Revision Notes: AI Project Cycle | Artificial Intelligence for Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Problem Scoping example |

|
| Data Acquisition |

|
| Big Data for AI |

|
| Data Exploration |

|
| Modelling |

|
Introduction
The AI project cycle involves a series of steps necessary for preparing an AI model or project. Although it shares some similarities with IT projects, there are distinct differences between the two. The process of IT projects typically includes the following stages:
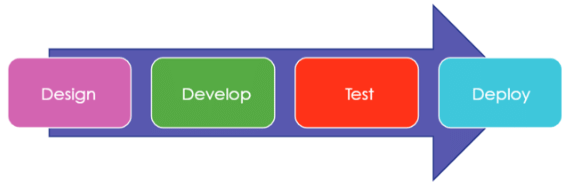
- Design: IT project starts with the design which refers to the process of thinking about interface design and its all aspects.
- Development: The secod stage is develop which is the process of develpping the solution with an interface design as well as coding.
- Testing: The third stage is testing the application which is a process of checking all the modules and functions are working as per requirement or not.
- Deployment: The final stage of IT project cycle is to deploy the application or software for use.
AI Project Cycle Stages
AI Class 10 AI Project Cycle Class has the following main stages:
- Problem Scoping
- Data Acquisition
- Data Exploration
- Data Modelling
What is Problem Scoping?
Whenever we are starting any work, certain problems always associated with the work or process. Actually we are surrounded by problems! These problems can be small or big, sometimes we ignore them, sometimes we need an urgent solution otherwise your work will suffer.
Important aspects of problem scoping
The following are few key points:
- When you start with an AI project or model you need to do problem scoping first.
- It the process of figure out the problem and what are the solutions.
- The AI project must have problem statement with required clarity
Problem Scoping example
Consider this example:
- The world’s largest diamond is in jeopardy because a person known as Mr. X has made threats to steal it.
- The situation is critical since Mr. X has not yet been located, increasing the urgency to act.
- As the newly appointed Chief Security Officer, your mission is to enhance the security measures surrounding the diamond, making it exceedingly challenging for Mr. X to carry out his plan.
- Utilizing your knowledge of AI concepts, you are required to devise a strategy on how to implement these technologies effectively to bolster the diamond’s security.
There are 3 main questions in this problem:
- Identify Mr. X: The first step is to gather intelligence and understand who Mr. X is. This may involve researching his background, motives, and possible locations.
- Track Mr. X: Once you have information about Mr. X, the next step is to track his movements. This could involve using surveillance technology, social media monitoring, and other tracking methods to locate him.
- Secure the Area: While tracking Mr. X, it is crucial to secure the area around the diamond. This includes setting up physical security measures such as guards, cameras, and alarms, as well as using AI technology to monitor for any suspicious activity.
The entire process of finding a specific solution is known as problem scoping.
Themes for problem scoping
Now look around you and find the specific field and select the problem which you want to resolve. The fields may be:
- Agriculture
- Education
- Banking
- Health
- Security
- Infrastructure Transportation
If we talk about agriculture, then the following aspects should be taken care:
- Pest issues
- Yield Rates
- Sowing and harvesting pattern
To solve these problems effectively you need to understand them and work for the solutions. To find a specific solution you must start with the 4Ws.
These 4Ws are:

