Experiment | Design Thinking - Class 6 PDF Download
This is the ideation phase where huge quantity of ideas are generated by brain storming using the ideation tools. The ideas are then prototyped to provide user with ideal user experience journey.
Purpose
- To brainstorm quantity and variety of ideas around user deep needs
- To make ideas tangible and visible through building prototypes and visualizing the ideal user experience
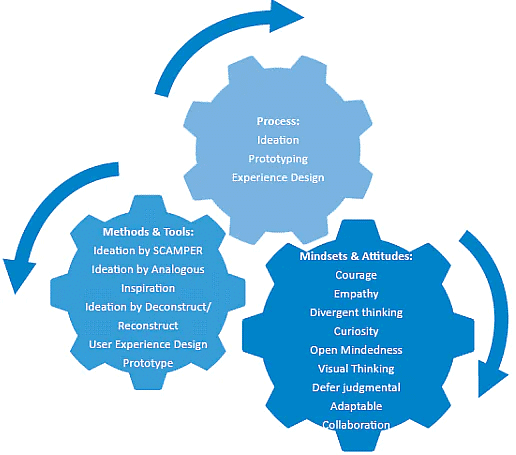 Methods & Tools
Methods & Tools
 Ideation by SCAMPER: A tool to generate new ideas from different perspective.
Ideation by SCAMPER: A tool to generate new ideas from different perspective.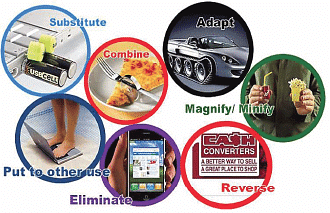
- Ideation by Analogous Inspiration: Draw insights and inspiration from seemingly unrelated industry to spark creative and innovative ideas.
- Ideation by Deconstruct and Reconstruct
- User Experience Design: It is the process of creating great experience through enhancing the user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided in the interaction between the user and the product/ services
- Prototyping

Ideation Using Scamper
SCAMPER is a creative brainstorming technique that stretches the parameters of thinking to generate new ideas from different perspective. Given any object you use SCAMPER to generate new ideas. When to use SCAMPER
When to use SCAMPER
- When there is need to generate huge quantities and variety of ideas
How to use SCAMPER for Ideation
- Each team to be given different objects
- Generate the most idea using the SCAMPER canvas. There is no sequential flow while using SCAMPER.
- As each team member has an idea, stick on the relevant column of the canvas. One idea per Post-its is used.
- Compete to see which team generates the most ideas within the given time.
- Within 10 minutes , 10 people are to generate 50 ideas
- Cluster the ideas by themes
Ideation using Analogous Inspiration
What is Analogous Inspiration?
Analogous inspiration helps to draw innovative ideas from various organization and industries. It provides different perspective and prompts new and creative ideas.
When to use Analogous Inspiration
- To generate variety and quantity of ideas How to use Analogous Inspiration for Ideation
How to use Analogous Inspiration for Ideation
- Based on user deep need, each team member is to get relevant case studies by looking across other industries, organization and innovation that might serve to inspire challenge at hand.
- Stick a large white paper on the wall and the case studies.
- Using Post-its and pen, from the case study, every team member to identify and articulate the desirable element of good experience that you can use and adapt as per the user need.
- As each team member has an idea, make them share and stick on the white paper.
- Using this method, generate as many ideas as possible.
- The ideas then are to be clustering by themes.
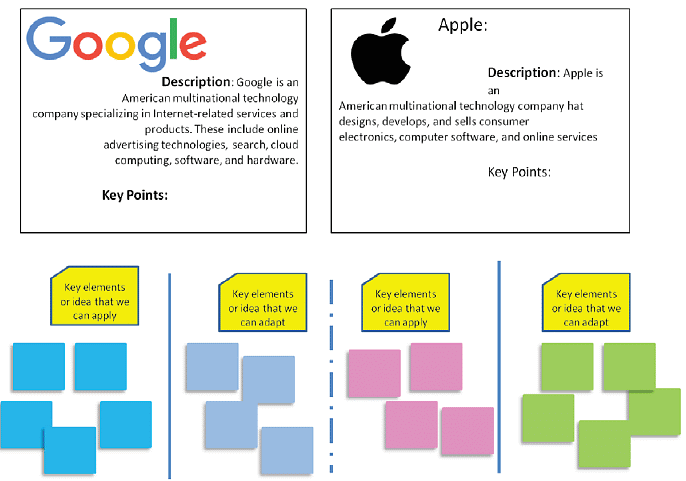
Example of Analogous Inspiration
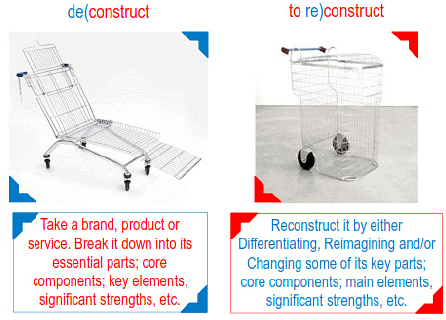
IDEATION USING Deconstruct & Reconstruct
Deconstruct & Reconstruct is the process of taking a product or service and initially breaking it down into its essential parts; core components; key elements, significant strengths etc and then reconstruct idea and imagine new possibilities by combining features/characteristic.
