Lines, Angles and Triangles / Geometry Class 5 Notes Maths
Point, Line, Line Segment and Plane
The three building blocks of geometry are points, lines and planes.
1. Point
A point is an exact location in plane or space.
A point has zero length, zero width and zero height. It represents a position only. We represent a point by a dot (.) and name it with a capital letter, as point P.
Some representations of a point in everyday life are:
2. Line
A line is a straight path of points that extends on and on in both the directions without ever ending.
The length of a line cannot be measured.
To show that a line extends endlessly in both the directions, you use arrowheads at both the ends.
A line is named by using any two points on a line.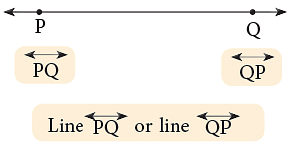 Thus, the line given alongside is named as
Thus, the line given alongside is named as 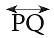 (line PQ) or
(line PQ) or  (line QP).
(line QP).
- A horizontal line goes straight across. (Sleeping Line)

- A vertical line goes straight up and down. (Standing Line)
- A line can also be curved. A curved line is called a curve.

2. Line Segment
A part of a line is called a line segment.
A line segment has a fixed length that can be measured. The points at which the line segment begins and ends are called its endpoints. Every line segment has two endpoints. A line segment is named by using endpoints
The given line segment has C and D as endpoints. The line segment given here is named as 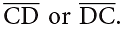

Thus, a line segment is also the shortest path between two points.
Some representations of a line segment from your everyday life are:
3. Ray
A ray is a straight path that has one endpoint and goes on and on in one direction.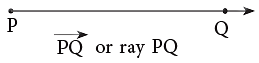 This ray begins at point P and goes through point Q. It does not stop at point Q. We name the given ray as
This ray begins at point P and goes through point Q. It does not stop at point Q. We name the given ray as  where the first letter is always the endpoint.
where the first letter is always the endpoint.
The symbol ‘ → ’ shows that a ray has a fixed endpoint and extends endlessly in the other direction.
Some representations of rays from your everyday life are:
4. Plane
A plane is a flat surface that extends infinitely in all directions. It has no thickness.
In mathematics, a plane goes on and on in all directions without end. We usually work with just a part of a plane. Points and lines lie on a plane. A plane can be named by using any three points on it. The given figure shows plane ABC. The order of the points does not matter.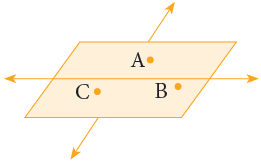 Some representations of a plane surface from your everyday life are:
Some representations of a plane surface from your everyday life are: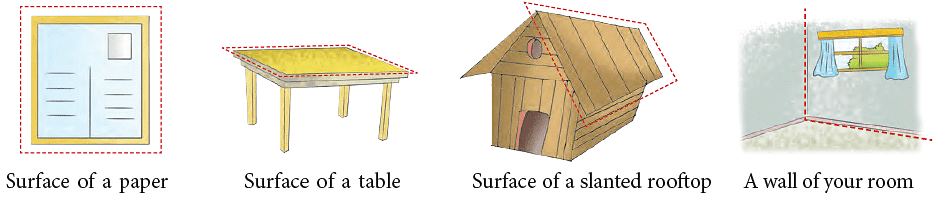
Angle
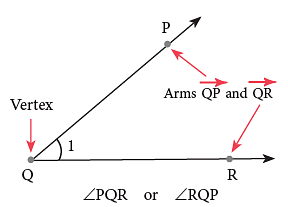
An angle is a figure formed by two rays meeting at a common endpoint.
The common endpoint is called the vertex of the angle and the two rays are called the arms of the angle.
Looking at these pictures, you can form some idea of an angle: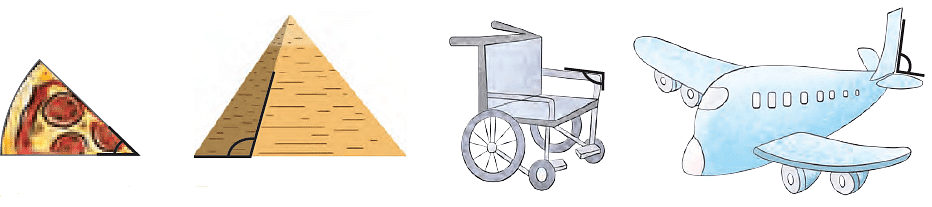
The symbol for angle is ∠.
1. Naming an Angle
You can name an angle in three ways:
- Using a three-letter name in the order: a point on oneray, vertex and a point on the other ray. ∠PQR or ∠RQP
- Using only one-letter name, i.e., the vertex ∠Q. (This can be used when there is only one angle with this vertex.)
- Using a number to name the angle, i.e., ∠1.
2. Interior and Exterior of an Angle
The region between the rays, that is, the inside of an angle, is called the interior of the angle and the region outside the arms of angle is called the exterior of the angle.
The point P is in the interior of the angle, whereas points S and U are in the exterior of the angle. Points Q and R lie on the arms of the angle.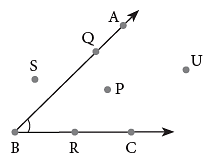
Measure the Angles
By measure of the angle, we mean the amount of rotation or turning.
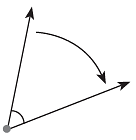 Just as there are standard units of length, area, weight, etc., there are also standard units for the measurement of angles. The standard unit of measure for angles is the degree. The symbol for degree is °.
Just as there are standard units of length, area, weight, etc., there are also standard units for the measurement of angles. The standard unit of measure for angles is the degree. The symbol for degree is °.
The angle formed by one complete rotation measures 360 degrees or 360°.
Look at the following example. The drawings below show angles of 40°, 150° and 270°.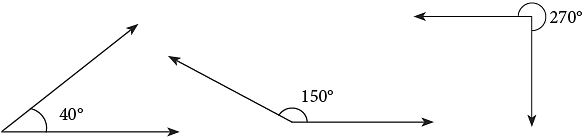
Edurev Tips: One complete rotation is divided into 360 equal parts.
The measure of one part is called one degree or 1°.
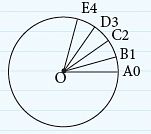
Look at the following clocks: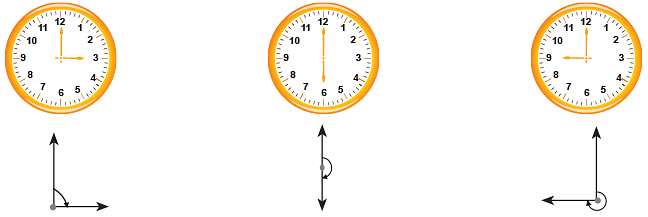 A hand of a clock turns from one position to another as it changes its direction. This change of direction or turning can be represented by drawing two arrows from one point.
A hand of a clock turns from one position to another as it changes its direction. This change of direction or turning can be represented by drawing two arrows from one point. The picture alongside shows one complete rotation.
The picture alongside shows one complete rotation.
The least amount of turning that brings the hand back to its starting position is called one complete rotation.
Example 1: If a circle is divided into 20 equal parts, what will be the measure of an angle of each part?
Angle formed by one complete rotation = 360°.
∴ Measure of angle of each of the 20 equal parts = 360° / 20 = 18°.
Example 2: Calculate the angle between neighbouring spokes on each wheel.
(a)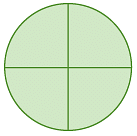
(b)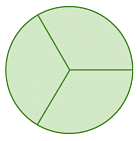
(c)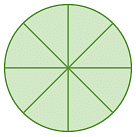
(a) As the wheel (circle) is divided into 4 equal parts, the angle between the neighbouring spokes = 360° / 4 = 90°.
(b) The wheel is divided into 3 equal parts, so the angle between the neighbouring spokes = 360° / 3 = 120°.
(c) The wheel is divided into 8 equal parts, so the angle between the neighbouring spokes = 360° / 8 = 45°.
Measuring an Angle
The instrument used for measuring angles is called a protractor.
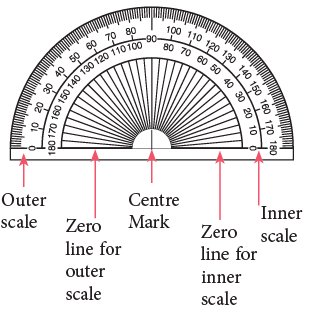 The diagram on the right shows a protractor. It has the shape of a semi-circle and the angle at the centre is divided into 180°.
The diagram on the right shows a protractor. It has the shape of a semi-circle and the angle at the centre is divided into 180°.
Edurev Tips: The inner scale of the protractor is marked from 0° to 180° anticlockwise. The outer scale of the protractor is marked from 0° to 180° clockwise. Each small division is 1°.
1. To Measure an Angle less than 180°
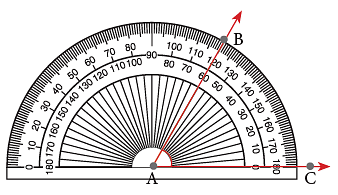
Step 1: Place the centre of the protractor at the vertex of the angle.
Step 2: Make sure that 0° line of the protractor is placed along one arm (AC) of the angle.
Step 3: Read the value on the protractor as indicated by the other arm (AB) of the angle. Thus, ∠ BAC = 60°.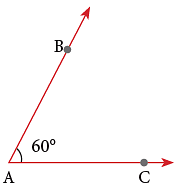
2. To Measure an Angle greater than 180°
Suppose, you are required to measure ∠x.
