Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Worksheet Science Chapter 1
Q.1. True/False
(i) The food synthesized by the plants is stored as starch.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View AnswerPlants make food (glucose) during photosynthesis. They store this food in the form of starch for future use.
(ii) Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their leaves.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View AnswerPlants have small openings called stomata on their leaves that allow them to take in carbon dioxide from the air.
 Stomata
Stomata
(iii) Solar energy is converted into electrical energy during photosynthesis.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View AnswerIn photosynthesis, plants convert solar energy into chemical energy stored in glucose, not electrical energy.
(iv) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis.
Ans: False
 View Answer
View AnswerDuring photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen as a by-product.
(v) The starch is also a carbohydrate.
Ans: True
 View Answer
View AnswerStarch is a form of carbohydrate that plants store as their food reserve.
Q.2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called ____.
Ans: Chlorophyll.
 View Answer
View Answer- The green pigment in plants that captures sunlight for photosynthesis is called chlorophyll.
- Chlorophyll is found primarily in the leaves, where it plays a critical role in converting solar energy into chemical energy.
 Chlorophyll & Chloroplast
Chlorophyll & Chloroplast
(ii) During photosynthesis plants take in ____ and release ____ .
Ans: Carbon dioxide, oxygen
 View Answer
View Answer- In the process of photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and use it, along with water, to produce glucose.
- As a by-product of this reaction, they release oxygen, which is essential for most life forms on Earth.
(iii) ____ in plant take in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis.
Ans: Stomata
 View Answer
View Answer- Stomata are tiny pores located on the surfaces of leaves.
- These stomata open and close to regulate gas exchange.
- During photosynthesis, stomata allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaf and oxygen to exit, facilitating the photosynthetic process.
(iv) ____ are the products of photosynthesis.
Ans: Carbohydrates
 View Answer
View Answer- The main products of photosynthesis are carbohydrates, particularly glucose.
- In addition to glucose, oxygen is also produced as a by-product.
- These carbohydrates serve as energy sources for the plant and can be used by other organisms that consume the plant.
 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
(v) Solar energy is converted into ____ energy during photosynthesis.
Ans: Chemical
 View Answer
View Answer- During photosynthesis, plants convert solar energy into chemical energy.
- This chemical energy is stored in the bonds of glucose molecules, which plants can later use for growth, development, and metabolism.
Q.3. What are legume plants examples?
Common examples of legume plants include:
- Gram (Chana): Often used in various dishes and rich in protein.
- Peas (Matar): A popular vegetable that is nutritious and sweet.
- Moong (Green Gram): A small green pulse used in many recipes and is high in protein.
- Beans (Rajma): Different varieties like kidney beans and black beans are staple foods in many cultures.
Q.4. From where do plants get raw materials to prepare their food?
Plants get raw materials to prepare their food from their surroundings.
- Carbon Dioxide: Absorbed from the air through stomata in the leaves.
- Water: Taken up from the soil through the roots.
- Sunlight: Captured by chlorophyll in the leaves. The energy from sunlight is crucial for converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Q.5. What is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms?
Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
- It provides the necessary light energy that plants use to perform photosynthesis, which is the foundation of most food chains.
- Plants convert this solar energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, which is then consumed by herbivores and further by carnivores, making the sun essential for life on Earth.
 Food Chain
Food Chain
Q.6. What are the components of food?
Food is composed of various nutrientsthat our bodies need to function properly. The main components of food include:
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy; found in grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Proteins: Essential for growth and repair; found in meat, legumes, and dairy products.
- Fats: Provide energy and support cell growth; found in oils, butter, and nuts.
- Vitamins: Important for various body functions; found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy.
- Minerals: Essential for health; include calcium, iron, and potassium, found in various foods.
Q.7. What do you mean by nutrition?
Nutrition refers to the process by which living organisms obtain and use food. It involves several stages:
- Ingestion: Taking in food through eating.
- Digestion: Breaking down food into smaller, absorbable components.
- Absorption: Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to cells.
- Utilization: The body uses these nutrients for energy, growth, repair, and maintenance of bodily functions.
Q.8. What are the different modes of nutrition found in plants?
Plants exhibit two primary modes of nutrition:
- Autotrophic Nutrition: This is where plants make their own food through photosynthesis using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. They are known as autotrophs.
- Heterotrophic Nutrition: Some plants cannot perform photosynthesis and instead rely on other organisms for food. They depend on other plants or animals for their nutritional needs, such as parasitic plants like Cuscuta.
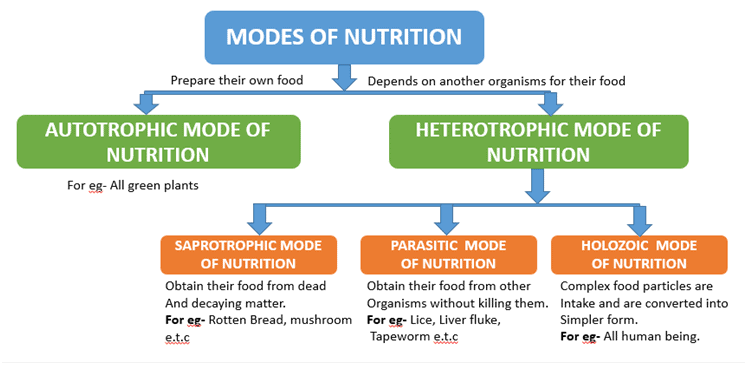 Modes of Nutrition
Modes of Nutrition
Q.9. Why photosynthesis is named so?
