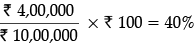Class 12 Business Studies: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term II (2021-22)- 5 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce PDF Download
Class-XII
Time:120
Max. Marks: 40
General instructions:
- This is a Subjective Question Paper containing 12 questions.
- This paper contains 4 questions of 2 marks each, 4 questions of 3 marks each and 4 questions of 5 marks each.
- 2 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 30-50 words.
- 3 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 50-80 words.
- 5 marks questions are Long Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 80-120 words.
- This question paper contains Case/Source Based Questions.
Short Answer Type Questions – I
Training helps employees to improve their knowledge and skill to make them perform their tasks more efficiently. It also helps them in promotion and improves their attitudes and confidence levels. Development refers to an information process which mainly improves the overall growth of the employees. Training and Development is an attempt to improve the current or future employee performance by increasing an employee’s ability to perform through learning, usually by changing the employee’s attitude or increasing his or her skills and knowledge.
The protective function implies the role that SEBI plays in protecting the investor interest and also that of other financial participants. Prohibition of fraudulent and unfair trade practices like making misleading statements, manipulations, price rigging, insider trading etc. is the function of SEBI.
The first two steps in the process of selection are as follows:
(i) Preliminary Screening: Preliminary screening helps the manager eliminate unqualified or unfit job seekers based on the information supplied in the application forms. Preliminary interviews help reject misfits for reasons, which did not appear in the application forms.
(ii) Selection Tests: An employment test is a mechanism (either a paper and pencil test or an exercise) that attempts to measure certain characteristics of individuals. These characteristics range from aptitudes, such as manual dexterity, to intelligence to personality.
Controlling: Controlling is one of the important functions performed by a manager. In order to seek planned results from the subordinates, a manager needs to exercise effective control over the activities of the subordinates. In other words, controlling means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as per the plans. Controlling also ensures that an organization’s resources are being used effectively and efficiently for the achievement of predetermined goals. Controlling is, thus, a goaloriented function.
Short Answer Type Questions – II
(i) Identify and explain the feature of motivation highlighted in the above case.
(ii) What type of leadership is followed by the manager? Justify your answer.
(i) Motivation can be either positive or negative: Positive motivation provides positive rewards like increase in pay, promotion, recognition etc., Negative motivation uses negative means like punishment, stopping increments, threatening etc. which also may induce a person to act in the desired way.
(ii) Autocratic leadership style: An autocratic leader gives orders and expects his subordinates to obey those orders. If a manager is following this style, then communication is only one way with the subordinate only acting according to the command given by the manager. This leader is dogmatic i.e., does not change or wish to be contradicted. His following is based on the assumption that reward or punishment both can be given depending upon the result. This leadership style is effective in getting productivity in many situations like in a factory where the supervisor is responsible for production on time and has to ensure labour productivity. Quick decision-making is also facilitated.
OR
“Directing is the heart of the Management Process.” Do you agree? Give any three reasons in support of your answer.
Positive aspects of informal communication:
(i) Sometimes, grapevine channels may be helpful as they carry information rapidly and therefore, may be useful to the manager at times.
(ii) Informal channels are used by the managers to transmit information so as to know the reactions of his/her subordinates.
Negative aspects of informal communication:
(i) The grapevine/informal communication sometimes gets distorted. It also leads to generating rumors and informal discussions and sometimes may hamper the work environment.
(ii) It is very difficult to detect the source of such communication.
OR
The importance of directing can be understood by the fact that every action in the organization is initiated through directing only. Directing guides towards achievement of common objectives. The points which emphasise the importance of directing is presented as follows:
(i) Directing initiates action: Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organization towards attainment of the desired objectives. For example, if a supervisor guides his subordinates and clarifies their doubts in performing a task, it will help the worker to achieve the targets given to him.
(ii) Directing integrates employees’ efforts: Directing integrates employees’ efforts in the organization in such a way that every individual effort contributes to the organizational performance. Thus, it ensures that the individuals work for organizational goals. For example, a manager with good leadership abilities will be in a position to convince the employees working under him that individual efforts and team effort will lead to achievement of organizational goals.
(iii) Directing guides employees to realize their potential: Directing guides employees to fully realize their potential and capabilities by motivating and providing effective leadership. A good leader can always identify the potential of his employees and motivate them to extract work up to their full potential.
(iv) Directing facilitates changes: Directing facilitates introduction of needed changes in the organization. Generally, people have a tendency to resist changes in the organization. Effective directing through motivation, communication and leadership helps to reduce such resistance and develop required cooperation in introducing changes in the organization. For example, if a manager wants to introduce new system of accounting, there may be initial resistance from accounting staff. But, if manager explains the purpose, provides training and motivates with additional rewards, the employees may accept change and cooperate with manager.
(v) Directing brings stability and balance in the organization: Effective directing helps to bring stability and balance in the organization since it fosters cooperation and commitment among the people and helps to achieve balance among various groups, activities and the departments.
The three major decisions every manager has to take while performing the finance function are:
(i) Investment Decisions: A firm’s resources are scarce in comparison to the uses to which they can be put. A firm, therefore, has to choose where to invest these resources, so that they are able to earn the highest possible return for their investors. The investment decision, therefore, relates to how the firm’s funds are invested in different assets. Investment decision can be long term or short-term. A long-term investment decision is also called a Capital Budgeting decision. It involves committing the finance on a long-term basis. Short-term investment decisions (also called working capital decisions) are concerned with the decisions about the levels of cash, inventory and receivables. These decisions affect the day-to-day working of a business. These affect the liquidity as well as profitability of a business.
(ii) Financing Decisions: This decision is about the quantum of finance to be raised from various long-term sources. Short-term sources are studied under the ‘working capital management’. It involves identification of various available sources. The main sources of funds for a firm are shareholders’ funds and borrowed funds. The shareholders’ funds refer to the equity capital and the retained earnings. Borrowed funds refer to the finance raised through debentures or other forms of debt. A firm has to decide the proportion of funds to be raised from either source, based on their basic characteristics and other factors. Interest on borrowed funds have to be paid regardless of whether or not a firm has earned a profit.
(iii) Dividend Decision: The third important decision that every financial manager has to take relates to the distribution of dividend. Dividend is that portion of profit which is distributed to shareholders. The decision involved here is how much of the profit earned by company (after paying tax) is to be distributed to the shareholders and how much of it should be retained in the business. While the dividend constitutes the current income re-investment as retained earnings increases the firm’s future earning capacity. The extent of retained earnings also influences the financing decision of the firm. Since the firm does not require funds to the extent of re-invested retained earnings, the decision regarding dividend should be taken keeping in view the overall objective of maximizing shareholder ’s wealth.
At the end of the first week, the production was 450 geysers. The next week, production increased to 470 geysers. A week later, production was 460 geysers.
On investigation, it was found out that fluctuation in production was due to irregular supply of electricity.
The above para discusses some of the steps of one of the functions of management. Explain the steps.
Steps in the process of Controlling discussed in the above para:
(i) Setting performance standards: The first step in the controlling process is setting up of performance standards. Standards are the criteria against which actual performance would be measured. Thus, standards serve as benchmarks towards which an organization strives to work. Standards can be set in both quantitative as well as qualitative terms. For instance, standards set in terms of cost to be incurred, revenue to be earned, product units to be produced and sold, time to be spent in performing a task, all represents quantitative standards. Sometimes standards may also be set in qualitative terms. Improving goodwill and motivation level of employees are examples of qualitative standards.
(ii) Measuring actual performance: Once performance standards are set; the next step is measurement of actual performance. Performance should be measured in an objective and reliable manner. There are several techniques for measurement of performance. These include personal observation, sample checking, performance reports, etc. As far as possible, performance should be measured in the same units in which standards are set as this would make comparison easier. It is generally believed that measurement should be done after the task is completed. However, wherever possible, measurement of work should be done during the performance.
(iii) Analyzing deviations: Before taking any corrective action, managers should try to ascertain the reasons for the occurrence of deviations. Some deviation in performance can be expected in all activities. It is, therefore, important to determine the acceptable range of deviations. Also, deviations in key areas of business needs to be attended more urgently as compared to deviations in certain insignificant areas. Critical point control and management by exception should be used by a manager in this regard.
Long Answer Type Questions
OR
Enumerate any five responsibilities of a Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
Rights of a Consumer under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019:
(i) Right to safety: The consumer has a right to be protected against goods and services which are hazardous to life, health and property.
(ii) Right to be informed: The consumer has a right to have complete information about the product he intends to buy including its ingredients, date of manufacture, price, quantity, directions for use, etc.
