NCERT Solution- Enterprise Marketing | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is meant by goal setting?
“Establishing short or long term objectives, usually incorporating deadlines and quantifiable measures.”
Question 2. What is marketing strategy?
Marketing strategy is defined by David Aaker as “A process that can allow an organization to concentrate its resources on the optimal opportunities with the goals of increasing sales and achieving a sustainable competitive advantage.”
Question 3. What are the components of marketing mix?
The 4Ps that make up a typical marketing mix are — Price, Product, Promotion and Place.
Question 4. Which is the shortest channel of distribution?
Producer-customer, Direct channel or zero level is the shortest channel of distribution.
Question 5. What are the components to a successful sales strategy?
Components of successful sales strategy are creating an effective sales strategy requires market knowledge, awareness of competitor activities, awareness of current trends and detailed business analysis.
Question 6. Define branding.
‘Branding’ is a process, a tool, a strategy, an orientation whereby a name, a sign, or a symbol etc. is given to a product by the entrepreneur so as to differentiate his/her product from the rival products.
Question 7. Why is a logo important for a company?
Logo is important for a company as it imparts a distinct identity to entrepreneur’s own brand.
Question 8. Give the meaning of tagline with the help of an example.
Taglines are simple but powerful messages that help to communicate an enterprise’s goals, mission, distinct qualities and so much more. Balsara Hygiene products, launched their ‘Promise toothpaste in 1978 and took an aggressive stand against its competitors. It then secured the second highest market share. It was due to the tagline—“The unique toothpaste with time-tested clove-oil.”
Question 9. Explain the term packaging.
Processes and materials employed to contain, handle, protect, or transport any commodity. Packaging is done to attract attention, assist in promotion, provide machine identification (barcodes, etc.), impart essential or additional information, etc.
Question 10. What is labelling?
It is the display of information about a product on its container, packaging, or the product itself.
Question 11. Define advertising.
Advertising is a paid form of communication designed to attract or persuade potential customers to choose the product or service over that of a competitor.
Question 12. What is negotiation?
Negotiation is a process where two or more parties with different needs and goals discuss an issue to find a mutually common and acceptable solution.
Question 13. Explain the meaning of CRM.
CRM is the abbreviation for customer relationship management.
Question 14. When do we conclude that a business has failed?
We can conclude that a business has failed when it does not generate adequate cash flow to meet expenses.
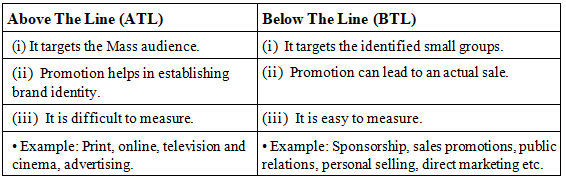
Question 15. Explain the following term: ATL.
ATL refers to above the line which targets mass audience and aims at establishing brand identity.
Question 16. Give the meaning of BTL.
BTL refers to Below the line which targets identified small groups and aimed at leading to an actual sale.
Question 17. What is TTL?
“Through the line” or TTL refers to an advertising strategy which involves both above-and below-the- line communications in which one form of advertising points the target to another form of advertising thereby crossing the “line”.
Short Answer Type Questions- I
Question 1. What are the rules for goal setting?
The rules of goal setting are:
- Relevant: To be relevant, a business goal has to be profitable in some fashion. Every business goal has to be measurable in rupees, and must possess a clear advantage to the specific business.
- Actionable: When we’re setting business goals, we have to be sure that we have developed them from general statements. Goals without action plans are just pretty words.
- Achievable stretches: The purpose of business goals is to move the businesses forward. If expectations are set too high, we set up for failure and disappointment. If the expectations are set too low then we won’t get enough satisfaction or recognition from the accomplishment.
A goal has to stretch us to be worth doing.
Question 2. What does the marketing strategy of a company include?
Marketing strategy includes:
- all basic and long-term activities in the field of marketing that deal with the analysis of the strategic initial situation of a company.
