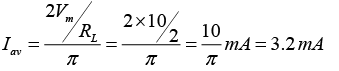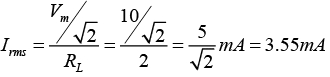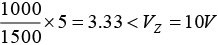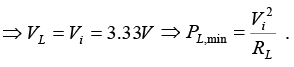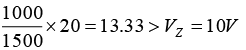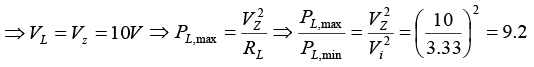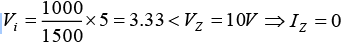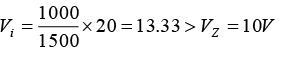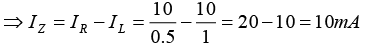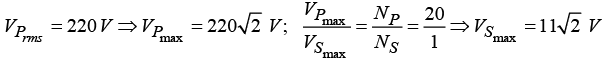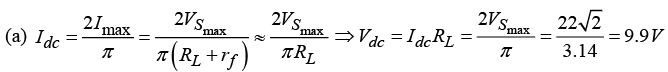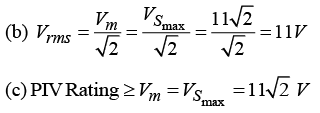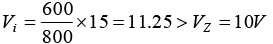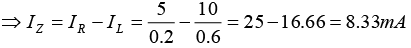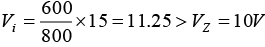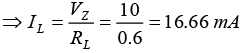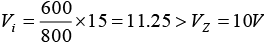P-N Junction Diode: Assignment | Solid State Physics, Devices & Electronics PDF Download
Q.1. An abrupt p-n junction diode is formed with two sides of resistivities 2 Ωcm in the p -side and 1 Ωcm on the n-side at temperature 300 K . Find the height of the potential energy barrier for Ge. (μn = 3800 cm2/Vs, μP = 1800 cm2/Vs, and ni = 2.5x1013 cm-3)
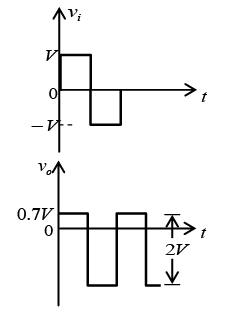
Q.2. Draw output waveforms for the circuit given below.
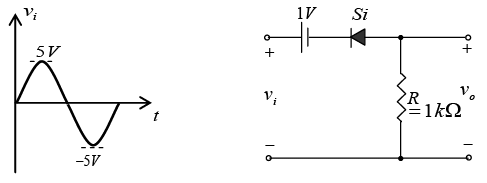
Let id = 0 and vd = -0.7V.
For transition voltage, apply KVL in input section
-vi + 1 - 0.7 + 0 = 0 ⇒ vi = 0.3V = VT
Thus if vi < 0.3 V, diode is ON and if vi > 0.3V, diode is OFF.
If vi = 0
0 + 1 - 0.7 + v0 = 0 ⇒ v0 = -0.3V
If vi = -5V
+ 5 + 1 - 0.7 + v0 = 0 ⇒ v0 = -5.3V
Q.3. A diode at room temperature (kT = 0.025eV )with a current of 1μA has a forward bias voltage VF = 0.4V. Find the diode current when VF = 0.5.
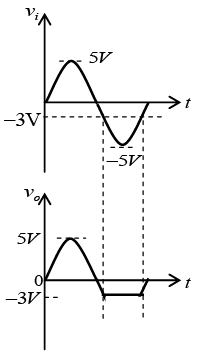
Q.4. A sine wave of 5V amplitude is applied at the input of the circuit shown in the figure. Draw output waveforms for the circuit given below. (Assume diode is ideal)
If Vin > -3V, diode is OFF and V0 = Vin.
If Vin < -3V, diode is ON and V0 = -3V
Q.5. (a) Consider a Si diode with η = 1.5 . Find the change in voltage if the current changes from 0.1 mA to 10 mA at 300 K.
(b) Consider a Si diode with η = 1 has v = 0.7V at i = 1 mA . Find the voltage drop at i = 0.1 mA and i = 10 mA at 300 K.
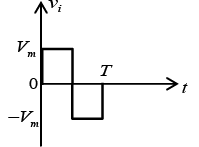
Q.6. Draw output waveforms for the circuit given below.
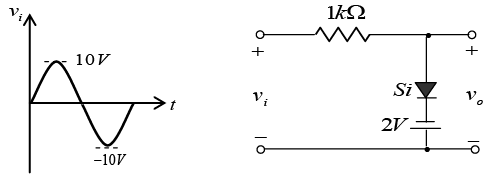
Let id = 0 and vd = 0.7V.
For transition voltage, apply KVL in input section -vi + 0 + 0.7 - 2 = 0 ⇒ vi = -1.3V = VT
Thus if vi > -1.3V, diode is ON then v0 = -1.3V and if vi < -1.3V, diode is OFF.
v0 = vi
Q.7. The circuit shown in figure has two oppositely connected ideal diodes in parallel. Assume diodes are ideal.
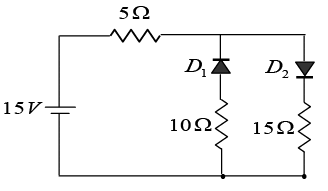
(a) Find current through diode D1.
(b) Find current through diode D2.
Diode D1 is OFF and diode D2 is ON.
Thus current through diode D1 is 0 A and
Thus current through diode D2 is
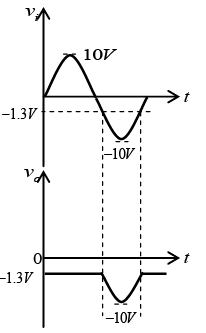
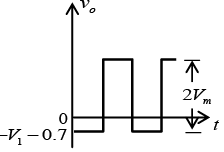
Q.8. Draw output waveforms for the circuit given below take |Vm| >|V|.
(Assume diodes to be ideal)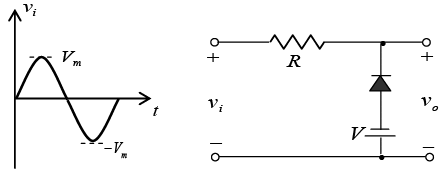
Let id = 0 and vd = 0V.
For transition voltage, apply KVL in input section -vi + 0 + 0 - V = 0 ⇒ vi = -V = VT
Thus if vi > -V, diode is OFF then v0 =vi
and if vi < -V, diode is ON then v0 = -V.
Q.9. For the circuit shown in figure below
(a) Find current through diode.
(b) Find output voltage Vo.
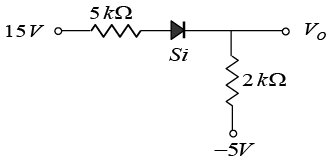
(a) Under given biasing condition diode is ON. Let current through 5 kΩ resistance
is I.
Apply KVL in the input section,
-15 + I x 5k + 0.7 + I x 2k - 5 = 0 ⇒ I = (19.3/7) mA = 2.76mA
(b) V0 = 2.76 x 2 - 5 = 0.51V
Q.10. Draw output waveforms for the circuit given below (RC >> T/2).
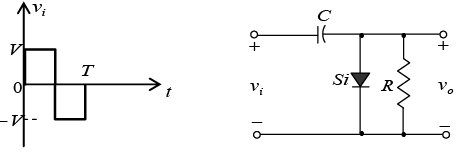
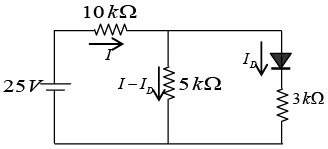
Q.11. In the following circuit, the voltage drop across the diode in forward bias condition ism 0.7 V. Find the current I and ID.
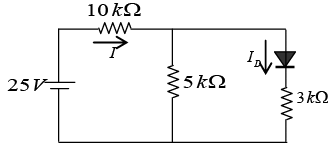
Apply KVL in two loops
-25 + I x 10 + (I-ID) x 5 = 0 ⇒ 15I - 5ID = 25 ...(i)
0.7 + ID x 3 -(I-ID) x 5 = 0 ⇒ 5I - 8ID = 0.7 ...(ii)From (i) and (ii), I = 2.06 mA and ID = 1.21mA.
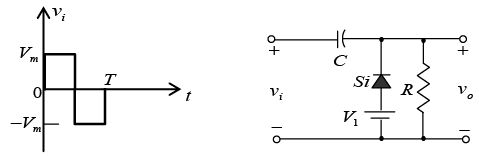
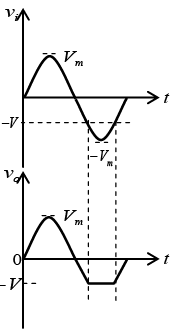
Q.12. Draw output waveforms for the circuit given below (RC >> T/2). Take |Vm| > |V1|.
Q.13. The I - V characteristics of the diode in the circuit below is given by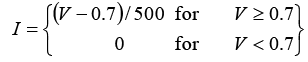
where V is measured in volts and I is measured in amperes. 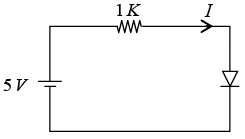
Find the current I in the circuit.
Applying K.V.L.
-5 + 1000 x I + V = 0 ⇒ -5 + 1000 x (V - 0.7)/500 +V = 0
⇒ -5 + 2 (V - 0.7) + V = 0 ⇒ 3V = 6.4 ⇒ V = 2.13 Volts
Thus I = (V - 0.7)/500 = (2.13 - 0.7)/500 = 1.43/500 = 2.86 mA
Q.14. Draw output waveforms for the circuit given below (RC >> T/2). Take |Vm| > |V1|.
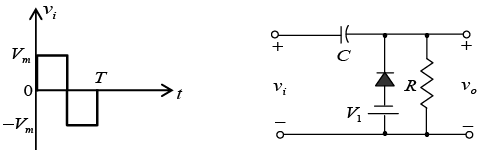
Q.15. An a.c. supply of 220 V, 50 Hz is applied to a half wave rectifier circuit through a transformer of turn ratio 5 :1 . The forward resistance of the diode is 100 Ω and the load
resistance is 5 kΩ.
(a) Find output d.c. voltage.
(b) Find r.ms. value of the output voltage.
(c) What should be PIV rating of the diode?
Q.16. Consider the circuit shown in figure below.
(a) Find the maximum Zener current IZ,max, when RL = 2kΩ.
(b) Find the minimum Zener current IZ,min, when RL = 4kΩ.
(c) Find IL and IZ with Vin = 22V and RL = 2kΩ.
(d) Find the power dissipated across the Zener when RL = 5kΩ and Vin = 20V.
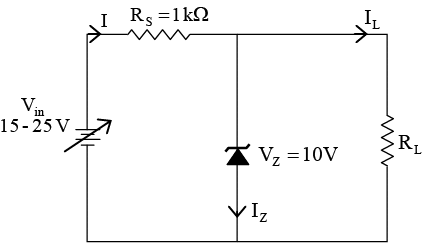
⇒ PZ = VZIZ = 10 x 8 = 80mW
Q.17 For the rectifier circuit shown in the figure, the sinusoidal voltage ( V1 or V2) at the output of the transformer has a maximum value of 10 V. The load resistance RL is 2 kΩ.
(a) Find the average current Iav through the resistor RL.
(b) Find the rms current Irms through the resistor RL.
(c) What should be PIV rating of the diode?
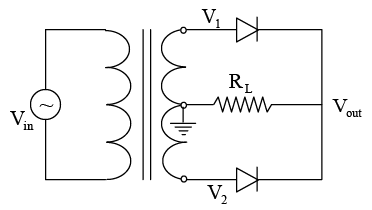
(a)
(b)
(c) PIV Rating ≥ 2Vm = 20V
Q.18. A variable power supply (5V - 20V) is connected to a Zener diode specified by a breakdown voltage of 10 V (see figure).
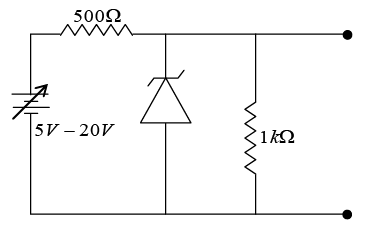
(a) The ratio of the maximum power to the minimum power dissipated across the load
resistor.
(b) Find the minimum power dissipated across the zener diode.
(c) Find the maximum power dissipated across the zener diode.
(a) When V = 5V ⇒ open circuit voltage Vi =

When V = 20V ⇒ open circuit voltage Vi =(b) When V = 5V ⇒ open circuit voltage

⇒ Pz,min = VZIZ = 0.
(c) When V = 20V ⇒ open circuit voltage
⇒ Pz,max = VZIZ = 10 x 10 = 100mW
Q.19. An a.c. voltage of 220 V , 50 Hz is applied to the primary of a 20 :1 step down transformer. The secondary of the transformer is bridge type and connected to a full wave rectifier with a load resistance 500Ω. Forward resistance of the diode is 10Ω.
