Class 11 Business Studies: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term II (2021-22)- 1 | Sample Papers for Class 11 Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class Xl Business Studies |

|
| Time: 2 Hours |

|
| Max. Marks: 40 |

|
| Section – A |

|
| Section – B |

|
| Section – C |

|
Class Xl Business Studies
Time: 2 Hours
Max. Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- This is a Subjective Question Paper containing 12 questions.
- This paper contains 4 questions of 2 marks each, 4 questions of 3 marks each and 4 questions of 5 marks each.
- Section A: 2 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 30-50 words.
- Section B: 3 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 50-80 words.
- Section C: 5 marks questions are Long Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 80-120 words.
- This question paper contains Case/Source Based Questions.
Section – A
Q.1. Finance is not only needed to open a business, even the day-to-day running of a business requires a constant stream of finance.’ Explain the meaning of finance and its importance in business.
For carrying out business, firms need money, which is also called finance. Finance can be defined as managing money and investing, borrowing, saving, etc. It can also be defined as the process of raising funds or capital for a business. A business needs to run its operations smoothly and successfully. No business can run its operations smoothly without the availability of the right amount of funds at the right cost and the right time.
Q.2. ‘Shriram Ltd.’ is dealing in electric vehicles. The demand for small electric vehicles has been increasing since a long time. They have planned to expand the company and need `2 crores. The finance manager, Rahul Sharma planned to raise funds through various sources. Identify the options Shriram Ltd. has to raise funds for expansion of the company.
Shriram Ltd. has following options to raise funds:
- Debentures: Debentures are debt instruments used by companies to raise loans. These are important instruments for raising long-term debt capital. A company can raise funds through issue of debentures, which bear a fixed rate of interest.
- Bonds: Bonds are secured non-convertible debt instrument issued by the government or specialised financial institutions.
- Shares: S hares are the indication of a unit of ownership of the company. The owner of shares of a company is a shareholder of the company.
Q.3. ‘Countries that can produce a product at lower cost will be able to gain a larger share in the market’. Which benefit of international trade is being talked about here? Elaborate.
International trade promotes efficiency in production as countries adopt better methods of production to produce at lower costs to remain competitive. By adopting this, countries can produce products at lower costs and will be able to gain a larger share in the market. Hence, the efficiency of production rises. This will also help in increasing the standards of the product and consumers will have a good quality of products to consume.
Q.4. Rohan is a dealer in grocery items. He has a warehouse to store extra items and deals with many small shops owners as well as customers to sell various products. Ritu is one of the shop owners who purchases the items from Rohan and sells them to the consumers further. What do you think is the difference between Rohan and Ritu?
Rohan is a wholesaler whereas Ritu is a retailer. A wholesaler buys in bulk from the producer and sells to the retailers for resale or intermediate use. A retailer buys from the wholesaler and sells to the ultimate consumer for final consumption.
Section – B
Q.5. Pepper Ltd. is a manufacturing company co-owned by Ratul and Shakti. The firm made a profit of `200 crore in 2010. Ratul and Shakti decided to expand the operations of the business and open a new department. To expand the business operations, what options do Ratul and Shakti have? Identify various sources of funds on the basis of ownership and discuss the different types of owner’s funds that are available.
Sources of funds based on ownership are:
- Owner ’s funds
- Borrowed funds
The owner’s funds can be raised by issuing preference shares, retained earnings, equity shares, etc.
- Preference shares: Preference shares are the types of shares for which dividends are paid to shareholders before the payment of common stock dividends.
- Retained earnings: Retained earnings are an accumulation of the company ’s net income over all the years that the business has been in operation.
- Equity shares: Equity shares are long-term financing sources for any company, which are issued to the general public and are non-redeemable.
Q.6. Define Start-up scheme. What are the benefits provided under the Start-up scheme?
Startup India is a flagship initiative of the Government of India, intended to catalyze startup culture and build a strong and inclusive ecosystem for innovation and entrepreneurship in India.
