Case Based Type Questions: The Solid State | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
Question 1: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The adjective, ‘crystalline’ when applied to solids, implies an ideal crystal in which the structural units, termed as unit cells, are repeated regularly and indefinitely in three dimensions in space. The unit cell, containing at least one molecule has definite orientation and shape defined by the translational vectors, a, b and c. The unit cell therefore has a definite volume, V that contains the atoms and molecules necessary for generating the crystal. Every crystal can be classified as a member of one of the seven possible crystal systems or crystal classes that are defined by the relationship between the individual dimensions, a, b and c of the unit cell and between the individual angles, α, β, and γ of the unit cell. The structure of the given crystal may be assigned to one of the 7 crystal systems, to one of the 14 Brevais lattices, and to one of the 230 space groups. This uniquely define the possible ways of rearranging atoms in a three-dimensional solid, Based on these observations, seven crystal systems were identified: triclinic, monoclinic, trigonal or rhombohedral, tetragonal, hexagonal, rhombic or orthorhombic and cubic.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
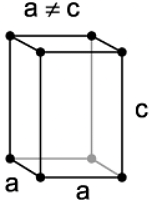
The crystal system of a compound with unit cell dimensions, a = 0.387 nm, b = 0.387 nm and c = 0.504 nm and α = β = 90° and γ =120° is
(a) cubic
(b) hexagonal
(c) orthorhombic
(d) rhombohedral
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In hexagonal crystal system-
a = b ≠ c
α = β = 90o
γ = 120o
Question 2: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All real structures are three dimensional structures. They can be obtained by stacking two dimensional layers one above the other while placing the second square close packed layer above the first we follow the same rule that was followed when one row was placed adjacent to the other. The second layer is placed over the first layer such that the spheres of the upper layer are exactly above there of the first layer. In his arrangement spheres of both the layers are perfectly aligned horizontally as well as vertically. A metallic element crystallise into a lattice having a ABC ABC pattern and packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice.
What type of structure is formed by this arrangement?
(a) ccp
(b) hcp
(c) ccp/fcc
(d) none of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Question 3: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The adjective, ‘crystalline’ when applied to solids, implies an ideal crystal in which the structural units, termed as unit cells, are repeated regularly and indefinitely in three dimensions in space. The unit cell, containing at least one molecule has definite orientation and shape defined by the translational vectors, a, b and c. The unit cell therefore has a definite volume, V that contains the atoms and molecules necessary for generating the crystal. Every crystal can be classified as a member of one of the seven possible crystal systems or crystal classes that are defined by the relationship between the individual dimensions, a, b and c of the unit cell and between the individual angles, α, β, and γ of the unit cell. The structure of the given crystal may be assigned to one of the 7 crystal systems, to one of the 14 Brevais lattices, and to one of the 230 space groups. This uniquely define the possible ways of rearranging atoms in a three-dimensional solid, Based on these observations, seven crystal systems were identified: triclinic, monoclinic, trigonal or rhombohedral, tetragonal, hexagonal, rhombic or orthorhombic and cubic.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
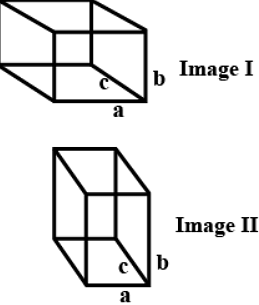
The unit cell with the structure given below represents ________crystal system.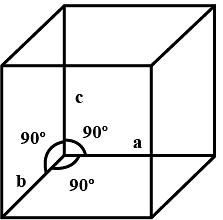
(a) cubic
(b) orthorhombic
(c) tetragonal
(d) trigonal
Correct Answer is Option (a)
If a = b = c and α = β = γ = 90o , the given structure will be a cubic crystal system.
Image I : a = b = call angles =90o (Isometric) cubic
Image II : a ≠ b ≠ c
all angles = 90o
Orthorhombic
Question 4: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All real structures are three dimensional structures. They can be obtained by stacking two dimensional layers one above the other while placing the second square close packed layer above the first we follow the same rule that was followed when one row was placed adjacent to the other. The second layer is placed over the first layer such that the spheres of the upper layer are exactly above there of the first layer. In his arrangement spheres of both the layers are perfectly aligned horizontally as well as vertically. A metallic element crystallise into a lattice having a ABC ABC pattern and packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice.
Name the non-stoichiometric point defect responsible for colour in alkali metal halides.
(a) Frenkel defect
(b) Interstitial defect
(c) Schottky defect
(d) F-centres
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Question 5: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The adjective, ‘crystalline’ when applied to solids, implies an ideal crystal in which the structural units, termed as unit cells, are repeated regularly and indefinitely in three dimensions in space. The unit cell, containing at least one molecule has definite orientation and shape defined by the translational vectors, a, b and c. The unit cell therefore has a definite volume, V that contains the atoms and molecules necessary for generating the crystal. Every crystal can be classified as a member of one of the seven possible crystal systems or crystal classes that are defined by the relationship between the individual dimensions, a, b and c of the unit cell and between the individual angles, α, β, and γ of the unit cell. The structure of the given crystal may be assigned to one of the 7 crystal systems, to one of the 14 Brevais lattices, and to one of the 230 space groups. This uniquely define the possible ways of rearranging atoms in a three-dimensional solid, Based on these observations, seven crystal systems were identified: triclinic, monoclinic, trigonal or rhombohedral, tetragonal, hexagonal, rhombic or orthorhombic and cubic.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
In a triclinic crystal
(a) a = b = c, α = β = γ ≠ 90°
(b) a ≠ b = c, α = β = γ = 90°
(c) a ≠ b ≠ c, α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°
(d) a ≠ b ≠ c, α = γ = 90°, β ≠ 90°
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Question 6: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All real structures are three dimensional structures. They can be obtained by stacking two dimensional layers one above the other while placing the second square close packed layer above the first we follow the same rule that was followed when one row was placed adjacent to the other. The second layer is placed over the first layer such that the spheres of the upper layer are exactly above there of the first layer. In his arrangement spheres of both the layers are perfectly aligned horizontally as well as vertically. A metallic element crystallise into a lattice having a ABC ABC pattern and packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice.
