C++ User Input & Data Types | C++ Programming for Beginners - Class 10 PDF Download
C++ User Input
- You have already learned that cout is used to output (print) values. Now we will use cin to get user input.
- cin is a predefined variable that reads data from the keyboard with the extraction operator (>>).
- In the following example, the user can input a number, which is stored in the variable x. Then we print the value of x:
Example
int x;
cout << "Type a number: "; // Type a number and press enter
cin >> x; // Get user input from the keyboard
cout << "Your number is: " << x; // Display the input value
Good To Know
- cout is pronounced "see-out". Used for output, and uses the insertion operator (<<)
- cin is pronounced "see-in". Used for input, and uses the extraction operator (>>)
Creating a Simple Calculator
In this example, the user must input two numbers. Then we print the sum by calculating (adding) the two numbers:
Example
int x, y;
int sum;
cout << "Type a number: ";
cin >> x;
cout << "Type another number: ";
cin >> y;
sum = x + y;
cout << "Sum is: " << sum;
There you go! You just built a basic calculator!
C++ Data Types
As explained in the Variables chapter, a variable in C++ must be a specified data type:
Example
int myNum = 5; // Integer (whole number)
float myFloatNum = 5.99; // Floating point number
double myDoubleNum = 9.98; // Floating point number
char myLetter = 'D'; // Character
bool myBoolean = true; // Boolean
string myText = "Hello"; // String
Basic Data Types
The data type specifies the size and type of information the variable will store:
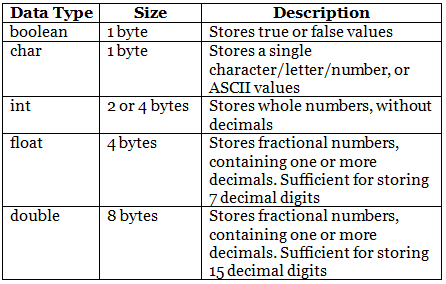
Numeric Types
Use int when you need to store a whole number without decimals, like 35 or 1000, and float or double when you need a floating point number (with decimals), like 9.99 or 3.14515.
int
int myNum = 1000;
cout << myNum;
float
float myNum = 5.75;
cout << myNum;
double
double myNum = 19.99;
cout << myNum;
float vs. double
The precision of a floating point value indicates how many digits the value can have after the decimal point. The precision of float is only six or seven decimal digits, while double variables have a precision of about 15 digits. Therefore it is safer to use double for most calculations.
Scientific Numbers
A floating point number can also be a scientific number with an "e" to indicate the power of 10:
Example
float f1 = 35e3;
double d1 = 12E4;
cout << f1;
cout << d1;
Boolean Types
A boolean data type is declared with the bool keyword and can only take the values true or false.
When the value is returned, true = 1 and false = 0.
Example
bool isCodingFun = true;
bool isFishTasty = false;
cout << isCodingFun; // Outputs 1 (true)
cout << isFishTasty; // Outputs 0 (false)
Character Types
The char data type is used to store a single character. The character must be surrounded by single quotes, like 'A' or 'c':
Example
char myGrade = 'B';
cout << myGrade;
Alternatively, you can use ASCII values to display certain characters:
Example
char a = 65, b = 66, c = 67;
cout << a;
cout << b;
cout << c;
String Types
The string type is used to store a sequence of characters (text). This is not a built-in type, but it behaves like one in its most basic usage. String values must be surrounded by double quotes:
Example
string greeting = "Hello";
cout << greeting;
To use strings, you must include an additional header file in the source code, the <string> library:
Example
// Include the string library
#include <string>
// Create a string variable
string greeting = "Hello";
// Output string value
cout << greeting;
|
15 videos|20 docs|13 tests
|




















