Entrepreneurial Planning: Notes | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
What is Entrepreneurial Planning?
Enterprise planning is the process where a detailed study is conducted on various aspects of starting a business.
- A broad-level plan is laid down in terms of organizational structure, operational and production, financial, marketing, etc.
- In this chapter, we will discuss in detail various aspects of enterprise planning.
What are different forms of Business Entities?
Different forms of Business Entities are
- Sole Proprietorship
- Joint Hindu Family Business
- Partnership
- Cooperative Societies
- Joint Stock Company etc.
1. Sole Proprietorship
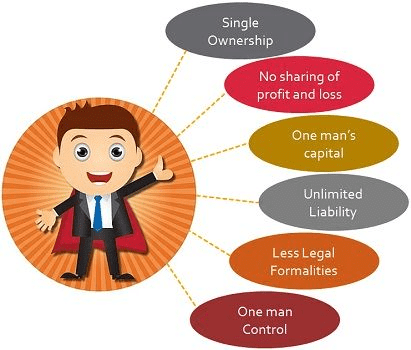
Sole proprietorship is a form of business, which is owned, managed, and controlled by an individual.
- It is the oldest and simplest form of business, established with the limited resources, ability, and capital.
- The business, if it is legal can be started anywhere, anytime at the sweet will of the individual. As such, a sole proprietorship is the form of business organization in which an individual introduces his own capital, uses his own skill in managing the affairs of the business, and is solely responsible for the result of the business operations.
 Sole Proprietorship
Sole Proprietorship
- The law does not make any distinction between the firm and the proprietor. The business and the businessmen are one and the same thing. In other words, the owner's personal property is also liable for business liabilities.
- If the business earns profit, the sole proprietor enjoys all the profit alone and if the business suffers a loss, it has to be borne by the sole trader himself.
In the words of Peterson and Plowman, "A sole proprietorship has no legal existence apart from the proprietor himself. He is the firm". It means that he has unlimited liability and even his personal property is always at stake for the payment of business debts and loans. - The sole proprietorship is also called sole trade, single ownership, single proprietorship, individual ownership and proprietorship, one-man business, etc. It has got the following important features.
2. Joint Hindu Family Business
Joint Hindu Family business is a form of business, which is owned by the members of a Joint Hindu family. It is also known as the Hindu undivided family business (HUF).

- It is a unique Indian business institution, governed by the provisions of Hindu law. It is managed by the head of the family, known as Karta, whose liability is unlimited.
- The liability of other members is limited. The male child attains the membership of the family business, since his birth in the family. It has the following special features.
3. Partnership
Sole proprietorship, as we know suffers from unlimited liability, limited resources, hasty decisions and temporary existence etc., so we tried to search for such a form of business organisation which could dispense with these demerits of sole proprietorship.
- As a remedy partnership emerged as a form of business organization.
- Definition of Partnership: Partnership as such is an agreement between two or more persons to carry on legal business with a profit motive, carried on by all or any one of them acting for all.
- According to the Indian Partnership Act, 1932 "Partnership is a relation between persons who have agreed to share the profit of the business carried on by all or any one of them acting for all".
4. Cooperative Societies
It was felt in the early nineteenth century that economic conditions of the weaker sections of the people can improve by cooperation not by competition.
- As such persons living in the same locality and having common needs join together in the form of association, known as the cooperative organization for mutual benefit.
- As this is a cooperative organization, the profit motive is missing and it is replaced by a service motive.
- In case there is surplus, it is distributed among members equitably honoring the principle of distributive justice.
- The dividend is paid on the basis of per member, not per share.
- Definition of Cooperative Societies: In the words of Saligman, "Cooperation in its technical sense means the abandonment of competition in distribution and production and elimination of middlemen of all kinds". In the words of Sir Horace Plankatte, "Cooperation is self-help made effective by the organization".
- According to International Labour Organization, "Cooperative is an association of persons usually of limited means, who have voluntarily joined together to achieve a common economic end through the formation of a democratically controlled business organization".
- As such cooperative societies are a voluntary association of persons having common needs joining together for mutual benefit.
5. Joint Stock Company:
The industrial revolution brought significant changes in the size of business structure. The unlimited liability and smaller size of business units could not meet the huge financial requirements of the modern business and provide limited liability to its individuals.
- The joint-stock company as a modern form of business emerged to meet the requirements of the large-sized business.
- Meaning of a Joint Stock Company: A joint-stock company is an artificial person, created by law with fixed capital, divisible into transferable shares, with perpetual succession and a common seal.
- The company has a separate legal entity. It must be compulsorily registered. The company is owned by shareholders, who subscribe to its shares.
- It is managed by the board of directors, the elected representatives of shareholders. In this way, the management and ownership are practically different. The company has permanent life, not at all affected by the death, insolvency, or lunacy of its members. The liability of the shareholders is limited to the face value of shares held by a particular shareholder.
- Definition of Company: According to Haney, "A joint-stock company is a voluntary association of persons for profit, whose capital is divided into transferable shares and ownership is required for its membership".
- In the opinion of Kimbal and Kimbel "Corporation by nature is an artificial person, which is created by law for a specific purpose."
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan may be defined as a written document of the business's future in terms of what you plan to do and how you plan to do it.
- In simple words, it is a broad-level strategy to start a business. There are 3 to 5 years of time horizons for preparing a business plan.
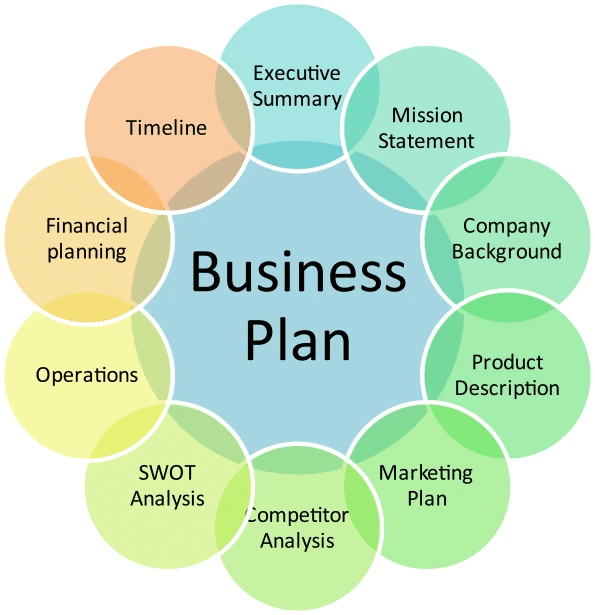
- Basically, detailed steps are put on a piece of paper in terms of where you intend to start and where you intend to reach after three to five years with a given level of resources and abilities.
- A business plan should be precise and lean and not necessarily be accurate. Instead of planning too much, a broad level structure should be laid down and changes be made as the entrepreneur progresses in implementing the plan.
However, in order to meet the challenges of carrying business and growing it, a good business plan is required which should have the following components:
- It should lay down the financial need of the business in terms of investment required for the business and expected return out of it year on a year basis.
- Strategy for business operation should be developed to give a firm direction to the business plan.
- A customer-oriented strategy should be in place in terms of what are the customer requirements and how it is going to be achieved.
- An effective monitoring plan should be prepared to identify the areas where achievements are less than expected and corrective steps can be taken.
- A business plan includes meticulous planning pertaining to organizational, operational and production, financial, marketing, and human resource planning. We will study each of them in detail in the coming paragraphs.
What is Organizational Planning?
Organizational planning depends on the forms of business selected by the entrepreneur.
- However, we need to understand that the initial phase of most entrepreneurs is to remain a low-cost organization.
- The need for a more formal and decentralized organization is felt once the business grows. We will study these stages as given below:
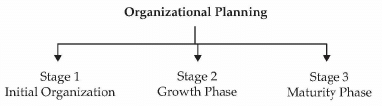
Stage 1: Initial Organization
This means that the initial organizational structure will be simple and decentralized.
- The entrepreneurs will most of the functions himself or herself with a bare minimum managerial and executive staff.
- There is also reluctance on part of the entrepreneur to delegate functions to others. Hence, the initial organization structure will be simple and centralized where most of the decision-making powers remain with the entrepreneur.
- This is also the first stage of the organization planning for an entrepreneur. In this phase, mostly the organization works as a proprietorship with one person managing and controlling most aspects of the business.
