Circles Class 5 Notes Maths
| Table of contents |

|
| Circle |

|
| Terms Related to Circle |

|
| Interior and Exterior of Circle |

|
| Drawing a Circle with Compass |

|
| Examples |

|
Have you ever noticed the wheels of your bicycle, the round face of a clock, or a yummy pizza? All of these things have something in common—they are circles! 
In this chapter, we will explore the magical world of circles. Get ready to have some fun while learning!
Circle
Circle
- A circle can be defined as a simple closed curve all of which points are equidistant (at an equal distance) from the fixed point called its centre.
- A bangle, a one-rupee coin and a cycle tyre are all examples of circular objects.

Terms Related to Circle
1. Centre
The fixed point in the centre of a circle is called its centre
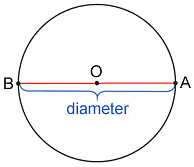
2. Diameter
- A Diameter is a line segment with endpoints on the circle that passes through the centre.
- In the picture given below,
the Diameter = AB
AB = (OA + OB) = 2 × OA or 2 × OB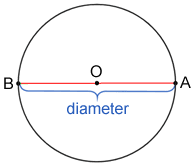
- The Radius is half of the Diameter.
Radius = (Diameter)/2 - This also implies that Diameter = 2 x Radius
3. Radius
- Radius is the distance between the centre of a circle and a point on the circumference.
- In the picture given below, the Radius = OA = OB
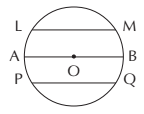
4. Chord
- A chord is a line segment whose endpoints lie on the circle.
- LM, PQ, and AB are all chords of the circle.
- The Diameter is the longest chord of the circle.
5. Arc
- Arc is any part of a circle.
- An arc is usually named by three points, two of which are the endpoints, and the third point lies between them. ABC is an arc and is denoted by
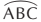 as shown in the picture below.
as shown in the picture below.
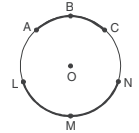
- Arcs are basically of two types,
(i) Minor Arc
(ii) Major Arc - The Minor Arc is shorter and the Major Arc is longer.
- ABC is a minor arc of the circle. LMN is a major arc of the circle.
 6. Circumference
6. Circumference
- Circumference is the perimeter or boundary of a circle.
- Circumference = 2 x π x r
= 2 x r x π
= diameter x π ( because diameter = 2 x radius )
Interior and Exterior of Circle
In this, we will see through a diagram about which points are interior and exterior point
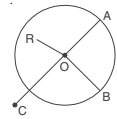
It is clear that
- R lies in the interior of the circle.
Thus, OR < OA. - C lies in the exterior of the circle.
Thus, OC > OA. - B lies on the boundary of the circle.
Thus, OA = OB.
Did You Know
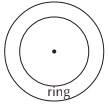
Concentric circles are circles with the same centre but different radii.
Drawing a Circle with Compass
- To draw a circle with a compass, fix a pointed pencil in the compass.
- Place a ruler on the table, fix the metal tip of the compass at 0 of the ruler and open the compass to fix the end of the pencil at the given measure (say = 3 cm.)
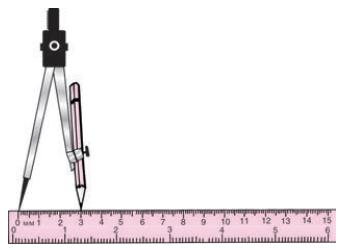
- Next, take a point ‘O’ on a plane paper and rest the metal tip of the compass at point ‘O’.
- Hold the head of the compass firmly and move the pencil around to form a circle of radius 3 cm.
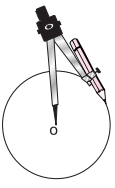
Examples
Example 1: Find the diameter of a circle whose radius is 1.4 cm.
Note: The region enclosed between two concentric circles is called a ring.
Sol: Radius = 1.4 cm
Diameter of a circle = 2 × radius = 2 × 1.4 cm = 2.8 cm.
Example 2: Find the radius of a circle whose diameter is 6.8 cm.
Sol: Diameter = 6.8 cm
Radius = Diameter ÷ 2 = 6.8 cm ÷ 2 = 3.4 cm.
Example 3: Find the circumference of a circle whose radius is (a) 7 cm (b) 3.5 cm. [Take π = 22/7]
Sol: (a) Radius = 7 cm
Circumference of the circle = 2 × π × radius = 2 × 22/7 × 7 = 44 cm.
(b) Radius = 3.5 cm = 7/2 cm.
Circumference of the circle = 2 × π × radius
= 2 × 22/7 x 7/2 cm = 44/2 = 22 cm.
Example 4: The length of the diameter of a circle is 2.8 cm. Find the circumference of the circle.
Sol: Diameter = 2.8 cm = 28/10 .
Circumference of the circle = π × diameter = 22/7 x 28/10
= 22 x 4/10 = 88/10
= 8.8 cm.
|
95 videos|462 docs|47 tests
|
FAQs on Circles Class 5 Notes Maths
| 1. What are the important terms related to a circle? |  |
| 2. How can we identify the interior and exterior of a circle? |  |
| 3. What steps should be followed to draw a circle with a compass? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a chord and a tangent in a circle? |  |
| 5. Can you give examples of real-life objects that resemble a circle? |  |