Long Answer Type Question- Resource Mobilization | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Stock Market – Raising Funds
Question.1: With regards to ‘public issue’ as a source of finance, answer the following questions:
(i) Which type of enterprise can raise funds by ‘Public Issue’?
(ii) What is the benefit to an investor while investing in ‘Public Issue’?
(iii) Despite many benefits, this source of finance has some additional obligations and reporting requirements. State any six such obligations and requirements.
(i) Public Limited Company
(ii) The reward investors seek is an appreciation of their investment and possibly dividends.
(iii) While there are benefits to going public, it also means additional obligations and reporting requirements such as:
- Increasing accountability to public shareholders.
- Need to maintain dividend and profit growth trends.
- Becoming more vulnerable to an unwelcome takeover.
- Need to observe and adhere strictly to the rules and regulations by governing bodies.
- Increasing costs in complying with higher level of reporting requirements.
- Relinquishing some control of the company following the public offering.
- Suffering a loss of privacy as a result of media interest.
Question.2: Explain the following as methods of new issues :
(i) Public issue; and
(ii) Rights issue.
(i) Public issue / going public: This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. When an entrepreneur offers shares to the public for subscription he/she is required to comply with all the restrictions and formalities pertaining to the initial issues, prospectus drafting and launch.
(ii) Rights issue: Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding. This method of issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive as it does not require any brokers, agents, underwriters, prospectus or enlistment, etc.
Question.3: What is meant by Capital Market? Why is it considered as the most important source of raising finance?
Capital Market may be defined as an organised mechanism meant for effective and smooth transfer of money capital from investors to the entrepreneurs.
Importance:
(i) Moblise the financial resources on a nationwide scale.
(ii) Secure the required foreign capital and knowhow to promote economic growth.
(iii) Ensure effective allocation of mobilized financial resources.
Question.4: State the objectives of SEBI.
The overall objectives of SEBI are to protect the interest of investors and to promote the development of stock exchange and to regulate the activities of stock market.
The objectives of SEBI are:
(i) To regulate the activities of stock exchange.
(ii) To protect the rights of investors and ensuring safety to their investment.
(iii) To prevent fraudulent malpractices by having balance between self-regulation of business and its statutory regulations.
(iv) To regulate and develop a code of conduct for intermediaries such as brokers, underwriters, etc.
Question.5: Explain briefly the organisation structure of SEBI.
SEBI is managed by its members, which consists of:
- Chairman, who is nominated by the Government of India.
- Two members, i.e., officers from the Union Finance Ministry.
- One member from the Reserve Bank of India.
- The remaining 5 members are nominated by the Union Government of India, out of them at least 3 shall be whole time members.
Question.6: ‘It is an organized mechanism meant for effective and smooth transfer of financial resources from the investors to the entrepreneurs’.
(a) Identify the mechanism and list its different types.
(b) Name the association of persons established under the mechanism identified in (a) above, Also explain any four points of its importance to investors.
(a) The mechanism is capital market : Capital market provides a platform to raise productive capital. It plays a very vital role of a financial intermediary. Different types of capital markets are :
(i) Primary market : Market for newly issued securities.
(ii) Secondary market : Market for existing securities.
(b) Association of persons established under the capital market is Stock Exchange.
Importance of Stock Exchange for investors :
Following are the importance of stock exchange from the investors point of view:(i) Dissemination of useful information : Stock exchange publish useful information
regarding price lists, quotations, etc., of securities through newspapers and journals.
Interested persons buy and sell their securities on the basis of information provided by the stock exchanges.
(ii) Ready market : Persons desirous of converting their shares into cash may easily do so through a member of stock exchange.
(iii) Investors’ interests protected: Stock exchanges formulate rules and regulations so that members may not exploit the investors.
(iv) Genuine guidance about the securities listed: The investors can safely depend upon the information provided by the stock exchanges.
(v) Barriers of distance removed : Stock exchange removes the barriers of distance in regard to securities listed there. Without stock exchange the securities of a Delhi company may have a limited market in Delhi only.