Stage 2: Growth Phase
The next stage comes when the business grows and the entrepreneur needs more managers and executives in the form of a helping hand to meet the demand of the growing business.
- Sub managers are hired to coordinate, organize and control the aspects of the business.
- Measurement, evaluation, rewards, training also becomes necessary at this stage. An entrepreneur needs to decentralize the organization at this stage in terms of delegating the authority to sub managers and tactical decision making and retaining the strategic decision making to himself or herself.
- An entrepreneur should put a formal structure of the organization with clear-cut authority and responsibility for each and every role. At this phase, the organization may change its form to either partnership or private limited company to give it a more formal structure as compared to a proprietorship.
Stage 3: Maturity Phase
This phase is reached when the firm is large enough to have a third level of managers.
- In this phase, the role of managers becomes important as he or she is required to adapt to changes in the environment.
- They have to evolve with new ideas and help entrepreneurs to achieve broad-level strategic objectives.
- The manager is also required to undertake the role of allocation of resources and handling pressures while maintaining the organization's progress in the right direction.
How to Build Organization Plan?
An entrepreneur should take the following steps in preparation of organization plan: - A structure needs to be built for broad-level organization where the roles and responsibilities are clearly defined.
- Job analysis should be done for each role to have the right candidate available for the job.
- An analysis should be performed to see what is the workload and how many people required to complete the organization structure already planned.
What is Production and Operational Planning?
Operational and production planning is one of the key components of business plan. We will study this in two parts namely production planning and operational planning.
Production Planning
The areas which need attention for production planning are the manufacturing process, physical plant, machinery and equipment, and names of suppliers of materials.
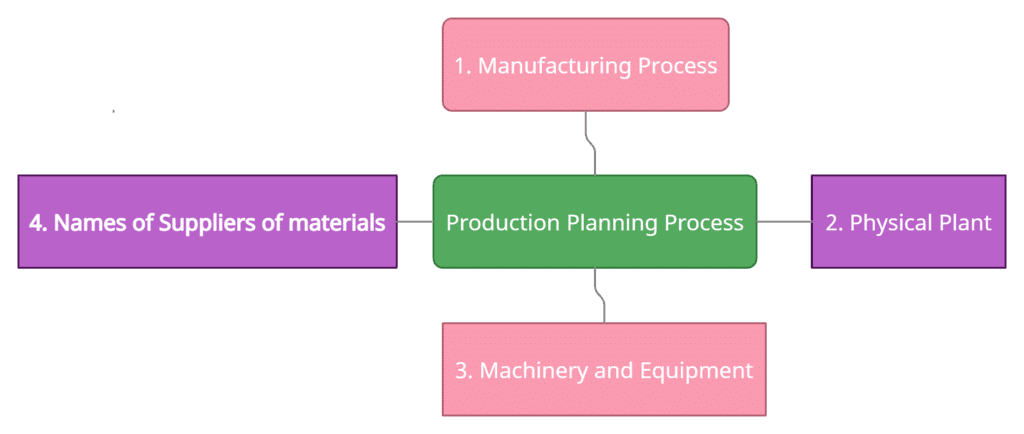
- Manufacturing Process: Under the manufacturing process, a key decision needs to be taken in terms of what should be manufactured by the entrepreneur himself or herself and what needs to be sub-contracted or outsourced. Generally, key processes like assembling; finishing, key components of the product are kept by the entrepreneur while ancillary items or components are sub-contracted. It also depends on the entrepreneur's willingness to keep full control of the manufacturing process or partial control. In a car manufacturing company, we see that the component manufacturing like steering, break, etc is subcontracted while the assembling, designing, finishing is done by the company itself.
- Physical Plant: Depending on the decision on sub-contracting and self-manufacturing, the entrepreneur has to devise a plan for setting up the physical plant. The plant capacity, location, layout, etc should be taken into consideration. Initially, the capacity should be low saved on the cost of managing a huge setup. However, the plant setup should be such that it is scalable to achieve higher production in case of surge in demand for the product in the market.
- Machinery and Equipment: The physical plant will consist of machinery and equipment which constitute the major part of plant infrastructure. An entrepreneur should plan as to which machinery in terms of technology should be installed in the plant. Installation of the machine will also depend on the decision that how much labor intensive or capital intensive plant is going to be. An entrepreneur may decide to go for capital intensive in which case the requirement of machines and equipment will be more as against labor-intensive where more labor is required than machines.
