Class 12 Political Science: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term I (2021-22)- 2 | CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Class-XII
Time: 90 Minutes
Max. Marks: 40
General Instructions
1. The question paper has three sections as A, B & C.
2. Section A has 24 questions, attempt any 20 questions.
3. Section B has 24 questions, attempt any 20 questions.
4. Section C has 12 questions, attempt any 10 questions.
5. There is only one correct option for every question. Marks will not be awarded for marking more than one option.
6. All questions carry equal marks. There is no negative marking
Section A
Q.1: On the reforms of structures and processes, the biggest discussions has been on the functioning of the
(a) Security Council.
(b) Health of the infants
(c) Child mortality rate
(d) Nuclear weapon possession
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Security Council has primary responsibility, under the United Nations Charter, for the maintenance of international peace and security. It is for the Security Council to determine when and where a UN peace operation should be deployed.
Q.2: With the disappearance of the Soviet Union, the US stands as the only:
(a) Major power
(b) Master power
(c) Superpower
(d) Inner power
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.3: Select the correct option for the Alliance and the organization it was formalized into:
(a) The Eastern Alliance was formalized into UNO.
(b) The Western Alliance was formalized into NATO.
(c) The Central Alliance was formalized into SEATO.
(d) The Neutral Alliance was formalized into Peace keeping forces.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Western alliance was formalized into the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO), which came into existence in April 1949 to provide security against USSR. It was an association of twelve states which declared that armed attack on any one of them would be regarded as an attack on all of them.
Q.4: When did Cuban Missile Crisis occur?
(a) 1967
(b) 1962
(c) 1960
(d) 1970
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In 1962 the Soviet Union began to secretly install missiles in Cuba to launch attacks on U.S. cities. The confrontation that followed, known as the Cuban missile crisis, brought the two superpowers to the brink of war before an agreement was reached to withdraw the missiles.
Q.5: What was the first among the three challenges to India while building a nation-state?
(a) building a united nation
(b) poverty
(c) communal tensions
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The first and the immediate challenge was to shape a nation that was united, yet accommodative of the diversity in our society.
Q.6: The ‘Two-Nation Theory’ was based upon:
(a) expansion of India
(b) bifurcation of the states
(c) partition of India
(d) All of the Above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Two Nation Theory is based on the hypothesis that India should be divided into two: Pakistan and Hindustan, the Muslim nation to occupy Pakistan and the Hindu nation to occupy Hindustan.
Q.7: The ............................ laid foundation for Non Alignment Movement established in 1961 with Nehru as the co-founder.
(a) Bandung Conference
(b) Foreign Policy
(c) US Aid
(d) Peace Treaty
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Bandung Conference and its final resolution laid the foundation for the non- aligned movement during the Cold War. Leaders of developing countries banded together to avoid being forced to take sides in the Cold War contest. The initial motivation for the movement was the promotion of peace.
Q.8: The first nuclear explosion undertaken by India was in May:
(a) 1964
(b) 1974
(c) 1984
(d) 1994
Correct Answer is Option (a)
During the tenure of Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, first underground nuclear explosion occurred at Pokhran in Rajasthan on May 18, 1974
Q.9: India opposed the indefinite extension of the NPT in:
(a) 1995
(b) 1985
(c) 1975
(d) 1965
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.10: Why stronger countries’ foreign policies were supported by many countries after WW2?
(a) Because stronger countries supported them and aided them financially.
(b) Because they were afraid of being colonized again.
(c) Because most countries in the world did so.
(d) Because they were poor.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Most of the newly independent countries feared of the war between the two blocs. They never wanted to face any financial as well as political consequences. Hence, they supported the stronger nations for financial as well as military aid.
Q.11: In which year CENTO was established?
(a) 1956
(b) 1957
(c) 1958
(d) 1955
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.12: Which of the following statements about the Cold War is wrong?
(a) It was an ideological war between the superpowers.
(b) It was a competition between the US and Soviet Union and their respective allies.
(c) It triggered of an arms race.
(d) The US and USSR were engaged in direct war.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Neither the Soviet Union nor the United States officially declared war on each other, both of them were trying to prove themselves as a superpower.
Q.13: Which one of the following statement related to the Iraq invasion by the US is incorrect?
(a) The UN had given consent to invade Iraq.
(b) The UN had given consent to invade Iraq.
(c) The invasion was to prevent Iraq from developing weapons of mass destruction.
(d) The US lost over 3000 military personnel in this war.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.14: Shock therapy involved a drastic change in the ...................... orientation of the economies.
