Practice Questions & Answers: The Cold War Era | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark]
Q.1. Why was the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation also called Western Alliance?
Ans. The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation was an association of twelve states. All these states belonged to western Europe. Therefore, this association was also called Western Alliance.
Q.2. Name the two superpowers responsible for the Cold War. When did the world become unipolar?
Ans. The US and USSR were responsible for the Cold War. The world became unipolar in 1991 after the disintegration of USSR.
Q.3. What does the USSR stand for?
Ans. Union of Soviet Socialist Republic.
Q.4. When did NATO and WARSAW PACT come into existence?
Ans. NATO: April 1949
WARSAW PACT: 1955
Q.5. Mention the period of the first and second World War.
Ans. First World War: 1914-1918
Second World: 1939-1945
Q.6. What is meant by the cold War?
Ans. Cold War is a state of extreme unfriendliness existing between two superpowers especially with opposing political system which expresses itself not through fighting but through political pressures and threats.
Q.7. “Non-alignment does not imply neutrality or equidistance.” What does this statement mean?
Ans. Neutrality refers to a policy of staying out of war and not to help end a war. Non-aligned states including India worked to prevent wars and rivalries between others.
Q.8. What was deterrence relationship between superpowers?
Ans. Deterrence relationship refers that both sides have the capacity to retaliate against an attack and to cause so much destruction that neither can afford to initiate war.
Q.9. How did superpowers maintain arms- control?
Ans. Superpowers maintained arms control by signing significant agreements within a decade as Limited Test Ban Treaty, Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty, Anti- Ballistic Missile Treaty and hold several rounds of arms limitation talks.
Q.10. What do you understand by Least Developed Countries?
Ans. Majority of NAM members were categorised as Least Developed Countries (LDCs) to be more developed economically and to lift their people out of poverty.
Q.11. What was the difference in the ideology of Western Alliances and that of Eastern Alliances?
Ans. The Western Alliance headed by the US represented ideology of liberal democracy and capitalism while the eastern alliance headed by Soviet Union committed to socialism and communism.
Q.12. What was India’s policy of Non-alignment?
Ans. India’s policy of Non-alignment was not a policy of ‘fleeing away’ instead India was in favour of actively intervening in world affairs to soften Cold War rivalries and prevented differences from escalating into a full scale war.
Q.13. Why did India not join either of the two camps during the Cold War?
Ans. India did not join either of the two camps during the Cold War because India played an active role in mediating between the two rival alliances for the sake of peace and stability. Their strength was based on unity of NAM members and their resolve to remain non-aligned despite the attempts and made by two superpowers to bring them into their alliances.
Q.14. How were the military alliances beneficial to smaller nations during the Cold War?
Ans. Smaller nations got the promise of protection, weapons and economic aid against their local and regional rivals. A state was supposed to remain tied to its protective superpowers to unite influence of other superpower and its allies.
Q.15. Name any two foreign leaders along with the countries they belonged to, who are recognised as the founders of NAM.
Ans. Yugoslavia’s Josip Broz Tito; Egypt’s leader Gamal Abdel Nasser.
Q.16. What was Limited Test Ban Treaty (LTBT)?
Ans. It was arms control treaty between superpowers. It banned nuclear weapon tests in the atmosphere, in outer space and under water. It was signed by the US, UK and USSR in Moscow on 5 August, 1963. It entered into force on 10 October, 1963.
Q.17. When and where the first NAM Summit was held?
Ans. The first NAM Summit was held in Belgrade in 1961 and it was attended by 25 member states.
Short Answer Type Questions [2 Marks]
Q.1. What is meant by the Cuban Missile Crisis?
Ans. Cuba was an ally of the Soviet Union and received both diplomatic and financial aid from it. In 1962, Soviet Union placed nuclear missiles in Cuba to convert it into a Russian base. This move fired the US. It ordered American warships to intercept any Soviet ships heading to Cuba as a way of warning the USSR of its seriousness. A clash seemed imminent in what came to be known as the Cuban Missile Crisis.
Q.2. What was the main objective of New International Economic Order?
Ans. The main objective of NIEO was to develop more to Least (Economic)
Developed countries of NAM and to lift them out of poverty by their sustainable development.
Q.3. Mention two military features of the Cold War.
Ans.
- Cold War divided the world into two divisions namely Western and Eastern alliances as well as SEATO and CENTO.
- Mad arms race had taken to manufacture atom bomb and nuclear weapons by Super Powers of the world.
Q.4. Explain Eastern and Western alliance during Cold war.
Ans.
- Cold War gave birth to Eastern Alliance known as Warsaw Pact headed by Soviet Union in 1955 with the principal function to counter NATO’s forces.
- Cold War created Western Alliance known as NATO in April 1949 by association of twelve states. Its policy was that an armed attack on any one of them would be regarded as an attack on all of them and everybody would be obliged to help each other.
Q.5. When did NATO come into existence? How many states joined it?
Ans. NATO came into existence in April 1949 and twelve sca+ joined it.
Q.6. Name any two arms control treaties signed between two superpowers in 1960s.
Ans.
- Limited Test Ban Treaty (5 August, 1963)
- Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty (1 July, 1960)
Q.7. Name two leaders who played crucial role in Cuban Missile Crisis.
Ans.
- Nikita Khrushchev—Leader of Soviet Union
- John F. Kennedy—US President
Q.8. Explain any four objectives on Non- aligned Movement.
Ans.
- NAM aimed at an end of colonisation and freedom to all nations.
- NAM promoted and maintained international peace and security.
- NAM aimed at removal of disparity among developed, poor and very small countries.
- NAM aimed at promotion of New International Economic Order to encourage cooperation among nations.
Q.9. Mention any four important events which took place during Cuban Missile Crisis.
Ans.
- In 1962, USSR installed Missiles in Cuba with intention to convert it into Russian base.
- America became aware of it and as a warning ordered American warship to intercept Soviet ships moving to Cuba.
- The US was feared of developing nuclear weapons on part of the USSR to challenge supremacy of the US.
- The Cuban Crisis divided the world into two power blocs to expand their own spheres of influence in the world.
Q.10. Who was the key leader of NAM who tried to reduce the Cold War conflicts?
Ans. Pt. Jawahar Lai Nehru was the key leader of NAM who played a crucial role in mediating between two Koreas. Nehru appealed for reduction of Cold War conflicts and the establishment of world peace and security through co-operative disarmament.
Q.11. Why were most of the countries categorised as Least Developed Countries?
Ans.
- The economic development of these countries was very low.
- They were dependent on richer countries for their sustainable development.
- Their natural resources were being exploited by developed countries.
- They could not participate in international economic institutions and they had a little say, if participated.
Short Answer Type Questions [4 Marks]
Q.1. Why did India distance itself from the two camps led by the U.S. and the Soviet Union? Explain.
Ans. The end of the Second World War was the beginning of the Cold War between the two superpowers of the world, namely the US and the USSR. These two superpowers were keen on expanding their spheres of influence in different parts of the world. Most countries of western Europe sided with the US and those of eastern Europe joined the USSR. But India kept a distance from these superpowers. It means, it became a member of the non-alignment-movement by not joining either alliance. Non-alignment was not a noble international cause which had little to do with India’s real interests. A non-aligned posture also served India’s interests very directly, in at least two ways.
- Non-alignment allowed India to take international decisions and stances that served its interests rather than the interests of the superpowers and their allies.
- India was often able to balance one superpower against the other. If India felt ignored or unduly pressurised by one superpower, it could tilt towards the other. Neither alliance system could take India for granted or bully it.
Q.2. “The drop of bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki by the US was a political game.” Justify the statement.
Ans. The Second World War ended when the United States dropped two atomic bombs on Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945 causing Japan to surrender. Moreover, this action was criticised on the ground that the US knew that Japan was about to surrender and dropping of bombs was not necessary. US action was intended to stop Soviet Union from making military and political gains in Asia and elsewhere and to show that the US was supreme.
Q.3. Explain the Cuban Missile Crisis.
Ans. In 1962, Soviet Union decided to convert Cuba into a Russian base as it provided USSR diplomatic and financial aid both. Hence, Soviet Union placed nuclear missiles in Cuba. The US became aware of it and ordered American warships to intercept to Soviet Union to remove missiles to avoid full scale nuclear war. A clash seemed imminent what came to be known as Cuban Missile Crisis.