- Names of Suppliers of Materials: The suppliers of raw material needs to be identified. A competitive selection process should be applied in terms of the supplier who is ready to supply better quality raw material at competitive rates. It should also be seen that the supplier should have scalable infrastructure to increase supply if the demand for an entrepreneur's product rises in the market.
Operational Planning
- Operational planning mainly consists of defining the workflow and processes. A process may be defined as the list of activities that are required to be carried out to achieve an output of the products carried in the plant.
- These activities are interconnected to each other and there are separate roles and responsibilities assigned to the people in the organization. A workflow refers to the approval and authorization routes for the activities to be undertaken at a different stage of the production process.
- For example, if the raw material is required for the production process then a material requisition note is approved with the approval of the production manager to the store department for a specified quantity of material to be issued to the production department.
- In this case, we can see that raw material requirement has gone through the workflow of approvals which needs to be defined in the production process. This is what is called operational planning. An entrepreneur should devise an effective operational plan to aid in the production process.
- From the above points, it is clear that production and operational planning sets the business plan in the right direction. This plan requires a very careful thought process on the part of the entrepreneur and his organizational team to ensure the successful journey of the venture to be started.
- An accurate projection of the demand of the product is key to the operational strategy. For example, a plan to sell a woolen sweater for ^100 will fall flat if there is no strategy to have a good amount of stock as the demand soars in the market. Similarly, there should also not be an excessive investment in the inventory which blocks the working capital of the entrepreneur.
Financial Planning
A financial plan is prepared to assess the requirement of funds for starting the venture and also a plan pertaining to future income flows, cash flows, break-even analysis, and sources and application of funds.
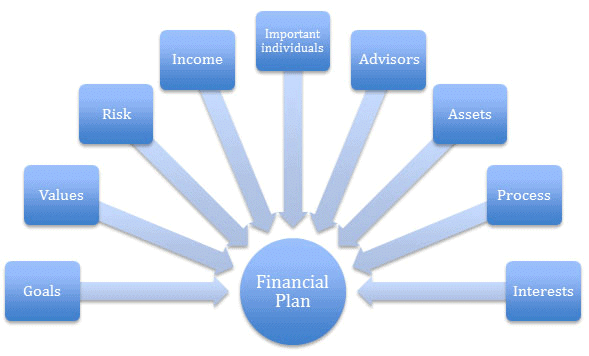
We must understand at this stage that the financial plan is the running oil for the business. The entrepreneur has to prepare a financial plan which projects adequate profitability and cash flows in the future so that the investment looks lucrative in the venture to be undertaken by the entrepreneur.
Following are the key components of the financial plan: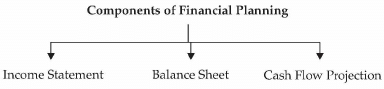
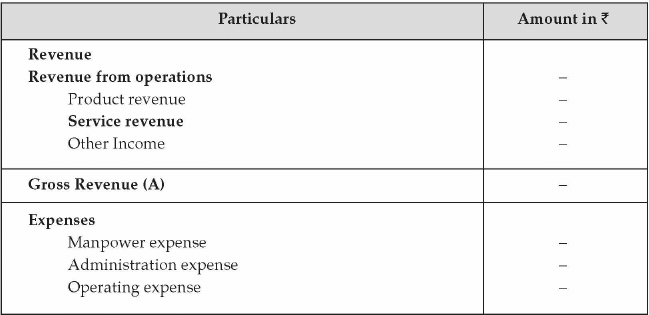
- Income Statement: A pro forma income statement is prepared to assess the profitability of the venture in the coming years. Revenue and expense need to be projected based on the pre-defined parameters. For revenue projection, the parameters will be the price of the product and projected quantity to be sold in the next few years. For expense, the parameter will be the projected quantity of product to be produced and other indirect expenses or overhead to be incurred on the business operations. The income statement will have components of revenue, expense, interest cost, depreciation, and amortization. The format of the income statement is as given below.