(vi) Knowledge of profit or loss on investments : The investors can estimate the profit or loss on the total amount of investments in securities, by comparing the original amount invested and the price of securities on a particular day.
Question.7: “An entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the Primary Market.” Explain the various methods of raising the funds in the Primary Market by an entrepreneur.
(i) Public issue : It is the most popular method of raising capital. This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. When an entrepreneur offers to the public for subscription he is required to comply with all the restrictions and formalities pertaining to the initial issues, prospectus drafting and launch.
(ii) Rights Issue : It is the method of raising finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis, i.e., giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding. In case the existing shareholders are not willing to subscribe, they can resource the same in favour of another person.
(iii) Private Placement : It means direct sale by a company of its securities to a limited number of sophisticated investors.
(iv) Offer to Employees : In stock option plan or offer to employees, company offer its shares to its employees at a rate lower than market price. This method enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company.
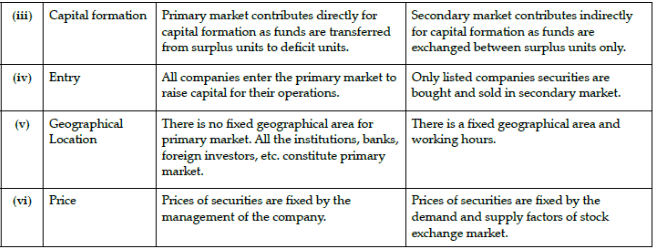
Question.8: Differentiate between Primary Market and Secondary Market.
Question.9: When an entrepreneur decides to go public and become a public company, he/she tends to be in advantageous positions and get many benefit out of it. Explain the benefits.
Advantages to an entrepreneur on going public are as follows :
(i) Access to capital : The primary advantage to an entrepreneur by going public is access to capital. This capital is not to be repaid and does not involve any charge on interest.(ii) Mergers and acquisitions : Public stock of a company can be used for businesses to grow through acquisitions.
(iii) Higher valuations : Public companies are typically valued more than private companies.
(iv) Benchmark trading price : The trading price of a public company’s stock serves
as a benchmark of the offer price of other securities.
(v) Capital formation : Raising capital later is typically easier because of the extra liquidity for the investors.(vi) Incentives : Stock options and stock incentives can be very helpful in attracting employees.
(vii) Reduced business requirements : While an underwritten initial public offering requires significant earnings, the lack of earnings does not keep a private company from going public.
(viii) Less dilution : There is less dilution of ownership control compared to an IPO.
(ix) Liquidity : A public company provides liquidity for management, minority shareholders and investors.
(x) Prestige : Added prestige and visibility with customers, suppliers, as well as the financial community.
Angel Investors and Venture Capital Funds
Question.1: Geeta has completed her B.Tech. in Chemical Engineering from a famous Indian Institute of Technology. She wants to start a chemical production unit wherein such chemicals will be produced which are used in automobile colouring and are being imported from other countries now a days. The technology to be used by Geeta is new and untried involving high risk factors along with high growth potential. She wants to raise funds for her project from such a source that provides private equity capital as seed funding to early stage, to give shape to her ideas.
(i) Suggest Geeta the source of finance from where she can fund her project.
(ii) Give the meaning of the source suggested in (i) above and state any four features of this source.
(i) Geeta can fund her project from ‘Venture Capital’
(ii) Venture capital is an equity based investment in a growth oriented small to medium business to enable the investors to accomplish objectives, in return for minority shareholding in the business on irrevocable right to acquire.
Features of Venture Capital are as follows :
(i) It is basically equity finance in relatively new companies.
(ii) It is a long term investment in growth oriented small or medium firms at early stage.
(iii) Venture capital not only provides capital but also business skills to investing firms.
(iv) It involves high risk return spectrum.
(v) It is a subset of private equity.
(vi) The venture capital institutions have a continuous involvement in business after making the investment.
(vii) Venture capital institutions disinvest the holdings either to the promoters or in the market.
Question.2: Explain the stages in which an entrepreneur should seek venture capital finance.
