Class 12 Political Science: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term I (2021-22)- 3 | CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Class-XII
Time: 90 Minutes
Max. Marks: 40
General Instructions
1. The question paper has three sections as A, B & C.
2. Section A has 24 questions, attempt any 20 questions.
3. Section B has 24 questions, attempt any 20 questions.
4. Section C has 12 questions, attempt any 10 questions.
5. There is only one correct option for every question. Marks will not be awarded for marking more than one option.
6. All questions carry equal marks. There is no negative marking
Section A
Q.1: Which one of the following statement related to the Iraq invasion by the US is incorrect?
(a) More than forty other countries were involved in this invasion.
(b) The UN had given consent to invade Iraq.
(c) The invasion was to prevent Iraq from developing weapons of mass destruction.
(d) The US lost over 3000 military personnel in this war.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.2: On the reforms of structures and processes, the biggest discussions has been on the functioning of the
(a) Security Council.
(b) Health of the infants
(c) Child mortality rate
(d) Nuclear weapon possession
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Security Council has primary responsibility, under the United Nations Charter, for the maintenance of international peace and security. It is for the Security Council to determine when and where a UN peace operation should be deployed.
Q.3: Which one of the following leaders played an important role in the integration of princely states with India?
(a) Jawahar Lal Nehru
(b) SardarVallabhbhai Patel
(c) C. Rajagopalchari
(d) Dr. B. R. Ambedkar
Correct Answer is Option (b)
At the time of independence, the problem of integration of princely states was a big challenge for the national unity and integrity of India. Under such difficult times, Sardar Patel undertook the daunting tasks of uniting all 565 princely states of India. Known as an ‘Iron Man’ of India, Patel’s approach to the question of the merger of princely states into independent India was very clear. He was not in favour of any compromise with the territorial integrity of India.
Q.4: Select the correct option for the leader and the country that helped to reach the Tashkent agreement between India and Pakistan:
(a) India, Nehru
(b) USSR, Kosygin
(c) Egypt, Nasser
(d) Indonesia, Sukarno
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Tashkent Declaration was a peace agreement between India and Pakistan signed on 10 January 1966 to resolve the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965. The meeting was held in Tashkent in the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Union represented by Premier Aleksey Kosygin.
Q.5: Select the correct option for the Alliance and the organization it was formalized into:
(a) The Eastern Alliance was formalized into UNO.
(b) The Western Alliance was formalized into NATO.
(c) The Central Alliance was formalized into SEATO.
(d) The Neutral Alliance was formalized into Peace keeping forces.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Western alliance was formalized into the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO), which came into existence in April 1949 to provide security against USSR. It was an association of twelve states which declared that armed attack on any one of them would be regarded as an attack on all of them.
Q.6: Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel faced key challenges of integration in which of the following states.
(a) Hyderabad, Moradabad, Junagarh
(b) Hyderabad, Sikandrabad, Jammu
(c) Hyderabad, Junagarh, Kashmir
(d) Jammu, Junagarh, Kashmir
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Sardar Patel faced key challenges of integration from three states, viz., Hyderabad, Junagarh and Kashmir. It was under his leadership that Indian forces compelled Hyderabad and Junagarh to merge with India. Like Hyderabad, he also wanted Kashmir’s integration with India through military operations. But due to political
decisions of some prominent leaders, Sardar could not succeed in integrating Kashmir fully with India which later turned into a major historical blunder for the country.
Q.7: Nehru was our first Prime Minister as well as:
(a) Health Minister
(b) Foreign Minister
(c) Education Minister
(d) Finance Minister
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.8: Where is the head quarter of UNICEF?
(a) Tokyo
(b) Chicago
(c) Los Angeles
(d) New York
Correct Answer is Option (d)
UNICEF founded on 11 December, 1946 at New York, an agency responsible for
providing humanitarian and developmental aid to children worldwide.
Q.9: In 1992, the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution related to:
(a) UN Security Council
(b) UNESCO
(c) UNICEF
(d) World Bank
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.10: How were the boundaries of the states decided?
(a) On the basis of locality
(b) On the basis of linguistic principles
(c) On the basis of area
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.11: The US, Japan, Germany, France, the UK, Italy, Canada and Russia are the:
(a) G8 members
(b) D8 members
(c) Cold War countries
(d) Dominating members
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Group of Eight + Five (G8+5) was an international group that consisted of the leaders of the heads of government from the G8 nations (Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States), plus the heads of government of the five leading emerging economies (Brazil, China, India, Mexico, and South Africa).
Q.12: When was UNESCO established?
(a) 6th November, 1946
(b) 5th November, 1945
(c) 4th November 1946
(d) 25th December 1946
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) was established on 4 November 1946 which aims to to contribute to the building of a culture of peace, the eradication of poverty, sustainable development and intercultural dialogue through education, the sciences, culture, communication and information
Q.13: The high point of Cold War was ....................... .
(a) Cuban Missile Crisis
(b) Atomic bomb attack on Hiroshima and Nagasaki
(c) Establishment of SEATO and CENTO
(d) Establishment of NATO
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Cuban Missile Crisis was a dangerous confrontation between the US andthe USSR in which both of them came closest to nuclear conflict.
Q.14: When did the American become aware of the weapon placed in Cuba by USSR?
(a) On the first day
(b) One week later
(c) Three weeks later
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
When USSR placed the missiles in Cuba, which was very closed to the American mainland. Three weeks later an American U-2 spy plane secretly photographed nuclear missile sites being built by the Soviet Union on the island of Cuba.
Q.15: How were the boundaries of the states decided?
(a) On the basis of locality
(b) On the basis of linguistic principles
(c) On the basis of area
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.16: Which of these statements about the princely states is incorrect:
(a) Some of the princely states clearly wanted to become part of the Indian Union.
(b) The Indian government was ready to give autonomy to some regions.
(c) The ruler of Junagadh had decided not be an independent state and be part of independent India.
(d) Princely states covered one third of the land area of the British Indian Empire.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Junagarh or Junagadh was a princely state in Gujarat ruled by the Muslim Babi dynasty in British India, until its annexation by the Union of India in 1948.
Q.17: Sri Lanka is a member of :
(a) SAARC
(b) UNESCO
(c) G7
(d) WHO
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is an organization of eight countries (Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka) in South Asia established in 1985.
Q.18: In post WW2 era, why the tensions were erupted between India and US?
(a) US feared that India would join USSR.
(b) US wanted to colonize India.
(c) The NAM pursued by India was not liked by USA.
(d) None of the above.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.19: The first nuclear explosion undertaken by India was in May:
(a) 1964
(b) 1974
(c) 1984
(d) 1994
Correct Answer is Option (a)
During the tenure of Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, first underground nuclear explosion occurred at Pokhran in Rajasthan on May 18, 1974.
Q.20: Why stronger countries’ foreign policies were supported by many countries after WW2?
(a) Because stronger countries supported them and aided them financially.
(b) Because they were afraid of being colonized again.
(c) Because most countries in the world did so.
(d) Because they were poor.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Most of the newly independent countries feared of the war between the two blocs. They never wanted to face any financial as well as political consequences. Hence, they supported the stronger nations for financial as well as military aid.
Q.21: Which of the following statements about the Cold War is wrong?
(a) It was an ideological war between the superpowers.
(b) It was a competition between the US and Soviet Union and their respective allies.
(c) It triggered of an arms race.
(d) The US and USSR were engaged in direct war.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Neither the Soviet Union nor the United States officially declared war on each other, both of them were trying to prove themselves as a superpower.
Q.22: The first non-aligned summit was held in the year 1961 in ................... .
(a) Venice
(b) Delhi
(c) Belgrade
(d) Dhaka
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.23: A system in which the affairs at the international level cannot be dominated by only one superpower but by a group of countries is known as:
(a) unipolar world
(b) capitalise world
(c) multi-polar world
(d) collective world
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Multi-polarity is a distribution of power in which more than two nation-states have nearly equal amounts of military, cultural, and economic influence.