When to use Deconstruct & Reconstruct
- To generate innovative and creative ideas How to use Deconstruct & Reconstruct for Ideation
How to use Deconstruct & Reconstruct for Ideation
- Identify 5 different brands/product/Companies for five teams.
- Using a large white paper, list minimum of 10 essential elements of the given brand/ Company by deconstructing each brand/product/company
- The team is to discuss and select 5 essential elements and circle.
- Using Post-its and pen, every team member is to reconstruct 2-3 imaginary new products with the 5 circled essential elements.
- As each team member has an idea, make them share and stick on the white paper. Use one idea per Post-its.
- Using this method, generate as many ideas as possible.
- Draw the new product on the white paper
Idea Generation for your Design Challenge
- Having gone through all the methods of ideation/brainstorming, now it is time to generate ideas for your design challenge/ problem.
What to Do?
- Reference your persona’s deep or unmet need.
- Phrase the personas’ unmet need into a possibility question as: “How Might we.....” Write the question on a big Post-it and place it in the middle of a large sheet of paper: “e.g. How might we make Anxious Andu feel Connected with RCSC and be Engaged in learning process while at RIM?”
- Generate quantity and variety of ideas around the person’s need.
- Sketch or write 1 idea on 1 post-it. Share ideas (1 at a time), and keep generating ideas. Go for for volume. (Use the 3 + 3 + 4 method)
- Use SCAMPER, POEMS, WHAT IF or other methods to inspire and spark creative and possibility thinking.
- Pick One Idea and brainstorm in more details.
- Cluster the ideas by intention and identify themes.
All the activities pointed out in the box above are detailed in four steps as below:
1. Start with your most realistic persona and the most compelling deep or unmet need
- Review and select the most compelling deep or unmet need. One that your team feels most eager to help.

2. Frame the need as a possibility question: how might we....to inspire possibility thinking
- Unmet need is an untapped opportunity.
- Write the HOW MIGHT WE possibility question In the center of a large sheet of paper so that all can see

3. Brainstorm for a range of different ideas
- Use POEMS, SCAMPER, What if, Analogous Inspiration to spark creative and innovative ideas.
- Write one idea per post it and Share on idea at a time.
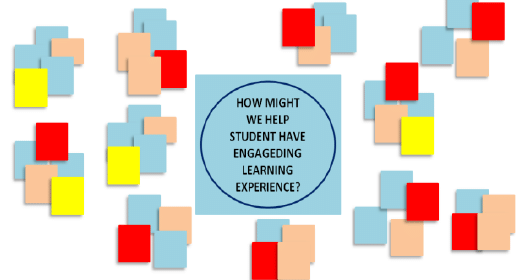
4. Cluster and identify Themes
- Organize and cluster the ideas. This involves grouping common ideas by their intention in addressing the unmet need.
- 'Discuss and give each cluster a theme: a succinct caption that aptly describes the ideas.
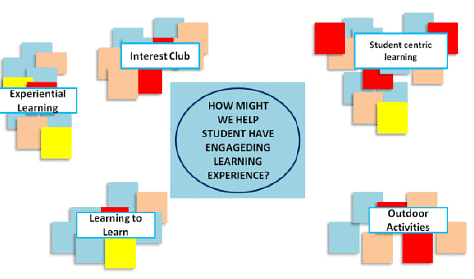
From Idea to Concept
What is Concept or Big Idea?
A concept is a meaningful and seamless combination and/or integration of related ideas to for a concept (or big idea) that best addresses the target user’s deep need(s).
The concept should clearly demonstrate and articulate the target user’s deep need(s) and benefits that the target user desires from you to deliver.
5. Idea selection & Deepening ideas
- Discuss and agree on a set of selection criteria.
- Select a few promising cluster of ideas based on the selection criteria.
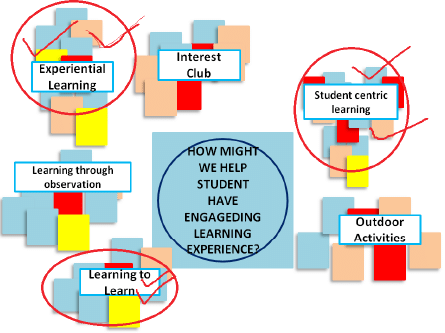
6. Concept Development
- Synthesize and combine ideas to form concept (integration of ideas or elements to form a more holistic system or process).
- Look for relationships among the ideas and how they reinforce and strengthen each other in addressing user deep needs.
