Class 12 Economics: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term I (2021-22)- 1 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-XIITime: 90Max. Marks: 40 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class-XII
Time: 90
Max. Marks: 40
General instructions:
- The Question Paper contains 3 sections.
- Section - A has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section - B has 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions.
- Section - C has 12 questions. Attempt any 10 questions.
- All questions carry equal marks.
- There is NO negative marking.
Section - A
Q.1: The volume of money held by the public _________, in an economy, is referred to as the money supply.
(a) At a point of time
(b) Over a period of time
(c) Both (A) and (B)
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Total of money (currency notes coin and demand deposit of banks) in circulation held by the public at a given point of time.
Q.2: Fiscal deficit is equal to excess of total expenditure over the sum of _________.
(a) Revenue receipts and capital expenditure
(b) Revenue receipts and capital receipts
(c) Revenue expenditure and capital expenditure
(d) Revenue expenditure and capital receipts
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Fiscal deficit is equal to excess of total expenditure over the sum of revenue receipts and capital receipts excluding borrowings, i.e., Fiscal deficit means borrowing of the government.
Q.3: Identify the correct sequence of items in Column B matching them to the items in Column A.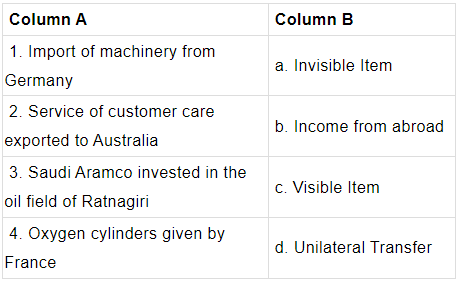
(a) 1 – a
(b) 2 – b
(c) 3 – c
(d) 4 – d
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Unilateral transfers are none way transfer of money goods or services which the residents of a country receive for fee.
Q.4: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement 1: The economic policies pursued by the colonial government in India were concerned more with the protection and promotion of the economic interests of their home country than with the development of the Indian economy.
Statement 2: India’s economy under the British colonial rule remained fundamentally agrarian.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The economic policies pursued by the colonial government in India were concerned more with the protection and promotion of the economic interests of their home country than with the development of the Indian economy. Such policies brought about a fundamental change in the structure of the Indian economy — transforming the country into supplier of raw materials and consumer of finished industrial products from Britain.
India’s economy under the British colonial rule remained fundamentally agrarian — about 85 percent of the country’s population lived mostly in villages and derived livelihood directly or indirectly from agriculture.
Q.5: In M1 component of money supply, demand deposits of all _________ are included.
(a) Commercial and Co-operative banks
(b) Commercial and Central bank
(c) Central and Co-operative banks
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (a)
In M1 component of money supply, demand deposits of all commercial and co-operative banks excluding inter-bank deposits, where demand deposits are those deposits which can be withdrawn by the depositor at any time by means of cheque. No interest is paid on such deposits.
Q.6: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement 1: Capital account of BoP records exports and imports of visible and invisible items and unilateral transfers.
Statement 2: Current Account of BoP records capital transfer such as loans and investments between one country and the rest of the world
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Current account is that account of BoP, which records exports and imports of visible and invisible items and unilateral transfers.
Capital Account of BoP records capital transfers such as loans and investments between one country and the rest of the world, which causes a change in the assets or liability status of the residents of the domestic country or its government.
Q.7: Tax reforms are concerned with the reforms in the government’s taxation and public expenditure policies, which are collectively known as its _________.
(a) Monetary policy
(b) Fiscal policy
(c) Supply side policy
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Government measures related to public expenditure, taxation and public debt are referred as fiscal measures and the policy related to these measures in called fiscal Policy.
Q.8: Which crop was benefitted most by green revolution?
(a) Wheat
(b) Tea
(c) Cotton
(d) Oil seeds
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Post-Green Revolution, the production of wheat doubled due to initiatives of the government. The stagnation in agriculture during the colonial rule was permanently broken by the green revolution. This refers to the large increase in production of food grains resulting from the use of high yielding variety (HYV) seeds especially for wheat and rice.
Q.9: Radhika and Siya went to the village for their project work assigned by their Economics teacher. In the village while looking at the conditions of poor people, Radhika said to Siya that these people are so poor that they are not able to access even basic necessities of life. They are also not able to meet the average per capita daily requirement.