(iii) Right to be assured: The consumer has the freedom to assess a variety of products at competitive prices.
(iv) Right to be heard: The consumer has a right to file a complaint and to be heard in case of dissatisfaction with a good or a service.
(v) Right to seek redressal: The consumer has a right to get relief against unfair trade practice of restrictive trade practices or unscrupulous exploitation in case the product or a service falls short of his expectation.
(vi) Right to consumer education: The consumer has a right to acquire knowledge and to be a well informed consumer throughout life.OR
Responsibilities of a Consumer under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019:
(i) Be aware of various goods and services available in the market so that an intelligent and wise choice can be made.
(ii) Buy only standardised goods as they provide quality assurance.
(iii) Learn about the risks associated with products and services, follow manufacturer ’s instructions and use the products safely.
(iv) Read labels carefully so as to have information about prices, net weight, manufacturing and expiry dates, etc.
(v) Assert yourself to ensure that you get a fair deal.
(vi) Be honest in your dealings. Choose only from legal goods and services and discourage unscrupulous practices.
(vii) Ask for a cash memo on purchase of goods or services.
(viii) File a complaint in an appropriate consumer forum in case of a shortcoming in the quality of goods purchased or services availed.
(ix) Form consumer societies which would play an active part in educating consumers and safeguarding their interests.
(x) Respect the environment.
Detailed Answer:
Rights of a Consumer under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019:
(i) Right to Safety: The consumer has a right to be protected against goods and services which are hazardous to life and health. For instance, electrical appliances which are manufactured with substandard products or do not conform to the safety norms might cause serious injury. Thus, consumers are educated that they should use electrical appliances which are ISI marked as this would be an assurance of such products meeting quality specifications.
(ii) Right to be Informed: The consumer has a right to have complete information about the product he intends to buy including its ingredients, date of manufacture, price, quantity, directions for use, etc. It is because of this reason that the legal framework in India requires the manufacturer’s to provide such information on the package and label of the product.
(iii) Right to be assured: The consumer has the freedom to choose from a variety of products at competitive prices. This implies that the marketers should offer a wide variety of products in terms of quality, brand, prices, size, etc. and allow the consumer to make a choice from amongst these. According to this right, every consumer has the right to choose the goods or services of his or her likings. The right to choose means an assurance of availability, ability and access to a variety of products and services at competitive price and competitive price means just or fair price. The producer or supplier or retailer should not force the customer to buy a particular brand only. The consumer should be free to choose the most suitable product from his point of view.
(iv) Right to be Heard: The consumer has a right to file a complaint and to be heard in case of dissatisfaction with a good or a service. It is because of this reason that many enlightened business firms have set up their own consumer service and grievance cells. Many consumer organizations are also working towards this direction and helping consumers in redressal of their grievances.
(v) Right to seek Redressal: The consumer has a right to get relief in case the product or service falls short of his expectations. The Consumer Protection Act provides a number of reliefs to the consumers including replacement of the product, removal of defect in the product, compensation paid for any loss or injury suffered by the consumer, etc.
(vi) Right to Consumer Education: The consumer has a right to acquire knowledge and to be a well informed consumer throughout life. He should be aware about his rights and the reliefs available to him in case of a product or service falling short of his expectations. Many consumer organizations and some enlightened businesses are taking an active part in educating consumers in this respect.
OR
Responsibilities of a Consumer under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019:
(i) Be aware about various goods and services available in the market so that an intelligent and wise choice can be made.
(ii) Buy only standardised goods as they provide quality assurance. Thus, look for ISI mark on electrical goods, FPO mark on food products, Hallmark on jewellery etc.
(iii) Learn about the risks associated with products and services, follow manufacturer ’s instructions and use the products safely.
(iv) Read labels carefully so as to have information about prices, net weight, manufacturing and expiry dates, etc.
(v) Assert yourself to ensure that you get a fair deal.
(vi) Be honest in your dealings. Choose only from legal goods and services and discourage unscrupulous practices like black-marketing, hoarding etc.
(vii) Ask for a cash memo on purchase of goods or services. This would serve as a proof of the purchase made.
(viii) File a complaint in an appropriate consumer forum in case of a shortcoming in the quality of goods purchased or services availed. Do not fail to take an action even when the amount involved is small.
(ix) Form consumer societies which would play an active part in educating consumers and safeguarding their interests.