What is the total volume of atoms in a face centred cubic unit cell of a metal? (r is atomic radius).
(a) 16/3 πr3
(b) πr3
(c) 24/3 πr3
(d) 12/3 πr3
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Number of atoms per unit cell in fcc = 4
∴ Total volume of atoms present in fcc unit cell
= 4 x (4/3)πr3 = 16/3πr3
Question 7: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The adjective, ‘crystalline’ when applied to solids, implies an ideal crystal in which the structural units, termed as unit cells, are repeated regularly and indefinitely in three dimensions in space. The unit cell, containing at least one molecule has definite orientation and shape defined by the translational vectors, a, b and c. The unit cell therefore has a definite volume, V that contains the atoms and molecules necessary for generating the crystal. Every crystal can be classified as a member of one of the seven possible crystal systems or crystal classes that are defined by the relationship between the individual dimensions, a, b and c of the unit cell and between the individual angles, α, β, and γ of the unit cell. The structure of the given crystal may be assigned to one of the 7 crystal systems, to one of the 14 Brevais lattices, and to one of the 230 space groups. This uniquely define the possible ways of rearranging atoms in a three-dimensional solid, Based on these observations, seven crystal systems were identified: triclinic, monoclinic, trigonal or rhombohedral, tetragonal, hexagonal, rhombic or orthorhombic and cubic.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
The unit cell with dimensions α = β = γ = 90°, a = b ≠ c is
(a) cubic
(b) triclinic
(c) hexagonal
(d) tetragonal
Or
An example of orthorhombic crystal system is
(a) SnO2
(b) KNO3
(c) ZnO
(d) K2Cr2O7
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The unit cell with crystallographic dimensions a=b≠c and α=β=γ=90o is tetragonal.
OR
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Question 8: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All real structures are three dimensional structures. They can be obtained by stacking two dimensional layers one above the other while placing the second square close packed layer above the first we follow the same rule that was followed when one row was placed adjacent to the other. The second layer is placed over the first layer such that the spheres of the upper layer are exactly above there of the first layer. In his arrangement spheres of both the layers are perfectly aligned horizontally as well as vertically. A metallic element crystallise into a lattice having a ABC ABC pattern and packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice.
Which of the following statements not true for the amorphous and crystalline solids?
(a) Amorphous solids are isotropic and crystalline solids are anisotropic.
(b) Amorphous solids are short range order and crystalline solids are long range order.
(c) Amorphous solids melt at characteristic temperature while crystalline solids melt over a range of temperature.
(d) Amorphous solids have irregular shape and crystalline solids have a geometrical shape.
Or
Which of the following statements is not true for unit cell?
(a) Each cubic unit cell has 8 atoms on its corners the total number of atoms in one unit cell is 1.
(b) A un it cell is characterized by its dimensions along the three edges a, b, c.
(c) Each body centred cube cell has 2 atoms in one unit cell.
(d) Each face centred cubic cell contains only one constituent particle present at the centre of each face.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Crystalline solids melt at characteristic temperature while amorphous solids melt over a range of temperature.
Or
Correct Answer is Option (d)Each fcc unit cell contains one constituent particle present at the centre of each face, besides the ones that are at its corners.
Question 9: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
In ideally ionic structures, the coordination numbers of the ions are determined by electrostatic considerations. Cations surround themselves with as many anions as possible and vice versa. This maximizes the attractions between neigh-bouring ions of opposite charge and hence maximizes the lattice energy of the crystal. This requirement led to the formulation of the radius ratio rule for ionic structures in which the ions and the structure adopted for a particular compound depend on the relative sizes of the ions. Thus, for the stable ionic crystalline structures, there is definite radius ratio limit for a cation to fit perfectly in the lattice of anions, called radius ratio rule. This depends upon the ratio of radii of two types of ions, r+/r–.
This ratio for coordination numbers 3, 4, 6 and 8 are respectively 0.155 – 0.225, 0.225 -0.414, 0.414 -0.732 and 0.732 – 1.000. The coordination number of ionic solids also depends upon temperature and pressure. On applying high pressure, coordination number increases. On the other hand, on applying high temperature, it decreases.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
The ionic radii of K+, Rb+ and Br– are 137, 148 and 195 pm. The coordination number of cation in RbBr and KBr structures are respectively
(a) 8,6
(b) 6,4
(c) 6,8
(d) 4,6
OR
For a coordination number 4, the maximum limiting radius ratio is
(a) 0.414
(b) 0.732
(c) 0.225
(d) 0.155
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Or
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Question 10: Study the diagram given below and answer the following questions: 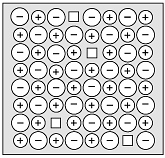
In these questions, a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): The diagram shows Schottky defect.
Reason (R): Schottky defect occurs in ionic solids.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true but R is false
(D) A is false and R is True
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The diagram shows Schottky defect as it has equal number of cationic and anionic vacancies.
|
117 videos|225 docs|239 tests
|
FAQs on Case Based Type Questions: The Solid State - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What is the definition of the solid state in NEET? |  |
| 2. How are solids different from liquids and gases in the NEET syllabus? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of crystalline solids mentioned in the NEET syllabus? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of a unit cell in the context of the solid state? |  |
| 5. What are the factors that affect the conductivity of solids, as per the NEET syllabus? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|