NCERT Solution- Enterprise Growth Strategies | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are the two ways in which an organisation can expand?
Internal Expansion and External Expansion are the two ways in which an organisation can expand.
Question 2. Who is a franchisor?
The owner or person offering the franchise is known as the franchisor.
Question 3. Who is a franchisee?
The franchisee is the person who purchases the franchise and is given the opportunity to enter a new business with a better chance to success than if he or she were to start a new business from nothing.
Question 4. What is franchising?
Franchising is an arrangement through which the manufacturer or sole distributor of a trademarked product or service gives exclusive rights of local distribution to independent retailers in return for royalties and conformance to standardized operating procedures.
Question 5. Which is the most popular form of franchising?
Business format franchise opportunity is the most popular form of franchising.
Question 6. What is acquisition?
Acquisition or take over is enveloping in itself a range of acquisition transactions by a firm.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Explain in brief the three ways in which an organisation can expand externally.
The three ways in which an organisation can expand externally are:
- Franchising: Franchising is an arrangement through which the manufacturer or sole distributor of a trademarked product or service gives exclusive rights of local distribution to independent retailers in return for royalties and conformance to standardized operating procedures,
- Merger: It is the combining of two firms into a single large firm.
- Acquisition: Acquisition or takeover is enveloping in itself a range of acquisition transactions by a firm.
Question 2. Enumerate the importance of franchising.
Importance of Franchising:
- Proven idea: Business is based on a proven idea. Success of the product can be checked in the market and is also known.
- Profit from brand recognition: Franchises develop an image in the marketplace. This saves both time and money of advertising, promotion, recognition, etc. Image of the product is a favourable one and is in the minds of consumers.
- Recognized brand name and trademarks: Entrepreneur gets a recognized brandname and trademarks. Benefit from any advertising or promotion by the parent company automatically benefits the franchise.
- Support from parent company: The franchisor gives support in the form of training, help setting up the business, a manual telling how to run the business and ongoing advice.
- Exclusive rights of the territory: The franchisor can’t sell any other franchises in the same territory which leads to the creation of monopoly power in the territory.
- Easier Financing: Financing the business becomes easier due to the associated brand name. Banks are more likely to lend money to buy a franchise with a good reputation.
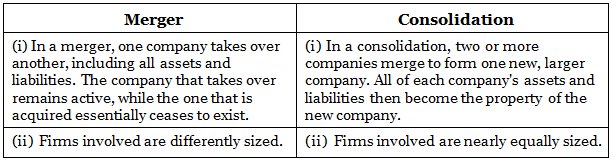
Question 3. Differentiate between consolidation and merger.
Question 4. Name the two forms that merger can take place.
Two forms of merger are:
- Amalgamation: Amalgamation is a union of two or more companies, made with an intention to form a new entity or company.
- Absorption: It means an existing company taking over one or more company. In this case one or more company will close down their business and this business will be continued by the name of the existing company.
Question 5. Explain the types of acquisition.
There are four types of acquisitions:
- Friendly acquisition: Here, both the companies approve of the acquisition under friendly terms. There is no use of force or pressure and every thing gets over cordially.
- Reverse acquisition: Here, a private company takes over a public company.
- Rack flip acquisition: Here, the purchasing company becomes a subsidiary of the purchased company.
- Hostile acquisition: Here, the entire process is based on force. The smaller company is forced to say yes to the acquisition or the bigger company just buys off all its share.
Question 6. What is value addition? Explain by giving examples.
Value addition refers to creation of a competitive advantage by, combining, packaging features and benefits or through any other method that results in greater customer acceptance. Its examples are:
- Offering one year of free support on a new computer would be a value-added feature.
- Turning cotton into fabric. Here, fabric has more usefulness than cotton.
- Turning milk into cheese. Cheese has got more specific uses than milk.
- Packaging ready-to-use grated cheese into serving size packets.
- Turning wood into paper. Utility of paper is more than wood.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Explain the types of franchising.
Following are the types of franchising:
- Product Franchise Business Opportunity: Here, the manufacturers use the product franchise to govern how a retailer distributes their products. The manufacturer grants a store owner the authority to distribute goods by the manufacturer and allows the owner to use the name and trademark owned by the manufacturer. The store owner purchases the inventory in return for these rights. Example: Some tire stores.