Q.24: Mikhail Gorbachev was elected as the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in:
(a) 1955
(b) 1965
(c) 1975
(d) 1985
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Section B
Q.25: Who was India’s Deputy Prime Minister at the time of integration of princely states?
(a) Jawahar Lal Nehru
(b) Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar
(c) Narsimha Rao Reddy
(d) Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Q.26: How many states signed United Nations Charter in 1945?
(a) 55
(b) 39
(c) 67
(d) 50
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The Charter was signed on 26 June 1945 by 50 countries; Poland signed on 15 October 1945.
Q.27: Which set of the countries belonged to the NATO Group?
(a) Poland, Britain, Romania
(b) USA, Czech Republic, France
(c) United Kingdom, France, West Germany
(d) Spain, France, East Germany
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Twelve countries took part in the founding of NATO: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In 1952, Greece and Turkey became members of the Alliance, joined later by West Germany (in 1955) and Spain (in 1982).
Q.28: When did India and China signed Panchsheel agreement?
(a) 24 April, 1954
(b) 29 April, 1954
(c) 30 April, 1954
(d) 1 March, 1959
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Panchsheel Agreement signed on 29 April 1954 by the Indian Prime Minister Jawahar Lal Nehru and the Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai to make stronger relationship between the two countries.
Q.29: The ‘Two-Nation Theory’ was based upon:
(a) expansion of India
(b) bifurcation of the states
(c) partition of India
(d) All of the Above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Two Nation Theory is based on the hypothesis that India should be divided into two: Pakistan and Hindustan, the Muslim nation to occupy Pakistan and the Hindu nation to occupy Hindustan.
Q.30: Arrange the following in the chronological order:
(i) Establishment of Human Rights Council
(ii) Yalta Conference
(iii) Atlantic Charter
(iv) India join the UN
(a) (ii), (iv), (i), (iii)
(b) (iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
(c) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
Correct Answer is Option (b)
(i) The Atlantic Charter issued on 14 August 1941. (ii) Yalta Conference held on 11 February 1945. (iii) On 26 June 1945, India join the UN. (iv) Human Rights Council established on 15 March 2006.
Q.31: When was UNESCO established?
(a) 6th November, 1946
(b) 5th November, 1945
(c) 4th November 1946
(d) 25th December 1946
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) was established on 4 November 1946 which aims to to contribute to the building of a culture of peace, the eradication of poverty, sustainable development and intercultural dialogue through education, the sciences, culture, communication and information.
Q.32: “The United Nations was not created to take humanity to the heaven, but to save it from the hell.” Who made this statement?
(a) Pt. Jawahar Lal Nehru
(b) Kofi Annan
(c) Ban Ki-moon
(d) Dag Hammarskj öld
Correct Answer is Option (d)
By making this statement he means that International organisations are there to resolve the conflicts between countries without going to war. They can discuss contentious issues and find peaceful solutions.
Q.33: Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The fact that the UN is physically located within the US territory gives Washington additional sources of influence.
Reason: Within the UN, the influence of the US is considerable.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The history of United States of America (USA) and the United Nations (UN) is long and complex. The United Nations owes a lot of what it is today to the US. It was the US that breathed life into the UN with its power and resources. ... Despite that, the UN does hold an important position in US foreign policy.
Q.34: Which U.N. agency concerned with the safety and peaceful use of nuclear technology?
(a) The UN Committee on Disarmament
(b) International Atomic Energy Agency
(c) UN International Safeguard Committee
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The main functions of the IAEA are to: encourage and assist research, development and practical application of atomic energy for peaceful uses throughout the world; establish and administer safeguards designed to ensure that such activity assisted by the Agency is not used to further any military purpose.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Q.35:
Assertion: The UN is an imperfect body, but without it the world would be worse off.
Reason: Given the growing connections and links between societies and issues—what we often call ‘interdependence’—it is hard to imagine how more than seven billion people would live together without an organization such as the UN.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The UN accomplishes this by working to prevent conflict, helping parties in conflict make peace, deploying peacekeepers, and creating the conditions to allow peace to hold and flourish. The UN Security Council has the primary responsibility for international peace and security.
