is known as
(a) 1 Joule
(b) One Kilojoule
(c) 1 Calorie
(d) 1 Ampere
Ans: (c)
Explanation: The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of water through 1° (from 14.5°C to 15.5°C), is called one calorie.
Measurement of Temperature
The measurement of temperature, a fundamental physical property, is achieved through specific scales using instruments called thermometers. These thermometers are calibrated to assign a numerical value to a given temperature.
Temperature measurement is typically expressed in units like Kelvin (K), degree Celsius (°C), and degree Fahrenheit (°F), with Kelvin (K) recognized as the SI unit. Various physical properties of materials that change with temperature, such as liquid volume, gas pressure, or metal resistance, form the basis of thermometer construction.
To define any temperature scale, two reference points are essential. For water, these are the ice point (where water freezes) and the steam point (where water boils) under standard pressure. On the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F, whereas on the Celsius scale, water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C. The Celsius scale has 100 equal intervals between these reference points, while the Fahrenheit scale has 180.
 Celsius versus Fahrenheit graph
Celsius versus Fahrenheit graph
The relationship between Fahrenheit (TF) and Celsius (TC) temperatures can be expressed as:

For Kelvin and Celsius, as they share the same unit size, the relation is:
 Different Scales to Measure the Temperature
Different Scales to Measure the Temperature
Ideal Gas Equation
By combining two previously mentioned gas laws, we get:
for a fixed quantity of gas. This relationship is known as the ideal gas law. In a more generalized form, it is expressed as:
where:
- μ represents the number of moles of gas,
- R is the universal gas constant, valued at

This expression is referred to as the ideal gas equation.
According to the ideal gas equation, This proportionality allows gases to be used in temperature measurement through volume gas thermometers, where p ∝ T when the gas volume is kept constant.
This proportionality allows gases to be used in temperature measurement through volume gas thermometers, where p ∝ T when the gas volume is kept constant.
Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law states that ‘The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if both the temperature and amount of gas remain unchanged’. In mathematical terms this law is given as:
P ∝ 1/V or that PV = K
where P=Pressure of the gas; V=Volume of the gas; K=constant. It means that both the pressure and volume of a given mass of gas are inversely proportional to each other at a constant temperature. Furthermore, it also expresses that the product of pressure and volume for any gas is a constant and thus can be used to study the comparison of the gas under different conditions as:
P’V’ = P”V”
where both the products are for the same gas but under different pressures and volumes.
Charles’ Law
Charles’ law states that ‘ When the pressure of a sample of air is held constant, then the volume of the gas is directly proportional to its temperature‘, that is
V ∝ T
where V= Volume of a gas sample; T= Absolute temperature. Quite simply put, it says that Gases expand on heating and contract on cooling.
Avogadro’s Law
Avogadro’s law states that ‘Equal volumes of all gases at conditions of same temperature and pressure have the same number of molecules’, written as:
V ∝ n or V/n =K
where V=volume of gas; n = Number of moles (1 mole=6.022 x 1023 molecules). It implies that under similar conditions of pressure, volume and temperatures all gases will have an equal number of molecules, independent of the weight and density of the gas.
Ideal Gas Equation
If we combine the results of all the above gas laws we get an equation that holds true for an ideal gas. The most common form of this equation is since PV= K and V/T =k then
PV/T = constant
Thus, the Ideal Gas Equation is given as
PV = n R T
where P= pressure of the gas; V=volume of the gas; n = Number of Moles; T = Absolute temperature; R = Ideal Gas constant also known as Boltzmann Constant = 0.082057 L atm K-1 mol-1.
Using this equation, the study of any gas is possible under assumptions of STP conditions and subjecting the gas to reasonable restrictions to make it behave similarly to an Ideal gas.
What is an STP condition?
STP is short for ‘Standard Temperature and Pressure’. STP condition is defined (as per the International Standard Metric Conditions) as the surrounding absolute temperature of 288.15 Kelvin (15° Celsius) and a pressure of 1 atmosphere i.e. 1 bar or 101.325 K pa.
Absolute Temperature
Thermodynamic temperature, which is also known as ‘Absolute Temperature’ is a basic parameter for the study of thermal properties of matter.
Using an ideal gas equation we can use gas for measuring temperature accurately. Again, as this law is universal in nature, all gases can be used to get the accurate temperature irrespective of their masses and other physical properties.
However, in actual use, it is observed that real gases often deviate from this law as compared to an ideal gas. But over a wide temperature base, all real gases more or less follow a linear path as can be seen in the case of gases taken above with pressure on the Y-axis and temperature on the X-axis.
Assuming that gases continue to be in a gaseous state at lower temperatures we can extrapolate the lowest minimum temperature for a gas. This lowest possible temperature is called Absolute Zero. The temperature is obtained at -273.15° Celsius on the Celsius scale.
It is also responsible for the creation of a new temperature scale called as ‘Kelvin’ scale where absolute zero is taken as 0 and so this scale is also called as Absolute temperature scale. It is represented as Kelvin. Thus,
T(Celsius) = T(Kelvin) + 273.15
This conversion helps to determine the absolute temperature of a gas under study. Thus, we have finally derived the Ideal Gas equation after studying all the concepts involved which make up the gas laws. Thorough knowledge of these concepts is paramount to ensure the proper understanding of properties of a gas being subjected to thermal study and thus its applications.
Q2: How many moles of ‘He’ are contained in a 6-litre canister at 101 KPa and 27 ° C. Take R= 8.314 J/mol K
Ans: Using the Ideal gas equation, n = PV/RT
Therefore, on substituting the values(T = 27 + 273 = 300) we get,
= 101 x 6/ 8.314 x 300 = 606/2494.2 = 0.2429 moles
Hence, 0.2429 moles of ‘He’ are contained in a 6-litre canister at 101 KPa and 27°C
Thermal Expansion
- When a liquid is heated, such as when a thermometer is placed in warm water, it expands. Conversely, it contracts when cooled.
- Similar to liquids, balloons demonstrate thermal expansion. A balloon inflated in a warm environment expands fully, while one in a cold environment shrinks when fully inflated due to air contraction.
- Sealed bottles with tightly screwed metallic lids may require dipping in hot water to loosen the lid, as the expansion of the metallic lid facilitates easier opening.
Most substances expand with heat and contract with cold. This change in dimensions with temperature variation is known as thermal expansion.
 Example of Thermal Expansion
Example of Thermal Expansion
Three types of expansion occur in solids:
- Linear expansion
- Area superficial or superficial expansion
- Volume expansion
Linear Expansion
The expansion in length of a body due to increase in its temperature is called the linear expansion.
Linear expansion is expressed by the formula:

Here, αl represents the coefficient of linear expansion for the specific solid.
The unit of α is per degree Celsius (°C^-1) in the CGS system and per Kelvin (K^-1) in the SI system.
 Linear Expansion
Linear Expansion
Superficial or Area expansion
It involves the increase in the surface area of a substance when heated. A slight change in temperature, ΔT, leads to deformation, where the fractional change in surface area, ΔA/A, is directly proportional to ΔT.
 Area Expansion
Area Expansion
- The formula for Area expansion is:

Here, αA represents the coefficient of area expansion of the given solid.
Volume expansion
It refers to the fractional change in the volume of a substance. A slight variation in temperature, ΔT, causes deformation, where the fractional change in volume, ΔV/V, is directly proportional to ΔT.
 Volume Expansion
Volume Expansion
- The formula for volume expansion is:

Here, αV is another characteristic of the substance, but it varies with temperature.
The coefficient of volume expansion only becomes constant at high temperatures. For instance, ethyl alcohol has a higher coefficient of volume expansion than mercury and thus expands more for the same temperature rise.
The graph depicts the Coefficient of volume expansion of copper concerning temperature:
 Coefficient of volume expansion of copper changes with temperature
Coefficient of volume expansion of copper changes with temperature
Water's Unique Behavior
- Between 0 and 4 degrees Celsius, water behaves unusually when heated.
- As water is cooled, its volume decreases until it reaches around 4°C.
- Below 4°C, water's volume increases, leading to a decrease in density.
- Water has maximum density at 4°C, impacting the freezing of lakes and ponds.
- Energy loss to the atmosphere causes denser water to sink while warmer water rises.
- When cooler water on top cools below 4°C, it becomes less dense and freezes at the surface.

Q3: Define the term thermal expansion.
Ans: Most substances expand with heat and contract when cooled, changing dimensions with temperature shifts.
- Linear expansion
- Area superficial or superficial expansion
- Volume expansion
Q4: Calculate the pressure needed to maintain the length of a steel wire when heated by 100°C.
Ans: Given:
ΔT = 100°C,
Y = 2 x 10^11 Nm^−2,
α = 1.1 x 10^−5 K^−1.
Thermal strain = 2.2 x 10^8 Pa.
Specific Heat Capacity
- Specific heat of substances is equal to heat gain or released by that substance to raise or fall its temperature by 1°C for a unit mass of a substance.
- When a body is heated, it gains heat. On the other hand, heat is lost when the body is cooled.
- The gain or loss of heat is directly proportional to :
(a) The mass of the body DQ µ m
(b) Rise or fall of temperature of the body DQ µ DT
where s is a constant and is known as the specific heat of the body s = .
. - S.I. unit of s is joule/kg-kelvin and C.G.S unit is cal/gm °C.
Specific heat of water: s = 4200 J/kg°C = 1000 cal/kg°C = 1 Kcal/kg°C = 1 cal/gm°C.
Specific heat of steam = half of specific heat of water = specific heat of ice
Heat capacity or Thermal capacity
The heat capacity of a body is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of that body by 1°C. If `m' is the mass and `s' the specific heat of the body, then
Heat capacity = m s
Units of heat capacity in CGS system is, cal °C-1 ; SI unit is, JK-1
Relation between Specific heat and Water equivalent
It is the amount of water which requires the same amount of heat for the same temperature rise as that of the object
ms AT = mw Sw ΔT 
In calorie sw = 1
∴ mw = ms
mw is also represented by W
so W = ms
Calorimetry
Calorimetry is the branch of science focused on measuring heat. When a hot body comes into contact with a cooler one, heat flows from the warmer to the cooler body until they reach the same temperature.
According to the principle of calorimetry, the heat lost by the hotter body equals the heat gained by the colder body.
For example, if there are two bodies with masses m1 and m2, and specific heats s1 and s2, then for a temperature change ΔT:

Calorimeter
A calorimeter is a tool for measuring heat. It consists of a copper container with a stirrer and is placed in a wooden jacket insulated with materials like glass wool. This setup prevents heat exchange with the surroundings. The polished surfaces further reduce heat loss by radiation.
 Calorimeter
Calorimeter
The calorimeter has holes for inserting a thermometer and a stirrer. When different temperature bodies are placed inside, heat is exchanged until thermal equilibrium is reached. If no heat is lost to the surroundings, the heat gained by colder bodies equals the heat lost by hotter bodies, following the principle of calorimetry.
Change of State
The process of changing a substance from one state to another, known as a "change of state," typically involves the absorption or release of heat.
Matter generally exists in three main states:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
These states can transition from one to another through processes like:
- Solid to liquid (and back)
- Liquid to gas (and back)
These transitions occur due to heat exchange between the substance and its environment.

Effect on Heat on Ice
- To observe the effect of heat on ice, place ice cubes in a beaker at 0°C and start heating it with a consistent heat source. Stir the ice and water mixture continuously while monitoring the temperature every minute.
- The temperature-time graph shows that while ice is present in the beaker, the temperature remains constant, even with continuous heating. This indicates that during the phase change from solid (ice) to liquid (water), the system maintains thermal equilibrium.
 Effect of heat on ice
Effect of heat on ice
- Once all the ice melts, the temperature begins to rise until it reaches approximately 100°C, where it stabilizes again. At this point, heat energy is used to change water from liquid to vapor.
- Throughout this phase transition, the temperature remains constant until all water is converted to vapor. This experiment illustrates that temperature does not increase during a phase change, despite ongoing heat absorption.
 Plot of change of state of ice on heating
Plot of change of state of ice on heating
Terms Related to Change of State
Melting and Melting Point:
- Melting is the process in which a solid changes to a liquid state.
- The melting point is the temperature at which this transformation occurs for a given solid.
- Note: The melting point under standard atmospheric pressure is referred to as the normal melting point.
Fusion and Freezing Point:
- Fusion is the process of a liquid turning into a solid.
- The freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid solidifies.
Vaporisation and Boiling Point:
- Vaporisation occurs when a liquid turns into a gas. During this process, the temperature remains constant as heat energy enables the liquid and gas phases to coexist in equilibrium.
- The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid fully transitions to vapor.
Sublimation:
- Sublimation is the direct transition from solid to gas without a liquid phase. Substances like camphor and naphthalene exhibit sublimation, and reversing this process isn’t possible under normal conditions.
Effect of Pressure on Boiling Point:
- The boiling point of a liquid increases with rising pressure. For instance, water boils at 100°C under 1 atm but at 128°C under 2 atm.

Latent Heat
The amount of heat transferred per unit mass during the change of phase of a substance without any change in its temperature is called latent heat of the substance for particular change.
Latent heat is denoted by L and having SI unit J kg−1. The value of latent heat is usually quoted at standard atmospheric pressure because it also depends upon the pressure.
Thus, if a mass m of a substance undergoes a change from one state to the other, then the quantity of heat required is given by

Hence, during the phase change, the heat required by the substance depends on the mass m of the substance and heat of transformation Q.
Types of Latent Heat
(a) Latent heat of Fusion (Lf)
The heat supplied to a substance which changes it from solid to liquid state at its melting point and 1 atm. pressure is called latent heat of fusion.

SI unit is J/Kg.
(b) Latent heat of vaporisation (Lv)
The heat supplied to a substance which changes it from liquid to vapour state at its boiling point and 1 atm. pressure is called latent heat of vaporization.