- the formulation, evaluation and selection of market-oriented strategies.
- several strategies for growth and interrelated components called the marketing mix.
Question 3. What is sales strategy?
- A sales strategy is a plan that places a company’s brand or product to gain a competitive advantage in the market.
- It help the sales to focus on target market customers and communicate with them in desired and required ways.
- It is aimed at targeting the correct customers at the right time.
Question 4. Explain the different types of sales strategies.
Following are the two types of sales strategies:
- Direct: In this strategy sales people talk about each feature of the competition’s product and compare it to theirs. It is also referred to as “negative selling”.
- Indirect: Indirect sales uses demonstrating features and benefits not available with the competition’s products or services without ever mentioning them by name. It is also referred as “positive selling
Question 5. Differentiate between trade mark and brand mark.
- Brand name is “that part of a brand which can be spoken like Asian Paints, Pepsi, Uncle Chips, etc.” Brand names are signals that carry meaning in the minds of consumers., E.g.“Wal-Mart”.
Trademark refers to words, names, symbols and product design features that are used to distinguish the products or services of one manufacturer or seller from another.- Brand helps in identification of the product of a company, while trademark helps in preventing others from copying.
- If a brand has not been registered, anyone can copy it, and there is no provision of any penalty, while in case of trademark violation, there is legal action available.
Question 6. What is the purpose of logo?
- Anchor: A logo anchors company’s brand.
- Identification: Corporate logo are intended to be the “Identity” of an enterprise because of displaying graphically enterprise’s uniqueness.
- Information: Using colour combination, fonts, images, impression or pattern, logos provide essential information about a company which allows customers to relate with the enterprise’s core brand.
- Visual effect: Logos act as the key visual component of an enterprise’s overall brand identity.
Question 7. Why should we advertise?
We should advertise to:
- Make business and product name familiar to the consumers and public,
- Create goodwill and build a favourable image of the product and the company.
- Educate and inform the public about the aspects related to product.
- Offer specific products or services.
- Attract customers.
Question 8. What is employee management?
Employee management:
- Is first concern of a manager at work.
- Allows manager to accomplish goals at work.
- Allow manager or entrepreneur to capitalize on the strengths of other employees and their ability to contribute to the accomplishment of work goals.
- Helps in promoting employee engagement, motivation, development, and employee retention.
Question 9. Is vendor management different from employee management? Enumerate.
Employee relationship management is a process that is directed to effectively manage all interactions with employees, ultimately to achieve the goals of the organisation. Where as vendor management is used to describe the process of finding, qualifying and doing business with vendors.
Question 10. Differentiate between ATL and BTL.
Short Answer Type Questions- II
Question 1. Explain in detail SMART goals.
SMART is made from following words:
- Specific: Great goals are well- defined and focused.
- The moment we focus on a goal, our goal becomes a magnet, pulling us and our resources towards. “The more focused are our energies, the more power we generate.”
- Measurable: A goal without a measurable outcome is like a sports competition without a scoreboard or scorekeeper. To know whether we are on track, we have to put concrete numbers in our goals.
- Attainable: It means dream big and aim for the stars but keep one foot firmly based in reality. Entrepreneur must get a handle on realistic growth in the industry to set smart goals.
- Relevant: Achievable business goals are based on the current conditions and realities of the business climate.
- Time-Based: Business goals and objectives just don’t get done when there’s no time frame tied to the goal-setting process.
Question 2. Explain the disadvantages of skimming price method.
Disadvantages of skimming price method:
- High promotional cost: In this method there is heavy expenditure on advertisement and other promotional techniques. All the entrepreneurs may not have such financial strength.
- Short run; This method is applicable only till the competitors are not entering. As the competitors enter from window, the price skimming method has to leave from the door.
- Innovation: Such method is applicable only to innovative products and ideas cannot be introduced for normal goods.
Question 3. What are the qualities of a good brand name?
A good brand name should have following qualities:
- Short, simple and easy to pronounce.
- Noticeable, easy to recognize and remember.
- Pleasing, impressive when uttered.
- Neither obscene, negative, offensive or vulgar.
- Adaptable to packaging, labelling requirements, to different advertising media and languages.
- Linked to product and eye catching.
- Contemporary, capable of being registered and protected legally.
Question 4. What are the rules for advertising?
There are four rules for advertising:
- Aim: It means the primary purpose of the advertisement and it aims to inform, sell, produce listings or improve the image of the business.
- Target: Who is targeted, i.e. which group of customers are targeted. For example, is it male, female, adult, teenager, child, mother, father, etc.
- Media: Based on aim and target which media is available and is most suitable i.e. TV, radio, press, etc.
- Competitors: Here, various aspects of the competitors are to be studied like moves of the competitors, media channel used, etc.
Question 5. What is AIDA?
Developing effective advertising (AIDA): Good advertising elicits the following four responses:
Attention: It catches the eye or ear and stands out amid the clutter of competing advertisements.
Interest: It arouses interest and delivers sufficient impact in the message or offering.
Desire: It creates a desire to learn more or crave ownership.
Action: It spurs an action which leads to achievement of the ad’s original objective.
Question 6. What are the different roles played by a salesperson?
A salesperson plays three different roles:
- Be persuasive: Salesmen have to persuade the customers to purchase the commodity. This effort is expected to be sincere. It may involve various aspects like clearing the queries of the customers, providing credit facilities, etc.
- A service provider: All the services related to the product are to be facilitated by the sales person. These services are related to various aspects like maintenance, repair, operation, etc.
- Be informative: Salesperson have to provide genuine information to the potential customers. Use of unfair information to the customers is not desired and not expected from the salesperson.
Question 7. What are Public Relations?
Public relations is the deliberate, planned and sustained effort to establish and maintain mutual understanding between an enterprise and their public. It is related to building good relations with the stakeholders of the business by having favourable publicity, building a goodwill and encouraging favourable informative system about the product and the enterprise.
Question 8. Who is a stakeholder?
Stakeholders are the different groups in a society which can affect the business decision: making and have an impact on its marketing performance. These groups include: Clients/customers, shareholders, media, financial institutions, community groups, etc.
Question 9. What are the main public relations tools?
The main public relations tools include:
- News creation and distribution (media releases)
- Special events such as news conferences, grand openings and product launches
- Speeches and presentations
- Educational programs
- Annual reports, brochures, news-letters, magazines and audio-visual presentations Community activities and sponsorships.
Question 10. Explain the benefits of CRM.
The benefits of CRM are:
- Storage: By CRM all business data is stored and accessed from a single location.
- Central location: Storing all the data of all departments like sales, marketing, customer service etc. in a central location provide immediate access to the recent data when it is required.
- Collaboration: Departments can collaborate with each other with ease.
- Improvement: It helps the enterprise to develop efficient automated process to improve business processes.
- 360-degree view: It provides a 360-degree view of all customer information, knowledge of what customers want and matching it with existing applications to consolidate all business information.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is penetration pricing method and enlist its advantages and disadvantages?
Penetrating pricing is the method of pricing in which the entrepreneur introduces its product in the market with low price compared to competitors. The low price increases the sale of the product tremendously. Normally for keeping low price, the profit margin is normally kept very low. The product thus captures the major part of the market e.g. Hero Honda, CD Dawn motorbike was introduced with the same pricing method. The CD Dawn penetrated into the market and captured major part of the market. Recently Bajaj CT- 100 also followed the tactics.
Wheel active detergent powder kept the price of Rs. 20 per half kilogram. This also captured the market quickly.Advantages: Following are the advantages of penetrating pricing method:
- Quick rise in sales: Penetrating pricing results in the increase in sales with a very high speed.
- High turnover: The turnover of the enterprise is raised in very short duration. This strengthens the position of enterprise in the market.