Q.4. Name any two founders of Non-aligned Movement. The first NAM summit was the culmination of which three factors?
Ans. Two founders of Non-aligned Movement were:
- Indonesia’s Sukarno and
- Ghana’s Kwame Nkrumah
The first NAM was held in Belgrade in 1961. This was the culmination of following three factors:
- Cooperation among member countries.
- Growing cold war tensions and its widening arenas.
- The dramatic entry of many new decolonised African countries into international arena.
Q.5. What is the rationale of Non-aligned movement after the end of Cold War?
OR
Which core values keep non-alignment relevant even after Cold War has ended?
Ans. The Non-aligned Movement was based on a recognition that decolonised states shared a historical affiliation and can become powerful force if they come together. It meant that very small and poor countries need not become followers of any big power, instead they could pursue an independent foreign policy also. It was based on a resolve to democratise the international system to redress existing inequities also.
Q.6. “Non-alignment posture was in the interest of India”. How?
Ans. Non-alignment posture was in the interest of India because:
- Non-alignment allowed India to take international decisions to serve her own interests.
- India maintained a balance between two superpowers as if India felt ignored by one. India would tilt towards other superpower.
Q.7. How did deterrence relationships prevent war between two superpowers?
Ans.
- Even if one of them tries to attack and disable the nuclear weapons of its rivals, the other would still be left with enough nuclear weapons to inflict unacceptable destruction.
- Both sides have capacity to retaliate against an attack and to cause so much destruction that neither can afford to initiate war.
- Both superpowers were expected to behave more rationally and in responsible manner in the sense that they understood the risks in fighting wars which may create a massive destruction.
Passage Based Questions [5 Marks]
Q.1. Read carefully the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The Cold War was not simply a matter of power rivalries, military alliances and of balance of power. These were accompanied by a real ideological conflict as well, a difference over- the best and most appropriate way of organising political, economic and social life all over the world.
Questions
(i) Why is a war like situation called Cold War?
(ii) Identify one military pact each signed by each of the two super powers to balance the power rivalries.
(iii) Differentiate between the ideologies represented by the rival blocs.
Ans.
(i) The Cold War referred to the competition, the tensions and a series of confrontations between the US and Soviet Union. It never escalated into a hot war, i.e. a full-scale war between these two powers.
(ii) The US and USSR decided to collaborate in limiting or eliminating certain kinds of nuclear and non-nuclear weapons.
(iii) A stable balance of weapon, they decided, could be maintained through ‘arms control’. Starting in the 1960s, the two sides signed significant agreements, namely, Limited Test Ban Treaty and Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
(iv) The Western alliance, headed by the US, represented the ideology of liberal democracy and capitalism while the eastern alliance, headed by the Soviet Union, was committed to the ideology of socialism and communism.
Q.2. Read the passage (NCERT Textbook, pages 2-3) given below carefully and answer the questions:
In April 1961… the Soviet Union were worried that the United States of America would invade communist ruled Cuba and overthrow the Cuban President Fidel Castro…. Nikita Khrushchev, the leader of Soviet Union, decided to convert Cuba into a Russian base. In 1962, placed nuclear missiles… Three weeks after the Soviet Union had placed the nuclear weapons in Cuba, the Americans became aware of it. They became reluctant to do anything that might lead to full scale war between the two countries… A clash seemed imminent in what came to be known as “Cuban Missile Crisis”. The prospects of this clash made the whole world nervous.
Questions:
(i) Why was the Soviet Union worried about America invading Cuba?
(ii) In response to the action taken by America, what did Nikita Khrushchev do?
(iii) Why were the two superpowers reluctant to start nuclear war?
Ans.
(i) The Soviet Union was worried about America invading Cuba that the US world overthrew Cuban President Fidel Castro to capture power in Cuba.
(ii) They became reluctant to do anything that might lead to full scale war between the two countries.
(iii) The two superpowers became reluctant because both of them knew that it might lead only a massive destruction and will not justify any gain for them.