Step 1: Measure ∠a.
Step 2: Then, reflex ∠BOC = 360° – a°.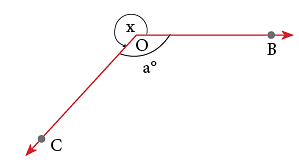
Drawing Angles using Protractor
To draw an angle that measures 80°.
Step 1: Draw any ray OA.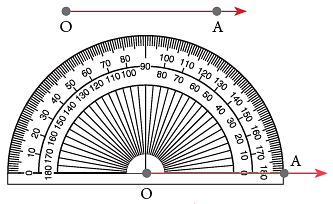 Step 2: Place the protractor such that its centre mark may fall on O, the endpoint of the ray. Align the ray with the 0° mark of one of the protractor scales. The endpoint O of the ray will be the vertex of the angle.
Step 2: Place the protractor such that its centre mark may fall on O, the endpoint of the ray. Align the ray with the 0° mark of one of the protractor scales. The endpoint O of the ray will be the vertex of the angle.
Step 3: Using the scale on which the ray OA aligns with 0°, mark the point at 80°. Label the point as B.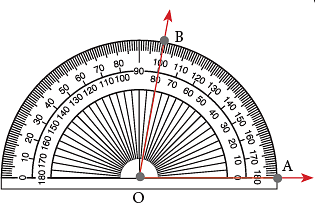 Step 4: Remove the protractor and join B to O.
Step 4: Remove the protractor and join B to O.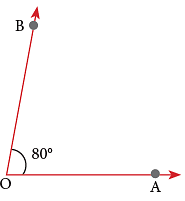 Thus, ∠AOB is the required angle.
Thus, ∠AOB is the required angle.
As you can see, we have drawn this angle using the inner scale on the protractor. What will be the angle like, if we use the outer scale on the protractor?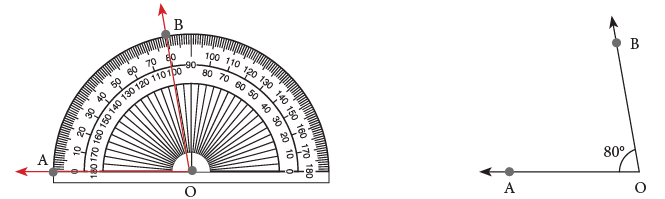 Observe the following angles.
Observe the following angles.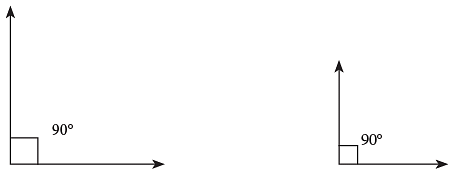 Irrespective of the length of the arms, each angle = 90°.
Irrespective of the length of the arms, each angle = 90°.
Types of Angles
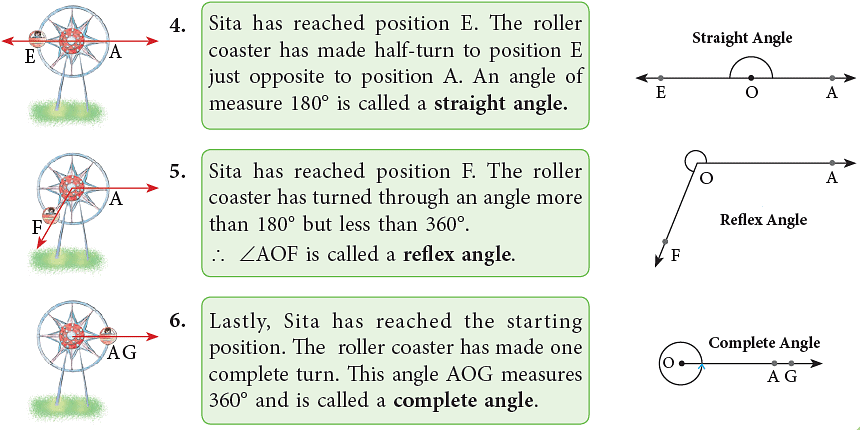
Angles are named according to their measure between 90° and 180° and 180° and 360°. Look at the following illustrations. Sita sat on a roller coaster. Let her position be A. The roller coaster starts moving in an anticlockwise direction and this movement brings a change in Sita’s position.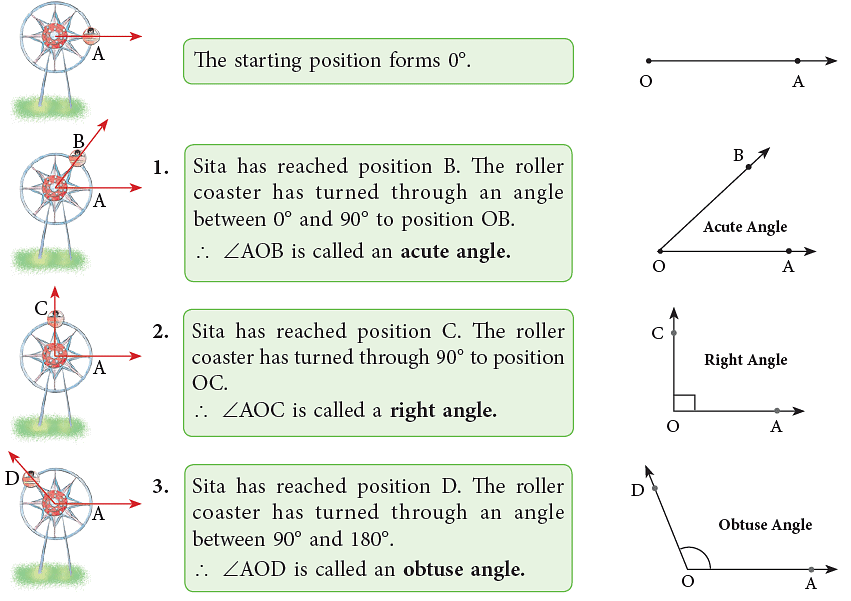
Equal Angles or Congruent Angles
When two angles have the same angle measure, we say that they are equal or congruent and write ∠ABC = ∠DEF.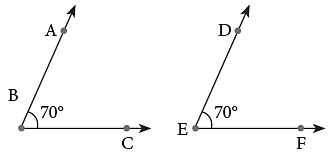 This means either angle can fit exactly over the other angle.
This means either angle can fit exactly over the other angle.
Parallel Lines