Identify the type of poverty which Radhika was talking about to Siya.
(a) Relative
(b) Absolute
(c) Both (A) and (B)
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The per capita consumption expenditure level which meets the average per capita daily requirement of 2,400 calories in rural areas and 2,100 calories in urban areas, along with a minimum of non-food expenditure, is called poverty line or absolute poverty.
Q.10: Identify the notable economist who estimated India’s per capita income during the colonial period.
(a) Dadabhai Naoroji
(b) William Digby
(c) Findlay Shirras
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The colonial government never made any sincere attempt to estimate India’s national and per capita income. Some individual attempts which were made to measure such incomes yielded conflicting and inconsistent results. Among the notable estimators — Dadabhai Naoroji, William Digby, Findlay Shirras, V.K.R.V. Rao and R.C. Desai It was Rao, whose estimates during the colonial period was considered very significant.
Q.11: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement 1: At the time of independence, moneylenders and traders exploited small and marginal farmers and landless labourers.
Statement 2: The Green Revolution was a harbinger of major changes in the credit system.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
At the time of independence, moneylenders and traders exploited small and marginal farmers and landless labourers by lending to them on high interest rates and by manipulating the accounts to keep them in a debt-trap.
The Green Revolution was a harbinger of major changes in the credit system as it led to the diversification of the portfolio of rural credit towards production-oriented lending.
Q.12: What will be the total money created in an economy, when the LRR is 20%, and initial deposit is ₹ 10,000.
(a) ₹ 10,000
(b) ₹ 50,000
(c) ₹ 20,000
(d) ₹ 15,000
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Legal Reserve Ratio (LRR) is the minimum ratio of deposits legally required to be kept as cash by the banks.
Money Multiplies = 1/LRR
Total Money Creation
= Initial Deposits × 1/LRR
= ₹10,000 × 1/20%
= ₹50,000
Q.13: Identify the objective of government budget which states that “there is no fluctuation in price level in an economy”.
(a) Re-distribution of income and wealth
(b) Re-allocation of resources
(c) Economic growth
(d) Economic stability
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Economic stability an objective of government budget Government tries to establish economic stability by its budgetary policies. It refers to a situation where there is no fluctuation in price level in an economy. Economic stability is achieved by saving the economy from harmful effects of various trade cycles and its phases, i.e. boom, recession, depression and recovery, through various budgetary tools.
Q.14: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement 1: Economic growth means the increase in real national income of a country.
Statement 2: The contribution of the educated person to economic growth is more than that of an illiterate person.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The labour skill of an educated person is more than that of an uneducated person and that the former generates more income than the latter. Economic growth means the increase in real national income of a country; naturally, the contribution of the educated person to economic growth is more than that of an illiterate person.
Q.15: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement 1: Flexible exchange rate is determined by the market forces.
Statement 2: Under fixed exchange rate system, the central authority or government maintains their exchange rate fixed either against gold or some other currency.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The rate of exchange which is determined by the market forces of demand and supply of foreign currencies in the foreign exchange market, is termed as flexible exchange rate system. Fixed exchange rate is determined by the government for conversion of domestic currency into foreign currency.
Q.16: What percentage of India’s share in World Trade has been targeted in Foreign Trade Policy, 2004-2009?
(a) 1 percent
(b) 2 percent
(c) 1.5 percent
(d) 2.5 percent
Correct Answer is Option (c)
India had a share of 0.8% in Foreign Trade between 2003-2004, the target in this policy was set to achieve 1.5% share in world trade by 2009.
Q.17: Balance of Payments of a country is a systematic record of all _________ transactions between its residents and residents of foreign countries.
(a) Non-economic
(b) Economic
(c) Productive
(d) Non-productive
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Balance of Payment (BoP) of a country is a systematic record of the transactions in goods, services and assets between residents of a country with the rest of the world for a specified time period.
Q.18: When the number of poor is estimated as the proportion of people below the poverty line, it is known as _________.
(a) Mortality Rate
(b) Head Count Ratio
(c) Poverty Ratio
(d) Poverty Line
Correct Answer is Option (b)
When the number of poor is rated as part of people below the poverty line, it is known as ‘Head Count Ratio’.
Head Count Ratio = Number of People deemed poor/Total Population
Q.19: Under NEP 1991, structural reform policies are _________ measures.
(a) Short-term
(b) Long-term
(c) Medium-term
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Structural reform policies are long-term measures, aimed at improving the efficiency of the economy and increasing its international competitiveness by removing the rigidities in various segments of the Indian economy.
Q.20: Identify the function performed by central bank as a banker to the government.
(a) It receives deposits from the government.
(b) It collects cheques and drafts deposited in the government account.
(c) It provides cash to the government.
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (d)
As a banker to the government, the central bank performs same functions as performed by the commercial banks to their customers. It receives deposits from the government and collects cheques and drafts deposited in the government account. It provides cash to the government as resumed for payment of salaries and wages to their staff and other cash disbursements.
Q.21: It is essential to develop proper storage facilities for agricultural produce in _________ areas.
(a) Rural
(b) Urban
(c) Semi-urban
(d) Semi-rural
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Farmers did not have proper storage facilities to keep back their produce for selling later at a better price. Therefore, it is essential to develop proper storage facilities in rural areas so that farmers can wait for better price for their products in the market.
Q.22: Investment from abroad is recorded as a _________ item, whereas investment to abroad is recorded as an _________ item BoP.
(a) Credit, Debit
(b) Debit, Credit
(c) Export, Import
(d) Import, Export
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Capital Account of BoP records capital transfer such as loans and investments between one country and the rest of the world, which causes a change in the assets or liability status of the residents of the domestic country or its government. Investments include investments to and from abroad in the form of FDI and Fll. Investment from abroad is a ‘credit’ item as it is an inflow of foreign currency, whereas investment to abroad is a ‘debit’ item as it is an outflow of foreign currency.
Q.23: Liberalisation measures were introduced in 1980s in areas of:
(a) Industrial licensing
(b) Export-import policy
(c) Technology upgradation
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Rules and laws which were aimed at regulating the economic activities became major hindrances in growth and development. Liberalisation was introduced to put an end to these restrictions and open various sectors of the economy. Though a few liberalisation measures were introduced in 1980s in areas of industrial licensing, exportimport policy, technology upgradation, fiscal policy and foreign investment. Reform policies initiated in 1991 were more comprehensive.
Q.24: In a class, Manoj, Mary and Muhammad read out a line that due to Covid – 19 the capital and revenue expenditure of the government was more than the capital and revenue receipts it earned. Manoj said that the government has a fiscal deficit, Mary said that it was a Revenue deficit and Muhammad said that it is difficult to say that as the data is inadequate. Identify who is right.
(a) Manoj is right.
(b) Mary is right.
(c) Muhammad is right.
(d) All of them are wrong.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government total expenditure and its total receipts excluding borrowing. Fiscal Deficit: [Revenue Expenditure + Capital Expenditure] – [Revenue Receipts + Capital Receipts (other than government borrowings)]
Section - B
(a) Demand deposits are not legal tender.
(b) Currency notes issued are not legal tender.
(c) Term deposits are not legal tender.
(d) Wheat is not legal tender.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
A legal tender is a type of money that the court of law need to see as a satisfactory payment of any financial debt. In India, the authentic legal tender of the Reserve Bank of India consists of coins and notes.
Q.26: Choose the correct alternatives given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Commercial banks have a contribution to the quantity of money supply in the economy.
Reason (R): Commercial banks have the power to issue currency.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Commercial banks have a contributions to the quantity of money supply in the economy as commercial bank create credit through deposits and loans.
Q.27: Choose the correct pair of statements from the set of statements given in Column I and Column II: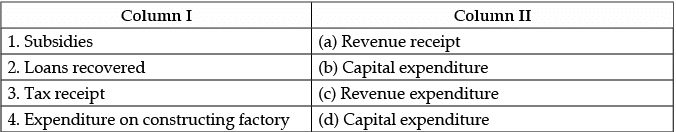
(a) 1 – a
(b) 2 – b
(c) 3 – c
(d) 4 – d
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Expenditure on constructing factory is a capital expenditure as it leads to creating asset. Whereas subsidy is a revenue expenditure. Tax receipt is a revenue receipt. Loans recovered is a capital receipt.
Q.28: Choose the correct alternatives given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Medical Tourism is great opportunity for India.