- Manufacturing Franchise Opportunity: It provides an organisation with the right to manufacture a product and sell it to the public, using the franchisor’s name and trade mark. This type of franchising is very common. For example, in the food and beverage industry, bottlers of soft drinks, etc.
- Business Franchise Opportunity Ventures: Here, a business owner purchases and distributes the products for one specific company. The company provides customers or accounts to the business owner. In return, the business owner pays a fee as compensation. Example, vending machine routes and distributorships.
- Business Format Franchise Opportunity: Here, a company provides a business owner with a proven method for operating a business using the name and trade mark of the company. The company provides a significant assistance to the business owner in starting and managing the company. The business owner pays a fee or royalty in return.
Question 2. What are the disadvantages of franchising to the franchisee?
Disadvantages of franchising :
- Higher cost: Costs may be higher than expectations. The costs include initial costs of buying the franchise, you pay continuing management service fees and you may have to agree to buy products from the franchisor, this may be more than the expectations.
- Huge restrictions: The franchise agreement usually includes strong restrictions on how to run the business. Franchise might not be able to make changes to suit the local market.
- Risk: There is a risk that the franchisor might go out of business and in this case a huge risk is involved.
- Bad reputation: Other franchisees could give the brand a bad reputation, so the selection process needs to be perfect.
- No sale option: Franchise finds it difficult to sell to someone if willing to sell due to any reason. It can only be sold to someone approved by the franchisor.
Question 3. What is synergy? In what forms can it take place?
Synergy is the benefit that results when two or more firms together achieve something either one couldn’t have achieved on its own. It’s the concept of the whole being greater than the sum of its parts.
For example, if firms A and B merge and the value of the combined entity— V(AB)—is expected to be greater than (VA+VB), the sum of the independent values of A and B, the combined entity is said to be benefitting through synergy. Synergy can take place in two forms:
- Operating synergy: This refers to the cost savings that come through economies of scale or increased sales and profits. It involves raising scale of production by changing all factors of productions of the firm. It leads to the overall growth of the firm.
- Financial synergy: It is the type of synergy which is due to financial factors such as lower taxes, higher debt capacity or better use of idle cash. When a loss making firm merges with a profitable firm and the combined firm can set off such losses against its profits, a financial synergy, known as tax shield, occurs.
Question 4. What are the different types of value added?
The different types of value added are as follows:
- Quality Added Value: It is adding convenience, ease of use, etc. that customers value. For example, turning a commodity into a branded product or design enhancements.
- Environmental Added Value: It is value added which employs methods or systems that do not harm the environment. For example, using less fuel, using recycled material for packaging.
- Cause-related Added Value: Here, the business contributes part of the revenue from a commodity to a cause. For example, a business may donate a percentage of revenue from each transaction to a orphanage.
- Cultural Added Value: It uses methods or systems of production involving cultural aspects. For example, using a combination of English and the regional language in written communications.
Very Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Explain the advantages of franchising, both for the franchisor and franchisee.
Merits of Franchising:
- Proven idea: Business is based on a proven idea. Success of the product can be checked in the market.
- Profit from brand recognition: Franchises develop an image in the marketplace. This saves both time and money of advertising, promotion, recognition, etc. Image of the product is a favourable one and is in the minds of consumers.
- Recognized brand name and trademarks: Entrepreneur gets a recognized brand name and trademarks. Benefit from any advertising or promotion by the parent company automatically benefits the franchise.
- Support from parent company: The franchisor gives support in the form of training, help setting up the business, a manual telling how to run the business and ongoing advice.
- Exclusive rights of the territory: The franchisor can’t sell any other franchises in the same territory which leads to the creation of monopoly power in the territory.
- Easier Financing: Financing the business becomes easier due to the associated brand name. Banks are more likely to lend money to buy a franchise with a good reputation.
Question 2. Explain in detail the types of mergers.
- Conglomerate: Here, two totally unrelated business activities mearge. Pure conglomerate mergers is between the firms with nothing in common.
Mixed conglomerate mergers involve firms which are going for product extensions or market extensions. Example: Walt Disney Company and the American Broadcasting Company. Here the new company formed had to face tough competition in both the products.- Horizontal merger: This merger is between companies in the same industry. It is a type of business consolidation that occurs between firms which are competitors and offering the same goods or service. It is in the condition where competition tends to be higher and the potential gains in market share are much greater for merging firms in such an industry.