Parallel Lines are lines that lie on the same plane and never meet, even if they are extended endlessly in both directions.
Parallel lines are always the same distance apart. The symbol || is used to show ‘‘is parallel to’’.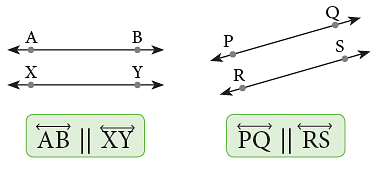 Here, Line AB is parallel to line XY and line PQ || line RS. The following are some of the representations of parallel lines in our everyday life.
Here, Line AB is parallel to line XY and line PQ || line RS. The following are some of the representations of parallel lines in our everyday life.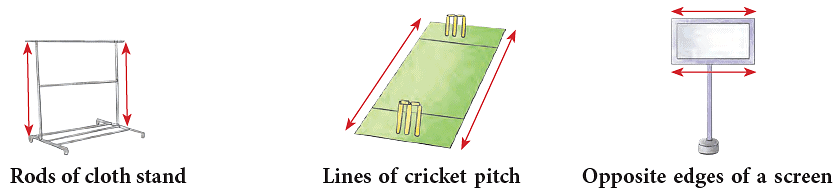
1. Intersecting Lines
Intersecting Lines are lines that cross each other at a point.
The following are some of the representations of intersecting lines in our everyday life.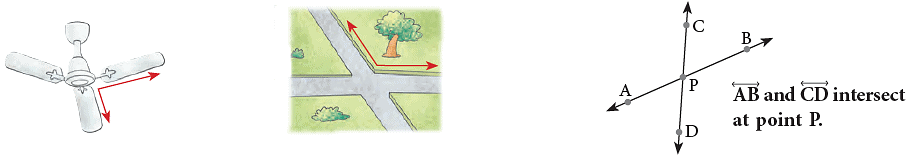 The letter X is also an example of intersecting line segments.
The letter X is also an example of intersecting line segments.
2. Perpendicular Lines
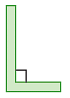
When two intersecting lines meet to form right angles, they are called perpendicular lines.
They are indicated by the symbol 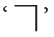 (a square corner) in the diagrams.
(a square corner) in the diagrams.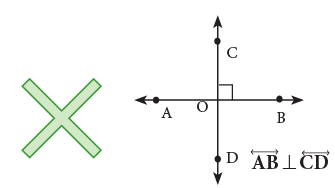 Line AB is perpendicular to line CD and is written in short as
Line AB is perpendicular to line CD and is written in short as 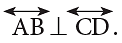
⊥ is the symbol for ‘‘is perpendicular to’’.
|
58 videos|122 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Lines, Angles and Triangles / Geometry Class 5 Notes Maths
| 1. What is the difference between a point, a line, a line segment, and a plane? |  |
| 2. How do you define an angle in geometry? |  |
| 3. What are parallel lines and how are they related to each other? |  |
| 4. Can two lines intersect at more than one point? |  |
| 5. How can you determine if two lines are parallel or perpendicular? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|
 The measure of one part is called one degree or 1°.
The measure of one part is called one degree or 1°.
















