Enterprise Growth Strategies: Notes | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Strategies to Adopt for Growth |

|
| Franchising |

|
| Merger and Acquisition |

|
| Moving up the Value Chain and Value Addition |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions |

|
Strategies to Adopt for Growth
- In earlier chapters, we studied the initial phase of setting an entrepreneurial organization and putting systems and processes in place to run the business.
- The next big challenge comes for the entrepreneur in the form of growing the business through various strategies.
- Once the product or service hits the market and it gains acceptability then it needs to be expanded into new areas.
- Here the question comes, which strategy is better to adopt. Should it be Franchising, Merger, and Acquisition or self-driven? In this chapter, we will discuss this aspect of an entrepreneurial organization.
Franchising
Franchising is one of the modes of enterprise growth strategy.
- Entrepreneurs need this strategy when they need to expand their business beyond the area they are currently operating in.
- The franchise model is used as a method for increasing sales and brand visibility through independent business owners.
What is Franchising?
A franchise is a license granted to an individual or business entity (the franchisee) to market a company's (the franchisor) product or service in a particular territory using the franchisor's business systems, trademarks, and methods of operation.
There are many reasons that an entrepreneur may decide to franchise.
The following are the advantages of Franchising:
- It offers the potential for rapid growth with relatively low capital investment.
- Entrepreneur retains a significant level of control over the use of his or her brand and system.
- The entrepreneur has the comfortable feeling that each location is being operated by an independent business owner that is highly motivated to maximize the sales and profits of the business.
Who Can Franchise?
Everybody or anybody cannot adopt the Franchising model of growth strategy.
It is suitable for the entrepreneur whose business has the following characteristics:
- A business is a good candidate for franchising when the entrepreneur has a method of doing business that is easily reproduced and can easily be adopted by others through training.
- The business has a proven track record of economic success with a unique trademark with a distinct identity - the "brand." The existence of an established brand owned by entrepreneurs makes it an easy case for Franchising as the person taking up the franchising will not have to spend too much on promotion and marketing of the product or service.
- When the business is expanding and customers ask about other locations where the brand is available.
Merger and Acquisition
There are two ways of growing a business i.e., internal expansion and external expansion.
An entrepreneur may grow its business in either of these two ways.
- Internal Expansion: A firm grows gradually over time in the normal course of the business, through the acquisition of new assets, replacement of technologically obsolete equipment, and the establishment of new lines of products.
- External Expansion: A firm acquires a running business and grows overnight through corporate combinations. These combinations are in the form of mergers, acquisitions, amalgamations, and takeovers and have now become important features of corporate restructuring. The external expansion has been playing an important role in the external growth of a number of leading companies the world over. They have become popular because of the enhanced competition, breaking of trade barriers, free flow of capital across countries, and globalization of businesses.
- From the above, we can see that mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are a common form of the external expansion strategy. Now, we will study the concept and other related aspects of M&A.
Mergers
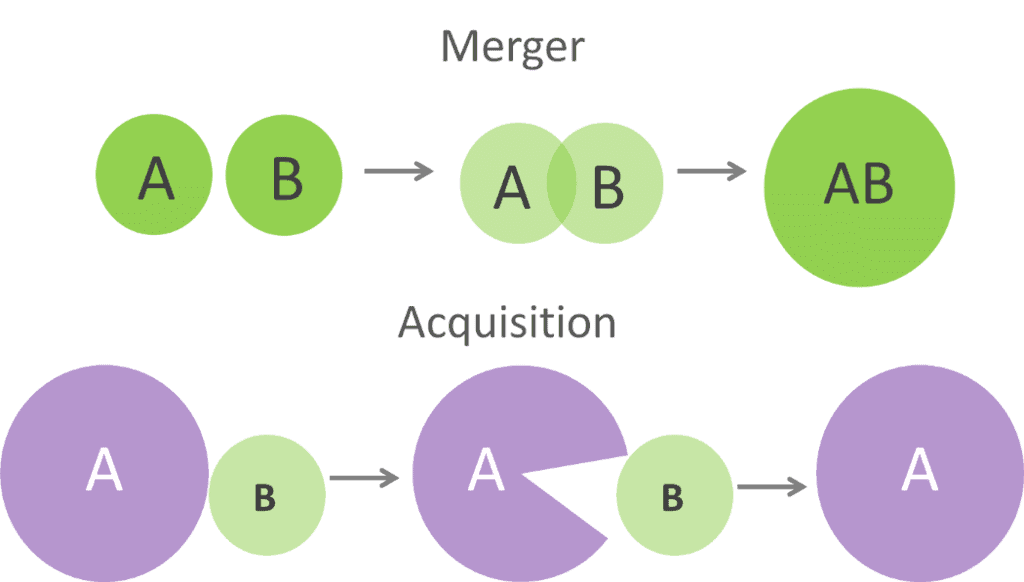
A merger is a combination of two or more businesses into one business.