Example: A merger between Coca-Cola and the Pepsi beverage division, would create a new, larger organisation with more market share.- Market extension mergers: It takes place between two companies that deal in the same products but in different markets. This merger is to make sure that the merging results in a bigger market and a bigger client base. Example: The acquisition of Eagle Bancshares Inc. by the RBC gave RBC a chance to deal in the financial market of Atlanta, which is among the leading upcoming financial markets in the USA. RBC has thus diversified due to this move.
- Product extension mergers: A product extension merger takes place between two business organizations that deal in products that are related to each other and operate in the same market. The product extension merger allows the merging companies to group together their products ‘ and get access to a bigger set of consumers. This ensures that they earn higher profits.
Example: The acquisition of Mobilink Telecom Inc. by Broadcom Broadcom deals in the’ manufacturing of Bluetooth personal area network hardware systems and chips for IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN. Mobilink Telecom Inc. deals in the manufacturing of product designs meant for handsets that are equipped with the Global System for Mobile Communications technology. It is expected that the products of Mobilink Telecom Inc. would be complementing the wireless products of Broadcom.- Vertical merger: A merger between two companies producing different goods or services for one specific finished product. A vertical merger occurs when two or more firms, operating at different levels within an industry’s supply chain, merge operations. Most often the logic behind the merger is to increase synergies created by merging firms that would be more efficient operating as one. Example: A vertical merger joins two companies that may not compete with each other, but exist in the same supply chain. An automobile company joining with a parts supplier would be an example of a vertical merger. Such a deal would allow the automobile division to obtain better pricing on parts and have better control over the manufacturing process. The parts division, in turn, would be guaranteed a steady stream of business.
Question 3. What do you think are the reasons for failure of merger and acquisition?
Following are the reasons for failure of merger and acquisition:
- Unrealistic price paid for target: Merger and acquisition involves valuation of the target company and paying a price. Many a time the price paid to the target company is much more than what should have been paid. Shareholders of the target company are benefited, the shareholders of the acquirer end up on the losing side.
- Difficulties in cultural integration: Merger involves combining of two or more different companies with different corporate cultures, styles of leadership, differing employee expectations etc. If the merger is not dealing sensitively with the companies people and their different corporate cultures, the merger may be a disaster. For example, the merger of Daimler Benz with Chrysler. While Daimler-Benz’s culture stressed on a more formal and structured management style, Chrysler favoured a more relaxed and freewheeling style.
- Overstated synergies: Mergers and acquisitions assumed to be for creating synergies through increased revenue, reduced costs and improvement in the investment intensity. Overestimation can lead to failure.
- Integration difficulties: The combined firm or entity has to adapt to a new set of challenges given by the new circumstances. Plans are thus prepared to integrate the operations of the combining entities. This is done on the present information. If the information available is inadequate, integration becomes difficult.
(a) Poor business fit: Mergers and acquisitions also fail when the products of the merging firms do not fit into the acquirer’s overall business plan.- Inadequate due diligence: Due diligence helps in detecting financial and business risks that the acquirer inherits from the target company. Inaccurate estimation of the related risk can result in failure of the merger.
Question 4. What is meant by moving up the value chain? Explain with the help of an example.
- Moving-up the value chain is a value chain in the whole series of activities that create and build value at every step. The total value delivered by the company is the sum total of the value built up gradually all throughout the company.
- It is the primary and secondary facilitations offered by a company.
Low facilitation to highest facilitation by a company then leads to movement from low level to highest level.
For example, in a steel industry, if they make specialized steel for automobiles, rather than selling basic steel, which is taken by another company who makes specialized steels to automobiles.
Since the company makes it directly now, they get more money for their product, and thus higher revenues. This will eventually lead to higher profits.
The value chain concept separates useful from the wasteful activities which hinder the company from becoming a leader in the market. Focusing on the value-creating activities gives the company many advantages.
It involves primary activities like Inbound logistics, Operations, Outbound logistics, Marketing, sales, Services, etc. and Support activities like Procurement, Technological development, Human resource management etc.
Value chain management requires coordination and collaboration, Technology investment, Organizational process, Leadership, Employee/ Human resources and Organizational culture and attitudes.
