Long Answer Type Question- Enterprise Growth Strategies | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Franchising
Question 1: What are the different activities that an entrepreneur can undertake to expand his enterprise?
An entrepreneur can undertake following activities to expand his enterprise :
(i) Raising tire level of production: By raising the level of production, the volume of the product produced increases. This leads to expansion.
(ii) Add ing another unit of production: By keeping the present unit and adding a new unit of production an enterprise can be expanded.
(iii) Increasing the number of employees: With the increase in the strength of the employees, the expansion takes place provided it is associated with the rise in production. (iv) Adding more machines: By adding more machines to the existing ones, the turnover also increases. This is referred as expansion.
(v) Opening an ancillary unit: If the product of one company can be used as a raw material for the other product, then a new enterprise can come into existence which is dependent on the main. If the parent company and the ancillary unit are of same enterprise, it is also leading to expansion.
Question 2: Explain how does franchising help Start-ups?
(i) Franchising help startups because already the product carriers a name in the market already which is the most difficult part of business to establish.
(ii) Startups take up training to understand the product and franchisors make franchises fully conversant with the product/services that they have to offer.
(iii) The start-ups can grow fast without having to increase labour, operating costs and blocking running expenses because normally buyers straight walk up to them.
(iv) Franchisors' efforts to boost their franchises are always sincere, so there is no-clash of interest.
Question 3: Identify the type of Franchising stated in following cases:
(i) The manufacturer grants the retailer or owner of the shop tire authority to distribute the goods to use tire name and trademark owned by the manufacturer.
(ii) When an organisation gets the right to manufacture a product and sell it to tire public using Franchisor's name.
(iii) When a company provides a business owner with proven method for operating a business using the name and trademark of the company.
(iv) The company provides customers to the business owners in return of distributing and purchasing the company's goods.
The following types of Franchising are stated in tire above cases:
(i) Product franchise business opportunity.
(ii) Manufacturing franchise business opportunity.
(iii) Business format franchise company,
(iv) Business franchise opportunity venture.
Question 4: Explain the different types of franchising.
Types of franchising:
(i) Product franchise business opportunity.
(ii) Manufacturing franchise opportunity.(iii) Business franchise opportunity ventures.
(iv) Business format franchise opportunity.
Question 5: Explain the main ingredients of a franchise agreement.
(i) Contract Explanation: The contract explanation is the part of the agreement that outlines the type of relationship a franchisee is entering into with the franchisor.
(ii) Operations Manual: The operations manual is the section of the agreement that details the guidelines that the franchisee must legally follow in operating the business as outlined by the franchisor. From time to time amendments may be made and the franchisee must be prepared to adjust operations accordingly. The franchisee needs to be aware that the contents of the document are confidential.
(iii) Proprietary Statements: Proprietary statements outline how the franchise name is to be used, as well as the marketing and advertising procedures in place that the franchisee will be required to follow. Also, the franchisor documents how much the franchisee will be required to contribute towards national advertising efforts.
(iv) Ongoing Site Maintenance: Ongoing site maintenance is another item that is outlined in the agreement. Included in it are the types and time frames regarding various maintenance items and upgrades that must be made to the franchisee's location.
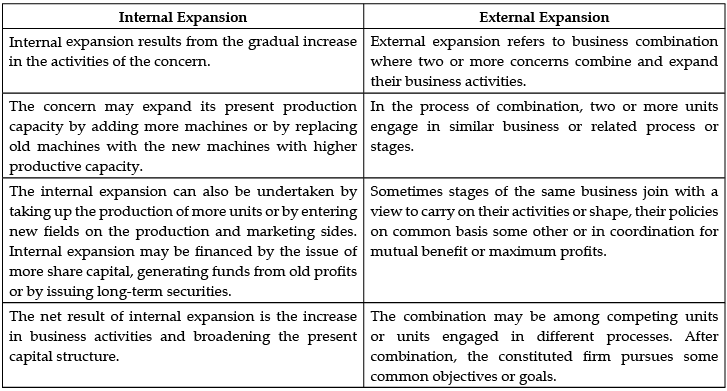
Question 6: Differentiate between Internal expansion and External expansion.
