Tenses and its Kinds | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Tenses in English
A tense is a form of the verb that allows you to express time. The tense of the verb tells us when an event or something existed or when a person did something. Past, present, and future are the three main types of tenses.
What are the three main types of tenses and why do we need them?
Past, present and future are the three main types of tenses.
Past tense
The past tense is used to describe an activity or an event that has happened in the past or a past state of being and needs to include a time marker for when the event or action took place.
Structural formula:
Subject + verb (2nd form) + object.
Examples:
- We met yesterday.
- He bought a new laptop last week.
Present tense
The simple present tense or present tense is one of the most basic tenses in English. We use present tense to talk about something that is currently going on, something that is habitually performed, or a state that generally or currently exists.
Structural formula:
Subject + verb (s/es) + object.
Examples:
- She lives in Spain.
- Bob drives a taxi.
Future tense
The future tense is a verb tense used to describe an event or action that has not yet happened and is expected to happen in the future. Structural formula, Subject + shall/will+ verb (s/es) + object.
Example:
He will be here soon.
Now that we have understood the three main types of tenses, communicating in English with a native English speaker will become easier. But to make communication in English easier and simpler, we need to learn more about tenses.
Apart from the three main types of tenses - present, past, and future - there are different subtypes of tenses which are mentioned below.
subtypes of tenses
1. Past continuous tense
The past continuous tense is used to describe events or actions that have already occurred in the past. It's employed to describe any action which has happened in the past.
Structural formula:
Subject + helping verb (was/were) + verb (ing) + object.
Examples:
- I was watching TV.
- We were sleeping.
- She wasn’t eating her lunch.
2. Past perfect tense
The past perfect tense is used to describe an event that occurred before a completed action in the past.
Structural formula:
Subject + had + verb (ed) + object.
Examples:
- He had gone when she became ill.
- She had not lived in New York.
- They had not been married long when I was born.
3. Past perfect continuous tense
The past perfect continuous tense represents any action or event that started in the past and sometimes continued into another action or another time.
Structural formula:
Subject + had been + Verb (ing) + object (optional) + time of action.
Examples:
- We had been playing games for 6 hours when Dad came home.
- She had been reading magazines for 1 month before she decided to apply for the job.
- Had she been washing dishes all day?
4. Present continuous tense
The present continuous tense is used to talk about the ongoing actions, events, or conditions that are still not finished.
Structural formula:
Subject + helping verb (is / am/ are) + main verb (ing) + object.
Examples:
- She is playing basketball.
- Birds are flying in the sky.
- I’m learning English.
5. Present perfect tense
The present perfect tense is used to describe a situation or event that has already occurred but has immediate ramifications. The present perfect tense can be used to describe experiences, and situations that occurred in the past but still have an influence on the present. We don't use it with time markers.
Structural formula:
Subject + helping verb (have/has) + verb (ed) + object.
Examples:
- She has not finished her work yet.
- I have seen that movie twice.
- We have visited LA several times.
6. Present perfect continuous tense
The present perfect continuous tense shows a situation that has started in the past and continues in the present.
Structural formula:
Subject + helping verb (have/has) + been + verb (ing) + object (optional) + since / for + time duration + object.
Examples:
- I have been learning English for many years.
- He has been working here since 2010.
- We have been saving money.
7. Future continuous tense
The future continuous tense is used to describe an ongoing action that will occur or occur in the future.
Structural formula:
Subject + shall/will be + verb (ing) + object.
Example:
- He will be coming to visit us next week.
- She will be watching TV.
- He will be writing a letter to Mary.
8. Future perfect tense
The future perfect is used to describe an action that will be completed between now and a certain point in the future.
Structural formula:
Subject + shall/will + have + verb (3rd form) + object.
Examples:
- They will have finished the film before we get home.
- She will have cleaned the house by 9pm.
9. Future perfect continuous tense
We use the future perfect continuous to focus on the duration of an action before a specific time in the future.
Structural formula:
Subject + shall/will + have been + verb (ing) + object (optional) + time instant.
Examples:
- He will have been studying hard for 2 weeks before the exam.
- By the time the alarm goes off, we will have been sleeping for 8 hours.
Examples of tenses in English
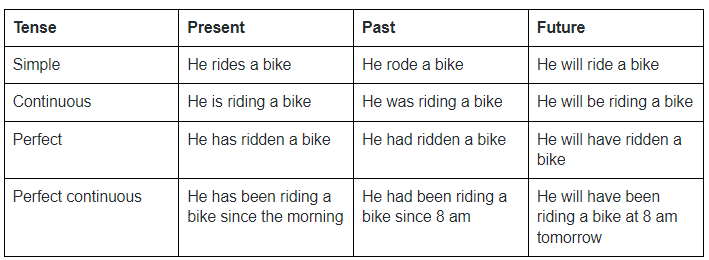
|
541 videos|683 docs|263 tests
|
FAQs on Tenses and its Kinds - IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What are the different tenses in English grammar? |  |
| 2. How many types of present tenses are there? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between simple past and past continuous tense? |  |
| 4. When do we use the future perfect tense? |  |
| 5. Can we use present perfect tense for past actions? |  |
|
541 videos|683 docs|263 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Bank Exams exam
|

|

