Reason (R): Indian health services combine the latest medical technologies with qualified professionals and are cheaper for foreigners. By upgrading health services, it can be a great opportunity for India.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.29: Government budget can be defined as an annual statement which shows estimated _________ and estimated _________ during a fiscal year.
(a) revenue, expenditure
(b) capital, expenditure
(c) revenue, capital
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Government budget can be defined as an annual statement which shows estimated revenue and estimated expenditure during a fiscal year.
Q.30: The transactions which are done to cover _________ in the balance of payments are called accommodating items.
(a) Deficit
(b) Surplus
(c) Either (A) or (B)
(d) Neither (A) nor (B)
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Accommodating items can be defined as those transactions which cover the gap in balance of payment or are done to cover deficit or surplus in balance of payments.
Q.31: Which out of the following is/are included in ‘Residents’ in BoP transactions?
(i) Firms
(ii) Foreign Military Personnel
(iii) Government agencies
(iv) Individual
Identify the correct alternatives from the following:
Alternatives:
(a) i
(b) ii
(c) iii and iv
(d) i, ii, and iii
Correct Answer is Option (d)
A resident is said to be a person (or institution) who ordinarily resides in a country and whose centre of economic interest lies in that country.
Q.32: Choose the correct alternatives given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): M1 and M2 are the narrow concepts of money.
Reason (R): In narrow sense, we include only liquid assets which are easily acceptable for payments.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
M1 and M2 which includes only liquid assets are the narrow concepts of money because it can be accepted as medium of exchange very easily.
Q.33: Identify the correct statement.
(a) During the British rule, there were large number of capital goods industries.
(b) There was low level of unemployment in the economy during the British rule.
(c) Indian handicraft industry was destroyed by the British government.
(d) Exported finished goods from India to Britain.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Indian handicraft industry was destroyed by the British government by supplying raw material to Britain at cheap rates and by importing their products in Indian market and selling them at huge prices.
Q.34: Choose the correct alternatives given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Government through tax incentives to industrialists to start industries in backward areas.
Reason (R): The main objective of Government Budget is to have a balanced regional growth.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The main objective of government budget is having a regional growth which is balanced. For this government has started giving incentives to industrialists to start industries in backward areas.
Q.35: The demographic condition of Indian economy during the British rule were _________ and _________.
(i) Low literacy rate
(ii) Low birth and death rate
(iii) Low life expectancy
(iv) High Infant mortality rate
Alternatives:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The demographic condition of Indian economy during British rule was stagnant and backward and it exhibited features like low literacy rate, low life expectancy and higher infant mortality rate.
Q.36: Choose the correct alternatives given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Tax is a revenue receipt.
Reason (R): Revenue Receipts are receipts of the government which neither create any liabilities nor reduce any assets.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Revenue receipts can be defined as those receipts which neither create liability nor cause any reduction in asset. For example, income tax, profits of PSUs dividend, fees and fines etc.
Q.37: Trade between more than two countries is called as _________ trade.
(a) Bilateral trade
(b) Multilateral trade
(c) Both (A) and (B)
(d) Neither (A) nor (B)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Trade between more than two countries is called multi-lateral trade.
Q.38: Choose the correct alternatives given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Profits received from investments abroad is recorded in Capital Account.
Reason (R): Profits neither affects foreign exchange assets nor foreign exchange liabilities.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Profits received from investments abroad is recorded in current account as it neither affects foreign exchange assets nor foreign exchange liabilities.
Q.39: Read the following statements and select the correct alternatives from the following:
Statement 1: Tariff barriers can be defined as those barriers which are levied on imports so as to make them expensive.
Statement 2: Tariff barriers restrict domestic production and imports facilities.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Tariff barriers can be defined as those barriers which are levied on imports so as to make them expensive. Tariff barriers improve domestic production and restrict imports.
Q.40: Credit that farmers need for consumption purpose such as on birth and death, etc. is called:
(a) Productive credit
(b) Unproductive credit
(c) Both (A) and (B)
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Unproductive credit refers to the credit taken to meet consumption expenditures for social and religious purposes.
Q.41: When migration takes place, then it leads to cost of migration from one place to another and _________ cost of living in the migrated place.