Q.3. Read the passage given below carefully and answer the questions:
The Western alliance was formalised into an organisation, the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO), which came into existence in April 1949. It was an association of twelve states which declared that armed attack on any one of them would be regarded as an attack on all of them. Each of these status would be obliged to help each other. The eastern alliance known as the Warsaw Pact was led by Soviet Union, created in 1955 and its principal function was to counter NATO’s forces in Europe.
Questions:
(i) What does NATO stand for?
(ii) What was NATO’s policy?
(iii) What was Warsaw Pact?
(iv) Mention the main function of Warsaw Pact.
Ans.
(i) NATO stands for North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
(ii) NATO was an association of twelve states which declared that armed attack on any one of them would be regarded as an attack on all of them and each of them would be obliged to help each other.
(iii) Warsaw Pact was eastern alliance, led by Soviet Union, created in 1955.
(iv) Main function of Warsaw Pact was to counter NATO’s forces in Europe.
Long Answer Type Questions [6 Marks]
Q.1. Describe any six factors responsible for the disintegration of USSR.
OR
What is meant by the New International Economic Order? Mention any four reforms of the global trading system proposed by UNCTAD in 1972.
Ans. Six factors responsible for the disintegration of USSR are —
- The internal weaknesses of Soviet political and economic institutions failed to meet the aspirations of the people.
- Economic stagnation for many years led to severe consumer shortages and a large section of Soviet society began to doubt and question the system and to do so openly.
- The Soviet Union had become stagnant in an administrative and political sense as well. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people. Ordinary people were alienated by slow and stifling administration, rampant corruption, the inability of the system to correct mistakes it had made, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government and the centralisation of authority in a-vast land.
- The Soviet economy used much of its resources in maintaining a nuclear and military arsenal and the development of its satellite states in Eastern Europe and within the Soviet system. This led a huge economic burden that the system could not cope with.
- When Gorbachev became the President, he carried out reforms and loosened the system. He set in motion forces and expectations that few could have predicted and became virtually impossible to control. There were sections of Soviet society which felt that Gorbachev should have moved much faster and were disappointed and impatient with his methods. Others, especially members of the Communist Party and those who were served by the system, took exactly the opposite view. In this tug of war, Gorbachev lost support on all sides.
- The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics, Ukraine, Georgia, and others proved to be the final and most immediate cause for the disintegration of the USSR.
The non-aligned countries were more than merely mediators during the’ Cold War. The challenge for most of the non-aligned countries — a majority of them were categorised as the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) — was to be more developed economically and to lift their people out of poverty. Economic development was also vital for the independence of the new countries. Without sustained development, a country could not be truly free.
It would remain dependent on the richer countries including the colonial powers from which political freedom had been achieved. The idea of a New International Economic Order (NIEO) originated with this realisation. The UNCTAD brought out a report in 1972 entitled Towards a New Trade Policy for Development. The report proposed a reform of the global trading system so as to:
- Give the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) control over their natural resources exploited by the developed western countries.
- Obtain access to western markets so that LDCs would sell their products and, therefore, make trade more beneficial for the poorer countries.
- Reduce the cost of technology from the western countries, and
- Provide the LDCs with a greater role in international economic institutions.
Q.2. What led to the emergence of bipolar world? What were the arenas of Cold War between the two power blocs?
Ans. Emergence of bipolar world:
- Two superpowers expanded their own spheres of influence in different parts of the world.
- It divided the world into two alliances namely Western and Eastern alliance headed by the US and Soviet Union respectively.
- The smaller states in alliances got the promise of protection of weapons and economic aid against their local rivals, hence they remained tied to its protective superpowers to limit influence of other superpower and its allies.
Arenas of Cold War:
- Crisis and war occurred between alliance systems but did not cross certain limits.
- Many lives were lost in Korea, Vietnam and Afghanistan, but world was spared from nuclear war and global hostilities.
- The Cold War led to several shooting wars but it did not lead to another World War despite direct confrontations in Korea (1950-53), Berlin (1958-62) and the Congo (the early 1960s).
Q.3. How did Europe become main arena of conflict between the superpowers?
Ans.
- Superpowers used their military power to bring countries into their respective alliances.
