Weather, Water and Air Class 4 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Atmosphere? |

|
| Weather |

|
| Season |

|
| What Changes the Weather? |

|
| Water |

|
| Evaporation |

|
| Condensation |

|
| Humid Weather |

|
| Water Cycle |

|
Air, water, and weather are interconnected elements that play crucial roles in Earth's systems. 
- Air is essential for life. Oxygen in the air is vital for the respiration of humans, animals, and many other organisms.
- Water is a molecule composed of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom (H₂O). Water is crucial for life. It sustains ecosystems, supports various biochemical processes, and is a key player in weather patterns.
- Weather is the atmospheric conditions in a specific location at a particular time. It includes elements such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, and atmospheric pressure.
What is Atmosphere?
The atmosphere is like a protective blanket of air around the Earth. It keeps us warm, gives us air to breathe, and shields us from harmful things in space.

The primary components of air are nitrogen (about 78%), oxygen (about 21%), and trace amounts of other gases such as carbon dioxide, argon, and others. It also contains water vapor, dust particles, and various pollutants.
Weather
Weather is the day-to-day condition of the atmosphere. It includes elements such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind speed and direction, cloud cover, and atmospheric pressure. It reflects the short-term variations in the atmosphere, typically observed over hours to days.
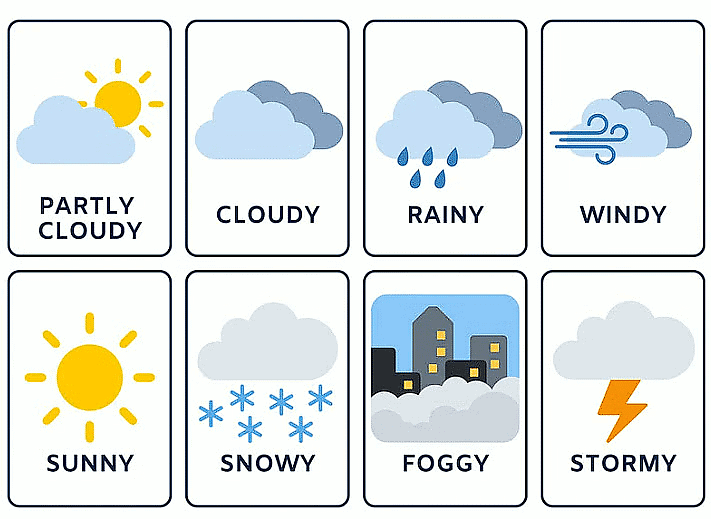 Different types of weather
Different types of weather
Season
Seasons are different times of the year when the weather and environment change in predictable ways. They happen because the Earth is tilted as it moves around the sun.
Let's see how seasons change
 There are four main seasons: spring, summer, autumn (fall), and winter.
There are four main seasons: spring, summer, autumn (fall), and winter.

What Changes the Weather?
They are caused mainly by the sun. Because of the rotation of the earth, and the revolution of the earth around the sun, different areas on the earth get heated differently. An area that faces the sun directly is heated more than the area that is at the back and does not receive sun rays directly.
 Revolution of Earth: Cause of Different Seasons
Revolution of Earth: Cause of Different Seasons
Sun Causes the Wind and Rain
When the sun shines brightly, it heats the ground. The air above the ground also becomes hot. Hot air is lighter than cold air. The hot air, therefore, rises. Cold air from the surrounding areas rushes to take its place. This causes the wind to blow. The heat of the sun changes water into water vapour. The water vapour upon cooling forms clouds. When the clouds become very heavy, they fall back on earth as rain.
Sun Causes Land and Sea Breezes
If you have gone to the seaside you will know that during the day, the wind blows from the sea to the land. At night, the wind blows from the land to the sea. Let us see why this happens.
1. Sea Breeze
- During the day, the land gets heated by the sun much quicker than water in the seas.
- As the land becomes warmer, it heats the air in the atmosphere above it.
This causes the air to become lighter and rise, creating a void or empty space just above the land. The water heats up at a much slower pace. - The air above sea takes longer to get heated up and is still cooler in comparison to the air above the land. This cooler and heavier air above the sea rushes towards the void created by the hot air above the land.
- This phenomenon causes a breeze to blow from the sea towards the land. This is known as a sea breeze.
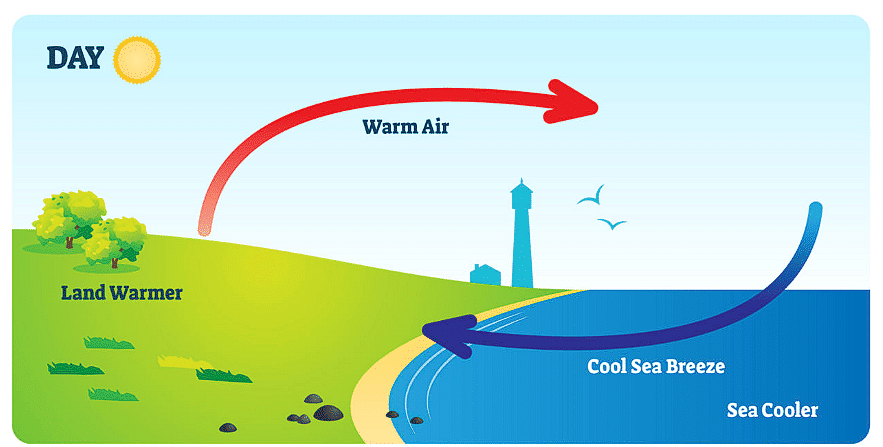 Sea Breeze
Sea Breeze
2. Land Breeze
- At night, the land cools down much faster than the sea. As the land becomes cooler, air above it also becomes cooler quickly.
- Since the sea is warmer than the land, the air above the sea also remains warmer.
- This warm air rises and now the cooler and heavier air above the land rushes towards the sea.
- This causes the breeze to blow from land towards the sea. This is referred to as land breeze.
 Land Breeze
Land Breeze
Water
Around 71% of the earth’s surface is covered with water. Water is found in rivers, seas, ponds, lakes and oceans. It is also present in the form of ice and glaciers. Water is also found underground. It is also present in the air. Water changes from one state to another due to heating and cooling.
Evaporation
The sun heats the water on the surface of the earth and changes it into water vapour. The process of change of water into water vapour is called evaporation.It is the process by which a liquid, such as water, changes into a gas or vapor.