Question 7: Explain any four advantages of franchising to a franchisee?
Advantages to the franchisee:
(i) Product acceptance
(ii) Management expertise(iii) Capital requirements
(iv) Knowledge of the market
(v) Operating and structural controls
Detailed Answer:
Advantages of franchising to the franchisee:
(i) Product acceptance: The franchisee usually enters into a business that has an accepted name, product or service. The franchisee does not have to spend resources trying to establish the credibility of the business. That credibility already exists based on the years the franchise has existed.
(ii) Management expertise: Another important advantage to the franchisee is the managerial assistance provided by the franchisor. Each new franchisee is often required to take a training program on all aspects of operating the franchise. This training could include classes in accounting, personnel management, marketing and production. In addition, some franchisors require their new franchisees to actually work with an existing franchise owner or at a company-owned store or facility to get on-the job training. Once the franchise has been started, most franchisors will offer managerial assistance on the basis of need.
(iii) Capital requirements: The franchise offers an opportunity to start a new venture with upfront support that could save the entrepreneur's significant time and possibly capital. Some franchisors conduct location analysis and market research of the area that might include an assessment of traffic, demographics, business condition and competition. In some cases, the franchisor also finances the initial investment to start the franchise operation.
(iv) Knowledge of tire market: Any established franchise business offers the entrepreneur years of experience in the business and knowledge of the market. This knowledge is usually reflected in a plan offered to the franchisee that details the profile of the target customer and the strategies that should be implemented once the operation has begun. This is particularly important because of regional and local differences in markets.
Question 8: Enumerate tire importance of franchising?
Importance of franchising are as follows:
(i) Proven idea: Business is based on a proven idea. Success of the product can be checked in the market and is also known.
(ii) Profit from brand recognition: Franchisee develop an image in the market place. This save both time and money of advertising, promotion, recognition, etc.
(iii) Recognized brand name and trademark: Entrepreneur gets a recognized brand name and trademark Benefit from any advertising or promotion by the parent company automatically benefits the franchisee.(iv) Support from parent company: The franchisor gives support in the form of training, helps setting up the business, etc.
(v) Exclusive rights of the territory: The franchisor can't sell any other franchise in the same territory which leads to the creation of monopoly power in the territory.(vi) Easier financing: Financing the business becomes easier due to the associated brand name. Banks are more likely to lend money to buy a franchise with a good reputation.
Question 9: Explain tire ways in which an organization can expand.
(i) Internal Expansion: Internal expansion means expansion within the internal boundaries of a company, It results from the gradual increase in the activities of the concern. The concern may expand its present production capacity by adding more machines or by replacing old machines with the new ones. Internal expansion can also be undertaken by entering new fields on the production and marketing sites. The net result of internal expansion is the increase in business activities and broadening the present capital structure.
(ii) External Expansion: External expansion means expansion beyond the boundaries of the company. It refers to a business combination where two or more concerns combine and expand their business activities. The combination may be among competing units or units engaged in different processes. After combination, the constituted firm pursues for common objectives or goals. The main forms of external expansion are franchising and mergers & acquisitions.
Question 10: Slurpy is a new mixed fruit juice introduced by Amit Beverages Ltd. The mixed fruit juice has been fortified using various vitamins and minerals. The company designed a unique package for the product which made it very attractive. Their sales figures were an indication of their success.
In order to capture huge market share, they decided to give exclusive rights to retailers to manufacture and sell the product to tire public.
Identify and explain this concept State two factors which help s tart - ups and also state the advantages to Amit Beverages Ltd. in doing so.
Manufacturing franchise opportunity: These types of franchises provide an organization with the right to manufacture a product and sell it to the public, using the franchisor's name and trademark. This type of franchise is found mostly in the food and beverage industry. Most bottlers of soft drinks receive a franchise from a company and must use its ingredients to produce, bottle and distribute the soft drinks.
How do Franchising help Start-ups
(i) Franchising help startups because already the product carriers a name in the market already which is the most difficult part of business to establish.