OR
Naveen after completing his M.Tech in Nano Technology wanted to start his own business. He thought to manufacture sophisticated instruments used in surgery. He knew that his knowledge of Nano Technology will help the surgeons to operate upon the patients with accuracy, with minimum blood loss and quick post operation recovery. Such types of instruments are used in advanced countries only and there was a risk in marketing the same. The cost price of machinery required for manufacturing such instruments was very high and more research was required in this field of Nano Technology. For seed funding, Naveen approached, ‘Himani Capital Ltd.’ who finance such types of projects. ‘Himani Capital Ltd.’ after analysing the proposal agreed to provide seed capital to Naveen. Explain the different stages of ‘Early Stage Financing’ to seek venture capital finance for the one discussed above.
Entrepreneurs can typically seek venture capital to assist in any of the following stages in the company’s development :
(i) Early stage financing
(ii) Last stage financing/bridge/pre-public stage
These are explained as under :
(i) Early stage financing : This stage includes :
- (a) Seed capital
- (b) Pre-start up and start up
- (c) Second-round financing
(a) Seed capital finance : It refers to the capital required by an entrepreneur for conducting research at pre-commercialization stage. During this stage, the entrepreneur has to convince the investor (venture capitalist) why his ideal product is worth while. A investor will investigate into the technical and the economical feasibility of the idea. In some cases, there is some sort of prototype of the idea/product that is not fully developed or tested. As the risk at this stage is very high, investor may deny to assist if he does not seeany potential in the investor.
(b) Start up finance : If the idea/product/ process is qualified for further investigation and/or investment, the process will go to the second stage. This is called the startup stage. A business plan is presented by the entrepreneur to the VC firm. A management team is being formed to run the venture. If the company has a board of director, a person from the VC firm will take a seat at the board of directors. While the organization is being set up, the idea/product gets its form. The prototype is being developed and fully tested. In some cases, the clients are being attracted for initial sales. The management-team establishes a feasible production line to produce the product. The VC firm monitors the feasibility of the product and the capability of the management team from the board of directors.
(c) Second round financing : At this stage, we presume that the idea has been transformed into a product and is being produced and sold. This is the first encounter with the rest of the market, the competitors and an attempt to squeeze the market and get some market share from the competitors. At this stage, larger funds than the other early stage financing are required for expansion, modernization, diversification. Here the entrepreneur should be extra careful because only if he and his team is able to prove their capability of standing against the competition, only then is the VC firm interested in financing.(ii) Last stage financing/bridge/pre-public stage: This is the last stage of the venture capital financing process. The main goal of this stage is for the venture to go public so that investors can exit the venture with a profit commensurate with the risk they have taken. At this stage, the venture achieves a certain amount of market share. This gives the ventures some opportunities like merger with other companies, eliminate competitors, etc. The entrepreneur must examine the product’s market position and if possible, reposition it to attract new market segmentation.
Question.3: What are the major considerations to be seen in Venture Finance?
A venture capitalist has to consider the following points before extending venture capital to an entrepreneur :
(i) Due Diligence : It refers to the process of investing the merits of a project or prospective investment. It includes qualification of the founding entrepreneur, size and growth characteristic of venture market, existing and potential competition, technical feasibility, etc.
(ii) Cost of Venture Capital : The cost of venture capital depends upon the investor’s perception of risk. The venture funds investor generally demands larger stake in equity in earlier stage than later stage. Investors in early stage expect 30% to 50% of compound annual return.
(iii) Exit Option : Venture capital is a patient investment by the venture capital supplier. Realization of capital gain occurs from 3 to 10 years from start-up. Venture investors need to know how and when they can expect to cash in their investment. Exit option includes selling the company, turning it into a publicly held company and buying back the investor’s share by the company itself or by its promoters.
|
19 videos|103 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Long Answer Type Question- Resource Mobilization - Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is resource mobilization in commerce? |  |
| 2. What are the key sources of resource mobilization in commerce? |  |
| 3. How does resource mobilization contribute to business growth? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges businesses face in resource mobilization? |  |
| 5. How can businesses optimize resource mobilization? |  |