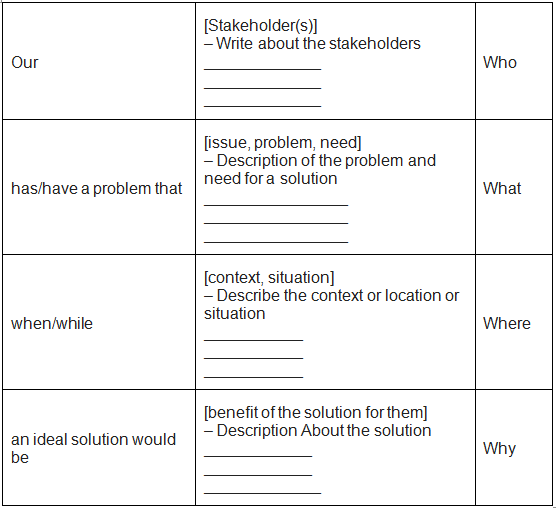
The problem scoping template
Problem scoping statement template is a format to be prepared at the end or initial stage of problem scoping. The format contains the following information:
Data Acquisition
Data Acquisition consists of two words:
- Data: Data refers to the raw facts , figures, or piece of facts, or statistics collected for reference or analysis.
- Acquisition: Acquisition refers to acquiring data for the project.
Note: The stage of acquiring data from the relevant sources is known as data acquisition.
Example of Data Acquisition
The example is continued which were discussed in the problem scoping stage.
- Now, as you interact with the authorities, you get to know that some people are allowed to enter the area where the diamond is kept.
- Some of them being – the maintenance people; officials; VIPs, etc.
- Now, your challenge is to make sure that no unauthorised person enters the premises.
- For this, you: (choose one)
- Get photographs of all the authorised people.
- Get photographs of all the unauthorised people.
- Get photographs of the premises in which the diamond has been kept.
- Get photographs of all the visitors
Types of data
Basically, there are four types of data:
- Numerical Data
- Categorical Data
- Time Series
- Text
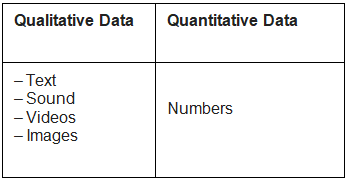
These data can be Qualitative and Quantitative.
Features of Data
- Data features refer to the type of data you want to collect.
- It should be relevant to the problem statement.
For example, while analyzing the weakness of a batsman, you will have data features such as- Speed of ball
- type of dismissal
- type of bowler
- Type of swing
- Type of spin
- number of balls faced etc.
Methods of Data Aqcuisition
The most common methods of data acquisition are:
- Surveys: Through Google Forms, MS Teams Forms or any other interface
- Web Scrapping: Some software are Scarpy, Scrape hero Cloud, ParseHub, OutHitHub, Visual Web Ripper, Import.io
- Sensors: to convert physical parameters to electrical signals, to convert sensor signals into a form that can be converted to digital values and to convert conditioned sensor signals to digital values
- Cameras: To capture images
- Observations: Way of gathering data by watching behavior, events, or noting physical characteristics in their natural setting
- API (Application Program Interface)
Open Source Datasets for Data Acquisition
Here are some open-source datasets that can be used for data acquisition:
- Lionbridge AI
- Amazon Mechanical Turk
- LabelBox
- Figure Eight
- Kaggle
- http://mospi.nic.in/data
Big Data for AI
- A collection of data that is huge in volume, yet growing exponentially with time.
- It is a data with so large size and complexity that none of traditional data management tools can store it or process it efficiently.
Examples of Big Data
- Stock Exchanges: Handle vast amounts of data related to stock trades, prices, and market trends.
- Social Media Platforms: Collect and analyze huge volumes of user-generated content, interactions, and behavior patterns.
- Streaming Services: Platforms like YouTube and other web series services manage large datasets of videos, user preferences, and viewing habits.
Types of Big Data
There are three types of big data:
Training, Testing and Validation of Data
- Training set: The data where the model is trained on
- Validation set: Data the model has not been trained on and used to tune hyperparameters
- Test set: In principle the same like the validation set, just used at the final end after the model has been tailored.
Data Exploration
Data Exploration refers to the techniques and tools used to visualize data through complex statistical methods.
Need of data visualization
- Quickly get a sense of the trends, relationships and patterns contained within the data.
- Define strategy for which model to use at a later stage.
- Communicate the same to others effectively.
- To visualise data, we can use various types of visual representations.
Data Visualization tools
- Microsoft Excel
- Tableau
- Qlikview
- DataWrapper
- Google Data Studio
Modelling