The term photosynthesis is derived from two Greek words:
- Photo means "light."
- Synthesis means "to combine." This name reflects the process where plants use light energy to combine carbon dioxide and water to create glucose. Hence, the name highlights the crucial role of sunlight in the synthesis of food.
Q.10. What are the other parts of plant where photosynthesis occurs except leaves?
While leaves are the primary site for photosynthesis, other green parts of the plant can also perform this process. These include:
- Green Stems: Some plants, like cacti and young stems of other plants, can carry out photosynthesis due to the presence of chlorophyll.
- Green Branches: Similar to stems, branches that have green tissues can also contribute to photosynthesis.
Q.11. What are stomata?
Stomata are tiny pores found primarily on the underside of leaves. They play a vital role in:
- Gas Exchange: Allowing carbon dioxide to enter the leaf for photosynthesis and oxygen to exit as a by-product.
- Transpiration: Enabling water vapor to leave the plant, helping to regulate temperature and maintain nutrient flow.
Q.12. What is heterotrophic nutrition?
Heterotrophic nutrition is the type of nutrition where organisms depend on other organisms (plants or animals) for their food.
- Unlike plants that make their own food through photosynthesis, heterotrophs cannot produce their own food. They must obtain nutrients by consuming organic substances.
- Examples: Animals, fungi, and some plants (like parasites) are heterotrophs. They consume either plants or other animals to get the energy they need to grow and survive.
 Types of Heterotrophic Nutrition
Types of Heterotrophic Nutrition
Q.13. What is chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the leaves of all green plants. It plays an essential role in photosynthesis by capturing the energy from sunlight.
- This pigment absorbs light, especially sunlight, which is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a sugar) during photosynthesis.
- The presence of chlorophyll is also what gives plants their characteristic green color.
Q.14. How do fungi grow and develop?
Fungi, unlike plants, do not need sunlight to grow. They reproduce through spores that are present in the air. When these spores land on warm and moist surfaces, they begin to germinate and grow into new fungal organisms.
- Moisture and warmth are essential for fungal growth, which is why fungi are often found in damp places like bathrooms, moist bread, or decaying leaves.
- Some common types of fungi include mushrooms, molds, and yeast.
Q.15. What are the tiny openings on the surface of a leaf called?
The tiny pores present on the surface of leaves are called stomata. These openings are crucial for the plant’s survival, as they allow for the exchange of gases.
- Gas Exchange: Stomata enable the plant to take in carbon dioxide from the air (necessary for photosynthesis) and release oxygen back into the atmosphere.
- They also play a role in transpiration, where water vapor exits the plant through these pores, helping regulate temperature and water balance.
Q.16. What are called parasites?
Parasites are organisms that rely on other living plants or animals for their food and survival. Unlike plants that perform photosynthesis, parasites cannot make their own food. Instead, they attach to a host and absorb nutrients from it, sometimes causing harm to the host in the process.
- Example: Cuscuta, also known as the dodder plant, is a parasitic plant that wraps around other plants to draw nutrients from them.
- Animal Example: Ticks and lice are parasites that feed on animals or humans.
Q.17. Why can't humans or animals prepare their own food using CO2 water and minerals as the green plants do?
Unlike plants, humans and animals cannot make their own food because they lack chlorophyll, the green pigment essential for photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis: In plants, chlorophyll captures sunlight and helps in converting carbon dioxide, water, and minerals into glucose (food).
- Since humans and animals do not have this pigment, they are unable to carry out photosynthesis and must consume plants or other organisms to obtain their nutrients.
Q.18. What are algae?
Algae are simple plant-like organisms that are often found in water bodies like ponds, rivers, or lakes. They can also grow on moist surfaces.
- You may notice slimy, green patches on stagnant water bodies. These green patches are made up of algae. They perform photosynthesis and produce oxygen but do not have the complex structures of higher plants like roots, stems, or leaves.
- Examples: Green algae, brown algae (seaweed), and red algae.
 Algae
Algae
Q.19. How fungus can be harmful and useful?
Fungi can be both harmful and useful to humans and the environment:
Useful Fungi:
- Yeast is a type of fungus used in baking (to make bread rise) and brewing (to make beer and wine).
- Mushrooms are a popular edible fungus.
- Some fungi are used to produce antibiotics like penicillin, which is used to treat bacterial infections.
Harmful Fungi:
- Certain fungi cause diseases in plants (like rust and blight) and humans (like athlete's foot and ringworm).
- Mold, a type of fungus, can grow on food and spoil it.
Q.20. Why do we boil the leaf in alcohol when we are testing it for starch?
In a starch test, we boil the leaf in alcohol to remove its chlorophyll, the green pigment that masks the presence of starch.
- When testing for starch in leaves, we need to see a color change to confirm the presence of starch.
- After removing chlorophyll by boiling the leaf in alcohol, the leaf becomes pale.
- Once iodine solution is added, it reacts with the starch in the leaf, turning it blue-black.
- This confirms that starch is present, proving that photosynthesis has taken place.
|
111 videos|246 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Worksheet Science Chapter 1
| 1. What are the main processes through which plants obtain nutrition? |  |
| 2. How do plants utilize sunlight in their nutritional process? |  |
| 3. What role do chlorophyll and chloroplasts play in plant nutrition? |  |
| 4. Why are minerals important for plant nutrition? |  |
| 5. How do environmental factors affect plant nutrition? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|


















