Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Mindmap: Practical Geometry
Mindmap: Practical Geometry - Class 6 PDF Download
FAQs on Mindmap: Practical Geometry - Class 6
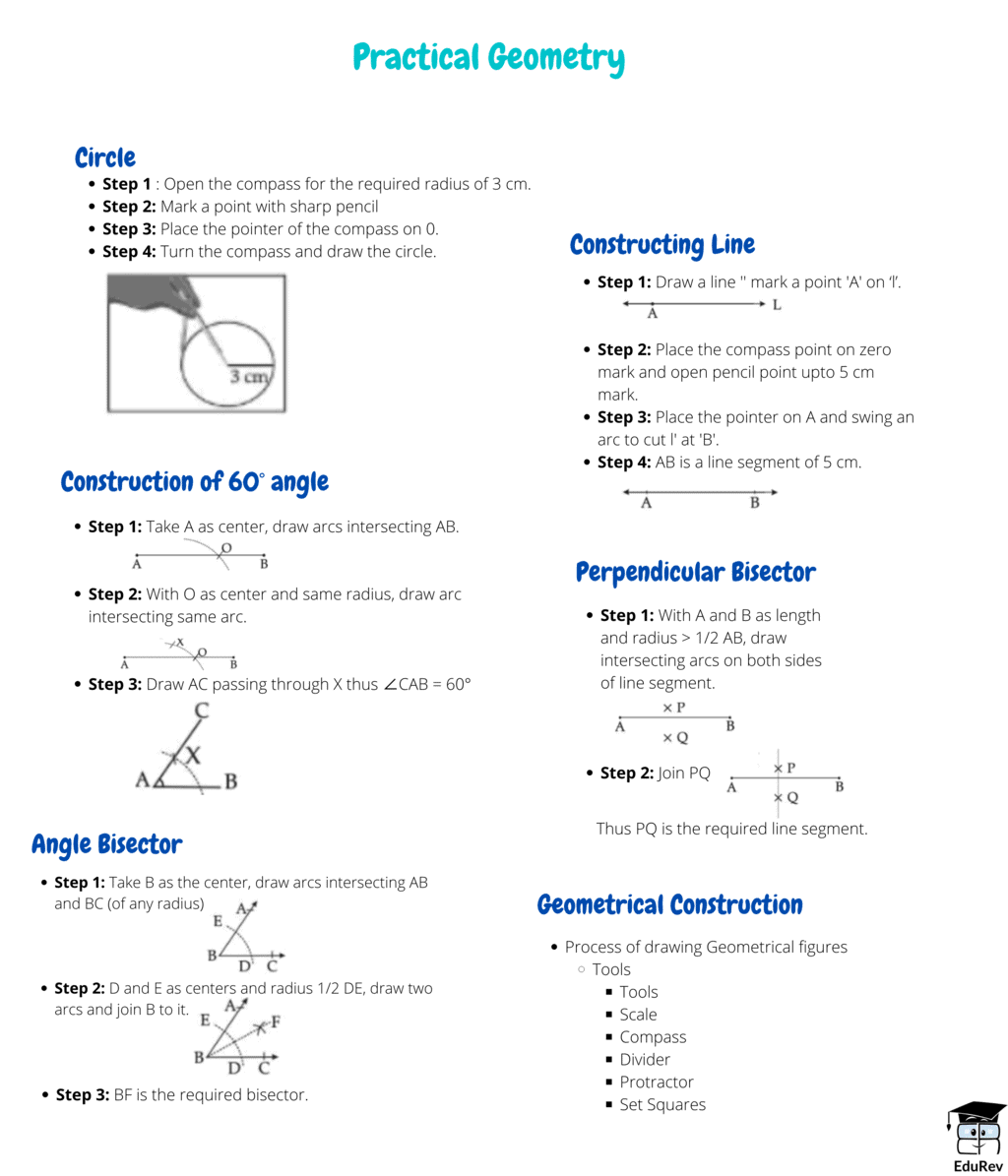
| 1. What is practical geometry? |  |
Ans. Practical geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the construction and properties of geometric figures in a real-world context. It involves using tools such as compass, ruler, and protractor to draw accurate shapes and solve problems related to measurements and angles.
| 2. How is practical geometry useful in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Practical geometry is useful in everyday life for various reasons. It helps in designing and constructing buildings, bridges, and other structures. It also assists in measuring and dividing land for agriculture or construction purposes. Additionally, practical geometry is applied in various crafts and art forms, such as woodworking, fashion designing, and architecture.
| 3. What are the basic tools used in practical geometry? |  |
Ans. The basic tools used in practical geometry include a compass, ruler, protractor, and pencil. A compass is used to draw circles and arcs, while a ruler helps in drawing straight lines and measuring lengths. A protractor is used to measure and draw angles accurately. A pencil is necessary for making precise markings on paper.
| 4. How do you construct a perpendicular bisector using practical geometry? |  |
Ans. To construct a perpendicular bisector using practical geometry, follow these steps:
1. Place the compass point on one end of the line segment.
2. Open the compass to a length greater than half of the line segment.
3. Draw two arcs intersecting the line segment from each side.
4. Without changing the compass width, place the compass point on the other end of the line segment.
5. Draw two more arcs intersecting the line segment.
6. Connect the intersection points of the arcs using a ruler.
7. The line connecting the intersection points is the perpendicular bisector of the line segment.
| 5. How do you find the area of a triangle using practical geometry? |  |
Ans. To find the area of a triangle using practical geometry, follow these steps:
1. Measure the length of the base of the triangle using a ruler.
2. Use a protractor to measure the angle between the base and one of the sides.
3. Multiply the length of the base by the length of the side and then multiply the result by the sine of the measured angle.
4. Divide the obtained value by 2 to find the area of the triangle.
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches