Thermodynamic Processes | Physics for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
Types of Thermodynamic Processes
- Isobaric process
- Isochoric process
- Isothermal process
- Adiabatic process
- Quasi-static process
Isobaric Process
”Iso” means the same, and ”baric” means pressure.
The processes during which the pressure of the system remains constant are called isobaric thermodynamic processes. Suppose there is a fuel in piston and cylinder arrangement. When this fuel burns the pressure of the gases, generated inside the engine. But if the gases are allowed to expand by allowing the piston to move outside, the pressure of the system can be constant.
PV Curve
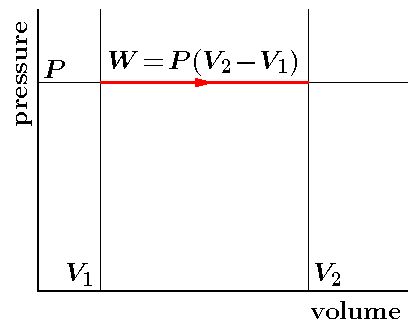
Practically, it is not possible to attain an ideal constant and constant pressure. An isobaric process is one in which the pressure is constant. The quantity of the gas in an isobaric process remains constant and the work done by the system is directly promotional to the change in volume or temperature of the system.
Isochoric Process
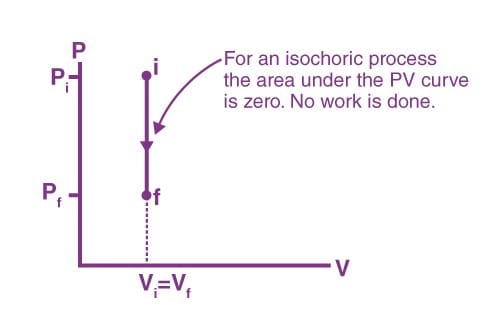
The process, during which the volume of the system remains constant, is an isochoric process. Heating of a gas in a closed cylinder is an example of the isochoric process. The change in temperature for a given amount of heat is determined by the specific heat of the gas at a constant volume.
Work done in an isochoric process
W = ∫ PdV
Here, dV = 0
Therefore, W = 0
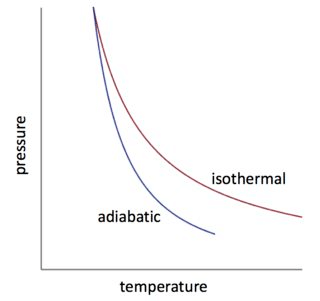
Isothermal Process
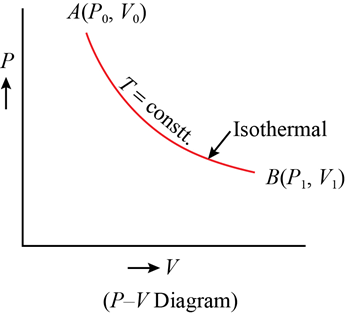
In an isothermal process, there is no change in temperature, that means the temperature remains constant.Like when hot water is kept in a thermos flask, if we remove a certain quantity of water from the flask, but keep its temperature constant then the process is said to be an isothermal process.
Adiabatic Process
The process, during which the heat content of the system remains constant, is an adiabatic process. During this process heat neither enters the system nor leaves the system.
For an adiabatic process,
ΔQ = 0
Then according to the first law of thermodynamics,
ΔU + ΔW = ΔQ = 0
where, Q is the heat supplied to the system and W is the work done by the system and U is the internal energy of the system.
Quasi-Static Process
When a process is which system remains close to an equilibrium state at each time, such process will be termed as the quasi-static process or quasi-equilibrium process. For example, if a person is coming down from roof to ground floor with the help of ladder steps then it is a quasi-static process. But if he jumps from roof to ground floor then it will not be a quasi-static process.
Question For You
Q. The process in which the internal energy of the system remains constant is:
(a) Adiabatic
(b) Isobaric
(c) Isochoric
(d) Isothermal
Ans: (d)
Solution: Internal energy is a function of temperature only. Therefore, in case of an isothermal process, it will be constant.
|
209 videos|327 docs|212 tests
|
