- You can use POEMS to brainstorm more ideas
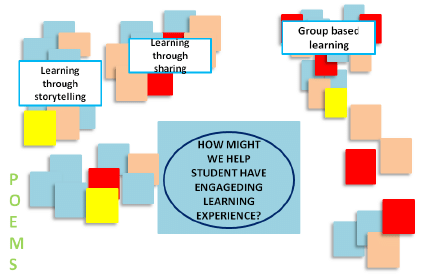
User Experience Journey
What is User Experience Journey?
User experience design is the process of creating positive and great experiences by enhancing the user satisfaction. It is focused on the user and involves the process from how the person discovers the product/ services to how he/she uses it to achieve a goal. It outlines the details as to whether the ideas may or may not work from user perspective.
When to use User Experience Design
- To generate details of the big idea.
- To check the viability of the big ideas
How to Map User Experience Journey
User experience journey includes the entire process from how the user discovers the product, service, process to how he/she uses it to achieve a goal. It consists of phases/stages of the behavior and touchpoints across time and space. The user journey is based on user insight, deep needs, behaviors and include interactions, emotions and experiences.
User Experience Journey mapping can be done in four steps:
- Start with your most realistic persona. Review your persona and gain a deep understanding of the personas in terms of goals and objectives, aspirations and motivations, challenges and pain points, behaviours, and deep or unmet needs.
- Identify and plot the steps or phases of the user journey. In each phases think broadly about the context, progression, objects, emotions.
- Unfold your related ideas (from your Big Idea) into the User Experience Journey. Identify keytouch points and/or gaps in the journey where you can integrate selected ideas to address their needs, enhance their gains and/or relieve their pains. Repeat this steps a few times.
- Deepen your ideas with POEMS framework to enrich the ideal User Experience Journey. Review each ideas being integrated into the User Journey. Envision how this idea will look like when implemented. Use POEMS framework to think through the implementation details.
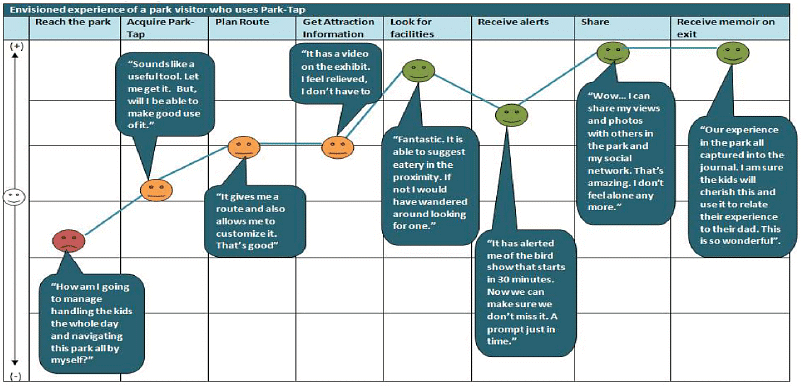 Sample User Journey till step 2. Under each emotion symbol, you can give naratives to describe behaviour and emotion of the persona in this journey.
Sample User Journey till step 2. Under each emotion symbol, you can give naratives to describe behaviour and emotion of the persona in this journey.
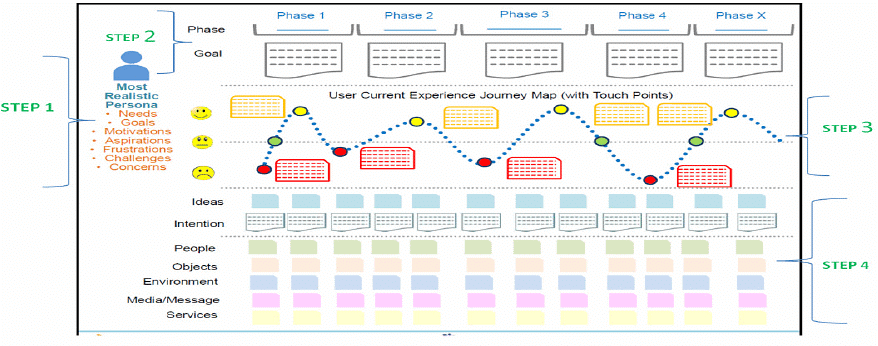
Complete User Experience Journey
Prototyping
Prototyping is an approach that makes ideas and concepts more tangible and visual as compared to written ideas. It helps us to empathize with the user in terms of the viability of the solution and further minimizes the risk of failure at large scale.
How to carry out Prototyping?
- Review the ideal user experience journey.
- As a team, decide what are the key elements from the ideal user experience journey that you need to test with real users to get their feedback and ideas on.
- For each of the selected key elements, determine what appropriate prototype to build. For example, if you want to test user interactions, consider putting on a skit with your team. If you are testing a logo, print it out and stick it on a t-shirt to seek feedback.
- Keep working and improving on the prototypes with the feedback. Make it, break it, and fix it.

Prototyping BIG Ideas
|
6 videos|5 docs|5 tests
|
