(a) external
(b) internal
(c) international
(d) opposition
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.15: Mikhail Gorbachev was elected as the General Secretary of the Communist
Party of the Soviet Union in:
(a) 1955
(b) 1965
(c) 1975
(d) 1985
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.16: The US, Japan, Germany, France, the UK, Italy, Canada and Russia are the:
(a) G8 members
(b) D8 members
(c) Cold War countries
(d) Dominating members
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Group of Eight + Five (G8+5) was an international group that consisted of the leaders of the heads of government from the G8 nations (Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States), plus the heads of government of the five leading emerging economies (Brazil, China, India, Mexico, and South Africa).
Q.17: Which state was carved out of Assam from the following:
(a) Meghalaya
(b) Sikkim
(c) Manipur
(d) Tripura
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Meghalaya was created as an autonomous state within the state of Assam on 2 April, 1970. The full-fledged State of Meghalaya came into existence on 21 January, 1972. It is bound on the north and east by Assam, and on the south and west by Bangladesh.
Q.18: The foreign policy of independent India vigorously pursued the dream of a peaceful world by advocating the policy of:
(a) non-alignment
(b) no nuclear weapons
(c) military expansion
(d) no Cold War
Correct Answer is Option (a)
India didn’t join US & USSR during cold war. India advocating the policy of non alignment by reducing the Cold war alliance and led the protest against Neocolonialism.
Q.19: Which set of the countries belonged to the NATO Group?
(a) Poland, Britain, Romania
(b) USA, Czech Republic, France
(c) United Kingdom, France, West Germany
(d) Spain, France, East Germany
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Twelve countries took part in the founding of NATO: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In 1952, Greece and Turkey became members of the Alliance, joined later by West Germany (in 1955) and Spain (in 1982).
Q.20: Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan, the undisputed leader of the North Western Frontier Province was known as:
(a) Frontier Gandhi
(b) Father of Pakistan
(c) Staunch Muslim
(d) Patriot of Pakistan
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Ghaffar Khan was a Pashtun who greatly admired Mahatma Gandhi and his nonviolence principles and saw support for the Congress as a way of pressing his grievances against the British frontier regime. Hence, he was called the Frontier Gandhi.
Q.21: Select the correct option for the leader and the country that helped to reach the Tashkent agreement between India and Pakistan
(a) India, Nehru
(b) USSR, Kosygin
(c) Egypt, Nasser
(d) Indonesia, Sukarno
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Tashkent Declaration was a peace agreement between India and Pakistan signed on 10 January 1966 to resolve the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965. The meeting was held in Tashkent in the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Union represented by Premier Aleksey Kosygin.
Q.22: The WHO has played a leading role in ...................
(a) public health achievement
(b) economic development
(c) children’s health
(d) resolving disputes among the nations
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The World Health Organization (WHO) plays an essential role in the global governance of health and disease; due to its core global functions of establishing, monitoring and enforcing international norms and standards, and coordinating multiple actors toward common goals.
Q.23: In 1992, the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution related to:
(a) UN Security Council
(b) UNESCO
(c) UNICEF
(d) World Bank
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.24: How were the boundaries of the states decided?
(a) On the basis of locality
(b) On the basis of linguistic principles
(c) On the basis of area
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Section B
Q.25: What was the stand of Indian Government on partition?
(a) India did not respond at all.
(b) India wanted peace, harmony and equality of religion.
(c) India wanted to become a Hindu nation.
(d) None of the above.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Indian Government believed in communal harmony and equality of religion for all. This highly important belief also found its place in the Constitution of India where India was declared a secular nation and the Fundamental Right of ‘Right to Religion’ was given to all citizens of India.
Q.26: The non-permanent members are elected in a manner so that they represent all the ...................... of the world.
(a) races
(b) sections
(c) continents
(d) grievances
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.27: The Cold War is referred to the competition, the tensions and a series of confrontations between the:
(a) United States and the Soviet Union
(b) France and Germany
(c) India and Pakistan
(d) America and Africa
Correct Answer is Option (a)
In 1945, Allied Forces defeated the Axis Powers that marked the end of the Second World War. Both the super powers indulged in Cold War so that they could prove their superiority over the other.
Q.28: It was in ........................ that full diplomatic relations were restored between India and Pakistan.
(a) 1976
(b) 1966
(c) 1956
(d) 1946
Correct Answer is Option (a)
India was attacked by China in October 1962. It took more than a decade for India and China to resume normal relations.
Q.29: Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel faced key challenges of integration in which of the following states.