(ii) Startups take up training to understand the product and franchisors make franchises fully conversant with the product/services that they have to offer.
(iii) The start-ups can grow fast without having to increase labour, operating costs and blocking running expenses because normally buyers straight walk up to them.
(iv) Franchisors' efforts to boost their franchises are always sincere, so there is no-clash of interest.
Advantages of franchising to the franchisor
(i) Quick expansion: A franchisor can expand a business nationally and even internationally by authorizing and selling franchises in selected locations. The capital necessary for this expansion is much less than it would be without franchising. Operating a franchised business requires fewer numbers of employees than a non-franchised business. Headquarters and regional offices can be lightly staffed, primarily to support the needs of the franchisees. This allows the franchisor to maintain low payroll and minimize personnel problems.
(ii) Cost advantages: The franchisor can purchase supplies in large quantities thus, achieving economies of scale that would not have been possible otherwise. Many franchise businesses produce parts, accessories, packaging and raw materials in large quantities, and then sell these to the franchisees. One of the biggest cost advantages of franchising a business is the ability to commit larger sums of money to advertising. This pooling of resources allows the franchisor to conduct advertising in major media across a wide geographic area.
Mergers, Acquisitions and Reasons for Failure
Question 1: What are the reasons for failure of Merger and Acquisition (M & A)?
(i) Unrealistic Price Paid for Target: Merger and acquisition involves valuation of the target company and paying a price for taking over the assets of the company. Many a times, the shareholders of the target company stand benefited while that of the acquirer company end up on the losing side. This is because the assets of the target company are overpriced which dilutes the future earnings of the acquirer.
(ii) Difficulty in Cultural Integration: The merger of two or more different entities reflect different corporate cultures, styles of leadership, differing employee expectation and functional differences. While the process of merger is being executed, these differences are known but often ignored. Such, ignorance may turn out to be a disaster.
(iii) Overstated Synergies: Over estimation of synergies may lead to failure of mergers.
(iv) Integration difficulties: It means the combined entity has to adopt to a new set of challenges given by the changed circumstances.
(v) Poor Business Fit: Merger and acquisition also fails when the products or services of the merging entities do not naturally fit into the acquirer's overall business plan. This delays efficient and effective integration and causes failure.
(vi) Inadequate Due Diligence: Due diligence helps in detecting financial and business risks that the acquirer inhabits from the target company. Inaccurate estimation of the related risk may result in failure of merger.
(vii) Regulatory Issues: The entire process of merger requires legal approvals. If any of the stake holders are not in favour of the merger, they might create legal obstacles and slow down the entire process. This results in regulatory delays and increases the risks of deterioration for the business.
(viii) Fiuman Resource Issues: Merger or acquisition is identified with job losses, restructuring and the imposition of a new corporate culture and identity. This can create uncertainty, anxiety and resentment among the company's employees.
Question 2: What do you mean by acquisition? Give some examples.
Acquisition is a more general term, enveloping in itself a range of acquisition transactions. It could be leading to takeover of a company. Acquisition refers a corporate action in which a company buys almost, the target company's ownership stakes in order to assmne control of the target firm. It is often made as part of a company's growth strategy whereby it is more beneficial to take over an existing firm's operations. It is often paid in cash, it could be the acquisition of company's stock, tangible assets, intangible assets, 'rights, acquisition of control, and other kinds of obligations. It is also known as a takeover, means the buying company takeover or acquire by another.
For Examples:
(i) Bharti Airtel is the largest mobile network in India. It is also expanding its reaches throughout the globe, Bharti Airtel added 180 million new customers in its list by acquiring an African Mobile Network provider called Zain Africa.
(ii) Tata Steel acquired 100% stake in Corns Group on January 30,2007. It was an all-cash deal which cumulatively amounted to ₹.12.2 billion.
Question 3: What is Synergy? In what forms it can take place ?
Synergy is the difference between the value of the combined firm and the value of the sum of participants in a merger. It occurs in the form of revenue enhancement and cost savings.
It can take place in tire following forms
(i) Operating synergy: It refers to cost savings that come through economies of scale or increased sales and profits.