(x) Respect the environment. Avoid waste, littering and contributing to pollution.
Regulatory Functions of Securities and Exchange Board of India:
(i) Registration of brokers and sub-brokers and other players in the market.
(ii) Registration of collective investment schemes and Mutual Funds.
(iii) Regulation of stock brokers, portfolio exchanges, underwriters and merchant bankers and the business in stock exchanges and any other securities market.
(iv) Regulation of takeover bids by companies.
(v) Calling for information by under- taking inspection, conducting enquiries and audits of stock exchanges and intermediaries.
(vi) Levying fee or other charges for carrying out the purposes of the Act.
(vii) Performing and exercising such power under Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act 1956, as may be delegated by the Government of India.
(i) Name the process and steps in the process of identifying and choosing the best person out of a number of prospective candidates for a job discussed above.
(ii) Also explain the next three steps in the process which can be subsequently performed by the company.
(i) Selection
Steps in the process of selection discussed:
(a) Preliminary Screening.
(b) Selection Tests.
(c) Employment interview
(ii) Next two steps:
- Reference and background checks: Many employers request names, addresses and telephone numbers of references for the purpose of verifying information and gaining additional information on an applicant. Previous employers, known persons, teachers and university professors can act as references.
- Selection Decision: The final decision has to be made from among the candidates who passed the tests, interviews and reference checks. The views of the concerned manager will be generally considered in the final selection.
- Medical Examination: After the selection decision and before the job offer is made, the candidate is required to undergo a medical fitness test. The job offer is given to the candidate being declared fit after the medical examination.
Q.12. Vansh Limited is a large and reputed company which manufactures ventilators. After the outbreak of ‘COVID-19’ in 2020 the company witnessed an increase in revenue by 40%. It has plans to further increase its production capacity and also start production of PPE kits, sanitizers and masks in 2022. The Finance manager of the Company Mr. Rajiv feels confident about the future of the company and its liquidity position. Discuss the meaning of Dividend Decision and in the light of the above statement explain any two factors which should be considered by ‘Vansh Limited’ while formulating the dividend policy of the company.
OR
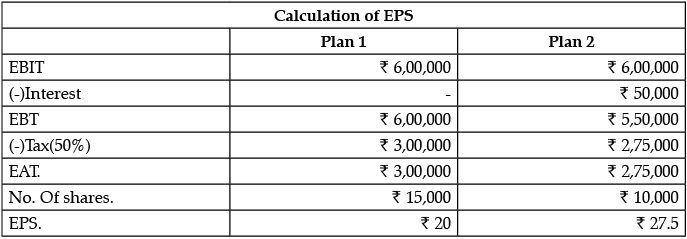
Vedansh Limited has a share capital of ₹ 10,00,000 divided into shares of ₹ 100. Expansion company requires additional funds of ₹ 5,00,000. The management is considering the following alternatives for raising funds : Alternative 1: Issue of 5000 Equity shares of ₹ 100 each Alternative 2: Issue of 10% Debentures of ₹ 5,00,000
The company’s present Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) is ₹ 4,00,000 p.a. Assuming that the rate of Return of Investment remains the same after expansion, which alternative should be used by the company in order to maximise the returns to the equity shareholders. The Tax rate is 50%. Show the working.
Dividend decision: The decision involved here is how much of the profit earned by the company (after paying tax) is to be distributed to the shareholders and how much of it should be retained in the business.
Factors affecting Dividend decision:
(i) Amount of Earnings: Dividends are paid out of current and past earnings. Therefore, earnings are a major determinant of the decision about dividend.
(ii) Growth Opportunities: Companies having good growth opportunities retain more money out of their earnings so as to finance the required investment. The dividend in growth companies is, therefore, smaller, than that in the non– growth companies.
(iii) Cash Flow Position: The payment of dividend involves an outflow of cash. A company may be earning profit but may be short on cash. Availability of enough cash in the company is necessary for declaration of dividend.
(iv) Access to Capital Market: Large and reputed companies generally have easy access to the capital market and, therefore, may depend less on retained earnings to finance their growth. These companies tend to pay higher dividends than the smaller companies which have relatively low access to the market.OR
Rate of Return of Investment is
EBIT after expansion = 40% × ₹ 15,00,000 = ₹ 6,00,000
The company should use Plan 2 in order to increase the return to the equity shareholders.
|
130 docs|5 tests
|