Q.36:
Assertion: Soviet Union, decided to convert Cuba into a Russian base.
Reason: Cuba was an ally of the Soviet Union and received both diplomatic and financial aid from it.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Nikita Khrushchev decided to convert Cuba into a Russian base as the ally,
Cuba, was very close to American cities or mainland.
Q.37:
Assertion: The hydrocarbon resources have brought an enormous prosperity to these countries.
Reason: The Central Asian Republics are areas with vast hydrocarbon resources.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
After the Soviet breakup, Central Asia has gained importance for several States because of its geographical location and abundance of hydrocarbon reserves. These hydrocarbon reserves are located mainly in three countries: Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.
Q.38:
Assertion: Shock Therapy was the transitional form from authoritarian socialist system to a democratic capitalist system in Russia, Central Asia and East Europe under the influence of the World Bank and IMF.
Reason: The model of transition in Russia, Central Asia and east Europe that was influenced by the World Bank and the IMF came to be known as ‘Shock therapy’.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q.39:
Assertion: Most of the former Soviet Republics are prone to conflicts, and many have had civil wars and insurgencies.
Reason: In Russia, two republics, Chechnya and Dagestan, have had violent secessionist movements.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
After the disintegration of soviet system, many of the soviet republics witnessed violent secessionist movements. Chechnya and Dagestan were two of them.
Q.40:
Assertion: It was decided to follow the principle of religious majorities for the partition.
Reason: The process of partition was smooth and none of the violence took place.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
During the Partition of India, violence against women was an extensive issue. It is estimated that during the partition between 75,000 and 100,000 women were kidnapped and raped. India and Pakistan later worked to repatriate the abducted women. Muslim women were to be sent to Pakistan and Hindu and Sikh women to India.
Q.41:
Assertion: The British Government took the view that all these 565 states were free to join either India or Pakistan or remain independent if they so wished.
Reason: This was a very serious problem and could threaten the very existence of a united India.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The official policy statement of the Government of India made by Sardar Patel on July 5, 1947 made no such threats. It reassured the princely states about the Congress’ intentions, and invited them to join independent India.
Q.42:
Assertion: India did not follow any of the two known paths to development – it did not accept the capitalist model of development in which development was left entirely to the private sector, nor did it follow the socialist model in which private property was abolished and all the production was controlled by the state.
Reason: It was India’s one of the biggest mistakes that India did not adopt any one of the two models suggested above.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Elements of both these models (capitalist and socialist) were taken and mixed together in India and hence, it did not accept the capitalist model of development in which development was left entirely to the private sector, nor did it follow the socialist model in which private property was abolished and all the production was controlled by central authority.
Q.43:
Assertion: Development could not be left to private actors, that there was the need for the government to develop a design or plan for -development.
Reason: The Bombay Plan wanted the state to take major initiatives in industrial and other economic investments.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Development could not be left to private actors because the idea of planning as a process of rebuilding economy earned a good deal of public support.
Q.44:
Assertion: A boundary dispute had surfaced between India and China. India claimed that the boundary was a matter settled in colonial time, but China said that any colonial decision did not apply.
Reason: The China war dented India’s image at home and abroad. India had to approach the Americans and the British for military assistance to tide over the crisis.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The Chinese denied any agreement happened between India and China regarding the borders. India continued to claim the territories which belonged to her. This dispute led to the war of 1962 for which India was never ready.
Q.45:
Assertion: NAM gave the members right not to choose any bloc over the other and yet gave them the right to deal with the global issues.
Reason: Jawahar Lal Nehru isolated India from the entire world.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Non-aligned posture served India’s interests in at least two ways. Firstly, Non-alignment allowed India to take international decisions and stances that served its interests rather than the interests of the superpowers and their allies. Secondly, India was often able to balance one superpower against the other.
Q.46:
Assertion: The example of Orissa shows us that it is not enough to say that everyone wants development.