The benefits provided to recognized start-ups under the Start-up India initiative are:
- Self-certification: S elf-certify and comply under 3 environmental and 6 labour laws.
- Tax exemption: Income tax exemption for a period of 3 consecutive years and exemption on capital and investments.
- Startup patent application and IPR protection: Fast track patent application with upto 80% rebate in filling patents.
OR
What services do wholesalers provide to the retailers?
Services provided by wholesalers to retailers are:
- Availability of goods: The wholesalers are in close contact with manufacturers, so they make the products readily available to the retailers.
- Grant of credit: Wholesalers help retailers financially by providing them credit facilities, which enables the retailers to manage their business with small amount of working capital.
- Marketing support: The wholesalers perform various marketing functions and provide support to the retailers through product promotion.
- Risk sharing: A retailer does not have to bother about risk of storage, reduction in price, fluctuation in demand, etc. All these risks are borne by the wholesaler.
Q.7. Discuss the services of retailers to manufacturers and wholesalers.
Retailers provide the following services to wholesalers and manufacturers:
- Help in the distribution of goods: Retailers assist in the dissemination of manufacturers’ products by making them available to end-users who may be dispersed across a vast geographical area.
- Personal selling: Retailers relieve producers of this work and considerably assist them in the process of actualizing product sales by engaging in personal selling efforts.
- Enabling large-scale operations: Retailers allow them to function at a somewhat large scale, allowing them to focus totally on their other tasks.
- Collecting market information: Retailers are a significant source of market data about customer tastes, interests, etc. which can help marketers to make critical marketing decisions.
Q.8. Ram opened a departmental store dealing in a variety of goods in his area. He deals in several goods which are necessary for the daily needs of consumers. Discuss three features of departmental stores.
(i) A departmental store is a large establishment offering a wide variety of products, classified into well-defined departments, aimed at satisfying practically every customer’s need under one roof.
(ii) It has a number of departments, each one confining its activities to one kind of product. e.g., there may be separate departments for toiletries, medicines, furniture, groceries, electronics, clothing and dress material within a store.
(iii) They satisfy diverse market segments with a wide variety of goods and services. Everything from ‘a pin to an elephant’ is the spirit behind a typical department store.
(iv) May provide all facilities such as restaurant, rest rooms, etc. in order to provide maximum service to customers for whom price is of secondary importance.
(v) Are generally located at a central place in the heart of a city which caters to a large number of customers.
(vi) Size of these stores is very large, hence, they are generally formed as a joint stock company managed by a board of directors. There is a managing director assisted by a general manager and several department managers.
Section – C
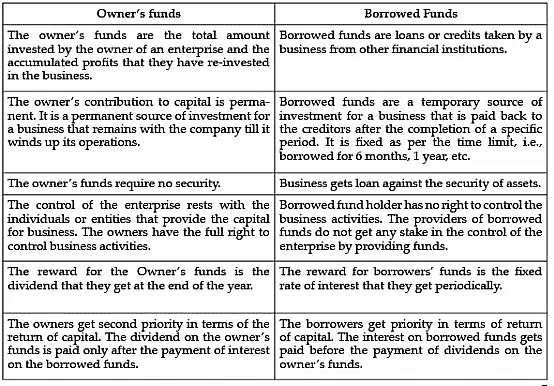
Q.9. Differentiate between owner ’s funds and borrowed funds.
OR
‘Public deposits are received by a company from the public as unsecured debt.’ Discuss the concept of public deposits.
Public deposits are the deposits raised by business organizations from the public. Any member of the public can fill-up the form and deposit money with the company. The company issues a deposit receipt in return. The rate of interest on these deposits depends upon the period of deposit and the reputation of the company. A company can invite public deposits for a period of 1 year to 5 years. Public deposits refer to the deposits received by a company from the public as unsecured debt. These are preferred by the companies because they are cheaper than bank loans. These are a very convenient source of business finance. Interest paid on public deposits is tax-deductible which reduces tax liability.
Q.10. Discuss any five advantages of chain/ multiple stores.
(i) Economies of scale: As there is central procurement, multiple-shop organizations enjoy economies of scale
(ii) Elimination of middlemen: By selling directly to the consumers, multiple-shop organizations are able to eliminate unnecessary middlemen in the sale of goods and services
(iii) No bad debts: Since all the sales are made on cash basis, there are no losses on account of bad debts
(iv) Transfer of goods: Goods not in demand in a particular locality may be transferred to another locality where they are in demand reducing the chances of dead stock in these shops
(v) Diffusion of risk: Losses incurred by one shop may be covered by profits in other shops reducing the total risk of an organization
(vi) Low cost: Because of centralised purchasing, elimination of middlemen, centralised promotion of sales and increased sales, multiple shops enjoy lower costs
(vii) Flexibility: If a shop is not operating at a profit, the management may decide to close it or shift it to some other place without really affecting the profitability of the organization as a whole
Q.11. Sheetal Ltd., a handbag manufacturing company owned by Shree, opens its shops in different Indian locations. She sells goods in cash only. The shops have identical decorations and fixed prices of goods. This way they help in eliminating unnecessary middlemen and benefit the customers. Keeping in mind the above situation, answer the following questions:
(i) Identify the type of shop referred to.
(ii) State a few characteristics of such shops.
(i) The shops being talked about in the para are multiple shops or chain stores. Many chain stores have sprouted up at various locations across the country. These shops sell standardized and branded consumer goods with high sales turnover. These stores use the same merchandising techniques and are owned by the same company.
(ii) Characteristics of chain stores are:
- The goods are dispatched to each shop by the head office.
- The shops are under the supervision of a Branch Manager, who is responsible for day-today management.
- The head office is in charge of creating policies and ensuring that they are executed.
- The prices of goods in such shops are fixed, and all sales are conducted in cash.
Q.12. ‘Ratul Car Ltd.’ is a well-known company in the industry, which has more equity share capital than long term debt in its capital structure. They are planning to expand and establish a new site in the backward region and to hire the local people. It also has some amount as reserve of `2000 crore. In lieu of the above case, answer the questions below:
(i) What is the status of capital structure of the company?
(ii) Which source of finance should be used by the company for establishing new units and why?
(iii) What values does the company exhibit in the case above?
(i) The company ’s financial structure is robust, with more equity share capital than the debt in its capital structure and a large cash reserve.
(ii) As the company has a large cash reserve, it should use retained earnings as a source of finance.
When a company earns profits, a certain amount of those profits are kept in reserve for business’ future use and is known as retained earnings. The reasons to use retained earnings as a financing source are:
- No initial fees: These funds do not have any floatation costs or interest because these are raised internally.
- Increase in share price: A large quantity of retained earnings can cause the price of equity shares to rise.
(iii) The values displayed by the company here are:
- Balanced regional development: The company is planning to expand the business to underprivileged sections of the society and contribute to the regional development.
- Women Empowerment: The company also intends to empower women by training them in skill development.
OR
‘Francis Ltd.’, a leading IT firm registered in India wants to hire resources from US for its growth and expansion. It also needs money for at least 2 years to meet its short-term needs. They are giving employment to underprivileged youth. They also generate 50% of their electricity through solar power. Keeping in mind the above case, answer the following questions:
(i) Which two sources of finance should be used by the company to meet its requirement? Write characteristics of each source as well.
(ii) What values does the company exhibit in the above case?
(i) ADRs and Public Deposits can be used by ‘Francis Ltd.’ to satisfy the company ’s needs.
- ADRs: T hese refer to American Depository Receipts and are issued by American companies to be traded in American Markets. It can only be issued to the citizens of America and can be traded in US stock exchanges.
- Public Deposits: These are the deposits raised directly from the public by organizations. RBI regulates these deposits and companies generally solicit public contributions over a three-year term.
(ii) The values demonstrated by the company are:
- Environmental protection: The company uses solar power to generate 50% of its electricity, which conserves the resources.
- Employment generation: The company is generating opportunities of employment by employing underprivileged young generation.
FAQs on Class 11 Business Studies: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term II (2021-22)- 1 - Sample Papers for Class 11 Commerce
| 1. What is the format of the Class Xl Business Studies exam? |  |
| 2. How much time is allotted for each section in the Class Xl Business Studies exam? |  |
| 3. What is the syllabus for Section A of the Class Xl Business Studies exam? |  |
| 4. What is the syllabus for Section B of the Class Xl Business Studies exam? |  |
| 5. What is the syllabus for Section C of the Class Xl Business Studies exam? |  |