(a) Hyderabad, Moradabad, Junagarh
(b) Hyderabad, Sikandrabad, Jammu
(c) Hyderabad, Junagarh, Kashmir
(d) Jammu, Junagarh, Kashmir
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Sardar Patel faced key challenges of integration from three states, viz., Hyderabad, Junagarh and Kashmir. It was under his leadership that Indian forces compelled Hyderabad and Junagarh to merge with India. Like Hyderabad, he also wanted Kashmir’s integration with India through military operations. But due to political decisions of some prominent leaders, Sardar could not succeed in integrating Kashmir fully with India which later turned into a major historical blunder for the country.
Q.30: Arrange the following in the chronological order:
(i) Establishment of Human Rights Council
(ii) Yalta Conference
(iii) Atlantic Charter
(iv) India join the UN
(a) (ii), (iv), (i), (iii)
(b) (iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
(c) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
(i) The Atlantic Charter issued on 14 August 1941. (ii) Yalta Conference held on 11 February 1945. (iii) On 26 June 1945, India join the UN. (iv) Human Rights Council established on 15 March 2006.
Q.31: Who was the Secretary of UN in 1997?
(a) Bill Clinton
(b) General Kofi Annan
(c) George W Bush
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Kofi Annan (Ghana) held the office from January 1997 to December 2006.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q.32:
Assertion: International organizations only solve the disputes among the countries.
Reason: International organizations are helpful in another way. Nations can usually see that there are some things they must do together. There are issues that are so challenging that they can only be dealt with when everyone works together. Disease is an example.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
International organizations, apart from resolving disputes, can play an important role to deal with the other issues like poverty, pandemic or any natural disaster which needs international attention.
Q.33:
Assertion: The fact that the UN is physically located within the US territory gives Washington additional sources of influence.
Reason: Within the UN, the influence of the US is considerable.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The history of United States of America (USA) and the United Nations (UN) is long and complex. The United Nations owes a lot of what it is today to the US. It was the US that breathed life into the UN with its power and resources. ... Despite that, the UN does hold an important position in US foreign policy.
Q.34: Which U.N. agency concerned with the safety and peaceful use of nuclear technology?
(a) The UN Committee on Disarmament
(b) International Atomic Energy Agency
(c) UN International Safeguard Committee
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The main functions of the IAEA are to: encourage and assist research, development and practical application of atomic energy for peaceful uses throughout the world; establish and administer safeguards designed to ensure that such activity assisted by the Agency is not used to further any military purpose.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q.35:
Assertion: With the end of the Cold War, we can see that the UN may have a slightly different role.
Reason: As the United States and its allies emerged victorious, there was concern amongst many governments and peoples that the Western countries led by the US would be so powerful that there would be no check against their wishes and
desires.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
After the Cold War ended, there was a rapid increase in the number of peacekeeping operations. With a new consensus and a common sense of purpose, the Security Council authorized a total of 20 new operations between 1989 and 1994, raising the number of peacekeepers from 11,000 to 75,000.
Q.36:
Assertion: The US President, John F. Kennedy, and his advisers were reluctant to do anything that might lead to full-scale nuclear war between the two countries.
Reason: The possible clash (Cold War) between the two countries was avoided.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
There were no direct military campaigns between the two main antagonists, the United States and the Soviet Union. Yet billions of dollars and millions of lives were lost in the fight.
Q.37:
Assertion: Each state from this bloc was now linked directly to the West and not to each other in the region.
Reason: The transition also involved a breakup of the existing trade alliances among the countries of the Soviet bloc.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.38:
Assertion: Gorbachev’s decision to normalize relations with the West and democratize and reform the Soviet Union had some other effects that neither he nor anyone else intended or anticipated.
Reason: People supported Gorbachev in his every decision he has taken.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Soviet economy was under great pressure and burden. What added to the problem was its corrupt governance and unrest among people.
Q.39:
Assertion: Central Asian countries were already in control of US.
Reason: Central Asia has also become a zone of competition between outside powers and oil companies.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Central Asia is a major focus of competition for the world’s political and economic powers because of its strategic position and rich oil and gas resources.
Q.40:
Assertion: The problem was that two of the Muslim majority provinces of British India, Punjab and Bengal, had very large areas where the non- Muslims were in majority.
Reason: It was decided that these two provinces would be bifurcated according to the religious majority at the district or even lower level.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Since there was no possibility of large-scale migration of the people, the decision was taken to divide it according to the religious majority.
Q.41:
Assertion: The interim government took a firm stance against the possible division of India into small principalities of different sizes.