For example: The ability to charge higher prices; lower cost of manufacture; better brand image, faster response to threats or opportunities.Outsourcing: The fragmentation of the production process across various countries has given rise to restructuring in firms including the outsourcing and off shoring of certain functions. Outsourcing involves the purchase of intermediate goods and services from outside specialist providers, while off shoring refers to purchases by firms of intermediate goods and services from foreign providers, or to the transfer of particular tasks within the firm to a foreign location. Off shoring includes both international outsourcing where activities are contracted out to third parties abroad and international in-sourcing to foreign affiliates.
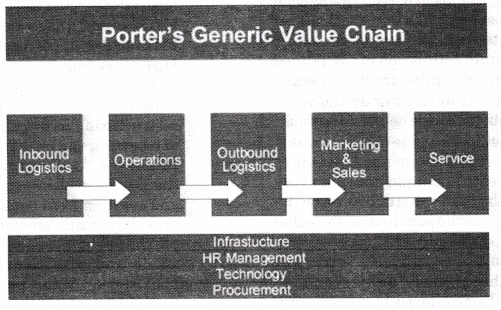
Question 5. Explain in detail Porter’s Generic Value Chain with the help of a diagram.
Michael Porter gave the value chain analysis concept in his 1985 book ‘The Competitive Advantage’. He suggested that activities within an organisation add value to the service and products that the organisation produces and all these activities should be run at optimum level if the organisation is to gain any real competitive advantage.
If these activities are run efficiently, the value obtained exceed the costs of running them and customers return to the organisation and transact freely and willingly.
He suggested that the organisation is split into ‘primary activities’ and ‘support activities’.
- Primary activities include:
- Inbound logistics: Here, goods are obtained from the suppliers and are used for producing the end product.
- Operations: Here, raw materials and goods are manufactured into the final product.
- Outbound logistics: Distribution of finished goods is known as outbound logistics.
- Marketing and sales: Here, marketing mix is used to form an effective strategy to the target group through the promotional mix.
- Services: After the product/service has been sold, sales training, guarantees and warranties etc. play its part.
- Support activities: These help the primary activities achieve competitive advantage. They include:
- Procurement: It is to obtain the best possible quality available in the market for their budget.
- Technological development: Technology can be used to obtain a competitive advantage. Technology can be used to reduce cost and thus adding value, research and development to develop new products on the internet so that customers can have all time access to the firm.
- Human resource management: Here, the organisation will have to recruit, train and develop the right people for the organisation to be successful. Staff will have to be motivated and paid the ‘market rate’, if they are to stay with the organisation and add value.
- Firm infrastructure: Organisation needs to ensure that their finances, legal structure and management structure work efficiently and help drive the organisation forward.
Question 6. Explain the requirements for value chain management.
Following are the six requirements for value chain management:
- Coordination and collaboration: It is essential to increase efficiency within an organization. Care should be taken that efforts are not duplicated. Firm is greater than the sum of its parts for achieving a common goal of the firm.
- Technology investment: With outdated technology, like old computers or machinery, an organization’s competitiveness is weakened due to a loss in productivity. This devoids the firm from gaining advantage.
- Organisational process: Improvement in processes through better technology and greater procedural knowledge is essential for the present and future success of a company. Continuity is to be maintained for the improvement and is to be made an integral part of the system.
- Leadership: Strong leaders adds to the successions value chain management. Good leaders earn the respect of their employees through neutral, effective and sound management practices. Conflict management, motivation and direction are the essential requirements of strong leaders.
- Employee/human resources: Without a knowledgeable and active human resources department, employees may feel they don’t have a voice within the company and this may lead to lack in belongingness from the employees. Also, an employee hesitant to go directly to the ultimate superiors with issues act as a hurdle in many situations.
- Organisational culture and attitudes: Organisations that foster strong cultural identity with positive attitudes tend to attract and retain top employees. Regular sponsored activities are suggested to help build cultural unity and keep attitudes positive while boosting productivity of the firm.
High Order Thinking Skill
Question 1. A merger between firms that are involved in totally unrelated business activities.
It is Conglomerate merger.
Question 2. A merger occurring between companies in the same industry.
It is Horizontal merger.
Question 3. It takes place between two companies that deal in the same products but in separate markets.
It is Market extension merger.
Question 4. It takes place between two business organisations that deal in products that are related to each other and operate in the same market.
It is Product extension merger.
Question 5. It is between two companies producing different goods or services for one specific finished product.
It is Vertical merger.
|
19 videos|103 docs|12 tests
|