(a) lower
(b) higher
(c) same
(d) both (A) and (B)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.42: On the basis of the above-mentioned information answer the following question: Which among the following has lowest increase in production?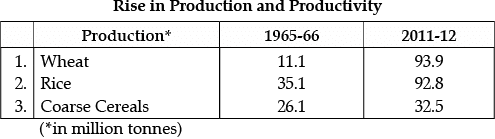
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Coarse Cereals
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.43: Read the following statements and select the correct alternatives from the following:
Statement 1: Absolute poverty can be defined as the number of people who are living below the poverty line.
Statement 2: Relative poverty can be defined as poverty of people when they are considered poor by comparing with other people or nation.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Relative Poverty: It refers to poverty of people in comparison to other people, regions or nations.
Absolute Poverty: It means the inability to arrange for the basic human needs such as food, clothing, health facilities, housing, etc.
Q.44: Identify the incorrect statement from the following.
(a) Population explosion is the reason for rise of poverty in the economy.
(b) Disparities in income is the cause of poverty in the economy.
(c) High level of literacy and high level of economic development are the reasons for the rising poverty.
(d) Rising inflation is one of the causes of poverty.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
High level of literacy and high level of economic development are the reasons for fall in poverty.
Q.45: Identify the correct statement from the following.
(a) Poverty alleviation programmes have been introduced by government to increase poverty.
(b) Growth oriented approach is the economic growth that occurred in the economy and removed the poverty of people from the poor sections of the society and it was successful.
(c) Minimum needs programme includes Public Distribution System (PDS) and Mid-day Meal scheme.
(d) ‘Rural employment Generation Programme’ and ‘Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana’ are the wage employment programmes.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Minimum needs programme was started in 5th five year plan and its objective is to provide minimum basic facilities to the poor through Public Distribution System (PDS), Mid-day Meal Scheme and Integrated Child Development Scheme (ICDS).
Q.46: Read the following statements and select the correct alternatives from the following:
Statement 1: According to human capital, education and health are the ways through which labour productivity can be increased.
Statement 2: According to human development, investment in education and health should be made even if such type of investment does not lead to increase in labour productivity.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
According to human capital, labour productivity can be increased through investment in education and health. Even if investments do not lead to increase in labour productivity, investment should be made in education and health which is termed as human development.
Q.47: Match the situations given in Column I with Column II: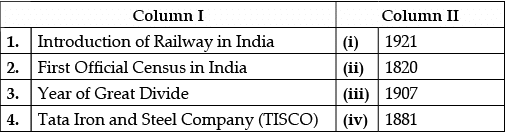
(a) 1-ii, 2-iii, 3-i, 4-iv
(b) 1-ii, 2-i, 3-iv, 4-iii
(c) 1-iv, 2-ii, 3-i, 4-iii
(d) 1-ii, 2-iv, 3-i, 4-iii
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.48: Physical capital is _________ whereas human capital is _________.
(a) Intangible, tangible
(b) Tangible, tangible
(c) tangible, intangible
(d) Intangible, tangible
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Physical capital like machines, equipment etc. are tangible as they can be seen and touched but human capital is intangible as it includes skills, expertise, etc. which cannot be seen.
Section - C
Both growth and equity are the two important objectives of Indian planning. While growth refers to the increase in national income over a long period of time, equity refers to an equitable distribution of this income so that the benefits of higher economic growth can be passed on to all sections of population to bring about social justice.
Growth is desirable as you must have the cake to distribute it but growth in itself does not guarantee the welfare of society. Growth is assessed by the market value of goods and services produced in the economy (GDP) and it does not guarantee an equitable distribution of the income from this production. In other words, the major share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) might be owned by a small proportion of population which may result in exploitation of weaker sections of society.
Hence, growth with equity is a rational and desirable objective of planning. This objective ensures that the benefits of high growth are shared by all people equally and hence, inequality of income is reduced along with growth in income.
What is the objective of Indian Economic Planning?
(a) Economic Growth
(b) Infrastructural Development
(c) Both (A) and (B)
(d) Neither (A) nor (B)
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The objective of economic planning is to achieve economic growth which implies higher production of goods and services in the economy.
Both growth and equity are the two important objectives of Indian planning. While growth refers to the increase in national income over a long period of time, equity refers to an equitable distribution of this income so that the benefits of higher economic growth can be passed on to all sections of population to bring about social justice.