- Return on investments: This method brings decent return on investments. The minimum profit margin is also assured with the sale of each unit.
- Best method for price elastic goods: When a small range in price brings more change in demand, such products have penetrating pricing as the best method.
Disadvantages: Following are the disadvantages of penetrating pricing method:
- This method is applicable only to the products and services, which have high price elasticity. Thus, it is not applicable to all the products.
- Profit margin is low in the price fixed by such method. This profit may not be sufficiently compared to the cost of production and promotion.
- Turnover of the enterprise increases tremendously. Such enterprises have to prepare themselves for a situation of more financial requirements.
Question 2. What are the various types of brand names from the entrepreneur’s perspective?
Various types of brands available are:
- Individual brand name: Here, every product is promoted by the entrepreneur on the basis of a separate brand name, like:
Liril - brand name with the “freshness” concept.
Lux - brand name for “beauty soap for film stars”- Family brand name (Umbrella branding): Here, the entrepreneur’s name or the company’s name is used for all the products, like: Kissan, is brand name for jam, sauces, etc.
AMUL, has been used to market a large variety of dairy products viz. milk, ghee, butter, chocolates, etc.- Corporate names: Here, entrepreneur can choose their corporate name or logo together with some brand names of individual products for example, Godrej, Tata, Bajaj, etc.
- Alpha-numeric names: It is mainly for industrial products. An alpha-numeric name signifies its physical characteristics. For example, SX4, Liv52, ANX Grindlay, ilO, i20, etc.
Question 3. What are the various factors which help in employee management?
- Identifying objectives: It is essential to define what is meant by employee relationship management and what areas of the relationship will be managed. Mainly relationship management centers around attracting and retaining employees.
- Determining employee needs: Needs varies depending on employee characteristics—age, gender, etc. and also on the type of job being performed. Directly asking the employees through one-on-one conversations is the best way to find the needs. Such contact is take place during formal employee evaluation meetings, through surveys and polls.
- Balancing work and life needs: Effective employee relationship management requires consideration of the whole employee i.e. taking steps to ensure that the employee’s work-life is well balanced. This can be done through creative staffing involving part-time, flex-time or even off-site work assignments.
- Open and honest communication: Managers and top level management must be committed to communicating regularly and honestly with employees about the various issues that affect their work. The more open the organizations are the more likely they are to establish strong relationships that lead to increased loyalty and productivity. It also helps in removing decreased turnover and dissatisfaction.
- Measuring and monitoring results: Managers and HR departments should be alert at all times for finding the signs of discontent, this can be done by monitoring the results of more formal assessments. Such results should also be shared with employees of the firm.
- Relationships are interpersonal: Steps must be taken to interact effectively with employees through various ways of communication channels, both interpersonal and formal. Measurement of the effectiveness of these efforts should be frequent and ongoing, with improvements and adjustments.
Question 4. How is vendor management done?
- Meaning: Vendor management is the process of finding, qualifying and doing business with vendors.
- Activities: Common activities of vendor management include researching vendors, negotiating contracts, obtaining quotes, evaluating performance, creating and updating vendor files, and ensuring that payments are made properly.
- Outsourcing: Vendor management begins with the decision of outsourcing.
- Finding vendors: The company then have to find one or more vendors that can supply the good or service needed.
- Evaluation of vendors: Next thing is to evaluate each vendor based on pricing, capabilities, turn-around time, quality of work, etc. This involves requesting pricing, checking references, and researching the company through online resources.
- Contract: After vendors are selected, contract terms are followed. Certain vendors might be preferred. Others might be backup vendors in case of further requirement
- Vendor files: It often involves a great deal of electronic or manual paperwork. As it include vendor contact information, certificates of insurance and taxpayer identification numbers. Many firms require vendor files to be updated annually in such case it is ensured to obtain the details every year.
Very Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Explain in detail any three pricing strategies.
Following are the various pricing strategies:
- Variable pricing technique: Variable pricing technique is the one in which different prices are charged from different categories of customers. There is price discrimination. Many factors are responsible for the variation in the price. If a customer is purchasing more quantity of the product, he will be offered lower price. If the demand for the product increases in the market then higher price can be charged. This method has both the objectives viz. selling more quality and also charging higher price but at , different times, e.g. Indian railways charges different fares for AC 3 tier, AC 2 tier, second class and general compartment.
- Base pricing and discount: Base pricing and discount method is the method in which the entrepreneur fixes one price for its commodity. This price is calculated in advance considering the point that discount will be offered during the sale. Here, the discount offered is of various types. Depending on the type of customers the various rates of discount are fixed. Discount is offered to all the customers but at different rates. The wholesaler discount may be different from, volume discount, discount for transaction and off-season discount.
- Skimming pricing method: Skimming price method is the method of pricing in which the product is introduced in the market with a very high price. High price is kept for recovering the cost of production quickly. Such entrepreneurs normally bring something new in the market with more utility value. Product is introduced with a lot of expenditure on advertisement. High price tends to bring back revenue quickly. High class people are the target of such method of pricing e.g. Philips introduces its new product with the same method, Rumalaya also follows the same trend.
- Cost plus pricing method: In this method the cost of production of one unit of the product is calculated. This cost covers all the types of costs including explicit cost, variable cost, fixed cost, etc. to this is now added the preplanned profit margin.
This method of pricing is very simple method. It can easily be used for determining the price. Any changes in the cost of production or the margin of profit change the price in the same direction. It automatically gets adjusted to the change. Profit margin is not to be calculated. It is already fixed. Thus, by multiplying the profit per unit with the volume of the product, the total profit can be determined. Any upward rise in cost is easily visible. This provides an idea to the entrepreneur to adjust his production for keeping the cost as low as possible. Comparatively less calculations are involved, which makes the implementation of this method simple. This method can easily be implemented because of its simplicity to understand and easy calculations.
Question 2. Explain the important factors affecting the choice of channels of distribution by the manufacturer.
While selecting a distribution channel, the entrepreneur should take into account the following factors:
- Considerations related to product: It includes the following:
- Unit value of the product: When the product is very costly distribution channel is preferred. For example, industrial machinery or gold ornaments. On the other hand, for less costly products long distribution channel is used.
- Standardised or customised product: Such products have pre-determined cost and there is no scope for alteration. For example: Utensils of MILTON, for these long distribution channel is used.
On the other hand, customised products are those which are made according to the discretion of the consumer and also there is a scope for alteration, for example; furniture. For such products face-to-face interaction between the manufacturer and the consumer is essential. So for these direct sales is a good option.- Perishability: Highly perishable goods should have short channel. On the contrary, a long distribution channel can be selected for durable goods.
- Technical nature: If a product is of technical nature, direct channel should be preferred. This will help the user to know the necessary technicalities of the product.
- Considerations related to market:
- Number of buyers: If the number of buyers is large then it is better to take indirect and long channel of distribution. On the contrary, the distribution should be done by the manufacturer directly if the number of buyers is less.
- Types of buyers: If the more buyers belong to general category then there can be more middlemen. But in case of industrial buyers there should be fewer middlemen.
- Buying habits: Manufacturer can take the services of middlemen if financial position does not permit to sell goods on credit to those consumers who are in the habit of purchasing goods on credit.
- Buying quantity: If the goods are bought in smaller quantity then middlemen can be employed.
- Size of market: If the market area of the product is scattered then the producer must take the help of middlemen, i.e., long channel.
- Considerations related to manufacturer/company:
- Goodwill: Good reputation need not depend on the middlemen as the firm can open his own branches easily.
- Desire to control the channel of distribution: A manufacturer’s ambition to control the channel of distribution affects its selection. Consumers should be approached directly by such type of manufacturer. For example, electronic goods sector with a motive to control the service levels provided to the customers at the point of sale are resorting to company owned retail counters.
- Financial strength: A strong financial base of a company can have its own channels. On the other hand, financially weak companies would have to depend upon middlemen.
- Considerations related to government: Only a license holder can sell medicines in the market according to the law of the government. In this situation, the manufacturer should take sell through middlemen who have the relevant license.
- Others:
- Cost: A manufacturer should select such a channel of distribution which is less costly and also useful from other angles.
- Availability: Other channel of distribution can be selected if the desired channel is not available.
- Possibilities of sales: Such a channel which has a possibility of large sale should be given weight age.
Question 3. Explain promotional mix in detail.
Promotion refers to all the activities undertaken to make the product or service known to the user and trade. It is a method to spread the word about the product or service to customers, stakeholders and the broader public. This can include advertising, word of mouth, press reports, incentives, commissions and awards to the trade. It can also include consumer schemes, direct marketing, contests and prizes. Various approaches a company can use to promote its products are:
- Above-the-include: It use mass media methods and focuses on advertising to a large audience. It include print, online, television and cinema advertising, press, online banner advertisements, place advertisements on billboards, etc. Above-the-line promotion is very expensive so before taking it a lots of thought must be given. Also at times they are not under the control of organisation.
- Below-the-line: These are very specific, memorable activities focused on targeted groups of consumers. They remain under the control of the organisation. It deals with developing the brand by creating awareness and building a brand profile. It include the activities like sponsorship, sales promotions, public relations, personal selling, direct marketing, etc.
- Through-the-line: It refers to an advertising strategy involving both above-and below-the-line communications in which one form of advertising points the target to another form of advertising thereby crossing the “line”.
Question 4. Explain any six commonly used media options.
Commonly used media options are as follows:
- Window display or office front: It is the external presentation of the firm/enterprise. An attractive, well maintained exterior with clear, bold sign writing is an essential start. Windows should be bright, attractively presented, clean and well lit at night. The display should be arranged neatly so that it has remarkable impact to attract attention.
- Press advertising: It is a form of general advertising and includes advertising in all press like newspapers, magazines and journals. This form is a key to image building, information dissemination and sales campaigns. It is also a very cheap compared to other forms.
- Radio: It is an ideal medium due as it has ability to reach specific target groups like teenagers, grocery buyers, etc. It has only sound effect. It covers spot adverts, promotions or talk back/ RJ discussions. Most radio stations offer packages for advertising.
- Television: It is a powerful advertising medium as it creates impact through sight, sound and movement. It has high producing cost which makes it prohibitive for small businesses.
- Direct mail: This is a broad category covering direct communication with the consumer through email, post or fax. It can include newsletters, catalogues and letters.
- Outdoor: This advertising is done outdoors, including static advertising such as billboards, backs of street benches and bus shelters or mobile advertising displayed on buses, trains, taxis or towed signage.
- Cinema: Firm can purchase cinema advertising for a set amount of screenings or runs. Most providers of this category offer packages which include production and screening of your advertisement.
Question 5. Enlist some typical sales promotion activities.
Following is the list of some typical sales promotion activities:
- Consumer promotions:
- Point of purchase display material
- In-store demonstrations, samplings and celebrity appearances
- Competitions, coupons, sweepstakes and games
- On-pack offers, multi-packs and bonuses
- Loyalty reward programmes
- Business promotions:
- Seminars and workshops
- Conference presentations –
- Trade show displays
- Telemarketing and direct mail campaigns
- Newsletters
- Event sponsorship
- Capability documents
- Trade promotions:
- Reward incentives linked to purchases or sales
- Reseller staff incentives
- Competitions
- Corporate entertainment
- Bonus stock
- Sales force promotions:
- Commissions
- Sales competitions with prizes or awards
- Back to top
Question 6. Explain the methods of negotiation.
Methods of negotiation are as follows: Integrative or win-win: Here each side is working towards a solution where everyone wins something. They can make trade offs and look at multiple issues. The involved parties may try to expand the pie rather than divide it. This method fosters trust and good working relationships.