Reason: For ‘development’ has same or similar meanings for different sections of the people.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Development has different meanings for different sections of the people. People do not have the same notion of development. This is because people have different occupations and different lifestyles. Since people have the different quality of life, so notions of development are not similar to each other.
Q.47:
Assertion: India adopted representative democracy based on the parliamentary form of government.
Reason: These features ensure that the political competition would take place in a democratic framework.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
India is a parliamentary Democratic Republic in which the President of India is the head of state and the Prime Minister of India is the head of government. It is based on the federal structure of government, although the word is not used in the Constitution itself. It assures a healthy and democratic political competition.
Q.48:
Assertion: Following the Arab-Israel War of 1973, the entire world was affected by the Oil Shock due to the massive hike in the oil prices by the Arab nations.
Reason: India was not at all affected by the crises at that time. India was already in a position to deal with any economic depression. Nor did oil prices hike in India.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Section C
Q.49: Read the following cartoon and answer the following questions: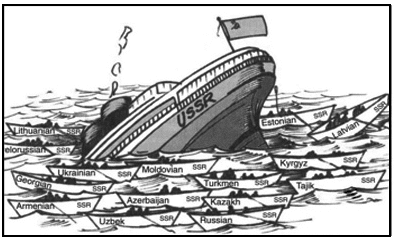
How many countries did the Soviet Union disintegrate?
(a) 15
(b) 14
(c) 13
(d) 18
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Study the cartoon given below carefully and answer the questions that follow.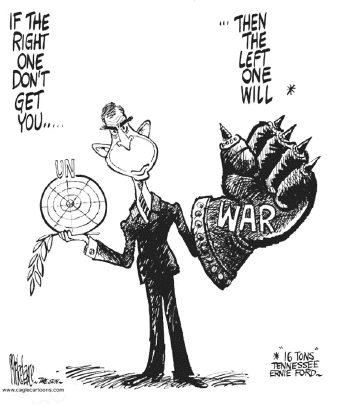
Q.50: What have been the reasons for immense influence of US on UN?
(a) USA’s economic superiority
(b) USA’s weapon capacity
(c) UN’s head quarter is in USA and USA’s financial contribution to UN.
(d) All of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Although the United States continues to play a leadership role at the UN, it has also accumulated massive arrears in its payments to the UN, owing the world organization approximately $1 billion, far more than any other member state.
Q.51: Why this cartoon is not relevant today?
(a) Because all the countries have their powerful organizations.
(b) US is now not as powerful as it used to, as the new centres of power emerged.
(c) Iraq and Afghanistan war has affected US economy.
(d) UN has become more powerful.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Study the cartoon given below carefully and answer the questions that follow:
Q.52: Which type of economic model was adopted by India?
(a) Capitalist
(b) Socialist
(c) Liberal socialist
(d) Mixed economic principle
Correct Answer is Option (d)
India did not accept the model in which development was left entirely to the private sector, nor did they follow in which private property was abolished and all the production was controlled by the state. Hence, they took elements from both these models and mixed together. That is why it was described as ‘mixed economy’.
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
The end of the Second World War is a landmark in contemporary world politics. In 1945, the Allied Forces, led by the US, Soviet Union, Britain and France defeated the Axis Powers led by Germany, Italy and Japan, ending the Second World War (1939- 1945). The war had involved almost all the major powers of the world and spread out to regions outside Europe including Southeast Asia, China, Burma (now Myanmar) and parts of India’s northeast. The war devastated the world in terms of loss of human lives and civilian property. The First World War had earlier shaken the world between 1914 and 1918.The end of the Second World War was also the beginning of the Cold War. The world war ended when the United States dropped two atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945, causing Japan to surrender. Critics of the US decision to drop the bombs have argued that the US knew that Japan was about to surrender and that it was unnecessary to drop the bombs. They suggest that the US action was intended to stop the Soviet Union from making military and political gains in Asia and elsewhere and to show Moscow that the United States was supreme. US supporters have argued that the dropping of the atomic bombs was necessary to end the war quickly and to stop further loss of American and Allied lives. Whatever the motives, the consequence of the end of the Second World War was the rise of two new powers on the global stage. With the defeat of Germany and Japan, the devastation of Europe and in many other parts of the world, the United States and the Soviet Union became the greatest powers in the world with the ability to influence events anywhere on earth.