SI unit is J/Kg.
If in question latent heat of water are not mentioned and to solve the problem it require to assume that we should consider following values.
Latent heat of ice : L = 80 cal/gm = 80 Kcal/kg = 4200 × 80 J/kg
Latent heat of steam : L = 540 cal/gm = 540 Kcal/kg = 4200 × 540 J/kg
Variation of Temperature During Change of State
The given figure, represents the change of state by different lines,
 Temperature versus hat for water at 1 atm pressure
Temperature versus hat for water at 1 atm pressure
Note : If we increases the temperature of liquid (phase) 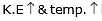 but at a later time K .E. stop increasing and the phase of the liquid starts changing.
but at a later time K .E. stop increasing and the phase of the liquid starts changing.
Mechanical Equivalent of Heat
- In the early days heat was not recognized as a form of energy. Heat was supposed to be something needed to raise the temperature of a body or to change its phase. Calorie was defined as the unit of heat.
- A number of experiments were performed to show that the temperature may also be increased by doing mechanical work on the system. These experiments established that heat is equivalent to mechanical energy and measured how much mechanical energy is equivalent to a calorie.
- If mechanical work W produces the same temperature change as heat H, we write,
W = JH - Where J is called the mechanical equivalent of heat. J is expressed in joule/calories. The value of J gives how many joules of mechanical work is needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C.
- 1 calorie: The amount of heat needed to increase the temperature of 1 gm of water from 14.5 to 15.5 °C at one atmospheric pressure is 1 calorie.
1 calorie = 4.186 Joule.
Q5: Heat required to increases the temperature of 1 kg water by 20°C
Ans: Heat required = ΔQ = m s Δθ
= 1 x 20 = 20 Kcal.
∴ S = 1 cal/gm°C = 1 Kcal/kg°C
Important Points:
(a) We know, s =
, if the substance undergoes the change of state which occurs at constant temperature (DT = 0), the s = Q/0 = ¥. Thus the specific heat of a substance when it melts or boils at constant temperature is infinite.
(b) If the temperature of the substance changes without the transfer of heat (Q = 0) then s =
= 0. Thus when liquid in the thermos flask is shaken, its temperature increases without the transfer of heat and hence and the specific heat of liquid in the thermos flask is zero.
(c) To raise the temperature of saturated water vapour, heat (Q) is withdrawn. Hence, specific heat of saturated water vapour is negative. (This is for your information only and not in the course)
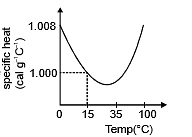
(d) The slight variation of specific heat of water with temperature is shown in the graph at 1 atmosphere pressure. Its variation is less than 1% over the interval form 0 to 100°C.
Q6: An iron block of mass 2 kg, fall from a height 10 m. After colliding with the ground it loses 25 % energy to surroundings. Then find the temperature rise of the block (Take specific heat of iron 470 J/kg° C)
Ans: 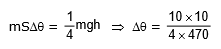
Q7: The temperature of equal masses of three different liquids A, B, and C are 10°C 15°C and 20°C respectively. The temperature when A and B are mixed is 13°C and when B and C are mixed, it is 16°C. What will be the temperature when A and C are mixed?
Ans:
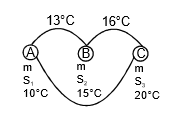
when A and B are mixed
mS1 x (13 - 10) = m x S2 x (15 - 13)
3S1 = 2S2 ...(1)
when B and C are mixed
S2 x 1 = S3 x 4 ...(2)
when C and A are mixed
S1(θ - 10) = s3 x (20 - θ) ,..(3)
by using equation (1), (2) and (3)

Q8: 500 gm of water at 80°C is mixed with 100 gm steam at 120°C. Find out the final mixture.
Ans: 120°C steam  100°C steam
100°C steam
Req. heat = 100 ×  ×20 = 1 kcal
×20 = 1 kcal
80°C water  100°C water
100°C water
Req. heat = 500 × 1 × 20 = 10 kcal
100gm steam  100 gm water at 100°C
100 gm water at 100°C
Req. heat = 100 × 540 = 54 kcal
Total heat = 55 kcal.
Remaining heat = 55 - 10 = 45 kcal
Now we have 600 gm water at 100°C ⇒ 4500 = m × 540 ⇒ 
So at last we have  gm steam and
gm steam and  of water
of water
|
97 videos|378 docs|103 tests
|
FAQs on Thermal Properties of Matter - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the Ideal Gas Equation and how is it used in thermodynamics? |  |
| 2. How does thermal expansion occur and what are its implications in everyday life? |  |
| 3. Why is water considered unique in its thermal properties compared to other substances? |  |
| 4. What is Young's Modulus and how does it relate to the stress-strain relationship in materials? |  |
| 5. What is the Law of Mixtures in relation to thermal properties, and how is it applied? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


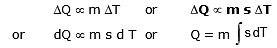
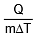 .
.