Growth is desirable as you must have the cake to distribute it but growth in itself does not guarantee the welfare of society. Growth is assessed by the market value of goods and services produced in the economy (GDP) and it does not guarantee an equitable distribution of the income from this production. In other words, the major share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) might be owned by a small proportion of population which may result in exploitation of weaker sections of society.
Hence, growth with equity is a rational and desirable objective of planning. This objective ensures that the benefits of high growth are shared by all people equally and hence, inequality of income is reduced along with growth in income.
What leads to the higher benefit from economic growth?
(a) Economic Development
(b) Unemployment
(c) Equitable Distribution of Income
(d) All of these
Correct Answer is Option (a)
It is important to ensure that the benefits of economic property reach the poor sections as wall instead of being enjoyed only by the rich.
Both growth and equity are the two important objectives of Indian planning. While growth refers to the increase in national income over a long period of time, equity refers to an equitable distribution of this income so that the benefits of higher economic growth can be passed on to all sections of population to bring about social justice.
Growth is desirable as you must have the cake to distribute it but growth in itself does not guarantee the welfare of society. Growth is assessed by the market value of goods and services produced in the economy (GDP) and it does not guarantee an equitable distribution of the income from this production. In other words, the major share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) might be owned by a small proportion of population which may result in exploitation of weaker sections of society.
Hence, growth with equity is a rational and desirable objective of planning. This objective ensures that the benefits of high growth are shared by all people equally and hence, inequality of income is reduced along with growth in income.
Growth does not guarantee _________.
(a) Higher Income
(b) Economic Development
(c) Welfare of the Society
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Economic growth does not guarantee that all sections of the society will be able to get the benefits of it or it will lead to welfare of all.
Both growth and equity are the two important objectives of Indian planning. While growth refers to the increase in national income over a long period of time, equity refers to an equitable distribution of this income so that the benefits of higher economic growth can be passed on to all sections of population to bring about social justice.
Growth is desirable as you must have the cake to distribute it but growth in itself does not guarantee the welfare of society. Growth is assessed by the market value of goods and services produced in the economy (GDP) and it does not guarantee an equitable distribution of the income from this production. In other words, the major share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) might be owned by a small proportion of population which may result in exploitation of weaker sections of society.
Hence, growth with equity is a rational and desirable objective of planning. This objective ensures that the benefits of high growth are shared by all people equally and hence, inequality of income is reduced along with growth in income.
Equity as the objective of Economic Planning guarantees _________.
(a) High Growth Benefits
(b) Reduction of Inequality
(c) Growth in income
(d) All of these
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Equity as the objective of economic planning guarantees that high growth will be achieved, reduction in inequality and growth in income will be achieved.
Both growth and equity are the two important objectives of Indian planning. While growth refers to the increase in national income over a long period of time, equity refers to an equitable distribution of this income so that the benefits of higher economic growth can be passed on to all sections of population to bring about social justice.
Growth is desirable as you must have the cake to distribute it but growth in itself does not guarantee the welfare of society. Growth is assessed by the market value of goods and services produced in the economy (GDP) and it does not guarantee an equitable distribution of the income from this production. In other words, the major share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) might be owned by a small proportion of population which may result in exploitation of weaker sections of society.
Hence, growth with equity is a rational and desirable objective of planning. This objective ensures that the benefits of high growth are shared by all people equally and hence, inequality of income is reduced along with growth in income.
Read the following statements and select the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: Economic growth can be defined as when the production of goods and services increases consistently over a period of time.
Statement 2: The benefits of economic growth with equity are shared by all and hence reducing inequalities of income.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Economic growth with equity as a desirable objective of planning means that benefits of economic growth are shared by all people equally.
Both growth and equity are the two important objectives of Indian planning. While growth refers to the increase in national income over a long period of time, equity refers to an equitable distribution of this income so that the benefits of higher economic growth can be passed on to all sections of population to bring about social justice.
Growth is desirable as you must have the cake to distribute it but growth in itself does not guarantee the welfare of society. Growth is assessed by the market value of goods and services produced in the economy (GDP) and it does not guarantee an equitable distribution of the income from this production. In other words, the major share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) might be owned by a small proportion of population which may result in exploitation of weaker sections of society.
Hence, growth with equity is a rational and desirable objective of planning. This objective ensures that the benefits of high growth are shared by all people equally and hence, inequality of income is reduced along with growth in income.