Q.53: Which countries comprised the “allied forces" ?
(a) US, Soviet Union, Britain and France.
(b) US, Germany, Soviet Union and Britain.
(c) US, Soviet Union, Britain, France and Japan.
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The major Allied Powers were Britain, France, Russia, and the United States. The Allies formed mostly as a defence against the attacks of the Axis Powers. The original members of the Allies included Great Britain, France and Poland.
Q.54: When did the First World War start?
(a) 1914
(b) 1918
(c) 1915
(d) 1920
Correct Answer is Option (a)
World War I, also known as the Great War, began in 1914 after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria.
Q.55: How long the Second World War lasted?
(a) five years
(b) seven years
(c) three years
(d) six years
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Lasting six years and one day, the Second World War started on 1 September 1939 with Hitler’s invasion of Poland and ended with the Japanese surrender on 2 September 1945.
Q.56: What is the critics’ opinion about USA dropping the atomic bombs on Japan
(a) USA was completely unaware that Japan was about to surrender.
(b) USA already had knowledge that Japan is going to surrender.
(c) USA wanted to control Japan as its colony.
(d) USA wanted to capture Japan’s natural resources.
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Read the following case and answer the questions that follows:
International Organizations (IOs) are formal institutional structures transcending national boundaries which are created by multilateral agreement among nation-states. Their purpose is to foster international cooperation in areas such as: security, law, economic, social matters and diplomacy. IOs are subdivided between Intergovernmental Organizations (IGOs) and Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs); Intergovernmental Organizations are entities created with sufficient organizational structure and autonomy to provide formal, ongoing, multilateral processes of decision making between states, along with the capacity to execute the collective of their member (states). NGOs are non-state voluntary organizations formed by individuals to achieve a common purpose, often oriented beyond themselves or to the public good. The development and expansion of these large representative bodies date back to the end of the World War II, where there was a need for world reconstruction through International Relations. Since then, there has been an incremental rise of organizations that work on different socio-political and economic aspects with various and specific aims in approaching states, societies, groups and individuals. Based on these key definitions, it is an attempt to explain how important are IOs and the extent to which they have an impact on global politics and international relations through an analysis of two main IR scholar theories namely Realism and Liberalism. Moreover, to understand the impact of IOs, these theories will be explored and analysed through contexts of different and conflicting realist and liberalists thinkers upon their view on these institutional structures. It will also distinguish and compare the two theories and determine which is more relevant to the contemporary world international relations.
Q.57: What is the purpose of International Organisations?
(a) To foster economic ties of the developed nations
(b) To foster international cooperation
(c) To eradicate terrorism
(d) To foster health care
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The role of international organizations is helping to set the international agenda, mediating political bargaining, providing a place for political initiatives and acting as catalysts for the coalition- formation. They facilitate cooperation and coordination among member nations.
Q.58: What are the sub divisions of International Organisations?
(a) State-governmental and Non-governmental
(b) Private and Public
(c) Governmental and Public
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (d)
It is usual to distinguish between three main types of “international organization”, namely: inter-governmental organizations, international non-governmental organizations, and multinational enterprises.
Q.59: Where can we find the development and expansion of these organisations?
(a) At the end of first world war
(b) At the beginning of second world war
(c) At the end of second world war
(d) In 2003
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.60: Which two main IR scholars theories are mentioned here?
(a) Realism and Liberalism
(b) Capitalism and Socialism
(c) Feminism and Humanism
(d) Human Rights and Welfare
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Traditionally there have been two central theories of IR: liberalism and realism. Although they have come under great challenge from other theories, they remain central to the discipline. At its height, liberalism in IR was referred to as a ‘utopian’ theory and is still recognised as such to some degree today.
|
129 docs|4 tests
|
