Reason: Before 15 August 1947, peaceful negotiations had brought almost all states whose territories were contiguous to the new boundaries of India, into the Indian Union.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The interim government took a firm stance against the possible division of India into smaller principalities of different sizes. The Muslim League opposed the Indian National Congress and took the view that the States should be free to adopt any course they liked.
Q.42:
Assertion: The Second Five Year Plan stressed on heavy industries. It was drafted by a team of economists and planners under the leadership of P. C. Mahalanobis.
Reason: However, the Second Five Year Plan was responsible for the ruin of the agriculture as it did not have enough funding to support it
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
During this plan, annual plans were made and equal priority was given to agriculture its allied sectors and the industry sector. Agriculture was never left out of the plan at all.
Q.43:
Assertion: ‘Development’ was about becoming more ‘modern’ and modern was about becoming more like the industrialized countries of the West.
Reason: It was believed that every country would go through the process of modernization as in the West, which involved the breakdown of traditional social structures and the rise of capitalism and liberalism.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.44: Assertion: Indian air crafts attacked parts of Pakistan and the army moved into POK and Swat Valley.
Reason: After months of diplomatic tension and military build-up, a full-scale war between India and Pakistan broke out in December 1971.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
India indeed had given the answer to Pakistan’s mischievous acts on the border. But, the attack was never initiated by Indian side, nor did Indian army entered Swat Valley.
Q.45:
Assertion: The two sides understood that war might occur in spite of restraint.
Reason: Because they wanted to confront each other with weapons.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Both of the superpowers had nuclear weapons, and the enormous possibility that any kind of escalation could potentially lead to their use and the end of human life. A stable balance of weapons, they decided, could be maintained through ‘arms control’.
Q.46:
Assertion: Development could not be left to private actors, that there was the need for the government to develop a design or plan for development.
Reason: The Bombay Plan wanted the state to take major initiatives in industrial and other economic investments.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Development could not be left to private actors because the idea of planning as a process of rebuilding economy earned a good deal of public support.
Q.47: Assertion: The Nizam of Hyderabad never negotiated with Sardar Patel. He was not at all agreed to accept any offer to join India.
Reason: The Nizam wanted an independent status for Hyderabad.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Nizam entered into what was called the Standstill Agreement with India in November 1947 for a year while negotiations with the Indian government were going on.
Q.48:
Assertion: Nehru had always put his faith in science and technology for rapidly building a modern India.
Reason: A significant component of his industrialization plans was the nuclear programme initiated in the late 1940s under the guidance of Homi J. Bhabha.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Nehru was a man of modern ideology. He was the great admirer of science and technology. He had initiated nuclear industry because India wanted to generate atomic energy for peaceful purposes. Nehru was against nuclear weapons.
Section C
Q.49: Study the picture below and answer the following questions (49- 50):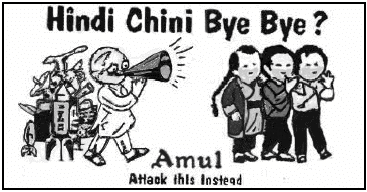
What message does this cartoon convey?
(a) Scenario of recession.
(b) Persisting Indo- China tensions.
(c) Boycotting foreign products.
(d) Reduce exports of Indian goods.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.50: Which year does the event happened?
(A) 1962
(B) 1974
(C) 1969
(D) 1950
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.51: Study the cartoon given below and answer the following question:
Which country is represented by this mighty soldier?
(a) Russia
(b) China
(c) USA
(d) Canada
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.52: Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows: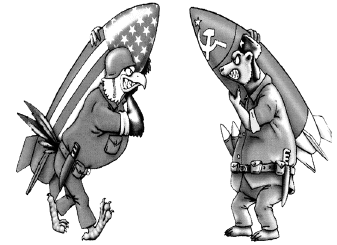
What could be the appropriate title for the picture given above?
(a) US vs USSR economic contestation.
(b) Capitalist vs Communist Model.
(c) Contestation between two superpowers; US vs USSR.
(d) Cuban Missile Crisis.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The main enemies were the United States and the Soviet Union. The Cold War got its name because both sides were afraid of fighting each other directly. In a “hot war,” nuclear weapons might destroy everything. So, instead, both sides fought a proxy war. The proxy warfare was motivated by fears that a conventional war between the United States and the Soviet Union would result in nuclear holocaust.
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
The Second Five Year Plan stressed on heavy industries. It was drafted by a team of economists and planners under the leadership of P.C. Mahalanobis. If the first plan had preached patience, the second wanted to bring about quick structural transformation by making changes simultaneously in all possible directions. Before this plan was finalized, the Congress party at its session held at Avadi near the then Madras city, passed an important resolution. It declared that ‘Socialist pattern of society’ was its goal. This was reflected in the Second Plan. The government imposed substantial tariffs on imports in order to protect domestic industries. Such protected environment helped both public and private sector industries to grow. As savings and investment were growing in this period, a bulk of these industries like electricity, railways, steel, machineries and communication could be developed in the public sector. Indeed, such a push for industrialisation marked a turning point in India’s development.
Q.53: Who drafted the Second Five Year Plan?
(a) Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar
(b) P. C. Mahalanobis
(c) Morarji Desai
(d) Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Second Plan focused on the development of the public sector and “rapid Industrialization”. The plan followed the Mahalanobis model, an economic development model developed by the Indian statistician Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis in 1953.
Q.54: What was anticipated from Second Five Year Plan?
(a) Structural transformation
(b) Economic transformation
(c) Infrastructural development
(d) Eradication of poverty
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The main objectives of the Second Plan are an increase of 25 per cent in real national income over the five-year period 1956– 57 to 1960–61; a large expansion of employment opportunities; rapid industrialization; and reduction of economic inequalities.
Q.55: What goal was declared by the Congress Party at the session held at Avadi?
(a) Religious pattern society
(b) Capitalist pattern society
(c) Socialist pattern society
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
“Socialist pattern of society” , according to the planning Commission, means “that the basic criterion for determining the lines of advance must not be private profit but social gain, and that the pattern of development and the structure of socio-economic relations should be so planned so that the result not only in appreciable in creases in national income and employment but also in greater equality in incomes and wealth”.
Q.56: Why did government impose substantial tariffs on imports?
(a) To increase the income from imports
(b) To create employment in import-export sector
(c) To restrict foreign goods
(d) To protect domestic industries
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Governments may impose tariffs to raise revenue or to protect domestic industries—especially nascent ones—from foreign competition. By making foreign produced goods more expensive, tariffs can make domestically produced alternatives seem more attractive.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow:
India has opposed the international treaties aimed at non-proliferation since they were selectively applicable to the non-nuclear powers and legitimised the monopoly of the five nuclear weapons powers. Thus, India opposed the indefinite extension of the NPT in 1995 and also refused to sign the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT). India conducted a series of nuclear tests in May 1998, demonstrating its capacity to use nuclear energy for military purposes. Pakistan soon followed, thereby increasing the vulnerability of the region to a nuclear exchange. The international community was extremely critical of the nuclear tests in the subcontinent and sanctions were imposed on both India and Pakistan, which were subsequently waived. India’s nuclear doctrine of credible minimum nuclear deterrence professes “no first use” and reiterates India’s commitment to global, verifiable and non-discriminatory nuclear disarmament leading to a nuclear weapons free world. Foreign policy is always dictated by ideas of national interest. In the period after 1990, Russia, though it continues to be an important friend of India, has lost its global pre-eminence. Therefore, India’s foreign policy has shifted to a more pro-US strategy.
Q.57: Which of the following nuclear treaties were rejected by India?
(a) NPT, CTBT
(b) Kyoto Protocol
(c) Panchsheel Agreement
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
India has refused to sign the Treaty on the grounds of CTBT, like the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), is discriminatory. Even before coming into force, the CTBT has helped the cause of test-ban and nuclear disarmament by discouraging member-states from testing for and developing nuclear weapons.
Q.58: When did India conduct series of nuclear tests?
(a) June 1998
(b) May 1998
(c) April 1998
(d) March 1998
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.59: Why India’s foreign policy shifted to become more pro-US?
(a) Because Russia betrayed India.
(b) Because Russia attacked India.
(c) Because US derived more profit to India.
(d) Because Russia lost its global pre-eminence.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The absolute increase in its military and economic resources began to compel India to think less like a developing, non-aligned country and more like an emerging and responsible power. India is also struggling to address the tension between the concepts of ‘strategic autonomy’ and ‘strategic influence’. This was the reason for India’s foreign policy shifted to become more pro-US.
Q.60: Which one of the following is India’s stand for the use of nuclear weapon?
(a) No use of nuclear weapon at all.
(b) No first use of nuclear weapon.
(c) Use nuclear weapon in case of war.
(d) None of the above.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
India’s adherence to a no-first use principle is long-standing. Ever since 1998, when the country went nuclear, New Delhi has rejected the idea of initiating the use of such weapons in any conflict scenario. Nukes, in Indian strategy, are purely retaliatory. And that stance has made good military and diplomatic sense.
|
129 docs|4 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Humanities/Arts exam
|

|

