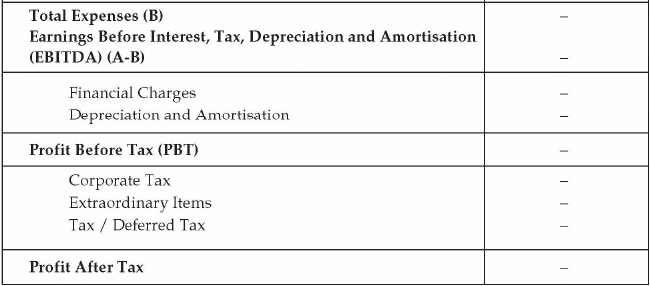
- Balance Sheet: Projected balance sheet is prepared based on the projected income statement. For the purpose of the balance sheet, projection for the future capital expenditure, funding structure in the form of debt and equity, projected loan repayment plan, debtors, creditors, inventory etc is required. Balance sheet reflects the statement of affair of the business. It is required to observe how the entrepreneur plans to structure his funding of the business and how the worth of the business is enhanced to provide value to the entrepreneur. The following format is required for the balance sheet:
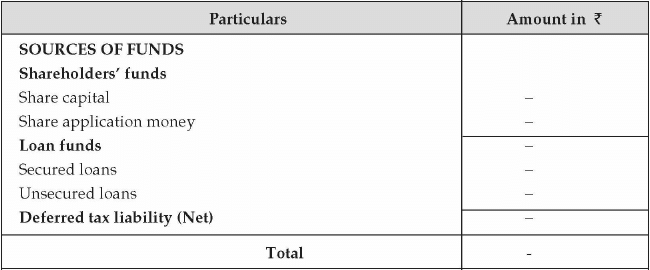
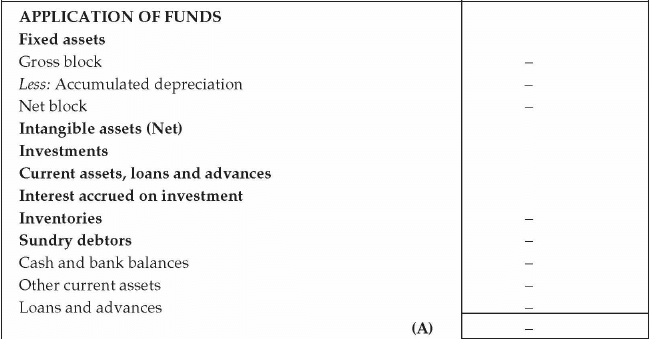
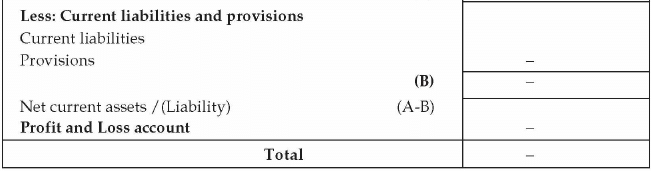
- Cash Flow Projection: The third component of financial statement is cash flow statement. Cash is the most important component for running a business. Entrepreneur should prepare a cash flow projection based on future revenue, expenses, capital expenditure, additional loan or loan repayment etc. Cash flow has three important components namely cash flow from operating activities, cash flow from financing activities and cash flow from investing activities. Operating activities comprise of the business operations like manufacturing of product and its sales in the market. Financing activities pertain to the funding of the business like debt, equity inflow and outflow. Investing activity is additional capital expenditure or disposal of assets.