- In other words, the merging of two companies where one new company will continue to exist is known as a merger.
- For example, Company A and Company B merge to form a new Company C. Company A and Company B will cease to exist and Company C will be formed. The merger is also known as amalgamation.
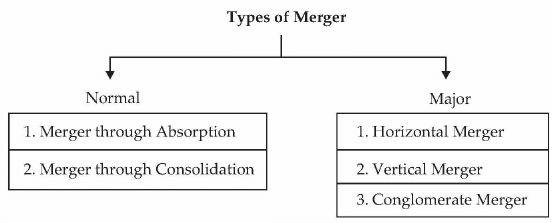
 There are two types of merger:
There are two types of merger: - Merger through Absorption: Absorption is a combination of two or more companies into an 'existing company'. All companies except one lose their identity in such a merger. For example, absorption of Tata Fertilizers Ftd., (TFF) by Tata Chemicals Ftd., (TCL). TCF, an acquiring company (a buyer), survived after merger while TFF, an acquired company (a seller), ceased to exist. TFF transferred its assets, liabilities and shares to TCF.
- Merger through Consolidation: A consolidation is a combination of two or more companies into a 'new company. In this form of merger, all companies are legally dissolved and a new entity is created. Here, the acquired company transfers its assets, liabilities, and shares to the acquiring company for cash or exchange of shares. For example, the merger of Hindustan Computers Ltd, Hindustan Instruments Ltd, Indian Software Company Ltd, and Indian Reprographics Ltd into an entirely new company called HCL Ltd.
- A fundamental characteristic of merger (either through absorption or consolidation) is that the acquiring company (existing or new) takes over the ownership of other companies and combines their operations with its own operations.
Besides, there are three major types of mergers:
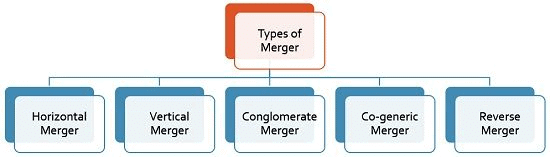
- Horizontal Merger: Two firms are merged across similar products or services. Horizontal mergers are often used as a way for a company to increase its market share by merging with a competing company. For example, combining of two book publishers or two luggage manufacturing companies to gain dominant market share.
- Vertical Merger: Two firms are merged along the value-chain, such as a manufacturer merging with a supplier. Vertical mergers are often used as a way to gain a competitive advantage within the marketplace. For example, joining of a TV manufacturing(assembling) company and a TV marketing company or joining of a spinning company and a weaving company. The vertical merger may take the form of forward or backward merger. When a company combines with the supplier of material, it is called backward merger and when it combines with the customer, it is known as forward merger.
- Conglomerate Merger: Two firms in completely different industries merge, such as a gas pipeline company merging with a high technology company. Conglomerates are usually used as a way to smooth out wide fluctuations in earnings and provide more consistency in long-term growth. For example, merging of different businesses like manufacturing of cement products, fertilizer products, electronic products, insurance investment, and advertising agencies. L&T and Voltas Ltd are examples of such mergers.