Distributive or win-lose: Here one party gets what it wants, and the other party has to give something up. This type of negotiation does not lead to lasting or positive relationships. Here one party remains unsatisfied and so it does not lead to a healthy relationship. Inductive: This method involves starting on small details and working upward until a settlement is reached. Here the solution is sought from the grass root level by understanding each and every minute detail. For example, an employer and labour union are negotiating the details of an employee pension and investment plan. Small details are addressed one at a time.
Deductive: Deductive negotiations start with an agreed upon strategy. They rely on established principles and a formula to frame the negotiation while the parties work out the details. Here each parties is the gainer and jointly the result is met. It is based on the mutual agreement.
Mixed: Mixed negotiations are the most common, they are a blend of inductive and deductive methods.
Question 7. Explain the reasons for business failures. Or Satnam, an IIT-IIM graduate, started three chemists shops at Amritsar, Patiala and Chandigarh in the name of ‘Quality Medicines’. Encouraged with the success of these shops Satnam opened 50 more shops in different parts of Punjab. His strategy was to cut price, focus on lower and upper middle class and open shops near hospitals. He operated on very thin margins. But he was not able to maintain sufficient funds to meet the day-to-day expenses of the business. The staff at the shops did not give much attention to the customers and there was very poor system of control. Because of this mismanagement he started incurring huge losses and his business failed.Based on the above paragraph, identify and explain any four causes of business failure of Satnam.
Following are the reasons of business failures:
- Lack of industry experience: The internal resources of a firm has to match the needs of the environment to which the firm belongs. Lack of experience in the field will lead to poor organization of a firm and resources. This may lead to loss and business failure.
- Inadequate financing: Financing is the lifeblood of a business at every stage. Many businesses fail due to lack of proper financing channels. The lack of planning for funding to support opportunities for growth is the root cause of failure. Planning in advance, rather than looking for financing just when needed, is a good practice. It includes lack of sufficient awareness of the costs involved in raising capital, lack of alternative sources in case of rejection from financiers, etc.
- Lack of adequate cash flow: Cash flow is the measure of a firm’s ability to maintain sufficient funding to meet its expenses for the day-to-day activities of the business. Many businesses fail because owners have a difficult time projecting what cash will come in every month, and thus, how much can be produced. Cash flow projections and its knowledge will help owners to understand how much they can afford to spend.
- Poor business planning: Ninety per cent of business failures are caused by a lack of general business management skills and planning. Owner, manager must have sufficient knowledge of such skills. This will lead to proper understanding of the practical situation which can then be resolved using basic management skills.
- Management incompetence: Ninety per cent of business failures are associated with “management inadequacy”, which can be due to either management inexperience or incompetence. A good strategic plan is only good as the management’s ability to implement changes in day- to-day operations.
- Ignoring the competition: Customers always looking for the better deal. If competition offers better products, services, or prices, the customers will succeed at the expense of the business. So keeping an eye on competitors and positioning the products accordingly is vital to staying in business.
- Unworkable goals: Setting goals is one thing and setting workable goals is another. Enterprises are influenced by uncertainty. Setting realistic goals, within the bounds of acceptable risk taking and optimism, is important.
- Diminished customer base
- Uncontrolled growth
- Inappropriate location
- Poor system of control
- Lack of entrepreneurial skills.
High Order Thinking Skill
Question 1. Varshini started her high end boutique in a posh locality, but she was not aware of how to make her boutique popular in the area. Suggest some measures for it.
Varshini is suggested the following:
- To create a brand name for the product.
- To have a simple logo and tag line for the boutique.
- Go for the advertising through pamphlets and door to door publicity.
- Arrange for seminars related to ladies.
- Sponsor the programmes of ladies like kitty party, etc.
- Cover the marriages and other social programmes and display the brand name and the products.
- Arrange for promotional schemes like buy two and get one free.
|
19 videos|103 docs|12 tests
|