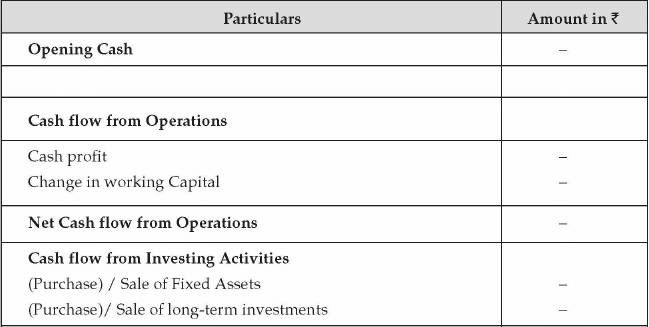
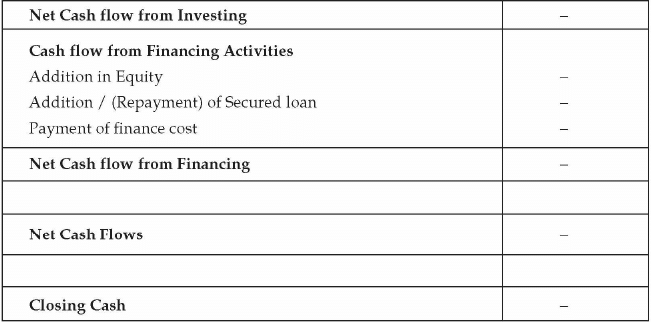
From the above discussion, it is clear that a comprehensive financial planning should be in place for the success of the business venture. Entrepreneur should put a careful thought process in this area to ensure that the funds management of the business is in place and working as per the plan.
Marketing Plan
Entrepreneurs are required to draw up marketing plan pertaining to pricing, distribution, promotion and control. Marketing plan lays out broad areas of product strategy to ensure that market share of the product improves. It is usually thought that the marketing starts when the product is ready to be sold. However, the truth is that marketing starts even before the product has come into existence. For example, a survey is conducted as to what features are key to the consumers requirement and it is communicated to the production department which works towards meeting those needs. Hence, the very first step of marketing starts with consumers and it ends with a consumer which indicates that understands consumer needs, come out with the best product and communicate to consumers to improve sales.
There are four important components of marketing plan: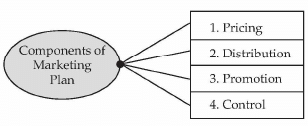
- Pricing: Pricing refers to the monetary value of the product which a consumer is willing to pay as per the product use and specification. Pricing plays an important role in pushing up or down the product's demand. It is impacted by the level of competition in the market, the cost of manufacturing the product, brand value of the product etc. An entrepreneur should set a competitive price of the product to ensure that the twin objective of higher demand and profit margin is achieved. The easiest way to determine product price is to add a profit margin to the product cost. However, there are other factors in terms of marketing strategy which affect the product price. The strategy may be in the form of Economy, penetration, skimming and premium pricing.
Economy Pricing: Economy pricing is done where the product is of good quality but sold at lower price to achieve high volume of sales at lower profit margin. A very basic low cost approach is taken where the consumers are offered with bare minimum requirement. This strategy is adopted to attract a specific segment of the market that is very price sensitive.
Penetration Pricing: This strategy is designed to capture market share by keeping low product price. It will help the entrepreneur to attract more customers for his entry level product. This strategy works well in a competitive environment where already a lot of sellers are available for the product. Although this strategy results in loss to the entrepreneur initially but it creates hope that more buyers will buy the product make it profitable at the later stage.
Skimming Pricing: An entrepreneur who has a competitive advantage in the market sells the product at higher price. This pricing strategy is followed to make more money initially before competitors enter the market.
Premium Pricing: It establishes a price higher than the competitors. This strategy is used when the product has some unique feature and has better quality than the competitors. Entrepreneur can earn more revenue at the early stage of the product life cycle and to establish a brand value in the premium range of the product.
The following picture shows the pricing strategy for a product.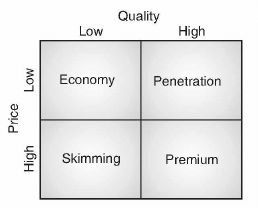
- Distribution: Marketing plan also determines the distribution strategy of the entrepreneur. It will decide which territory to be covered for product supply and what channels of distribution will be taken up. The decision regarding territory depend on the factors like connectivity to the place of production, demographic profile of the territory like population, income distribution etc. Generally, entrepreneurs chose less territory and expand it as the product demand goes up. Channels of distribution may be through wholesalers, retailers, dealers, online selling etc. The entrepreneur has decided which channel of distribution is the most cost effective and has the widest reach to the customers.
- Promotion: Product promotion strategy covers the advertising, discount schemes, lucky draw etc. In today's age, promotion has to be good to overcome the competitive pressure of the market. Entrepreneur has to make a detailed plan pertaining to promotional schemes keeping in view that the product profitability is maintained. Advertising can be done through print media, TV, radio etc. The choice of advertising media will depend on the target segment of the market and its effectiveness in spreading the desired message to the potential customers. Generally, discount schemes, lucky draw etc is clubbed with the product advertising effort to educate consumers about the product and the scheme.