Acquisitions
Acquisition is another form of external expansion strategy available to an entrepreneur.
- An acquisition may be defined as an act of acquiring effective control by one company over assets or management of another company without any combination of companies.
- In other words, in an acquisition, two or more companies may remain independent, separate legal entities, but there may be a change in control of the companies.
When an acquisition is 'forced' or 'unwilling', it is called a takeover. - In an unwilling acquisition, the management of 'target' company would oppose a move of being taken over. But, when managements of acquiring and target companies mutually and willingly agree to the takeover, it is called an acquisition or friendly takeover.
Advantages of Mergers & Acquisitions
The following are the advantages of Mergers & Acquisition:
- Achieving Business Growth: M&A helps in achieving business growth in a situation when its internal growth is constrained due to a paucity of resources. Internal growth requires that a company should develop its operating facilities- manufacturing, research, marketing, etc. But, lack or inadequacy of resources and time needed for internal development may constrain a company's pace of growth. Hence, a company can acquire production facilities as well as other resources from outside through M&A. Also, for entering new products/markets, the company may lack technical skills and may require special marketing skills and a wide distribution network to access different segments of markets. The company can acquire an existing company or companies with the requisite infrastructure and skills and grow quickly.
- Economies of Scale: It arises when large-scale production leads to a reduction in per unit cost of production. This is because, with merger, fixed costs like rent, administration costs, etc. are distributed over a large volume of production causing the unit cost of production to decline. Economies of scale may also arise from other indivisibilities such as production facilities, management functions, and management resources and systems. This is because a given function, facility or resource is utilized for a large scale of operations by the combined firm.
- Operating Synergy: It indicates a situation where the combined firm is more valuable than the sum of the individual combining firms. It refers to benefits other than those related to economies of scale. Operating economies are one form of synergy benefits.
- Managerial Synergy: Apart from operating economies, synergy may also arise from enhanced managerial capabilities, creativity, innovativeness, R&D and market coverage capacity due to the complementarity of resources and skills and a widened horizon of opportunities.
- Financial Synergy: A merger may result in financial synergy and benefits for the firm in many ways like the elimination of financial constraints, enhancement of debt capacity, and lowering the financial costs in the form of lower interest.
Procedure for Evaluating the Decision for Mergers and Acquisitions
An entrepreneur should analyze three important steps for evaluating mergers and acquisitions are:
- Planning: It includes analysis of industry-specific and firm-specific information. An entrepreneur should review its objective of acquisition in the context of its strengths and weaknesses and corporate goals. For this purpose, industry data will be required on market growth, nature of competition, ease of entry, capital and labor intensity, degree of regulation, etc. This data will help in indicating the product-market strategies that are appropriate for the company. It will also help the firm in identifying the business units that should be dropped or added. On the other hand, the target firm (which is going to be acquired) will need information about the quality of management, market share, and size, capital structure, profitability, production and marketing capabilities, etc. of the entrepreneur's firm.
- Search and Screening: Search focuses on how and where to look for suitable candidates for acquisition. The screening process short-lists a few candidates from many available and obtains detailed information about each of them.
- Financial Evaluation: Financial evaluation of a merger is needed to determine the earnings and cash flows, areas of risk, the maximum price payable to the target company, and the best way to finance the merger. In a competitive market situation, the current market value is the correct and fair value of the share of the target firm. The target firm will not accept any offer below the current market value of its share.
The target firm may, in fact, expect the offer price to be more than the current market value of its share since it may expect that merger benefits will accrue to the acquiring firm. - From the above discussion, it can be inferred that the decision pertaining to merger and acquisition involves careful analysis of various factors before taking the final decision. An entrepreneur should look at all these factors and decide in favour of it if it works in the direction in which the firm should grow and expand.
Moving up the Value Chain and Value Addition
- In previous sections, we discussed the growth strategy of franchising and mergers and acquisition which is externally oriented. However, an entrepreneur should also strive to achieve an internal growth strategy in the form of moving up the value chain and value addition.
- In fact, internal strategy comes ahead of external strategy which means that a strong internal foundation will attract new business combinations in the form of franchising and merger and acquisition.
- The value chain is defined as a combination of processes that help in converting the inputs of the raw material into the finished product. In other words, it is interlinked value-adding activities that convert inputs into outputs which, in turn, help to create a competitive advantage for the firm.
A value chain typically consists of:
- Bound Distribution or Logistics: This includes the transportation of raw material and other inputs for the production process.
- Manufacturing Operations: This includes the process of converting the raw material into output.
- Outbound Distribution or Logistics: This refers to the distribution of output at various marketplaces so that it reaches customers in adequate quantities and frequency as per customers' demand.
- Marketing and Selling: This pertains to the promotion and advertising of the product in existing as well as new markets.
- After-Sales Service: After-sales service is available for the product already sold in the market.
From the above discussion, we can see that value chain or value addition analysis and finding ways to constantly improve this value chain is an important activity on the part of the entrepreneur. This will ensure the growth in business add to the competitive advantage of the firm.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. What are the disadvantages of franchising to the franchisee?
Disadvantages of franchising to the franchisee are:
- A specific way of doing things: Franchising limits the degree of freedom for franchisee and this looses his spirit of innovation
- Additional costs: Franchisors also demands a percentage of revenues along with fees and royalties
- Risk of failure or takeover of franchisor: In case franchisor fails or gets bought out by another company, franchisee faces serious problems and difficulties.
- Not adhering to the agreement: In case franchisor is unable to provide services as promised, franchises are left without any support in important areas such as advertising, training, quality control, etc.
Q.2. Explain the types of acquisition.
Types of acquisition are:
- Friendly acquisition: Such acquisition is approved by entities. It is not a forceful acquisition and the process is cordial.
- Reverse acquisition: This is when a private company takes over a public company
- Backflip acquisition: In this purchasing company becomes a subsidiary of the purchased company.
- Hostile acquisition: It is a forceful acquisition. The target company is taken to such extreme situations, that it has to agree with the acquisition.
Q.3. Explain in brief the three ways in which an organization can expand externally.
Ways in which an organization can expand externally are:
- Franchising: It is an agreement whereby the manufacturer or sole distributor of a product or service that is trademarked gives exclusive rights of local distribution to independent retailers in return for payment of royalty and conforming to the standardised operating procedures
- Merger: It is the combination of two companies into one larger company. In this case, the company that acquires the other one, takes over assets and liabilities of the merged company. Finally one new entity continues to operate.
- Acquisition: The process of acquiring majority shares of the target company to assume control over it.
Q.4. What is meant by moving up the value chain? Explain with the help of an example.
- Moving up the value chain refers to using business processes to manufacture products that generate high profits for the company.
Before a product is to be sold in the market, it needs to pass through certain stages like development, production, quality check, delivery, retailers, after slaes services, etc.
Business activities includes primary and support activities. When a product goes through all these activities, some value is added to the product as it moves along the value chain. This increases the worth of the products when it passes through different stages and helps businesses to earn more profits.
Example:
- A company makes steel for some other industry, which modifies the steel as per the automobiles industry.
But instead of making basic steel, the company decides to make steel directly for the automobile industry by adding some value to it so that it meets the requirement.
This will help the company to gain more profits as through value addition, the company can sell the product directly and increase revenues.
|
19 videos|62 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Enterprise Growth Strategies: Notes - Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is franchising and how can it help a business to grow? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of mergers and acquisitions for business growth? |  |
| 3. How can moving up the value chain and value addition contribute to business growth? |  |
| 4. What are the potential risks or challenges associated with franchising as a growth strategy? |  |
| 5. How can businesses determine if a merger or acquisition opportunity is suitable for their growth strategy? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
 There are two types of merger:
There are two types of merger:
