(a) Find output d.c. voltage.
(b) Find r.ms. value of the output voltage.
(c) What should be PIV rating of the diode?
Q.20. The figure below shows the current voltage characteristics of a diode over a range of voltage and current where it is safe to operate the diode.
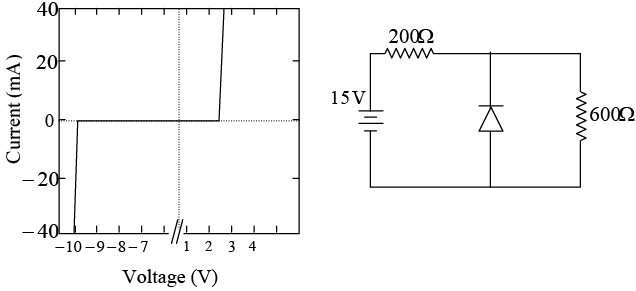 (a) Find the approximate diode current, in mA .
(a) Find the approximate diode current, in mA .
(b) Find the approximate current, in mA , through the 600 Ω resistance.
(c) Find the approximate current, in mA , through the 200 Ω resistance.
Characteristics shows that the diode used is a zener diode.
(a) Open circuit voltage
(b) Open circuit voltage
(c) Open circuit voltage
⇒ IR = 5/0.2 = 25mA
|
91 videos|21 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on P-N Junction Diode: Assignment - Solid State Physics, Devices & Electronics
| 1. What is a P-N junction diode? |  |
| 2. How does a P-N junction diode work? |  |
| 3. What is the forward voltage drop of a P-N junction diode? |  |
| 4. What are the applications of P-N junction diodes? |  |
| 5. What is the breakdown voltage of a P-N junction diode? |  |
|
91 videos|21 docs|25 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
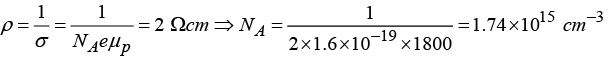
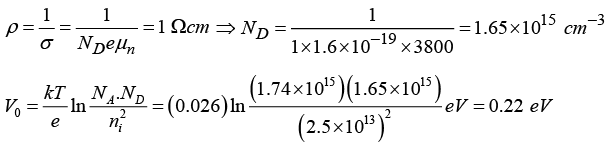
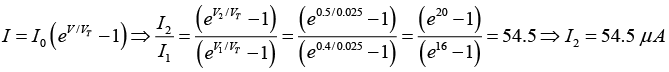
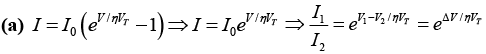
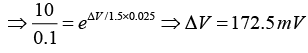
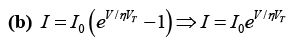
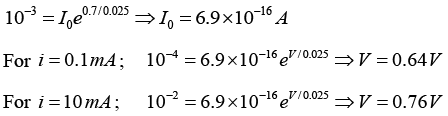
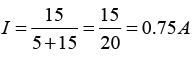
 Apply KVL in two loops
Apply KVL in two loops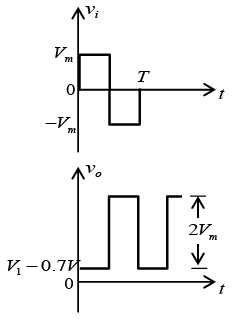
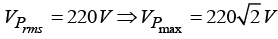
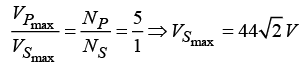
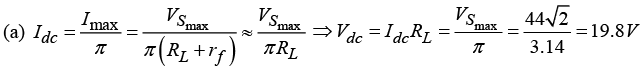
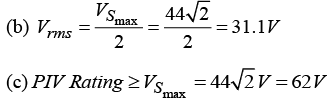
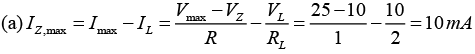
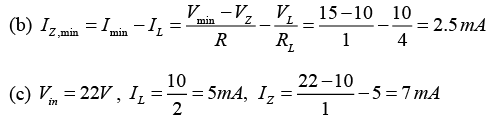
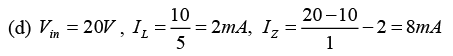 ⇒ PZ = VZIZ = 10 x 8 = 80mW
⇒ PZ = VZIZ = 10 x 8 = 80mW