(ii) Financial Synergy: It is the result of financial factors such as lower taxes, higher debt capacity or better use of idle cash.
Question 4: Mergers and Acquisitions are inspired by a desire to diversify or achieve higher growth rate. What are tire other reasons for merger and acquisitions?
(i) Synergy: Synergy refers to the difference between the value of the combined firm and the value of the sum of the participants. Synergy accrues in the form of revenue enhancement and cost savings.
(ii) Acquiring new technology: To remain competitive, companies need to constantly upgrade their technology and business applications. By buying another company with unique technology, the buying company can maintain or develop a competitive edge.
(iii) Improved profitability: Companies explore the possibilities of a merger when they anticipate that it will improve their profitability.
(iv) Acquiring a competency: Companies opt for mergers and acquisitions to acquire a competency or capability that they do not have and which the other firm has.
(v) Entry into new markets: Mergers are often looked upon as a tool for hassle-free entry into new markets. Through mergers one can enter the market with greater ease and avoid too much competition.
(vi) Access to funds: Often companies find it difficult to access funds from capital market. In such a case company may decide to merge with another company which is fund-rich.
(vii) Tax benefits: By merging with a loss-making entity, a company with high tax liability can set off the accumulated losses of the target against its profits gaining tax benefits.
Question 5: Explain the four types of acquisitions.
There are four types of acquisitions:
(i) Friendly acquisition: Both the companies approve of the acquisition under friendly terms. There is no forceful acquisition and the entire process is cordial.
(ii) Reverse acquisition: A private company takes over a public company.
(iii) Back flip acquisition: A very rare case of acquisition in which the purchasing company becomes a subsidiary of the purchased company.
(iv) Hostile acquisition: Here, as the name suggests, the entire process is done by force. The smaller company is either driven to such a condition that it has no option but to say yes to the acquisition or the bigger company just buys off all its share, thereby establishing majority and hence, initiating the acquisition.
Question 6: In the following cases identify the type of merger.
(i) A merger between firms that are involved in totally unrelated business activities.
(ii) A merger occurring between companies in the same industry.
(iii) It takes place between two companies that deal in the same products but in separate markets.
(iv) Ittakes place between two business organisations that deal in products that arerelatedtoeach other and operate in tire same market
(i) Conglomerate merger
(ii) Horizontal merger(iii) Market extension
(iv) Product extension
Question 7: Unicon Ltd. and Nahata Communications provide cable TV network in adjacent areas of Delhi. After sometime the market was slowly taken over by big cable companies. Both Unicon Ltd. and Nahata communications understood the competition and decided to come together so as to increase their markets share. This strategy helped them in cost saving through economies of scale as they could cover more areas now. It led to the overall growth of both the companies.
(i) Identify tire enterprise growth strategy adopted by the two.
(ii) State the benefits that the companies have after this arrangement
(i) A market extension merger takes place between the two companies that deal in the same products but in separate markets. The main purpose of the market extension merger is to make sure that the merging companies can get access to a bigger market and that ensures a bigger client base.
(iii) (a) Synergy: Synergy refers to the difference between the value of the combined firm and the value of the sum of the participants. Synergy accrues in the form of revenue enhancement and cost savings.
(b) Acquiring new technology: To remain competitive, companies need to constantly upgrade their technology and business applications. By buying another company with unique technology, the buying company can maintain or develop a competitive edge.
(c) Improved profitability: Companies explore the possibilities of a merger when they anticipate that it will improve their profitability.
(d) Acquiring a competency: Companies opt for mergers and acquisitions to acquire a competency or capability that they do not have and which the other firm has.
(e) Entry into new markets: Mergers are often looked upon as a tool for hassle-free entry into new markets. Through mergers one can enter the market with greater ease and avoid too much competition.
(f) Access to funds: Often companies find it difficult to access funds from capital market. In such a case company may decide to merge with another company which is fund-rich.
(g) Tax benefits: By merging with a loss-making entity, a company with high tax liability can set off the accumulated losses of the target against its profits gaining tax benefits.
|
19 videos|62 docs|12 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|