- Control: Market plan is prepared but it has to be effectively controlled to achieve the desired results as per the plan. A periodic review needs to take place to ensure that the planned targets are met and any adverse deviation is identified and its reasons investigated. Those reasons to be corrected to ensure that the plan is met by the end of its applicable period. Control mechanism determines the success of the plan. Entrepreneur should take interest in the progress of the plan to achieve the desired results.
Human Resource Planning
Business plan should include a description of organizational structure. The organization structure should include management and human resources capabilities, philosophy and needs, the number of employees an entrepreneur intends to hire, how he or she will manage them and estimated personnel costs. An entrepreneur has to begin human resource planning by outlining his/her own managerial experience and skills as well as that of his/her team. It should also be what roles each member will play also determine any particular strength or deficiency in the team.
Entrepreneur should not worry if he/she doesn't yet have a complete team in place when the plan is being written.
The objective of the human resource plan is to:
- Outline the organizational structure
- Complete with job descriptions
- How you plan to recruit key team members, and
- What their respective responsibilities will be.
Entrepreneur should consider recruiting a human resources manager or at least use an HR consulting firm. The reason is that human resource management requires an immense amount of time and paperwork. An experienced HR consultant should be able to quickly get payroll and benefits running, giving entrepreneur more time to concentrate on growing the business.
Human resource strategy is another component of human resource planning. The strategy will outline the kind of corporate culture that needs to be nurtured in the organization. It will also help the investors to understand the philosophy of the organization towards its employees and the cost of administering employee related matters. Some of the important aspect of HR strategy may be pay scale, leaves, employee insurance and additional benefits to employees.
Creating the Plan
The last step of business plan is to create the plan. Once all the above discussed plans are formalized and all the relevant information is gathered then the process for writing the complete business plan should be undertaken. The plan should created in such a way that it is easy to understand and covers all major aspects of business operations like finance, human resource, production, marketing etc.
The following important components should form part of the business plan:
- Executive Summary: The executive summary will follow the title page. The summary should tell the reader what entrepreneur wants from the project he or she is planning to undertake.
- Business Description: It usually begins with a short description of the industry in terms present outlook as well as future possibilities. Entrepreneur should also provide information on various market segments within the industry including any new products or developments that will benefit or adversely affect his or her business. Business description should help the readers to understand the business idea of the entrepreneur.
- Financial Plan: Financial plan should spell out the plan for projected financial statements of the business. Financial statement includes income statement, balance sheet and cash flow. It should also indicate the sources and application of funds for smooth operation of the business. It should be noted that the financial plan is dependent on the other components of the business plan like production, operation, marketing and human resource plan.
- Organization Plan: Organization plan is prepared to define the roles and responsibilities of various organizational hierarchies. Job analysis is done to hire the right person for the predefined job role.
- Marketing plan: Marketing plan is the result of a meticulous market analysis. A market analysis forces the entrepreneur to become familiar with all aspects of the market so that the target market can be defined and the company can be positioned in order to garner its share of sales.
- Human Resource Plan: A description of organizational structure should be given which should include management and human resources capabilities, philosophy and needs, the number of employees an entrepreneur intends to hire, how he or she will manage them and estimated personnel costs.
Formalities of Starting a Business
Once business plan is created covering majorly all aspects of the business operations, the formalities for starting the business should be undertaken.
It requires all the procedures to be completed so that the business operations can be started. These procedures include obtaining all necessary licenses and permits and completing any required notifications, verifications or inscriptions for the company and employees with relevant authorities.
Internal processes, policies and procedures for the conduct of the business should be ready. Employee orientation should be conducted to ensure that everyone is aware of the organizational culture and values to be exhibited while dealing with day to day business affairs.
|
19 videos|103 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Entrepreneurial Planning: Notes - Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is entrepreneurial planning? |  |
| 2. What are the different forms of business entities? |  |
| 3. What is a business plan? |  |
| 4. What is organizational planning? |  |
| 5. What is production and operational planning? |  |
