- Soviet Union used its influence in Eastern Europe so that the eastern half of Europe remained within its sphere of influence.
- In East and Southeast Asia and in West Asia, the US built an alliance called South East Asian Treaty Organisation (SEATO) and the Central Treaty Organisation (CENTO).
- The Soviet Union responded by having close relations with regional countries such as North Vietnam, North Korea and Iraq.
Q.4. “India’s policy of non-alignment was criticised on a number of counts.” Explain.
Ans. A non-aligned posture also served India’s interests very directly as well as India intervened in world affairs to soften cold war rivalries by reducing differences between the alliances and from escalating into a full scale war. Though India’s policy of non-alignment was criticised on a number of counts:
- India’s non-alignment was said to be ‘unprincipled’ in the name of persuing in national interest.
- India often refused to take firm stand on crucial international issues.
- Sometimes India took contradictory postures, having criticised others for joining alliances, Indian signed the Treaty of friendship in August 1971 with the USSR for 29 years
- During Bangladesh crisis also India developed good relations even with the US in the name of diplomatic and military support.
Q.5. Explain various arms control treaties.
OR
Define the various treaties to control arms.
Ans.
- Limited Test Ban Treaty: Banned nuclear weapon tests in the atmosphere, in outer space and under water signed by the US, UK and USSR in Moscow on 5 August 1963 came into force on 10 October, 1963.
- Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty: It allows only nuclear weapon states to have nuclear weapons and stops others from acquiring them. A nuclear weapon state is one which had manufactured and exploded nuclear explosive device prior to 1 January, 1967. So there are five nuclear weapon states: US, USSR, Britain, France and China.
- Strategic Arms Limitation Talks I and II (Salt I and II): The first round began in November 1969. The Soviet Union leader Leonid Brezhnev and the US President Richard Nixon signed the following in Moscow on 26 May 1972 - (a) Anti Ballistic Missile System Treaty, (b) Interim Agreement on limitation of strategic offensive arms.
- It came into force on 3 October, 1972. The second round started in November 1972. The US President Jimmy Carter and the Soviet leader Brezhnev signed Treaty on limiting strategic offensive arms in Vienna on 18 June, 1979.
- Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty I and II (START I and II): Treaty I signed by the USSR president Mikhail Gorbachev and the’ US president George Bush (Senior) on the reduction and limitation of strategic offensive arms in Moscow on 31 July 1991.
- Treaty II was signed for same purpose in Moscow on 3 January, 1993 between Russian President Boris Yeltsin and the US President George Bush (Senior).
Map Based Questions [5 Marks]
On the political map of world locate and level the following by giving symbols to them
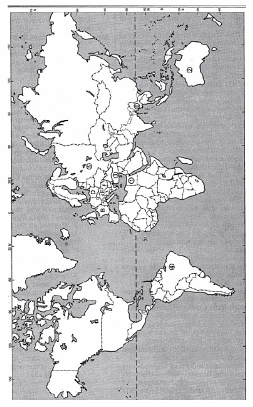
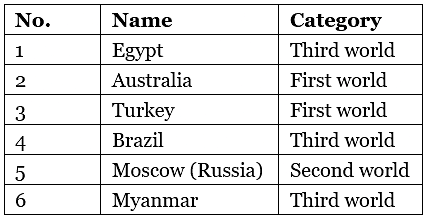
Q.1. Study the given map of the world in which six different countries have been marked 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Identify these countries with their names and classify them as first, second, third world countries.
Ans.
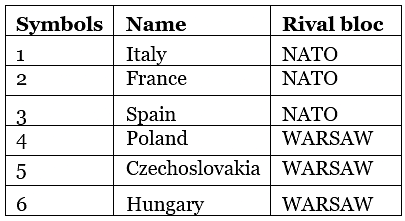
Q.2. Study the given map of the world in which six different countries have been marked 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Identify these countries with their names and classify them as first, second, third world countries.
Ans.
|
34 videos|246 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Practice Questions & Answers: The Cold War Era - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What was the Cold War era? |  |
| 2. What were the main causes of the Cold War? |  |
| 3. What were the major events of the Cold War? |  |
| 4. How did the Cold War affect other countries? |  |
| 5. How did the Cold War end? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|