- Artificial Intelligence, or AI, refers to any technique that enables computers to mimic human intelligence.
- Machine Learning, or ML, enables machines to improve at tasks with experience. The machine learns from its mistakes and takes them into consideration in the next execution.
- Deep Learning, or DL, enables software to train itself to perform tasks with vast amounts of data. In deep learning, the machine is trained with huge amounts of data which helps it into training itself around the data.
- AI Modelling refers to developing algorithms, also called models which can be trained to get intelligent outputs. That is, writing codes to make a machine artificially intelligent.
Types of AI models
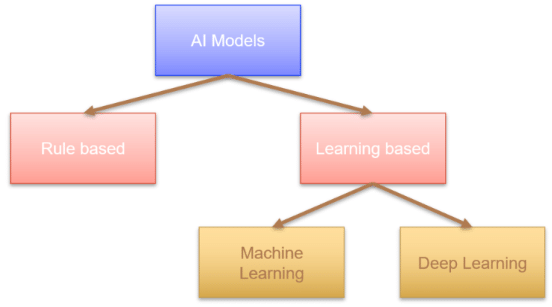
Rule-Based model refers to setting up rules and training the model accordingly. It follows an algorithm or code to train, test and validate data.
Learning-based refer to identifying the data by its attributes and behaviour and training the model accordingly. There is no code or algorithm to train, test and validate the data. It learns from past behaviour and attributes received from data.
Decision Tree
- Decision tree builds classification or regression models in the form of a tree structure.
- It breaks down a dataset into smaller and smaller subsets while at the same time an associated decision tree is incrementally developed.
- The final result is a tree with decision nodes and leaf nodes.
Types of learning
There are three types of learning:
- Supervised
- Unsupervised
- Reinforcement
1. Supervised Learning
- The dataset which is fed to the machine is labelled.
- A label is some information which can be used as a tag for data.
- For example, students get grades according to the marks they secure in examinations.
- These grades are labels which categorise the students according to their marks.
Classification
- Where the data is classified according to the labels.
- The entries are divided in two classes normally.
- The boundary condition is defined to classify.
Regression
- Regression deals with continuous data.
- For example, if we know the growth rate, we can predict the salary of someone after a certain number of years.
- Regression is linear as well as non-linear.
2. Unsupervised Learning
- An unsupervised learning model works on unlabelled dataset.
- This means that the data which is fed to the machine is random and there is a possibility that the person who is training the model does not have any information regarding it.
- The unsupervised learning models are used to identify relationships, patterns and trends out of the data which is fed into it.
- It helps the user in understanding what the data is about and what are the major features identified by the machine in it.
Culstering
- Refers to the unsupervised learning algorithm which can cluster the unknown data according to the patterns or trends identified out of it.
- The patterns observed might be the ones which are known to the developer or it might even come up with some unique patterns out of it
Dimensionality reduction
- We humans are able to visualise upto 3-Dimensions only.
- If we have a ball in our hand, it is 3-Dimensions right now.
- But if we click its picture, the data transforms to 2-D.
- Hence, to reduce the dimensions and still be able to make sense out of the data, we use Dimensionality Reduction.
3. Reinforcement Learning
- Reinforcement Learning is defined as a Machine Learning method that is concerned with how software agents should take actions in an environment.
- Reinforcement Learning is a part of the deep learning method that helps you to maximize some portion of the cumulative reward.
|
24 videos|64 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: AI Project Cycle - Artificial Intelligence for Class 10
| 1. What is the AI project cycle? |  |
| 2. Why is the AI project cycle important? |  |
| 3. How does the AI project cycle help in problem identification? |  |
| 4. What is the role of data collection in the AI project cycle? |  |
| 5. How is the AI project cycle different from traditional project management? |  |