- The sun evaporates water from oceans, lakes, rivers, ponds and soil.
Human beings also release water vapour into the air. The water from the pores in the human skin escapes and converts into vapour in the air. This is the reason why we feel very thirsty in summer. - Plants are also the sources of evaporation. Plants give out water vapour from their leaves.
- It is a key component of the water cycle, where water from oceans, lakes, and rivers evaporates into the atmosphere and later condenses to form clouds, ultimately leading to precipitation.
- The water is present in the air in the form of tiny droplets called moisture.
Factors Affecting Evaporation
Evaporation depends on many other things.

- Temperature: The high temperature makes clothes dry faster in the sun than in shade.
- Exposed area: The larger exposed area speeds up the evaporation. The clothes that are spread out dry faster than the ones that are folded.
- Wind: Blowing wind helps things to dry faster.
- Moisture: When there is less moisture in the air, clothes dry faster in summer. They take more time to dry in the rainy season when there is more moisture in the air.
Condensation
The process of changing water vapour into water due to cooling is called condensation.
Water condenses and returns to the ground in several ways.
If you take a look at the plants and flowers in cold mornings, you will see tiny drops of water on them. This is dew. It is formed when the temperature is low and water vapor condenses on cool objects in the form of droplets.
Frost is formed in very cold places where the temperature at ground level is lower than 0 degree and the dew turns into ice. It causes damage to crops.
Fog and mist are formed when small droplets of water suspend in the air. Fog is denser than mist. When the visibility is less than 1 km we call it ‘fog’, but when the visibility is greater than 1 km we call it ‘mist’.

Humid Weather
In the hot weather, you sweat a lot. When this sweat evaporates it makes you feel cool. When you sit under the fan, your sweat evaporates faster and you feel cooler. But if there is already a lot of water vapor in the air, the sweat cannot evaporate quickly. Such weather is called humid weather.
During the rainy season, the weather is often humid. Humidity refers to the amount of moisture or water vapor present in the air. The combination of rainfall and increased temperatures during the rainy season contributes to higher humidity levels.
Why do you feel very uncomfortable on a hot day during the rainy season?
Because during rainy season, it is very humid. Your sweat cannot evaporate quickly even under a fan, and you feel hot and uncomfortable.
Water Cycle
The water present on the earth keeps on moving between lakes, rivers, oceans and the atmosphere. It is known as water cycle.

- Evaporation: The sun heats up water from oceans, lakes, and rivers, turning it into water vapor (a gas).
- Condensation: The water vapor rises into the air and cools down, turning back into tiny water droplets. These droplets gather to form clouds.
- Precipitation: When the clouds become heavy with water droplets, they release the water as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
- Runoff: The precipitation on the ground may flow into rivers, lakes, or oceans, or it can be absorbed into the soil.
- Collection: The water that flows into rivers and oceans starts the process again by being heated by the sun and turning into water vapor through evaporation.
So, the water cycle is a continuous process where water moves between the Earth's surface, the atmosphere, and back again.
|
53 videos|44 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Weather, Water and Air Class 4 Notes Science
| 1. What is the atmosphere and why is it important for weather? |  |
| 2. How do water and evaporation affect weather changes? |  |
| 3. What is condensation and how does it relate to weather? |  |
| 4. What is humid weather and how does it impact daily life? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the water cycle and its significance in weather patterns? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 4 exam
|

|


