Choose the correct alternative given below from the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Economic growth can be defined as rise in national income over a long period of time.
Reason (R): Social justice can be achieved without equity.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Economic growth is the increase in the real output of the country in a particular span of time. Without equitable distribution of income, benefits of economic growth cannot reach to all sections of the society.
Q.55: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following diagram: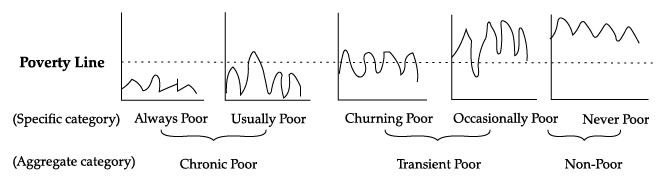
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement 1: The poverty line can be defined as the cut-off point on the line of distribution which differentiates between poor and non-poor.
Statement 2: While deciding poverty line, standard is fixed in terms of minimum level of consumption.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the Statement are true.
(b) Both the Statement are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The poverty line can be defined as the cut-off point on the line of distribution which differentiates between poor and non-poor. Also, it is decided in terms of minimum level of consumption.
Q.56: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following diagram:
Read the following statements and select the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: The people who fall under the ‘chronic poor’ category are to be benefitted with poverty alleviation programmes.
Statement 2: The people who fall under the ‘non poor’ category are to be benefitted with poverty alleviation programmes.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the Statements are true.
(b) Both the Statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but Statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Chronic poor includes people who are always poor and those who are usually poor but sometimes have a little more money. Thus, this section should be benefitted most with the poverty allevition programmers.
Q.57: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following diagram:
Read the following statements and select the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1: High level of indebtedness and income inequalities are the reasons for poverty in India.
Statement 2: Lack of infrastructure and lack of active participation of poor people are the critical evaluation of poverty alleviation programmes.
Alternatives:
(a) Both the Statements are true.
(b) Both the Statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true but Statement 2 is false.
(d) Statement 1 is false but Statement 2 is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Poverty in India is rising due to huge indebtedness and rising income inequalities. Also, poverty alleviation programmes were criticized due to lack of infrastructure and lack of active participation of poor people.
Q.58: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following diagram: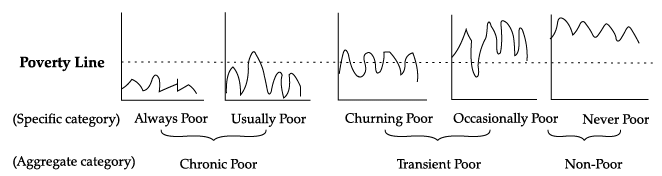
The dotted line in the given diagram depicts _________.
(a) Poverty line
(b) Employment
(c) Poverty ratio
(d) Inflation
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Poverty line is the dotted line which divides the people of the region as poor and non-poor.
Q.59: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following diagram:
Chronic poor includes:
(i) Always poor
(ii) Churning poor
(iii) Usually poor
(iv) Never poor Alternatives:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Chronic poor includes those who leads constant lives of poverty but sometimes they may have small amount of money.
Q.60: Question are to be answered on the basis of the following diagram: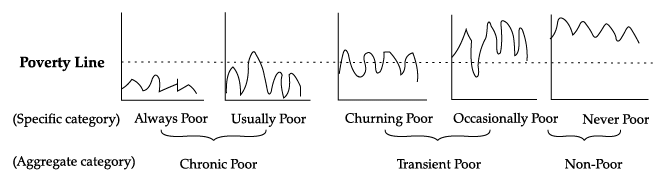
Identify the correct statement from the following:
(a) Churning poor are those who regularly move in and out of poverty.
(b) Small farmers are consider as occasionally poor.
(c) Never poor are those who are rich most of the time may have a patch of bad luck.
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
|
130 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Economics: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term I (2021-22)- 1 - Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce
| 1. What is the format of the Class 12 Economics exam? |  |
| 2. What is the maximum marks for the Class 12 Economics exam? |  |
| 3. What is the time duration for the Class 12 Economics exam? |  |
| 4. What is the purpose of Section A in the Class 12 Economics exam? |  |
| 5. What can be expected in Section C of the Class 12 Economics exam? |  |




















